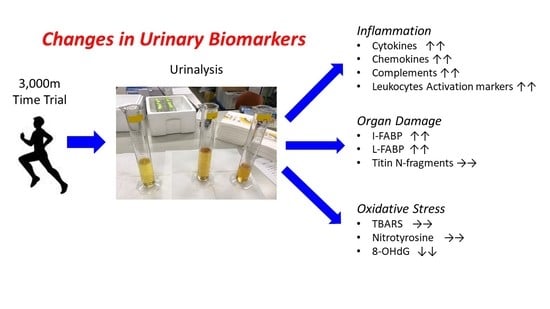
Changes in Urinary Biomarkers of Organ Damage, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Bone Turnover Following a 3000-m Time Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. 3000-m Time Trial
2.3. Urine Sampling
2.4. Assays for Urinary Biomarkers
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Urinary Organ Damage Markers
3.2. Urinary Inflammation-Related Factors (IRFs)
3.3. Oxidative Stress Markers
3.4. Urinary Metabolites
3.5. Urinary Bone Resorption Markers and Minerals
4. Discussion
4.1. The Changes of Urinary Biomarkers Following Acute Exercise
4.2. The Problems of Urinary Biomarkers as a Non-Invasive Method in the Situation of Exercise
4.3. Limitation
4.4. The Potential Applications in Sports Field
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sugama, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yoshitani, K.; Shiraishi, K.; Kometani, T. IL-17, neutrophil activation and muscle damage following endurance exercise. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 18, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugama, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yoshitani, K.; Shiraishi, K.; Kometani, T. Urinary excretion of cytokines versus their plasma levels after endurance exercise. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 19, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugama, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yoshitani, K.; Shiraishi, K.; Miura, S.; Yoshioka, H.; Mori, Y.; Kometani, T. Changes of thioredoxin, oxidative stress markers, inflammation and muscle/renal damage following intensive endurance exercise. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 21, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Nakaji, S.; Yamada, M.; Liu, Q.; Kurakake, S.; Okamura, N.; Kumae, T.; Umeda, T.; Sugawara, K. Impact of a competitive marathon race on systemic cytokine and neutrophil responses. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Peake, J.; Nosaka, K.; Okutsu, M.; Abbiss, C.R.; Surriano, R.; Bishop, D.; Quod, M.J.; Lee, H.; Martin, D.T.; et al. Changes in markers of muscle damage, inflammation and HSP70 after an Ironman Triathlon race. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 98, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Tominaga, T.; Ruhee, R.T.; Ma, S. Characterization and modulation of systemic inflammatory response to exhaustive exercise in relation to oxidative stress. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wijck, K.; Lenaerts, K.; van Loon, L.J.C.; Peters, W.H.M.; Buurman, W.A.; Dejong, C.H.C. Exercise-induced splanchnic hypoperfusion results in gut dysfunction in healthy men. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bloomer, R.J. Chapter 1 Effect of exercise on oxidative stress biomarkers. In Advances in Clinical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 46, pp. 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Peake, J.M.; Suzuki, K.; Coombes, J.S. The influence of antioxidant supplementation on markers of inflammation and the relationship to oxidative stress after exercise. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 18, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Nakaji, S.; Yamada, M.; Totsuka, M.; Sato, K.; Sugawara, K. Systemic inflammatory response to exhaustive exercise. Cytokine kinetics. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2002, 8, 6–48. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.; Shiraishi, K.; Yoshitani, K.; Sugama, K.; Kometani, T. Effect of a sports drink based on highly-branched cyclic dextrin on cytokine responses to exhaustive endurance exercise. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2014, 54, 622–630. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg, J.G.; Ba, A.; Brégeon, F.; Delliaux, S.; Jammes, Y. Cytokine and oxidative responses to maximal cycling exercise in sedentary subjects. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiecek, M.; Maciejczyk, M.; Szymura, J.; Szygula, Z. Effect of maximal-intensity exercise on systemic nitro-oxidative stress in men and women. Redox Rep. 2017, 22, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Northoff, H.; Weinstock, C.; Berg, A. The cytokine response to strenuous exercise. Int. J. Sports Med. 1994, 15 (Suppl. 3), S167–S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.G.; Verma, G.; Pata, R.W.; Martin, T.G.; Perazella, M.A.; Parikh, C.R. Kidney injury and repair biomarkers in marathon runners. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 70, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sprenger, H.; Jacobs, C.; Nain, M.; Gressner, A.M.; Prinz, H.; Wesemann, W.; Gemsa, D. Enhanced release of cytokines, interleukin-2 receptors, and neopterin after long-distance running. