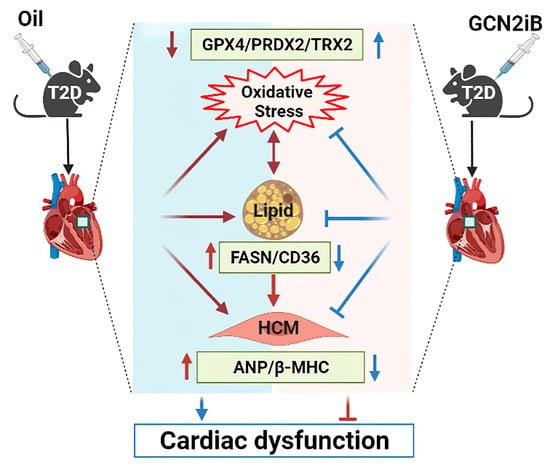
Inhibition of GCN2 Alleviates Cardiomyopathy in Type 2 Diabetic Mice via Attenuating Lipotoxicity and Oxidative Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Animals and Treatment
2.3. Echocardiography
2.4. Tissue Processing and Histopathology Staining
2.5. RNA Sequencing
2.6. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis
2.7. Western Blots
2.8. Real-Time PCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. GCN2iB Attenuates Cardiac Dysfunction and Myocardial Fibrosis in HFD Plus STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice
3.2. GCN2iB Affects Myocardial Metabolomic Profiles in HFD Plus STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice
3.3. GCN2iB Affects Gene Expression Profiles in T2D Mice
3.4. GCN2iB Alleviates Myocardial Lipid Accumulation and Oxidative Stress in T2D Mice
3.5. GCN2iB Improves Cardiac Function and Alleviates Myocardial Lipid Accumulation and Oxidative Stress in db/db Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, G.; Hill, M.A.; Sowers, J.R. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: An update of mechanisms contributing to this clinical entity. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; Whaley-Connell, A.; Sowers, J.R. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: A hyperglycaemia- and insulin-resistance-induced heart disease. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knapp, M.; Tu, X.; Wu, R. Vascular endothelial dysfunction, a major mediator in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.; Garg, R.; Bahl, A.; Khullar, M. Molecular Mechanisms and Epigenetic Regulation in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 725532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.D.; Langenberg, C.; Rapsomaniki, E.; Denaxas, S.; Pujades-Rodriguez, M.; Gale, C.P.; Deanfield, J.; Smeeth, L.; Timmis, A.; Hemingway, H. Type 2 diabetes and incidence of cardiovascular diseases: A cohort study in 1∙9 million people. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wek, R.C.; Jiang, H.Y.; Anthony, T.G. Coping with stress: eIF2 kinases and translational control. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Jiang, H.; Yin, H.; Jiang, X.; Jiao, F.; Chen, S.; Ying, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhai, Q.; Guo, F. Activation of GCN2/ATF4 signals in amygdalar PKC-delta neurons promotes WAT browning under leucine deprivation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Hu, J.; McGrath, B.C.; Cavener, D.R. GCN2 regulates the CCAAT enhancer binding protein beta and hepatic gluconeogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 305, E1007–E1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, F.; Cavener, D.R. The GCN2 eIF2alpha kinase regulates fatty-acid homeostasis in the liver during deprivation of an essential amino acid. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Yuan, J.; Yue, W.; Bi, Y.; Shen, X.; Gao, J.; Xu, X.; Lu, Z. GCN2 deficiency protects against high fat diet induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance in mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 3257–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, L.; Lei, T.; Hou, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, Y. The amino acid sensor general control nonderepressible 2 (GCN2) controls T(H)9 cells and allergic airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 1091–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindran, R.; Loebbermann, J.; Nakaya, H.I.; Khan, N.; Ma, H.; Gama, L.; Machiah, D.K.; Lawson, B.; Hakimpour, P.; Wang, Y.C.; et al. The amino acid sensor GCN2 controls gut inflammation by inhibiting inflammasome activation. Nature 2016, 531, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa-Mattioli, M.; Gobert, D.; Harding, H.; Herdy, B.; Azzi, M.; Bruno, M.; Bidinosti, M.; Ben Mamou, C.; Marcinkiewicz, E.; Yoshida, M.; et al. Translational control of hippocampal synaptic plasticity and memory by the eIF2alpha kinase GCN2. Nature 2005, 436, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Nyirimigabo, E.; Wei, B.; Lu, Z.; Ji, G. GCN2 deficiency protects mice from denervation-induced skeletal muscle atrophy via inhibiting FoxO3a nuclear translocation. