Evaluation of Physicochemical and Microbial Properties of Extracts from Wine Lees Waste of Matelica’s Verdicchio and Their Applications in Novel Cosmetic Products
Abstract
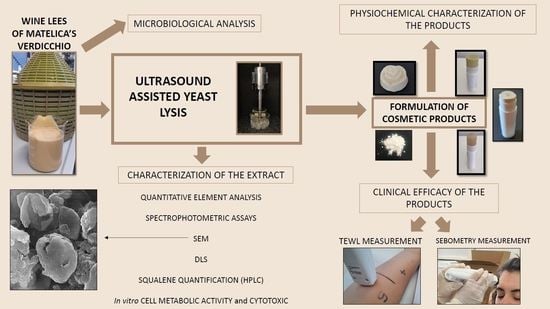
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wine Lees
2.2. Reagents and Materials Other Than Wine Lees
2.3. Microbiological Analysis of Native Wine Lees
2.3.1. Extraction of Total DNA
2.3.2. Quality Check by PCR and Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
2.3.3. Preparation and Shipment of Samples
2.3.4. Preparation and Inoculation of Microbial Growth Media
2.3.5. Bacterial Population Enrichment
2.3.6. Microbial Growth on Selective and Differential Media
2.3.7. DNA Extraction by GenElute Bacterial Genomic DNA Kit
2.3.8. Quality Check by PCR and Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
2.3.9. Preparation and Shipment of Samples for NGS Analysis
2.3.10. NGS Bioinformatic Analysis Using DADA2
2.4. Ultrasound-Assisted Yeast Lysis of NWLs and Physicochemical Characterization of the Aqueous Extract
2.4.1. Ultrasound-Assisted Yeast Lysis of NWLs
2.4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.3. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.4.4. Bio-Rad Protein Assay
2.4.5. Quantitative Element Analysis
2.4.6. Total Phenol Content (Folin-Ciocalteu Assay)
2.4.7. Antioxidant Assays
DPPH Radical Scavenging Method
ABTS Radical Scavenging Method
Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP)
2.4.8. Quantitation of Squalene by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Diode Array Detection
2.5. Determination of Cell Metabolic Activity and Cytotoxicity
2.5.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.5.2. Cell Metabolic Activity Test (MTT)
2.5.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.6. Statistics
2.7. Formulation of Cosmetic Products
2.8. Physicochemical Characterization of Formulations
2.9. Challenge Test
2.10. Local Compatibility Test with Human Skin (Irritant Potential)
2.11. Measurement of the Trans Epidermal Water Loss (TEWL)
2.12. Measurement of the Sebometry
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Microbiological Analysis
3.1.1. Analysis of the Microbiome in the Lees
3.1.2. Count of Mesophilic Bacteria, Anaerobes, and Fungi
3.1.3. Growth of Isolates on Selective Media
3.1.4. Identification of Mesophiles Isolates Grown onto MSA by 16S rDNA Analysis
3.2. Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction Method for the Yeast Cells Breakdown in Water and Evaluation of the Properties of the Aqueous Extract
3.3. In Vitro Metabolic Activity and Cytotoxicity Assays
3.4. Cosmetic Products
3.4.1. General Characteristics of the Cosmetic Products
3.4.2. Evaluation of Clinical Efficacy
3.4.3. Measurements of the Sebometry
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- No 337/79; Council Regulation (EEC) of 5 February 1979 on the Common Organization of the Market in Wine. Council of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 1979; pp. 1–47, 5 February 1979; Official Journal.