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1992, 63, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, C.; König, D.; Harnischmacher, R.; Keul, J.; Berg, A.; Northoff, H. Effect of exhaustive exercise stress on the cytokine response. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1997, 29, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, H.; van Holland, B.; Krab, B.; Moeken, J.; Vermeulen, N.P.E.; Hollander, P.; Meerman, J.H.N. Evaluation of a multi-parameter biomarker set for oxidative damage in man: Increased urinary excretion of lipid, protein and DNA oxidation products after one hour of exercise. Free Radic. Res. 2004, 38, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K. Characterization of exercise-induced cytokine release, the impacts on the body, the mechanisms and modulations. Int. J. Sports Exerc. Med. 2019, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Gao, Y. Physiological conditions can be reflected in human urine proteome and metabolome. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2015, 12, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, K.; Sakuma, J.; Akimoto, T.; Kawakami, Y.; Suzuki, K. Detection of titin fragments in urine in response to exercise-induced muscle damage. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Suzuki, K.; Kanda, K.; Inami, T.; Okada, J. Changes in urinary titin N-terminal fragments as a biomarker of exercise-induced muscle damage in the repeated bout effect. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2020, 23, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Suzuki, K.; Kanda, K.; Okada, J. N-terminal fragments of titin in urine as a biomarker for eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage. J. Phys. Fit. Sports Med. 2020, 9, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myburgh, K.H.; Hutchins, J.; Fataar, A.B.; Hough, S.F.; Noakes, T.D. Low bone density is an etiologic factor for stress fractures in athletes. Ann Intern Med 1990, 113, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banfi, G.; Lombardi, G.; Colombini, A.; Lippi, G. Bone metabolism markers in sports medicine. Sports Med. 2010, 40, 697–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Tominaga, T.; Kanda, K.; Sugama, K.; Omae, C.; Hashimoto, S.; Aoyama, K.; Yoshikai, Y.; Suzuki, K. Effects of an 8-week protein supplementation regimen with hyperimmunized cow milk on exercise-induced organ damage and inflammation in male runners: A randomized, placebo controlled, cross-over study. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraki, K.; Kamijo-Ikemori, A.; Yasuda, T.; Hotta, C.; Izawa, K.P.; Watanabe, S.; Sugaya, T.; Kimura, K. Moderate-intensity single exercise session does not induce renal damage. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2013, 27, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, K.; Sugama, K.; Sakuma, J.; Kawakami, Y.; Suzuki, K. Evaluation of serum leaking enzymes and investigation into new biomarkers for exercise-induced muscle damage. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 20, 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kosaki, K.; Kamijo-Ikemori, A.; Sugaya, T.; Kumamoto, S.; Tanahashi, K.; Kumagai, H.; Kimura, K.; Shibagaki, Y.; Maeda, S. Incremental short maximal exercise increases urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein in adults without CKD. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2020, 30, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.J.S.; Snipe, R.M.J.; Kitic, C.M.; Gibson, P.R. Systematic review: Exercise-induced gastrointestinal syndrome-implications for health and intestinal disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarikaya, M.; Ergül, B.; Doğan, Z.; Filik, L.; Can, M.; Arslan, L. Intestinal fatty acid binding protein (I-FABP) as a promising test for Crohn’s disease: A preliminary study. Clin. Lab. 2015, 61, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, S.Y.; Young, P.Y.; Churchill, T.A.; Khadaroo, R.G. Urine intestinal fatty acid-binding protein predicts acute mesenteric ischemia in patients. J. Surg. Res. 2017, 209, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, V.S.; Ferguson, M.A.; Bonventre, J.V. Biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 48, 463–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poortmans, J.R.; Vanderstraeten, J. Kidney function during exercise in healthy and diseased humans. An update. Sports Med. 1994, 18, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezil, Y.A.; Allison, D.; Kish, K.; Ditor, D.; Ward, W.E.; Tsiani, E.; Klentrou, P. Response of bone turnover barkers and cytokines to high-intensity low-impact exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.L.; Weiss, J.; Kelley, E.T. Bone turnover response to acute exercise with varying impact levels: A preliminary investigation. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2015, 8, 154–163. [Google Scholar]