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 966–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, S.; Gay, D.; Uthe, F.W.; Denk, S.; Paauwe, M.; Matthes, N.; Diefenbacher, M.E.; Bryson, S.; Warrander, F.C.; Erhard, F.; et al. A MYC-GCN2-eIF2α negative feedback loop limits protein synthesis to prevent MYC-dependent apoptosis in colorectal cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Xu, X.; Fassett, J.; Kwak, D.; Liu, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Xu, D.; Yan, S.; et al. Loss of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2α kinase general control nonderepressible 2 protects mice from pressure overload-induced congestive heart failure without affecting ventricular hypertrophy. Hypertension 2014, 63, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Lei, T.; Yuan, J.; Wu, Y.; Shen, X.; Gao, J.; Feng, W.; Lu, Z. GCN2 deficiency ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by decreasing cardiomyocyte apoptosis and myocardial oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2018, 17, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Lei, T.; Wang, Y.; Feng, R.; Yuan, J.; Shen, X.; Wu, Y.; Gao, J.; Ding, W.; Lu, Z. GCN2 deficiency ameliorates cardiac dysfunction in diabetic mice by reducing lipotoxicity and oxidative stress. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 130, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.Z.; Tian, Y.; Li, J. GCN2 suppression attenuates cerebral ischemia in mice by reducing apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress through the blockage of FoxO3a-regulated ROS production. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 516, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yu, Z.; Gao, J.; Luo, K.; Shen, X.; Cui, B.; Lu, Z. Inhibition of GCN2 alleviates hepatic steatosis and oxidative stress in obese mice: Involvement of NRF2 regulation. Redox Biol. 2022, 49, 102224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, R.; Porter, A.C.; Olsen, D.A.; Cavener, D.R.; Wek, R.C. A mammalian homologue of GCN2 protein kinase important for translational control by phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor-2alpha. Genetics 2000, 154, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Xu, X.; Hu, X.; Lee, S.; Traverse, J.H.; Zhu, G.; Fassett, J.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, P.; dos Remedios, C.; et al. Oxidative stress regulates left ventricular PDE5 expression in the failing heart. Circulation 2010, 121, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Shen, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, C.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Ding, W.; Lu, Z. The effect of exposure time and concentration of airborne PM(2.5) on lung injury in mice: A transcriptome analysis. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Yuan, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Ding, W.; Ji, G.; Lu, Z. Adipose-derived stem cells therapy effectively attenuates PM(2.5)-induced lung injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prandi, F.R.; Evangelista, I.; Sergi, D.; Palazzuoli, A.; Romeo, F. Mechanisms of cardiac dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy: Molecular abnormalities and phenotypical variants. Heart Fail. Rev. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.M.; Waqar, T.; Howarth, F.C.; Adeghate, E.; Bidasee, K.; Singh, J. Hyperglycemia-induced cardiac contractile dysfunction in the diabetic heart. Heart Fail. Rev. 2018, 23, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Sadoshima, J. Cardiomyopathy in obesity, insulin resistance and diabetes. J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 2977–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Geest, B.; Mishra, M. Role of Oxidative Stress in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldin, A.; Beckman, J.A.; Schmidt, A.M.; Creager, M.A. Advanced glycation end products: Sparking the development of diabetic vascular injury. Circulation 2006, 114, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, J.