- Delgado de la Torre, M.P.; Priego-Capote, F.; Luque de Castro, M.D. Characterization and Comparison of Wine Lees by Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry in High-Resolution Mode. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacobbo, A.; Dias, B.B.; Onorevoli, B.; Bernardes, A.M.; de Pinho, M.N.; Caramão, E.B.; Rodrigues, E.; Jacques, R.A. Wine lees from the 1st and 2nd rackings: Valuable by-products. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Iseppi, A.; Lomolino, G.; Marangon, M.; Curioni, A. Current and future strategies for wine yeast lees valorization. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jara-Palacios, M.J. Wine Lees as a Source of Antioxidant Compounds. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaspar, L.R.; Camargo, F.B., Jr.; Gianeti, M.D.; Maia Campos, P.M. Evaluation of dermatological effects of cosmetic formulations containing Saccharomyces cerevisiae extract and vitamins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 3493–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabiscol, E.; Piulats, E.; Echave, P.; Herrero, E.; Ros, J. Oxidative stress promotes specific protein damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 27393–27398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falabiba, N.E. Pengaruh Penerapan Spiritualitas Di Tempat Kerja Terhadap Kinerja Pegawai Dimediasi Oleh Perilaku Menyimpang Di Tempat Kerja Pada Instansi Balai Pengkajian Teknologi Pertanian (BPTP) Jawa Timur. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitas Islam Negeri Maulana Malik Ibrahim, Malang, Indonesia, 2019; pp. 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Beres, C.; Costa, G.N.S.; Cabezudo, I.; da Silva-James, N.K.; Teles, A.S.C.; Cruz, A.P.G.; Mellinger-Silva, C.; Tonon, R.V.; Cabral, L.M.C.; Freitas, S.P. Towards integral utilization of grape pomace from winemaking process: A review. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florencio Maluf, D.; Gonçalves, M.M.; D’Angelo, R.W.O.; Girassol, A.B.; Tulio, A.P.; Pupo, Y.M.; Farago, P.V. Cytoprotection of Antioxidant Biocompounds from Grape Pomace: Further Exfoliant Phytoactive Ingredients for Cosmetic Products. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brenn-O-Kem. Grape Pomace. Available online: https://www.brenn-o-kem.co.za/grape-pomace/ (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Dimou, C.; Vlysidis, A.; Kopsahelis, N.; Papanikolaou, S.; Koutinas, A.A.; Kookos, I.K. Techno-economic evaluation of wine lees refining for the production of value-added products. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 116, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimou, C.; Kopsahelis, N.; Papadaki, A.; Papanikolaou, S.; Kookos, I.K.; Mandala, I.; Koutinas, A.A. Wine lees valorization: Biorefinery development including production of a generic fermentation feedstock employed for poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) synthesis. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Iseppi, A.; Marangon, M.; Vincenzi, S.; Lomolino, G.; Curioni, A.; Divol, B. A novel approach for the valorization of wine lees as a source of compounds able to modify wine properties. LWT 2021, 136, 110274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, C.; Pradal, M.; Sanchez, I.; Noble, J.; Tesnière, C.; Blondin, B. A set of nutrient limitations trigger yeast cell death in a nitrogen-dependent manner during wine alcoholic fermentation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, H.; Guilloux-Benatier, M. Yeast autolysis in sparkling wine—A review. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2006, 12, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naziri, E.; Mantzouridou, F.; Tsimidou, M.Z. Recovery of squalene from wine lees using ultrasound assisted extraction-a feasibility study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9195–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Serradilla, J.A.; Luque de Castro, M.D. Microwave-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from wine lees and spray-drying of the extract. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1652–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arboleda Meija, J.A.; Parpinello, G.P.; Versari, A.; Conidi, C.; Cassano, A. Microwave-assisted extraction and membrane-based separation of biophenols from red wine lees. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 117, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varelas, V.; Tataridis, P.; Liouni, M.; Nerantzis, E.T. Valorization of Winery Spent Yeast Waste Biomass as a New Source for the Production of β-Glucan. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2016, 7, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Iseppi, A.; Marangon, M.; Lomolino, G.; Crapisi, A.; Curioni, A. Red and white wine lees as a novel source of emulsifiers and foaming agents. LWT 2021, 152, 112273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petravić-Tominac, V.; Zechner-Krpan, V.; Grba, S.; Srečec, S.; Panjkota-Krbavčić, I.; Vidović, L. Biological Effects of Yeast β-Glucans. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2010, 75, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.-R.; Lin, Y.-K.; Fang, J.-Y. Biological and Pharmacological Activities of Squalene and Related Compounds: Potential Uses in Cosmetic Dermatology. Molecules 2009, 14, 540–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menaa, F.; Menaa, A.; Tréton, J. Polyphenols against skin aging. In Polyphenols in Human Health and Disease; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 819–830. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, S.; Tomita, J.; Nishioka, K.; Hisada, T.; Nishijima, M. Development of a prokaryotic universal primer for simultaneous analysis of Bacteria and Archaea using next-generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ISO 18415:2017; Cosmetics-Microbiology-Detection of Specified and Non-Specified Microorganism. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 17516:2014; Cosmetics-Microbiology-Microbiological Limits. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afgan, E.; Baker, D.; Batut, B.; van den Beek, M.; Bouvier, D.; Cech, M.; Chilton, J.; Clements, D.; Coraor, N.; Grüning, B.A.; et al. The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W537–W544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emami Bistgani, Z.; Siadat, S.A.; Bakhshandeh, A.; Ghasemi Pirbalouti, A.; Hashemi, M. Interactive effects of drought stress and chitosan application on physiological characteristics and essential oil yield of Thymus daenensis Celak. Crop J. 2017, 5, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliobianco, M.R.; Cortese, M.; Nannini, S.; Di Nicolantonio, L.; Peregrina, D.V.; Lupidi, G.; Vitali, L.A.; Bocchietto, E.; Di Martino, P.; Censi, R. Chemical, Antioxidant, and Antimicrobial Properties of the Peel and Male Flower By-Products of Four Varieties of Punica granatum L. Cultivated in the Marche Region for Their Use in Cosmetic Products. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.T.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, F. Determination of squalene using high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection. Chromatographia 2004, 59, 367–371. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, A.; Gallorini, M.; Feghali, N.; Sampò, S.; Cataldi, A.; Zara, S. Snail Slime Extracted by a Cruelty Free Method Preserves Viability and Controls Inflammation Occurrence: A Focus on Fibroblasts. Molecules 2023, 28, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 11930:2012; Cosmetics-Microbiology- Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Protection of a Cosmetic Product. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Walker, A.P.; Basketter, D.A.; Baverel, M.; Diembeck, W.; Matthies, W.; Mougin, D.; Röthlisberger, R.; Coroama, M. Test guidelines for the assessment of skin tolerance of potentially irritant cosmetic ingredients in man. European Cosmetic, Toiletry and Perfumery Association. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1997, 35, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, F.L.; Pimentel, N.H.; Teixeira, A.; Fonseca, A. Saccharomyces bacillaris is not a synonym of Candida stellata: Reinstatement as Starmerella bacillaris comb. nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2012, 102, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciani, M.; Comitini, F. Yeast interactions in multi-starter wine fermentation. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palleroni, N.J. The Pseudomonas story. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porto, M.C.; Kuniyoshi, T.M.; Azevedo, P.O.; Vitolo, M.; Oliveira, R.P. Pediococcus spp.: An important genus of lactic acid bacteria and pediocin producers. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maragkoudakis, P.A.; Nardi, T.; Bovo, B.; D’Andrea, M.; Howell, K.S.; Giacomini, A.; Corich, V. Biodiversity, dynamics and ecology of bacterial community during grape marc storage for the production of grappa. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 162, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, K.L. Medical microbiology. 2. Nurs. Mirror 1978, 146, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Miquel, S.; Martín, R.; Rossi, O.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Chatel, J.M.; Sokol, H.; Thomas, M.; Wells, J.M.; Langella, P. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and human intestinal health. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracchetti, F.; Felis, G.; Del Casale, A.; Torriani, S. Il controllo microbiologico in vinificazione: I batteri. In Mille Vigne Enologia; Università degli Studi di Verona: Verona, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Satola, B.; Wübbeler, J.H.; Steinbüchel, A. Metabolic characteristics of the species Variovorax paradoxus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 541–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palleroni, N.J. Pseudomonas. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Trujillo, M.E., Dedysh, S., DeVos, P., Hedlund, B., Kämpfer, P., Rainey, F.A., Whitman, W.B., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, P.N. Methylobacterium. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, A.I.; Griffiths, M.W.; Mittal, G.S.; Deeth, H.C. Combining nonthermal technologies to control foodborne microorganisms. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 89, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, I.D.; Zadorina, E.V.; Kravchenko, I.K.; Boulygina, E.S.; Tourova, T.P.; Sorokin, D.Y. Natronobacillus azotifigens gen. nov., sp. nov., an anaerobic diazotrophic haloalkaliphile from soda-rich habitats. Extremophiles 2008, 12, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parker, B.J.; Wearsch, P.A.; Veloo, A.C.M.; Rodriguez-Palacios, A. The Genus Alistipes: Gut Bacteria with Emerging Implications to Inflammation, Cancer, and Mental Health. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boracchi, S. Il Controllo Qualità e i Limiti Microbiologici del Prodotto Cosmetico; SICC: Milano, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dao, H.; Lakhani, P.; Police, A.; Kallakunta, V.; Ajjarapu, S.S.; Wu, K.-W.; Ponkshe, P.; Repka, M.A.; Narasimha Murthy, S. Microbial Stability of Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Products. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyrman, J.; De Vos, P. Oceanobacillus. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, I.; Yokota, A.; Yamazoe, A.; Fujiwara, T. Proposal of Lysinibacillus boronitolerans gen. nov. sp. nov., and transfer of Bacillus fusiformis to Lysinibacillus fusiformis comb. nov. and Bacillus sphaericus to Lysinibacillus sphaericus comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaishampayan, P.; Probst, A.; Krishnamurthi, S.; Ghosh, S.; Osman, S.; McDowall, A.; Ruckmani, A.; Mayilraj, S.; Venkateswaran, K. Bacillus horneckiae sp. nov., isolated from a spacecraft-assembly clean room. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Priest, F.G. Genus I Paenibacillus. In Genus I Paenibacillus. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; Vos, P., Garrity, G., Jones, D., Krieg, N.R., Ludwig, W., Rainey, F.A., Eds.; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 3, pp. 269–295. [Google Scholar]
- Heyrman, J.; Logan, N.A.; Rodríguez-Díaz, M.; Scheldeman, P.; Lebbe, L.; Swings, J.; Heyndrickx, M.; De Vos, P. Study of mural painting isolates, leading to the transfer of ‘Bacillus maroccanus’ and ‘Bacillus carotarum’ to Bacillus simplex, emended description of Bacillus simplex, re-examination of the strains previously attributed to ‘Bacillus macroides’ and description of Bacillus muralis sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, M.; Martinko, J. Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 11th ed.; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Sun, G.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Xu, M. Lysinibacillus varians sp. nov., an endospore-forming bacterium with a filament-to-rod cell cycle. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 3644–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yumoto, I.; Hirota, K.; Nodasaka, Y.; Nakajima, K. Oceanobacillus oncorhynchi sp. nov., a halotolerant obligate alkaliphile isolated from the skin of a rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), and emended description of the genus Oceanobacillus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1521–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Wang, R.; Gao, J.-R.; Niu, D.; Li, J.; Wen, Q.-H.; Zeng, X.-A. The effect of moderate pulsed electric fields on autolysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the amino acid content in autolysates. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhartsev, M.; Reuss, M. Cell size and morphological properties of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae in relation to growth temperature. FEMS Yeast Res. 2018, 18, foy052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Zeng, X.-A.; Sun, D.-W.; Han, Z. Disruption and protein release by ultrasonication of yeast cells. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 18, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimonti, A.B.B.; Buratti, F.M.; Fabbri, E.; Testai, E. Metalli in Prodotti Cosmetici: Procedure Raccomandate per la Determinazione e Valutazione dei Rischi per la Salute; Rapporti ISTISAN 19/18; Istituto Superiore di Sanità: Roma, Italy, 2019; Volume IV, 57p. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, D.; Zhang, P.; Li, S.; Ho, C.-T.; Zhao, H. Antioxidant activity evaluation of dietary phytochemicals using Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a model. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.M.M. Antioxidant and Immunostimulating Activities of Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) Autolysates. World Appl. Sci. J. 2011, 8, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Aresta, A.; Damascelli, A.; De Vietro, N.; Zambonin, C. Measurement of squalene in olive oil by fractional crystallization or headspace solid phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 1845–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Medium | Sample | Incubation Temperature (°C) | Atmospheric Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| TSA | F1:10 | 37 | Aerobiosis |
| TSA | F1:100 | 37 | Aerobiosis |
| TSA | F1:10 | Room temperature | Aerobiosis |
| TSA | F1:100 | Room temperature | Aerobiosis |
| SDA | F1:10 | 37 | Aerobiosis |
| SDA | F1:100 | 37 | Aerobiosis |
| SDA + chloramphenicol | F1:10 | 37 | Aerobiosis |
| SDA+ chloramphenicol | F1:100 | 37 | Aerobiosis |
| MRS | F1:10 | Room temperature | Aerobiosis |
| MRS | F1:100 | Room temperature | Aerobiosis |
| MRS | F1:10 | Room temperature | Anaerobiosis |
| MRS | F1:100 | Room temperature | Anaerobiosis |
| Step | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | 150 | 190 | 50 |
| P (Bar) | 36 | 36 | 0 |
| POWER (%) | 70 | 90 | 0 |
| RAMP (Min) | 5 | 5 | 1 |
| Step (Min) | 10 | 20 | 20 |
| Commercial name | Ingredients (INCI) | Supplier |
|---|---|---|
| TEGO® Betain CK D MB | Cocamidopropyl BetaineSodium Chloride, Aqua | Evonik, Essen, Germany |
| Stearic acid | Acef, Fiorenzuola d’Arda (PC), Italy | |
| Cetearyl alcol | ||
| Theobroma Cacao Seed Butter | ||
| Butyrospermum Parkii Butter | ||
| Citric acid | ||
| Glycerin | ||
| Kaolin | ||
| Zinc oxide | ||
| Helianthus Annuus Seed Oil | ||
| Cera Alba | ||
| Hydrogenated castor oil | ||
| Oryza Sativa Starch | ||
| Argania Spinosa Kernel Oil | ||
| Oryza Sativa Bran Oil | ||
| ACNIBIO PE 9010 | Phenoxyethanol, ethylhexylglycerin | |
| GLDA Chelating | Aqua, Tetrasodium glutamate diacetate, Sodium hydroxide | |
| Butylene Glycol | ||
| Oryza Sativa Bran Oil | ||
| Sodium Stearate | ||
| Thocopheryl Acetate | Basf, Ludwigshafen, Germany | |
| Sodium Coco-Sulfate | ||
| Glyceryl Stearate | ||
| Betaine | ||
| Erylite | Eurotrading, Civitanova Marche (MC), Italy | |
| Cocos nucifera oil | Esperis, Milan, Italy | |
| Copernicia Cerifera Cera | Natura Tec, Louis Lépine Fréjus, France | |
| Turkey Red Oil | Castor Oil Sulfated, Sodium Salt, Aqua | Zschimmer & Schwarz, Lahnstein, Germany |
| PROTELAN ENS | Stearic acid, Sodium lauroyl glutamate, Cetearyl alcohol, Glyceryl stearate | |
