Differentiation of Phenolic Composition Among Tunisian Thymus algeriensis Boiss. et Reut. (Lamiaceae) Populations: Correlation to Bioactive Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
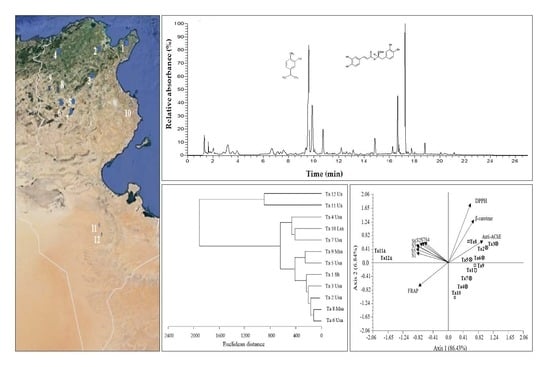
2.2. Plant Material
2.3. Preparation of Extracts
2.4. Analysis of Phenolic Compounds
2.4.1. Determination of Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents
2.4.2. Identification and Quantification of Phenolic Compounds by UHPLC-DAD-ESI/MSn
2.5. Antioxidant Assays
2.5.1. DPPH• Scavenging Test
2.5.2. β-Carotene Bleaching Test
2.5.3. Ferric-Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) Assay
2.6. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition Assay
2.7. Antibacterial Activity
2.7.1. Bacterial Strains
2.7.2. Well-Diffusion Method
2.7.3. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory (MIC) and Bactericidal (MBC) Concentrations
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Total Phenol and Flavonoid Contents
3.2. Characterization of Phenolic Compounds in T. algeriensis Populations
3.3. Antioxidant Activity
3.4. Anti-Acetylcholinesterase Activity
3.5. Antibacterial Activity
3.6. Correlations between Bioactivity and Phenolic Components
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kasrati, A.; Jamali, C.A.; Fadli, M.; Bekkouche, K.; Hassani, L.; Wohlmuth, H.; Leach, D.; Abbad, A. Antioxidative activity and synergistic effect of Thymus saturejoides Coss. essential oils with cefixime against selected food–borne bacteria. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2014, 61, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, A.; Pereira, O.; Neto, R.; Silva, A.; Cardoso, S. Health–Promoting Effects of Thymus herba barona, Thymus pseudolanuginosus, and Thymus caespititius Decoctions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohidi, B.; Rahimmalek, M.; Arzani, A. Essential oil composition, total phenolic, flavonoid contents, and antioxidant activity of Thymus species collected from different regions of Iran. Food Chem. 2017, 220, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickavar, B. Analysis of the essential oils of two Thymus species from Iran. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 609–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei-Ghomi, J.; Ebrahimabadi, A.; Djafari-Bidgoli, Z.; Batooli, H. GC/MS analysis and in vitro antioxidant activity of essential oil and methanol extracts of Thymus caramanicus Jalas and its main constituent carvacrol. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 1524–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, A.; Kyunn, W.W. Antioxidant and anti–cholinergic activities of phenolic compounds isolated from Thymus linearis collected from dir, Pakistan. Vegetos 2016, 29, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, E.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Salgueiro, L.; Goncalves, M.J.; Costa-de-Oliveira, C.; Cavaleiro, C.; Ana Palmeira, A.; Aca’cio Rodrigues, A.; Martinez-de-Oliveira, J. Antifungal activity of the essential oil of Thymus pulegioides on Candida, Aspergillus and dermatophyte species. J. Med. Microbio. 2006, 55, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordani, R.; Hadef, Y.; Kaloustian, J. Compositions and antifungal activities of essential oils of some Algerian aromatic plants. Fitoterapia 2008, 79, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loziene, K.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Sipailiene, A.; Labokas, J. Radical scavenging and antibacterial properties of the extracts from different Thymus pulegioides L. chemotypes. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, L.; Bruno, M.; Formisano, C.; De Feo, V.; Napolitano, F.; Rosselli, S.; Senatore, F. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of the Essential Oils from Two Species of Thymus Growing Wild in Southern Italy. Molecules 2009, 14, 4614–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazzit, M.; Baaliouamer, A.; Veríssimo, A.R.; Faleiro, M.L.; Miguel, M.G. Chemical composition and biological activities of Algerian Thymus oils. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, M.; Glamočlija, J.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Calhelha, R.C.; Fernandes, Â.; Marković, T.; Marković, D.; Giweli, A.; Soković, M. Chemical composition, antimicrobial, antioxidant and antitumor activity of Thymus serpyllum L., Thymus algeriensis Boiss. and Reut and Thymus vulgaris L. essential oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 52, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghi-Abyaneh, M.; Shams-Ghahfarokhi, M.; Rezaee, M.-B.; Jaimand, K.; Alinezhad, S.; Saberi, R.; Yoshinari, T. Chemical composition and antiaflatoxigenic activity of Carum carvi L., Thymus vulgaris and Citrus aurantifolia essential oils. Food Control 2009, 20, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Pottier-Alapetite, G. Flore de la Tunisie Angiospermes Dicotylédones Gamopétales; Ministère de l’Enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche Scientifique et le Ministère de l’Agriculture: Tunis, Tunisie, 1981; pp. 809–811.