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y. CD36 Signaling in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 826–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sambandam, N.; Han, X.; Gross, R.W.; Courtois, M.; Kovacs, A.; Febbraio, M.; Finck, B.N.; Kelly, D.P. CD36 deficiency rescues lipotoxic cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonen, D.P.; Febbraio, M.; Bonnet, S.; Nagendran, J.; Young, M.E.; Michelakis, E.D.; Dyck, J.R. CD36 expression contributes to age-induced cardiomyopathy in mice. Circulation 2007, 116, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, S.; Suzuki, J.; Hirose, M.; Yamada, M.; Zenimaru, Y.; Nakaya, T.; Ichikawa, M.; Imagawa, M.; Takahashi, S.; Ikuyama, S.; et al. Cardiac overexpression of perilipin 2 induces atrial steatosis, connexin 43 remodeling, and atrial fibrillation in aged mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 317, E1193–E1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Chang, B.; Wu, X.; Li, L.; Sleeman, M.; Chan, L. Inactivation of Plin4 downregulates Plin5 and reduces cardiac lipid accumulation in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 304, E770–E779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Byrne, N.J.; Rajasekaran, N.S.; Abel, E.D.; Bugger, H. Therapeutic potential of targeting oxidative stress in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 169, 317–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaed, E.; Wang, J.; Almoiliqy, M.; Song, Y.; Liu, W.; Chu, P.; Alademi, S.; Alademi, M.; Li, H.; Alshwmi, M.; et al. Phosphocreatine Improves Cardiac Dysfunction by Normalizing Mitochondrial Respiratory Function through JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway In Vivo and In Vitro. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 6521218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.G.; Li, W.; Lu, X.H.; Zhao, X.; Xu, L. Taurine attenuates oxidative stress and alleviates cardiac failure in type I diabetic rats. Croat. Med. J. 2013, 54, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robert, F.; Williams, C.; Yan, Y.; Donohue, E.; Cencic, R.; Burley, S.K.; Pelletier, J. Blocking UV-induced eIF2alpha phosphorylation with small molecule inhibitors of GCN2. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2009, 74, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazeau, J.F.; Rosse, G. Triazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine Derivatives as Inhibitors of GCN2. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heydt, Q.; Xintaropoulou, C.; Clear, A.; Austin, M.; Pislariu, I.; Miraki-Moud, F.; Cutillas, P.; Korfi, K.; Calaminici, M.; Cawthorn, W.; et al. Adipocytes disrupt the translational programme of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia to favour tumour survival and persistence. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Cui, A.Q.; Zhang, W.W.; Li, X.L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.H.; et al. Microcystin-LR inhibits testosterone synthesis via reactive oxygen species-mediated GCN2/eIF2α pathway in mouse testes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, J.; Li, F.; Cui, B.; Gao, J.; Yu, Z.; Lu, Z. Inhibition of GCN2 Alleviates Cardiomyopathy in Type 2 Diabetic Mice via Attenuating Lipotoxicity and Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071379
Yuan J, Li F, Cui B, Gao J, Yu Z, Lu Z. Inhibition of GCN2 Alleviates Cardiomyopathy in Type 2 Diabetic Mice via Attenuating Lipotoxicity and Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(7):1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071379
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Juntao, Fang Li, Bingqing Cui, Junling Gao, Zhuoran Yu, and Zhongbing Lu. 2022. "Inhibition of GCN2 Alleviates Cardiomyopathy in Type 2 Diabetic Mice via Attenuating Lipotoxicity and Oxidative Stress" Antioxidants 11, no. 7: 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071379
APA StyleYuan, J., Li, F., Cui, B., Gao, J., Yu, Z., & Lu, Z. (2022). Inhibition of GCN2 Alleviates Cardiomyopathy in Type 2 Diabetic Mice via Attenuating Lipotoxicity and Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants, 11(7), 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071379