| Hydrogenated Coco-glycerides | Farmalabor, Canosa di Puglia (BT), Italy | |
| Polyglyceryl-10 Caprylate | Bregaglio, Biassono (MB), Italy | |
| SORBOSIL™ AC 36 | Hydrated silica, Aqua | |
| Cetyl Alcohol | ||
| Sodium Cocoyl Glutamate | Prodotti Gianni, Milan, Italy | |
| Hydroxyethylcellulose | Vevy Europe, Genova, Italy |
| Cosmetic Formulation/ Consistency | List of Ingredients According to the International Nomenclature Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) | Method of Preparation |
|---|---|---|
| Facial cleanser Solid | Sodium Coco-sulfate, Oryza Sativa Starch, Sodium Cocoyl Glutamate, Cetearyl Alcohol, Glyceryl Stearate, Hydrogenated Coco-glycerides, Saccharomyces/Grape Lees Ferment Extract, Butyrospermum Parkii Butter, Betaine, Hydrogenated Coco—glycerides, Aqua, Theobroma Cacao Seed Butter, Tocopheryl Acetate, Tocopherol, Parfum, Citric Acid | The lipidic phase A was weighed and heated in a water bath up to 85 °C until complete melting. Vitamin E was added to the Phase A once the latter was removed from the water bath and allowed to cool under stirring. Sodium coco-sulfate, oryza sativa starch and the Saccharomyces/Grape Lees Ferment were weighed and homogenized to the lipidic phase at 3500 rpm to obtain a pasty texture. Citric acid was weighed and stirred until complete solubilization in water and added to the paste to reach the desired pH. Perfume was added as the last step. |
| Facial cleansing Powder | Oryza Sativa Starch, Saccharomyces/Grape Lees Ferment Extract, Oryza Sativa Bran Oil, Sodium Cocoyl Glutamate, Erylite, Silica, Betaine, Cocamidopropyl Betaine, Sodium Chloride, Parfum, Aqua | The oil was added drop by drop to be adsorbed into the weighed starch by using a pestle and a mortar. Thus, first Saccharomyces/Grape Lees Ferment, and then betaine, silica and erylite were added and mixed with a mortar to obtain a homogeneous powder. Perfume was added as the last step. |
| Make-up remover Solid | Helianthus Annuus Seed Oil, Hydrogenated Coco-glycerides, Cera Alba, Polyglyceryl-10 Caprylate, Saccharomyces/Grape Lees FermentExtract, Theobroma Cacao Seed Butter, Castor Oil Sulfated, Cocos Nucifera Oil, Butyrospermum Parkii Butter, Hydrogenated Castor Oil, Sodium Salt, Tocopheryl Acetate, Parfum, Aqua. | The lipidic phase was weighed and heated in a water bath up to 90 °C until complete melting. Vitamin E was added after the removal from the water bath of the mixture and allowed to cool under stirring. Saccharomyces/Grape Lees Ferment was dispersed in water and added to sulfated castor oil s, heated up to 40 °C under stirring to promote the formation of the mixture and added to the lipidic phase. Perfume was added as the last step. |
| Melting face mask Solid | Cocos Nucifera Oil, Kaolin, Saccharomyces/Grape Lees FermentExtract, Butyrospermum Parkii Butter, Copernicia Cerifera Cera, Castor Oil Sulfated, Sodium Salt, Zinc Oxide, Tocopheryl acetate, Parfum, Aqua. | Cocos nucifera oil, butyrospermum parkii butter and cera carnauba were weighed and heated up to 80 °C for 30 min under stirring with kaolin and zinc oxide. After removing the ingredients from the water bath, vitamin E was added. Saccharomyces/Grape Lees Ferment was dispersed in water and added to sulfated castor oil, heated up to 40 °C under stirring to promote the formation of the mixture and added to the other ingredients. Perfume was added as the last step. |
| Purifying face mask Solid | Aqua, Kaolin, Glycerin, Saccharomyces/Grape Lees FermentExtract, Butyrospermum Parkii Butter, Sodium Stearate, Butylene Glycol, Glyceryl Stearate, Cetearyl alcohol, Cera Alba, Stearic Acid, Sodium Lauroyl Glutamate, Tocopheryl Acetate, Phenoxyethanol, Hydroxyethylcellulose, Parfum, Ethylhexylglycerin, Tetrasodium Glutamate Diacetate, Sodium Hydroxide. | Phase A, composed of water, chelating and wetting agents, kaolin, sodium stearate and Saccharomyces/Grape Lees Ferment, was weighed and heated up to 75 °C under stirring. Hydroxyethylcellulose was then slowly added to the phase A under stirring. Phase B, composed of the lipidic ingredients, was heated up to 75 °C and added to the phase A under homogenization (3500 rpm) until the temperature reached 40 °C. Vitamin E, preservative and parfum were added as the last step. |