- Ashizawa, N.; Fujimura, R.; Tokuyama, K.; Suzuki, M. A bout of resistance exercise increases urinary calcium independently of osteoclastic activation in men. J. Appl. Physiol. 1997, 83, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashizawa, N.; Ouchi, G.; Fujimura, R.; Yoshida, Y.; Tokuyama, K.; Suzuki, M. Effects of a single bout of resistance exercise on calcium and bone metabolism in untrained young males. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1998, 62, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maïmoun, L.; Manetta, J.; Couret, I.; Dupuy, A.M.; Mariano-Goulart, D.; Micallef, J.P.; Peruchon, E.; Rossi, M. The intensity level of physical exercise and the bone metabolism response. Int. J. Sports Med. 2006, 27, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.P.R.; Sale, C.; Greeves, J.P.; Casey, A.; Dutton, J.; Fraser, W.D. The effect of training status on the metabolic response of bone to an acute bout of exhaustive treadmill running. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 3918–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barcroft, H.; Foley, T.H.; McSwiney, R.R. Experiments on the liberation of phosphate from the muscles of the human forearm during vigorous exercise and on the action of sodium phosphate on forearm muscle blood vessels. J. Physiol. 1971, 213, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanda, K.; Sugama, K.; Hayashida, H.; Sakuma, J.; Kawakami, Y.; Miura, S.; Yoshioka, H.; Mori, Y.; Suzuki, K. Eccentric exercise-induced delayed-onset muscle soreness and changes in markers of muscle damage and inflammation. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 19, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heller, F.; Frischmann, S.; Grünbaum, M.; Zidek, W.; Westhoff, T.H. Urinary calprotectin and the distinction between prerenal and intrinsic acute kidney injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wyss, M.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R. Creatine and creatinine metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 1107–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongers, C.C.W.G.; Alsady, M.; Nijenhuis, T.; Hartman, Y.A.W.; Eijsvogels, T.M.H.; Deen, P.M.T.; Hopman, M.T.E. Impact of acute versus repetitive moderate intensity endurance exercise on kidney injury markers. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, C.C.W.G.; Alsady, M.; Nijenhuis, T.; Tulp, A.D.M.; Eijsvogels, T.M.H.; Deen, P.M.T.; Hopman, M.T.E. Impact of acute versus prolonged exercise and dehydration on kidney function and injury. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.J.S.; Camões-Costa, V.; Snipe, R.M.J.; Dixon, D.; Russo, I.; Huschtscha, Z. Impact of exercise-induced hypohydration on gastrointestinal integrity, function, symptoms, and systemic endotoxin and inflammatory profile. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Hashimoto, H.; Oh, T.; Ishijima, T.; Mitsuda, H.; Peake, J.M.; Sakamoto, S.; Muraoka, I.; Higuchi, M. The effects of sports drink osmolality on fluid intake and immunoendocrine responses to cycling in hot conditions. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2013, 59, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leon, L.R.; Helwig, B.G. Heat stroke: Role of the systemic inflammatory response. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 1980–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.L.; Suzuki, K. Systemic inflammation mediates the effects of endotoxemia in the mechanisms of heat stroke. Biol. Med. 2017, 9, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tominaga, T.; Ma, S.; Sugama, K.; Kanda, K.; Omae, C.; Choi, W.; Hashimoto, S.; Aoyama, K.; Yoshikai, Y.; Suzuki, K. Changes in Urinary Biomarkers of Organ Damage, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Bone Turnover Following a 3000-m Time Trial. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10010079
Tominaga T, Ma S, Sugama K, Kanda K, Omae C, Choi W, Hashimoto S, Aoyama K, Yoshikai Y, Suzuki K. Changes in Urinary Biomarkers of Organ Damage, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Bone Turnover Following a 3000-m Time Trial. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(1):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10010079
Chicago/Turabian StyleTominaga, Takaki, Sihui Ma, Kaoru Sugama, Kazue Kanda, Chiaki Omae, Wonjun Choi, Shunsuke Hashimoto, Katsuhiko Aoyama, Yasunobu Yoshikai, and Katsuhiko Suzuki. 2021. "Changes in Urinary Biomarkers of Organ Damage, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Bone Turnover Following a 3000-m Time Trial" Antioxidants 10, no. 1: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10010079
APA StyleTominaga, T., Ma, S., Sugama, K., Kanda, K., Omae, C., Choi, W., Hashimoto, S., Aoyama, K., Yoshikai, Y., & Suzuki, K. (2021). Changes in Urinary Biomarkers of Organ Damage, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Bone Turnover Following a 3000-m Time Trial. Antioxidants, 10(1), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10010079