- Le Floc’h, E.; Boulos, L. Flore de la Tunisie, Catalogue Synonymique Commente; Le Floc’h: Montepellier, France, 2008; p. 461. [Google Scholar]
- Ben El Hadj Ali, I.; Zaouali, Y.; Bejaoui, A.; Boussaid, M. Variation of the Chemical Composition of Essential Oils in Tunisian Populations of Thymus algeriensis Boiss.et Reut. (Lamiaceae) and Implication for Conservation. Chem. Biodivers 2010, 7, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Zouari, N.; Ayadi, I.; Fakhfakh, N.; Rebai, A.; Zouari, S. Variation of chemical composition of essential oils in wild populations of Thymus algeriensis Boiss. et Reut., a North African endemic Species. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarti, F.; Satrani, B.; Ghanmi, M.; Farah, A.; Abderrahman Aafi, A.; Aarab, L.; El Ajjouri, M.; Chaouch, A. Composition chimique et activité antimicrobienne des huiles essentielles de Thymus algeriensis Boiss. & Reut. et Thymus ciliatus (Desf.) Benth. du Maroc. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2010, 14, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- El Ajjouri, M.; Ghanmi, M.; Satrani, B.; Amarti, F.; Rahouti, M.; Aafi, A.; Ismaili, R.; Farah, A. Composition chimique et activité antifongique des huiles essentielles de Thymus algeriensis Boiss. & Reut. et Thymus ciliatus (Desf.) Benth. contre les champignons de pourriture du bois. Acta Bot. Gall. 2010, 157, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Kouache, B.; Brada, M.; Saadi, A.; Fauconnier, M.L.; Lognay, G.; Heuskin, S. Chemical Composition and Acaricidal Activity of Thymus algeriensis Essential Oil against Varroa destructor. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dob, T.; Dahmane, D.; Benabdelkader, T.; Chelghoum, D. Studies on the essential oil composition and antimicrobial activity of Thymus algeriensis Boiss. et Reut. Int. J. Aromather. 2006, 16, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkiniouar, R.; Rhouati, S.; Touil, A.; Seguin, E.; Chosson, E. Flavonoids from Thymus algeriensis. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2007, 43, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guesmi, F.; Ben Farhat, M.; Mejri, M.; Landoulsi, A. In–vitro assessment of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of methanol extracts and essential oil of Thymus hirtus sp. algeriensis. Lipids Health Dis. 2014, 13, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziani, B.E.C.; Heleno, S.A.; Bachari, K.; Dias, M.I.; Alves, M.J.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Phenolic compounds characterization by LC–DAD– ESI/MSn and bioactive properties of Thymus algeriensis Boiss. & Reut. and Ephedra alata Decne. Food Res. Int. 2018, 116, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ben El Hadj Ali, I.; Guetat, A.; Boussaid, M. Chemical and genetic variability of Thymus algeriensis Boiss. et Reut. (Lamiaceae), a North African endemic species. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2012, 40, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetoui, I.; Messaoud, C.; Boussaid, M.; Zaouali, Y. Antioxidant activity, total phenolic and flavonoid content variation among Tunisian natural populations of Rhus tripartita (Ucria) Grande and Rhus pentaphylla Desf. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2013, 51, 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Rocchetti, G.; Blasi, F.; Domenico Montesano, D.; Ghisoni, S.; Marcotullio, M.C.; Sabatini, S.; Cossignani, L. Luigi Lucinia Impact of conventional/non–conventional extraction methods on the untargeted phenolic profile of Moringa oleifera leaves. Food Res. Int. 2019, 115, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela–Raventos, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin–Ciocalteu reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, O.R.; Catarino, M.D.; Afonso, A.F.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Salvia elegans, Salvia greggii and Salvia officinalis Decoctions: Antioxidant Activities and Inhibition of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolic Enzymes. Molecules 2018, 23, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.R.; Peres, A.M.; Silva, A.M.S.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Cardoso, S.M. Simultaneous characterization and quantification of phenolic compounds in Thymus x citriodorus using a validated HPLC–UV and ESI–MS combined method. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaouali, Y.; Bouzaine, T.; Boussaid, M. Essential oils composition in two Rosmarinus officinalis L. varieties and incidence for antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 3144–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeen, I.M.S.; Elgorashi, E.E.; Van Staden, J. Antibacterial, anti–inflammatory, anti cholinesterase and mutagenic effects of extracts obtained from some trees used in South African traditional medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 102, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.R.; Baron, E.J.; Pfaller, M.A.; Tenover, F.C.; Yolken, H.R. Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 6th ed.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Okeke, M.I.; Iroegbu, C.U.; Eze, E.N.; Okoli, A.S.; Esimone, C.O. Evaluation of the root of Landolphia owerrience for antibacterial activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 78, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tang, G.Y.; Zhao, C.N.; Feng, X.L.; Xu, X.Y.; Cao, S.Y.; Meng, X.; Li, S.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, H.B. Comparison of antioxidant activities of different grape varieties. Molecules 2018, 23, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulanouar, B.; Abdelaziz, G.; Aazza, S.; Gago, C.; Miguel, M.G. Antioxidant activities of eight Algerian plant extracts and two essential oils. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2013, 46, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgen, U.; Mavi, A.; Terzi, Z.; Kazaz, C.; Asçı, A.; Kaya, Y.; Seçen, H. Relationship between chemical structure and antioxidant activity of luteolin and its glycosides isolated from Thymus sipyleus subsp. sipyleus var. sipyleus. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2011, 5, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Gonçalves, S.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Coelho, N.; Romano, A. Thymus lotocephalus wild plants and in vitro cultures produce different profiles of phenolic compounds with antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, T.; Marinero, P.; Manzanera, M.C.A.S.; Asensio, C.; Herrero, B.; Pereira, J.A.; Ramalhosa, E. Antioxidant activity of twenty wild Spanish Thymus mastichina L. populations and its relation with their chemical composition. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 412–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saija, A.; Speciale, A.; Trombetta, D.; Leto, C.; Tuttolomondo, T.; La Bella, S.; Licata, M.; Virga, G.; Bonsangue, G.; Gennaro, M.C.; et al. Phytochemical, Ecological and Antioxidant Evaluation of Wild Sicilian Thyme: Thymbra capitata (L.) Cav. Chem. Biodivers 2016, 13, 1641–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, T.O.; Solar, S.; Sontag, G.; Koenig, J. Identification of phenolic components in dried spices and influence of irradiation. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.R.; Cardoso, S.M. Overview on Mentha and Thymus Polyphenols. Current Analytical Chemistry. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2013, 9, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, A.F.; Pereira, O.R.; Válega, M.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Metabolites and Biological Activities of Thymus zygis, Thymus pulegioides, and Thymus fragrantissimus Grown under Organic Cultivation. Molecules 2018, 23, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schött, G.; Liesegang, S.; Gaunitz, F.; Gleß, A.; Basche, S.; Hannig, C.; Speer, K. The chemical composition of the pharmacologically active Thymus species, its antibacterial activity against Streptococcus mutans and the antiadherent effects of T. vulgaris on the bacterial colonization of the in situ pellicle. Fitoterapia 2017, 121, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adzet, T.; Vila, R.; Caaigural, S. Chromatographic analysis of polyphenols of some Iberian thymes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1988, 24, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwath, A.B.; Grayer, R.J.; Keith–Lucas, D.M.; Simmonds, M.S.J. Chemical characterisation of wild populations of Thymus from different climatic regions in southeast Spain. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2008, 36, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaouadi, R.; Cardoso, S.M.; Silva, A.M.S.; Ben Hadj Yahia, I.; Boussaid, M.; Zaouali, Y. Variation of phenolic constituents of Tunisian Thymus capitatus (L.) Hoff. et Link. populations. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2018, 77, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickavar, B.; Esbati, N. Evaluation of the Antioxidant Capacity and Phenolic Content of Three Thymus Species. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2012, 5, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Gonçalves, S.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Romano, A. Accumulation of phenolic compounds in in vitro cultures and wild plants of Lavandula viridis L’Hér and their antioxidant and anti–cholinesterase potential. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 57, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, I.; Kartal, M.; Tosun, F.; Şener, B. Screening of Various Phenolic Acids and Flavonoid Derivatives for their Anticholinesterase Potential. Z. Nat. C. 2007, 62, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, I.; Senol, F.S.; Gülpinar, A.R.; Kartal, M.; Sekeroglu, N.; Deveci, M.; Kan, K.; Sener, B. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory and antioxidant properties of Cyclotrichium niveum, Thymus praecox subsp. caucasicus var. caucasicus, Echinacea purpurea and E. pallida. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1304–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindl, M.; Blažeković, B.; Bucar, F.; Vladimir-Knežević, S. Antioxidant and Anticholinesterase Potential of Six Thymus Species. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 403950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic’, N.V.; Petrovic’, S.S.; Dzˇamic’, A.M.; C’iric’, A.D.; Risti’c, M.S.; Milovanovi’c, S.L.; Petrovi’c, S.D. Chemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of Thymus praecox supercritical extracts. J. Supercrit Fluids. 2016, 110, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.N.; Hadian, J.; Mirjalili, M.H.; Sonboli, A.; Yousefzadi, M. Essential oil composition and antibacterial activity of Thymus caramanicus at different phenological stages. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chizzola, R.; Michitsch, H.; Franz, C. Antioxidative Properties of Thymus vulgaris Leaves: Comparison of Different Extracts and Essential Oil Chemotypes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faleiro, L.; Miguel, G.; Gomes, S.; Costa, L.; Venâncio, F.; Teixeira, A.; Figueiredo, A.C.; Barroso, J.G.; Pedro, L.G. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities of Essential Oils Isolated from Thymbra capitata L. (Cav.) and Origanum vulgare L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8162–8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fachini-Queiroz, F.C.; Kummer, R.; Estevão-Silva, C.F.; de Barros Carvalho, M.D.; Cunha, J.M.; Grespan, R.; Bersani-Amado, C.A.; Cuman, R.K.N. Effects of Thymol and Carvacrol, Constituents of Thymus vulgaris L. Essential Oil, on the Inflammatory Response. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2012, 2012, 657026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Asada, T.; Sato, A.; Koi, Y.; Nishiwaki, H.; Tamura, H. Rosmarinic Acid Extract for Antioxidant, Antiallergic, and α–Glucosidase Inhibitory Activities, Isolated by Supramolecular Technique and Solvent Extraction from Perilla Leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aazza, S.; Lyoussi, B.; Miguel, M.G. Antioxidant and Antiacetylcholinesterase Activities of Some Commercial Essential Oils and Their Major Compounds. Molecules 2011, 16, 7672–7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jukic, M.; Politeo, O.; Maksimovic, M.; Milos, M.; Milos, M. In Vitro acetylcholinesterase inhibitory properties of thymol, carvacrol and their derivatives thymoquinone and thymohydroquinone. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Populations | Code | Bioclimatic Zone a | Rainfall (mm/year) | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Korbous | Ta 1 | Sub humid (Sh) | 550 | 36°50′ | 10°35′ |
| Essabahia | Ta 2 | upper semi-arid (Usa) | 450 | 36°36′ | 10°10′ |
| Dj Mansour | Ta 3 | 450 | 36°17′ | 9°36′ | |
| Jendouba | Ta 4 | 660 | 36°25′ | 8°44′ | |
| Dj chahid | Ta 5 | 520 | 36°22′ | 9°18′ | |
| Makther | Ta 6 | 520 | 35°51′ | 9°12′ | |
| Kesra | Ta 7 | 520 | 35°48′ | 9°21′ | |
| Siliana | Ta 8 | mean semi-arid (Msa) | 520 | 35°51′ | 9°12′ |
| Sers | Ta 9 | 245 | 36°6′ | 9°40′ | |
| Sousse | Ta 10 | lower semi-arid (Lsa) | 167 | 35°30′ | 10°50′ |
| Toujene | Ta 11 | upper arid (Ua) | 100 | 33°27′ | 10°08′ |
| Matmata | Ta 12 | 100 | 33°32′ | 9°58′ |
| Sh | Usa | Msa | Lsa | Ua | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ta 1 | Ta 2 | Ta 3 | Ta 4 | Ta 5 | Ta 6 | Ta 7 | Ta 8 | Ta 9 | Ta 10 | Ta 11 | Ta 12 | |||||
| TPC | 9.1 hi ± 0.1 | 9 hi ± 0.2 | 8.0 i ± 0.1 | 14.8 d ± 0.8 | 12.0 ef ± 0.3 | 9.8 gh ± 0.4 | 12.9 e ± 0.3 | 8.2 hi ± 0.2 | 11.1 gf ± 0.2 | 17.1 c ± 0.3 | 34.4 a ± 0.8 | 31.6 b ± 1 | ||||