| Bacterial Genus | Temperature Range(°C) | pH Range | Salt Range (%) | Oxygen | Mannitol Fermentation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus | 4–49 | 6–9 | 0–10 | aerobic | + | [58] |
| Lysinibacillus | 10–45 | 5.5–9.5 | 5–7 | aerobic | − | [59] |
| Oceanobacillus | 10–40 | 6.5–10 | 3–10 | aerobic | +/− | [60] |
| SAMPLES | FREEZE-DRYING | SONICATION | SIZE | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NWL0 | − | − | 2945 ± 26 | 0.084 |
| SWL0 | − | + | 1476 ± 64 | 0.442 |
| NWL1 | + | − | 2447 ± 28 | 0.676 |
| SWL1 | + | + | 1723 ± 35 | 0.291 |
| ELEMENT ANALYSIS | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| NWLs (ppm) | Supernatant of the NWLs (ppm) | Supernatant of the SWLs (ppm) | |
| Li | 0.06 ± 20.29 | 0.20 ± 6.41 | 47.26 ± 3.12 |
| B | 58.18 ± 1.11 | 168.94 ± 1.35 | 236.22 ± 1.90 |
| Na | 68.98 ± 2.91 | 315.89 ± 1.18 | 729.07 ± 4.23 |
| Mg | 577.88 ± 2.07 | 1735.23 ± 1.55 | 2125.98 ± 2.94 |
| P | 10,888.45 ± 1.56 | 9146.64 ± 1.27 | 7862.77 ± 2.56 |
| S | 3593.28 ± 3.11 | 4928.72 ± 1.78 | 5383.26 ± 5.85 |
| K | 13,514.31 ± 1.74 | 19,195.52 1.68± | 65,338.26 ± 3.23 |
| Ca | 2687.06 ± 1.45 | 1130.35 ± 1.34 | 7927.05 ± 2.49 |
| Cr | 0.43 ± 2.15 | 1.10 ± 1.12 | 1.39 ± 3.41 |
| Mn | 10.72 ± 1.13 | 8.48 ± 1.40 | 20.63 ± 2.80 |
| Fe | 11.48 ± 1.92 | 8.28 ± 2.03 | 4.49 ± 6.68 |
| Cu | 227.34 ± 1.74 | 588.19 ± 0.91 | 262.41 ± 2.67 |
| Zn | 5.16 ± 4.94 | 14.46 ± 2.47 | 45.54 ± 2.25 |
| Rb | 12.21 ± 1.14 | 35.03 ± 1.72 | 62.21 ± 2.80 |
| Sr | 9.11 ± 1.81 | 11.93 ± 0.70 | 25.66 ± 1.62 |
| Ba | 2.16 ± 1.25 | 3.25 ± 1.12 | 10.53 ± 1.85 |
| Hg | 0.00 ± 6.49 | 0.02 ± 5.91 | 0.00 ± 14.57 |
| ABTS | DPPH | FOLIN | FRAP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (mg/mL) | μmol TE/g | IC50 (mg/mL) | μmol TE/g | mg GAE/g | mg TEA/g | |
| NWL | 0.107 ± 0.003 | 204.525 ± 4.756 | 0.457 ± 0.009 | 870.692 ± 17.961 | 81.333 ± 9.905 | 55.048 ± 6.419 |
| SWL | 0.068 ± 0.001 | 182.489 ± 2.643 | 0.228 ± 0.020 | 607.195 ± 64.368 | 136.533± 8.942 | 82.133 ± 8.987 |
| TROLOX | 0.004 ± 0.000 | 7.991 ± 0.190 | 0.003± 0.000 | 120.577 ± 14.872 | ||
| Cosmetic Formulation | pH | Physicochemical Stability | Challenge Test | Mean Irritation Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accelerated Stability | Long Term Stability | 15 min | 24 h | |||
| Solid facial cleanser | 5.85 | Stable | Stable | Passed | 0 | 0 |
| Facial cleansing powder | 5.84 | Stable | Stable | Passed | 0 | 0 |
| Make-up remover | 6.08 | Stable | Stable | Passed | 0 | 0 |
| Melting mask | 6.05 | Stable | Stable | Passed | 0 | 0 |
| Purifying mask | 5.80 | Stable | Stable | Passed | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Nicolantonio, L.; Ferrati, M.; Cristino, M.; Peregrina, D.V.; Zannotti, M.; Vitali, L.A.; Ciancia, S.I.; Giovannetti, R.; Ferraro, S.; Zara, S.; et al. Evaluation of Physicochemical and Microbial Properties of Extracts from Wine Lees Waste of Matelica’s Verdicchio and Their Applications in Novel Cosmetic Products. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12040816
Di Nicolantonio L, Ferrati M, Cristino M, Peregrina DV, Zannotti M, Vitali LA, Ciancia SI, Giovannetti R, Ferraro S, Zara S, et al. Evaluation of Physicochemical and Microbial Properties of Extracts from Wine Lees Waste of Matelica’s Verdicchio and Their Applications in Novel Cosmetic Products. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(4):816. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12040816
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Nicolantonio, Lucrezia, Marta Ferrati, Maria Cristino, Dolores Vargas Peregrina, Marco Zannotti, Luca Agostino Vitali, Sonia Ilaria Ciancia, Rita Giovannetti, Stefano Ferraro, Susi Zara, and et al. 2023. "Evaluation of Physicochemical and Microbial Properties of Extracts from Wine Lees Waste of Matelica’s Verdicchio and Their Applications in Novel Cosmetic Products" Antioxidants 12, no. 4: 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12040816
APA StyleDi Nicolantonio, L., Ferrati, M., Cristino, M., Peregrina, D. V., Zannotti, M., Vitali, L. A., Ciancia, S. I., Giovannetti, R., Ferraro, S., Zara, S., Di Valerio, V., Cataldi, A., Gigliobianco, M. R., Censi, R., & Di Martino, P. (2023). Evaluation of Physicochemical and Microbial Properties of Extracts from Wine Lees Waste of Matelica’s Verdicchio and Their Applications in Novel Cosmetic Products. Antioxidants, 12(4), 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12040816