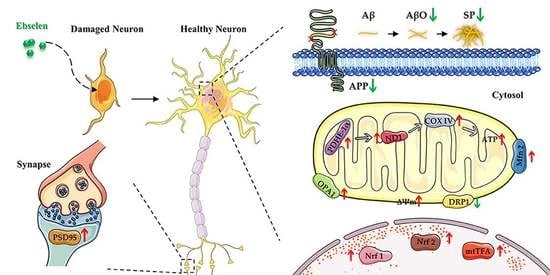
Ebselen Interferes with Alzheimer’s Disease by Regulating Mitochondrial Function
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Ebselen Promoted Glutathione Peroxidase Activities of N2a-SW Cells
3.2. The Effect of Ebselen on Serum Biochemical Indicators
3.3. Ebselen Rescued Behavioral Deficits of 3×Tg-AD Mice
3.3.1. Ebselen Rescued Memory Deficits of 3×Tg-AD Mice
3.3.2. Ebselen Significantly Improved Locomotor and Exploring Ability and Alleviated the Anxiety of AD Mice
3.4. Ebselen Restored the Reduction of Synaptic Protein Levels and Repaired Synaptic Morphologies of AD Mice
3.5. Ebselen Inhibited Aβ Pathologies in AD Mice Brains
3.6. Ebselen Alleviated the Structural and Functional Damage of Mitochondria in AD Models
3.6.1. Ebselen Rescued Mitochondrial Health
3.6.2. Ebselen Repaired the Mitochondria by Improving Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism, Enhancing Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Balancing Mitochondrial Fission/Fusion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Graff-Radford, J.; Yong, K.X.X.; Apostolova, L.G.; Bouwman, F.H.; Carrillo, M.; Dickerson, B.C.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Schott, J.M.; Jones, D.T.; Murray, M.E. New insights into atypical Alzheimer’s disease in the era of biomarkers. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Ayton, S.; Bush, A.I. The essential elements of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rataan, A.O.; Geary, S.M.; Zakharia, Y.; Rustum, Y.M.; Salem, A.K. Potential Role of Selenium in the Treatment of Cancer and Viral Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, B.R.; Cominetti, C.; Seale, L.A. Editorial: Selenium, Human Health and Chronic Disease. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 827759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, L.; Wang, B.; Qu, X.; Ni, J.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X. Se-Methylselenocysteine Ameliorates Neuropathology and Cognitive Deficits by Attenuating Oxidative Stress and Metal Dyshomeostasis in Alzheimer Model Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Wu, Q.Y.; Zheng, R.; Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hoffmann, P.R.; Ni, J.Z.; Song, G.L. Selenomethionine Mitigates Cognitive Decline by Targeting Both Tau Hyperphosphorylation and Autophagic Clearance in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. J. NeuroSci. 2017, 37, 2449–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Wu, Q.Y.; Chen, C.; Zheng, R.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ni, J.Z.; Song, G.L. Selenomethionine Attenuates the Amyloid-beta Level by Both Inhibiting Amyloid-beta Production and Modulating Autophagy in Neuron-2a/AbetaPPswe Cells. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 59, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Chen, C.; Wu, Q.Y.; Zheng, R.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ni, J.Z.; Song, G.L. Selenomethionine Ameliorates Neuropathology in the Olfactory Bulb of a Triple Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, L.; Chen, C.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, J.; Liu, Q. Selenomethionine ameliorates cognitive decline, reduces tau hyperphosphorylation, and reverses synaptic deficit in the triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 41, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, B.R.; Ong, T.P.; Jacob-Filho, W.; Jaluul, O.; Freitas, M.I.; Cozzolino, S.M. Nutritional status of selenium in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aaseth, J.; Skalny, A.V.; Roos, P.M.; Alexander, J.; Aschner, M.; Tinkov, A.A. Copper, Iron, Selenium and Lipo-Glycemic Dysmetabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barchielli, G.; Capperucci, A.; Tanini, D. The Role of Selenium in Pathologies: An Updated Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waløen, K.; Jung-Kc, K.; Vecchia, E.D.; Pandey, S.; Gasparik, N.; Døskeland, A.; Patil, S.; Kleppe, R.; Hritz, J.; Norton, W.H.J.; et al. Cysteine Modification by Ebselen Reduces the Stability and Cellular Levels of 14-3-3 Proteins. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 100, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakita, K.M.; Capoci, I.R.G.; Conrado, P.C.V.; Rodrigues-Vendramini, F.A.V.; Faria, D.R.; Arita, G.S.; Becker, T.C.A.; Bonfim-Mendonça, P.S.; Svidzinski, T.I.E.; Kioshima, E.S. Efficacy of Ebselen Against Invasive Aspergillosis in a Murine Model. Front. Cell Infect. MicroBiol. 2021, 11, 684525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, G.K.; Tomar, R.S. Ebselen, a promising antioxidant drug: Mechanisms of action and targets of Biological pathways. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4865–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, N. Ebselen, a useful tool for understanding cellular redox Biology and a promising drug candidate for use in human diseases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 595, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Serres, F.; Toker, L.; Sade, Y.; Blackburn, V.; Batra, A.S.; Saiardi, A.; Agam, G.; Belmaker, R.H.; Sharp, T.; et al. Effects of the putative lithium mimetic ebselen on pilocarpine-induced neural activity. Eur. J. Pharm. 2020, 883, 173377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, F.; Rosa, S.G.; Klann, I.P.; Fulco, B.C.W.; Carvalho, F.B.; Rahmeier, F.L.; Fernandes, M.C.; Nogueira, C.W. A multifunctional compound ebselen reverses memory impairment, apoptosis and oxidative stress in a mouse model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2019, 109, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klann, I.P.; Martini, F.; Rosa, S.G.; Nogueira, C.W. Ebselen reversed peripheral oxidative stress induced by a mouse model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Du, X.; Liu, Q. Ebselen ameliorates beta-amyloid pathology, tau pathology, and cognitive impairment in triple-transgenic Alzheimer’s disease mice. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 22, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santofimia-Castaño, P.; Izquierdo-Alvarez, A.; Plaza-Davila, M.; Martinez-Ruiz, A.; Fernandez-Bermejo, M.; Mateos-Rodriguez, J.M.; Salido, G.M.; Gonzalez, A. Ebselen impairs cellular oxidative state and induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and activation of crucial mitogen-activated protein kinases in pancreatic tumour AR42J. cells. J. Cell BioChem. 2018, 119, 1122–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laboratory, J. Comparison of Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Models. Available online: https://www.jax.org/research-and-faculty/research-centers/alzheimers-disease-center/alzheimers-mouse-model-repository/alzheimers-resource-comparison-table (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- Kandimalla, R.; Manczak, M.; Fry, D.; Suneetha, Y.; Sesaki, H.; Reddy, P.H. Reduced dynamin-related protein 1 protects against phosphorylated Tau-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and synaptic damage in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 4881–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, T.; Sun, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G. Ebselen-Agents for Sensing, Imaging and Labeling: Facile and Full-Featured Application in BioChemical Analysis. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 2217–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caeran Bueno, D.; Meinerz, D.F.; Allebrandt, J.; Waczuk, E.P.; dos Santos, D.B.; Mariano, D.O.; Rocha, J.B. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity evaluation of organochalcogens in human leucocytes: A comparative study between ebselen, diphenyl diselenide, and diphenyl ditelluride. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 537279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santofimia-Castaño, P.; Salido, G.M.; González, A. Ebselen alters mitochondrial physiology and reduces viability of rat hippocampal astrocytes. DNA Cell Biol. 2013, 32, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guérin, P.J.; Gauthier, E.R. Induction of cellular necrosis by the glutathione peroxidase mimetic ebselen. J. Cell BioChem. 2003, 89, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meotti, F.C.; Borges, V.C.; Zeni, G.; Rocha, J.B.; Nogueira, C.W. Potential renal and hepatic toxicity of diphenyl diselenide, diphenyl ditelluride and Ebselen for rats and mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 143, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yan, Q.; Gao, C.; Lin, L.; Wei, J. Study on antioxidant effect of recombinant glutathione peroxidase 1. Int. J. Biol. MacroMol. 2021, 170, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, B.R.; Hare, D.J.; Bush, A.I.; Roberts, B.R. Glutathione peroxidase 4: A new player in neurodegeneration? Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, F.; Ma, X.; Perry, G.; Zhu, X. Mitochondria dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Recent advances. Mol. Neurodegener 2020, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadenbach, B. Complex IV—The regulatory center of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Mitochondrion 2021, 58, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, L.; Han, L.; Ge, J.; Ma, R.; Zhang, X.; Moley, K.; Schedl, T.; Wang, Q. Differing roles of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases during mouse oocyte maturation. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 2319–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liang, M.; Li, Q.; Jin, X.; Wei, Y.; Meng, F.; et al. Contribution of mitochondrial ND1 3394T>C mutation to the phenotypic manifestation of Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Mercado-Ayon, E.; Mercado-Ayon, Y.; Dong, Y.N.; Halawani, S.; Ngaba, L.; Lynch, D.R. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the development and progression of neurodegenerative diseases. Arch BioChem. Biophys 2021, 702, 108698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpulla, R.C. Nuclear control of respiratory chain expression in mammalian cells. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1997, 29, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Su, B.; Lee, H.G.; Li, X.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A.; Zhu, X. Impaired balance of mitochondrial fission and fusion in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 9090–9103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitken, P.G.; Braitman, D.J. The effects of cyanide on neural and synaptic function in hippocampal slices. Neurotoxicology 1989, 10, 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Sudhof, T.C. Neurotransmitter release: The last millisecond in the life of a synaptic vesicle. Neuron 2013, 80, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, P.J.; Krnjevic, K. Adenosine release mediates cyanide-induced suppression of CA1 neuronal activity. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 2355–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Shi, Q.; Xu, H.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, C.; Le, L.; Lian, J.; Wu, G.; Peng, F.; Liu, Q.; et al. Ebselen Interferes with Alzheimer’s Disease by Regulating Mitochondrial Function. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071350
Li X, Shi Q, Xu H, Xiong Y, Wang C, Le L, Lian J, Wu G, Peng F, Liu Q, et al. Ebselen Interferes with Alzheimer’s Disease by Regulating Mitochondrial Function. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(7):1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071350
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuexia, Qingqing Shi, Hao Xu, Yufang Xiong, Chao Wang, Linfeng Le, Junliang Lian, Guoli Wu, Feiyuan Peng, Qiong Liu, and et al. 2022. "Ebselen Interferes with Alzheimer’s Disease by Regulating Mitochondrial Function" Antioxidants 11, no. 7: 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071350
APA StyleLi, X., Shi, Q., Xu, H., Xiong, Y., Wang, C., Le, L., Lian, J., Wu, G., Peng, F., Liu, Q., & Du, X. (2022). Ebselen Interferes with Alzheimer’s Disease by Regulating Mitochondrial Function. Antioxidants, 11(7), 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071350