Tissue Distribution of Oleocanthal and Its Metabolites after Oral Ingestion in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Animals and Diets
2.3. Tissue Distribution Experiments
2.4. Liquid–Liquid Extraction for Bioanalysis
2.5. LC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS Equipment and Conditions
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Metabolite Identification
3.1.1. Phase I Metabolism
3.1.2. Phase II Metabolism
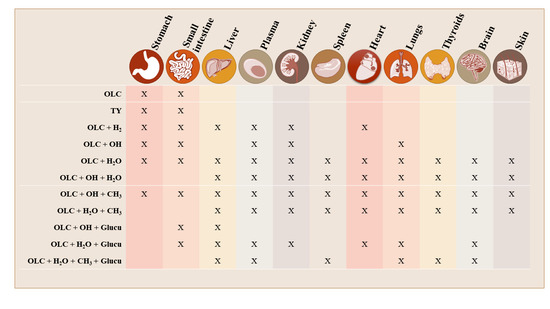
3.2. Brief Summary of OLC Metabolite Distribution by Tissue
4. Conclusions and Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organisation. The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 9 December 2020).
- Dinu, M.; Pagliai, G.; Casini, A.; Sofi, F. Mediterranean Diet and Multiple Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies and Randomised Trials. European J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzella, J.; Townsend, N.; Jewell, J.; Breda, J.; Roberts, N.; Rayner, M.; Wickramasinghe, K. What National and Subnational Interventions and Policies Based on Mediterranean and Nordic Diets Are Recommended or Implemented in the WHO European Region, and Is There Evidence of Effectiveness in Reducing Noncommunicable Diseases. World Health Organization, Regional Office for Europe: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 92-890-5301-1. [Google Scholar]
- Romani, A.; Ieri, F.; Urciuoli, S.; Noce, A.; Marrone, G.; Nediani, C.; Bernini, R. Health Effects of Phenolic Compounds Found in Extra-Virgin Olive Oil, By-Products, and Leaf of Olea Europaea L. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piroddi, M.; Albini, A.; Fabiani, R.; Giovannelli, L.; Luceri, C.; Natella, F.; Rosignoli, P.; Rossi, T.; Taticchi, A.; Servili, M.; et al. Nutrigenomics of Extra-Virgin Olive Oil: A Review. BioFactors 2017, 43, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano-Castellón, J.; López-Yerena, A.; Rinaldi de Alvarenga, J.F.; Romero del Castillo-Alba, J.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Escribano-Ferrer, E.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Health-Promoting Properties of Oleocanthal and Oleacein: Two Secoiridoids from Extra-Virgin Olive Oil. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2532–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikou, T.; Liaki, V.; Stathopoulos, P.; Sklirou, A.D.; Tsakiri, E.N.; Jakschitz, T.; Bonn, G.; Trougakos, I.P.; Halabalaki, M.; Skaltsounis, L.A. Comparison Survey of EVOO Polyphenols and Exploration of Healthy Aging-Promoting Properties of Oleocanthal and Oleacein. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicerale, S.; Lucas, L.J.; Keast, R.S.J. Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Phenolic Activities in Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Curr. Opinion Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchamp, G.K.; Keast, R.S.J.; Morel, D.; Lin, J.; Pika, J.; Han, Q.; Lee, C.-H.; Smith, A.B.; Breslin, P.A.S. Ibuprofen-like Activity in Extra-Virgin Olive Oil. Nature 2005, 437, 45–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeGendre, O.; Breslin, P.A.S.; Foster, D.A. (-)-Oleocanthal Rapidly and Selectively Induces Cancer Cell Death via Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khanfar, M.A.; Bardaweel, S.K.; Akl, M.R.; El Sayed, K.A. Olive Oil-Derived Oleocanthal as Potent Inhibitor of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin: Biological Evaluation and Molecular Modeling Studies. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1776–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddique, A.B.; Ebrahim, H.Y.; Akl, M.R.; Ayoub, N.M.; Goda, A.A.; Mohyeldin, M.M.; Nagumalli, S.K.; Hananeh, W.M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Meyer, S.A.; et al. (−)-Oleocanthal Combined with Lapatinib Treatment Synergized against HER-2 Positive Breast Cancer in Vitro and in Vivo. Nutrients 2019, 11, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qosa, H.; Batarseh, Y.S.; Mohyeldin, M.M.; El Sayed, K.A.; Keller, J.N.; Kaddoumi, A. Oleocanthal Enhances Amyloid-β Clearance from the Brains of TgSwDI Mice and in Vitro across a Human Blood-Brain Barrier Model. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1849–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monti, M.C.; Margarucci, L.; Riccio, R.; Casapullo, A. Modulation of Tau Protein Fibrillization by Oleocanthal. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1584–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oracz, J.; Nebesny, E.; Zyzelewicz, D.; Budryn, G.; Luzak, B. Bioavailability and Metabolism of Selected Cocoa Bioactive Compounds: A Comprehensive Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelino, D.; Cossu, M.; Marti, A.; Zanoletti, M.; Chiavaroli, L.; Brighenti, F.; Del Rio, D.; Martini, D. Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability of Phenolic Compounds in Bread: A Review. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 2368–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lanao, J.; Fraile, M. Drug Tissue Distribution: Study Methods and Therapeutic Implications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 3829–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G. Preclinical Drug Development. In Pharmaceutical Medicine and Translational Clinical Research; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2017; ISBN 9780128021033. [Google Scholar]
- de Bock, M.; Thorstensen, E.B.; Derraik, J.G.B.; Henderson, H.V.; Hofman, P.L.; Cutfield, W.S. Human Absorption and Metabolism of Oleuropein and Hydroxytyrosol Ingested as Olive ( Olea Europaea L.) Leaf Extract. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 2079–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Villalba, R.; Carrasco-Pancorbo, A.; Nevedomskaya, E.; Mayboroda, O.A.; Deelder, A.M.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. Exploratory Analysis of Human Urine by LC–ESI-TOF MS after High Intake of Olive Oil: Understanding the Metabolism of Polyphenols. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubió, L.; Farràs, M.; de La Torre, R.; Macià, A.; Romero, M.-P.; Valls, R.M.; Solà, R.; Farré, M.; Fitó, M.; Motilva, M.-J. Metabolite Profiling of Olive Oil and Thyme Phenols after a Sustained Intake of Two Phenol-Enriched Olive Oils by Humans: Identification of Compliance Markers. Food Res. Int. 2014, 65, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khymenets, O.; Farré, M.; Pujadas, M.; Ortiz, E.; Joglar, J.; Covas, M.I.; de la Torre, R. Direct Analysis of Glucuronidated Metabolites of Main Olive Oil Phenols in Human Urine after Dietary Consumption of Virgin Olive Oil. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, M.; Valls, R.M.; Romero, M.-P.; Macià, A.; Fernández, S.; Giralt, M.; Solà, R.; Motilva, M.-J. Bioavailability of Phenols from a Phenol-Enriched Olive Oil. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, S.; Garcia-aloy, M.; Figueira, M.E.; Combet, E.; Mullen, W.; Ros, M. High Resolution Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Secoiridoids and Metabolites as Biomarkers of Acute Olive Oil Intake — An Approach to Study Interindividual Variability in Humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 1700065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serra, A.; Rubió, L.; Borràs, X.; Macià, A.; Romero, M.-P.; Motilva, M.-J. Distribution of Olive Oil Phenolic Compounds in Rat Tissues after Administration of a Phenolic Extract from Olive Cake. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.; Paiva-Martins, F.; Corona, G.; Debnam, E.S.; Jose Oruna-Concha, M.; Vauzour, D.; Gordon, M.H.; Spencer, J.P.E. Absorption and Metabolism of Olive Oil Secoiridoids in the Small Intestine. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López de las Hazas, M.-C.; Piñol, C.; Macià, A.; Romero, M.-P.; Pedret, A.; Solà, R.; Rubió, L.; Motilva, M.-J. Differential Absorption and Metabolism of Hydroxytyrosol and Its Precursors Oleuropein and Secoiridoids. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 22, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domínguez-Perles, R.; Auñón, D.; Ferreres, F.; Gil-Izquierdo, A. Gender Differences in Plasma and Urine Metabolites from Sprague–Dawley Rats after Oral Administration of Normal and High Doses of Hydroxytyrosol, Hydroxytyrosol Acetate, and DOPAC. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Yerena, A.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Mols, R.; Augustijns, P.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Escribano-Ferrer, E. Absorption and Intestinal Metabolic Profile of Oleocanthal in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darakjian, L.I.; Rigakou, A.; Brannen, A.; Qusa, M.H.; Tasiakou, N.; Diamantakos, P.; Reed, M.N.; Panizzi, P.; Boersma, M.D.; Melliou, E.; et al. Spontaneous In Vitro and In Vivo Interaction of (−)-Oleocanthal with Glycine in Biological Fluids: Novel Pharmacokinetic Markers. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serreli, G.; Deiana, M. In Vivo Formed Metabolites of Polyphenols and Their Biological Efficacy. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6999–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Yerena, A.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Mols, R.; Augustijns, P.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Escribano-Ferrer, E. Reply to “Comment on López-Yerena et al. ‘Absorption and Intestinal Metabolic Profile of Oleocanthal in Rats’ Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 134.”. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Castellón, J.; López-Yerena, A.; Olmo-Cunillera, A.; Jáuregui, O.; Pérez, M.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A. Total Analysis of the Major Secoiridoids in Extra Virgin Olive Oil: Validation of an UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS Method. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panel, E.; Nda, A. Scientific Opinion on the Substantiation of Health Claims Related to Polyphenols in Olive and Protection of LDL Particles from Oxidative Damage (ID 1333, 1638, 1639, 1696, 2865), Maintenance of Normal Blood HDL Cholesterol Concentrations (ID 1639), Mainte. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, K.-H.; Hull, R.; Morton, D.; Pfister, R.; Rabemampianina, Y.; Smith, D.; Vidal, J.-M.; Vorstenbosch, C.V.D. A Good Practice Guide to the Administration of Substances and Removal of Blood, Including Routes and Volumes. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2001, 21, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.P.; Dinger, N.; Levine, B.S. Stress Produced by Gavage Administration in the Rat. Contemp. Top. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2000, 39, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, M.; Sakata, N.; Ise, I.; Ono, T.; Shimura, M.; Ishii, K.; Murakami, M.; Takadate, T.; Aoki, T.; Kudo, K. The Comparative Anatomy of the Folds, Fossae, and Adhesions around the Duodenojejunal Flexure in Mammals. Folia Morphol. 2018, 77, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polson, C.; Sarkar, P.; Incledon, B.; Raguvaran, V.; Grant, R. Optimization of Protein Precipitation Based upon Effectiveness of Protein Removal and Ionization Effect in Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 785, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Tzounis, X.; Dessì, M.A.; Deiana, M.; Edward, S.; Visioli, F.; Spencer, J.P.E.; Corona, G.; Tzounis, X.; Dessì, M.A.; et al. The Fate of Olive Oil Polyphenols in the Gastrointestinal Tract: Implications of Gastric and Colonic Microflora-Dependent Biotransformation. Free Radic. Res. 2006, 40, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Ye, A.; Horne, D. Structuring Food Emulsions in the Gastrointestinal Tract to Modify Lipid Digestion. Prog. Lipid Res. 2009, 48, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Flórez, A.; Pereira-Caro, G.; Sánchez-Quezada, C.; Moreno-Rojas, J.M.; Gaforio, J.J.; Jimenez, A.; Beltrán, G. Effect of Olive Cultivar on Bioaccessibility and Antioxidant Activity of Phenolic Fraction of Virgin Olive Oil. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, A.; Romero, M.P.; Macià, A.; Saha, S.; Furniss, C.S.M.; Kroon, P.A.; Motilva, M.J. Digestion Stability and Evaluation of the Metabolism and Transport of Olive Oil Phenols in the Human Small-Intestinal Epithelial Caco-2/TC7 Cell Line. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassine Ben, A.; Verger, R.; Abousalham, A. Lipases or Esterases: Does It Really Matter? Toward a New Bio-Physico-Chemical Classification. In Lipases and Phospholipases; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 31–51. [Google Scholar]
- Menendez, C.; Dueñas, M.; Galindo, P.; González-Manzano, S.; Jimenez, R.; Moreno, L.; Zarzuelo, M.J.; Rodríguez-Gómez, I.; Duarte, J.; Santos-Buelga, C.; et al. Vascular Deconjugation of Quercetin Glucuronide: The Flavonoid Paradox Revealed? Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1780–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubió, L.; Serra, A.; Macià, A.; Piñol, C.; Romero, M.-P.; Motilva, M.-J. In Vivo Distribution and Deconjugation of Hydroxytyrosol Phase II Metabolites in Red Blood Cells: A Potential New Target for Hydroxytyrosol. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 10, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressman, J.B.; Thelen, K. Cytochrome P450-Mediated Metabolism in the Human Gut Wall. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canaparo, R.; Finnström, N.; Serpe, L.; Nordmark, A.; Muntoni, E.; Eandi, M.; Rane, A.; Zara, G.P. Expression of CYP3A Isoforms and P-Glycoprotein in Human Stomach, Jejunum and Ileum. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 34, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, M. Cytochrome P450 Enzymes, Drug Transporters and Their Role in Pharmacokinetic Drug-Drug Interactions of Xenobiotics: A Comprehensive Review. Open J. Chem. 2017, 001–011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heleno, S.A.; Martins, A.; Queiroz, M.J.R.P.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Bioactivity of Phenolic Acids: Metabolites versus Parent Compounds: A Review. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karhunen, T.; Tilgmann, C.; Ulmanen, I.; Julkunen, I.; Panula, P. Distribution of Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Enzyme in Rat Tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1994, 42, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Meech, R.; Mackenzie, P.I. Structure and Function of Uridine Diphosphate Glucuronosyltransferases. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1997, 24, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroy, G.; Martiny, V.Y.; Vayer, P.; Villoutreix, B.O.; Miteva, M.A. Toward in Silico Structure-Based ADMET Prediction in Drug Discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira De Sousa, I.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Pre-Systemic Metabolism of Orally Administered Drugs and Strategies to Overcome It. J. Control. Release 2014, 192, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, A.; Miners, J.O.; Mackenzie, P.I. The UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases: Their Role in Drug Metabolism and Detoxification. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billat, P.-A.; Roger, E.; Faure, S.; Lagarce, F. Models for Drug Absorption from the Small Intestine: Where Are We and Where Are We Going? Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Lu, L.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Shi, J.; Yan, T.; Xie, C.; Li, Q.; Hu, M.; Liu, Z. Oral Absorption Basics: Pathways and Physicochemical and Biological Factors Affecting Absorption. In Developing Solid Oral Dosage Forms; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 297–329. ISBN 978-0-12-802447-8. [Google Scholar]
- Chmiel, T.; Mieszkowska, A.; Kempińska-Kupczyk, D.; Kot-Wasik, A.; Namieśnik, J.; Mazerska, Z. The Impact of Lipophilicity on Environmental Processes, Drug Delivery and Bioavailability of Food Components. Microchem. J. 2019, 146, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Yerena, A.; Perez, M.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Escribano-Ferrer, E. Insights into the Binding of Dietary Phenolic Compounds to Human Serum Albumin and Food-Drug Interactions. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castejón, M.L.; Montoya, T.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M. Potential Protective Role Exerted by Secoiridoids from Olea Europaea L. in Cancer, Cardiovascular, Neurodegenerative, Aging-Related, and Immunoinflammatory Diseases. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.M. Drug Metabolism and Pharmacogenetics. In Pharmacology and Physiology for Anesthesia. Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 70–90. ISBN 978-0-323-48110-6. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, Y.; Williams, G.; Walles, M.; Manevski, N.; Krähenbühl, S.; Camenisch, G. Comparison of Rat and Human Pulmonary Metabolism Using Precision-Cut Lung Slices (PCLS). Drug Metab. Lett. 2019, 13, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatouros, M.; Bourantas, K.; Bairaktari, E.; Elisaf, M.; Tsolas, O.; Cassioumis, D. Role of the Spleen in Lipid Metabolism. Br. J. Surg. 1995, 82, 1675–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miners, J.; Yang, X.; Knights, K.; Zhang, L. The Role of the Kidney in Drug Elimination: Transport, Metabolism, and the Impact of Kidney Disease on Drug Clearance. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Yerena, A.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Jáuregui, O.; Garcia-Sala, X.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Escribano-Ferrer, E. Tissue Distribution of Oleocanthal and Its Metabolites after Oral Ingestion in Rats. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10050688
López-Yerena A, Vallverdú-Queralt A, Jáuregui O, Garcia-Sala X, Lamuela-Raventós RM, Escribano-Ferrer E. Tissue Distribution of Oleocanthal and Its Metabolites after Oral Ingestion in Rats. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(5):688. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10050688
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Yerena, Anallely, Anna Vallverdú-Queralt, Olga Jáuregui, Xavier Garcia-Sala, Rosa M. Lamuela-Raventós, and Elvira Escribano-Ferrer. 2021. "Tissue Distribution of Oleocanthal and Its Metabolites after Oral Ingestion in Rats" Antioxidants 10, no. 5: 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10050688
APA StyleLópez-Yerena, A., Vallverdú-Queralt, A., Jáuregui, O., Garcia-Sala, X., Lamuela-Raventós, R. M., & Escribano-Ferrer, E. (2021). Tissue Distribution of Oleocanthal and Its Metabolites after Oral Ingestion in Rats. Antioxidants, 10(5), 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10050688