| TF | 2.8 h ± 0.1 | 4.8 f ± 0.2 | 7.2 e ± 0.2 | 9.3 b ± 0.1 | 7.5 e ± 0.1 | 7.0 e ± 0.2 | 4.0 g ± 0.2 | 4.0 g ± 0.1 | 7.8 cd ± 0.1 | 8.2 c ± 0.2 | 10.6 a ± 0.2 | 10.3 a ± 0.3 | ||||
| Peak | tR (min) | λmax (nm) | (m/z) | MS2ions (m/z) | Probable Compound |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.4 | ND | 341 | 179 | Caffeoyl hexoside b |
| 2 | 1.6 | 271, 330 | 593 | 473, 503, 575 | Apigenin-di-C-hexoside b |
| 3 | 2.8 | 284, 325sh | 449 | 259,287 | Eriodictyol-O-hexoside a |
| 4 | 3.2 | 268, 339 | 447 | 285 | Kaempferol-O-hexoside b |
| 5 | 5.9 | 255, 266, 345 | 461 | 285 | Luteolin-O-hexuronide b |
| 6 | 8.8 | 267, 343 | 445 | 269 | Apigenin-O-hexuronide b |
| 7 | 9.2 | 288, 330sh | 287 | 151, 269 | Eriodictyol a |
| 8 | 9.5 | 287sh, 328 | 359 | 161,179, 224 | Rosmarinic acid a |
| 9 | 9.7 | 268, 339 | 461 | 285 | Kaempferol-O-hexuronide b |
| 10 | 10.1 | 288sh, 324 | 555 | 493, 357, 393, 313 | Salvianolic acid K b |
| 11 | 10.7 | 291sh, 324 | 537 | 493, 359 | Caffeoyl rosmarinic acid b |
| 12 | 12.2 | 289sh, 325 | 717 | 519 | Salvianolic acid E b |
| 13 | 13.0 | 273, 330 | 623 | 461, 285 | Scutellarein-O-hexoside-hexuronide b |
| 14 | 14.5 | 298sh, 325 | 551 | 519, 359 | Monomethyl lithospermate b |
| 15 | 14.9 | 289 | 271 | 151 | Naringenin a |
| 16 | 16.3 | 277, 333 | 313 | 298, 271 | Cirsimaritin b |
| 17 | 16.6 | 283, 331 | 343 | 329, 313, 299 285 | Tetramethyl-scutellarein b |
| 18 | 17.3 | 276 | ND | - | Carvacrol a |
| Compounds | Sh | Usa | Msa | Lsa | Ua | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ta 1 | Ta 2 | Ta 3 | Ta 4 | Ta 5 | Ta 6 | Ta 7 | Ta 8 | Ta 9 | Ta 10 | Ta 11 | Ta 12 | ||||||
| Phenolic acids | |||||||||||||||||
| Rosmarinic acid | 531.3 g ± 0.5 | 383.8 j ± 0.5 | 410.4 h ±0.7 | 1157.8 a ±2.7 | 593.6 f ±2.1 | 410.9 h ±0.7 | 756.3 e ± 0.7 | 391.3 i ± 0.5 | 596.4 f ± 0.3 | 1083.2 b ± 3.5 | 957.0 c ± 1.0 | 807.2 d ± 3.0 | |||||
| Caffeoyl rosmarinic acid | 39.2 j ± 0.1 | 64.9 h ± 0.1 | 78.9 f ± 0.1 | 85.5 e ± 0.1 | 73.9 fg ± 0.2 | 45.8 i ± 0.0 | 232.2 a ± 0.2 | 74.3 g ± 0.1 | 101.6 d ± 0.1 | 186.1 c ± 0.3 | 206.6 b ± 1.1 | 183.0 c ± 0.5 | |||||
| Flavanones | |||||||||||||||||
| Eriodictyol hexoside | -h | 6.3 f ± 0.1 | 31.9 c ± 0.1 | 40.0 b ± 0.1 | 39.1 b ± 0.1 | 3.5 g ± 0.2 | 5.7 f ± 0.1 | 28.7 d ± 0.1 | 52.8 a ± 0.1 | -h | 9.1 e ± 0.2 | 6.0 f ± 1.1 | |||||
| Eriodictyol | 4.1 h ± 0.1 | 16.9 b ± 0.1 | 4.4 hg ± 0.3 | 12.4 d ± 0.7 | 4.4 hg ± 0.8 | 8.2 f ± 0.1 | 11.4 d ± 0.1 | 1.1 i ± 0.1 | 5.5 g ± 0.2 | 9.9 e ± 0.4 | 14.7 c ± 0.1 | 42 a ± 0.1 | |||||
| Flavonols | |||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol-O-hexoside | -j | 83.9 h ± 0.3 | 228.1 d ± 0.1 | 326.3 c ± 0.2 | 360.4 b ± 0.5 | -j | 118.4 e ± 0.2 | 95.3 g ± 0.1 | 439.6 a ± 0.3 | 10.0 i ± 0.2 | -j | 108.4 ± 0.1 f | |||||
| Kaempferol-O-hexuronide | 256.3 h ± 0.3 | 363.2 f ± 1.9 | 202.9 j ± 1.7 | 552.0 c ± 0.6 | 213.2 ij ± 12.7 | 216.5 ij ± 0.7 | 526.4 d ± 0.5 | 225.2 i ± 0.4 | 446.6 e ± 9.4 | 297.1 g ± 0.3 | 862.8 a ± 1.2 | 655.7 b ± 2.6 | |||||
| Flavones | |||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin-O-hexuronide | -g | -g | -g | 25.3 b ± 0.1 | 20.6 c ± 0.1 | -g | 12.7 d ± 0.1 | 3.0 f ± 0.1 | 27.9 a ± 0.1 | 5.7 e ± 0.1 | -g | -g | |||||
| Apigenin-C-di-hexoside | 18.4 f ± 2.7 | 10.7 g ± 0.1 | 21.7 e ± 0.1 | 54.1 b ± 0.1 | 53.3 b ± 0.1 | 10.4 g ± 0.1 | 55.3 b ± 0.3 | 53.4 b ± 0.1 | 62.6 a ± 0.1 | 37.7 d ± 0.2 | 40.2 c ± 0.1 | 54.2 b ± 0.1 | |||||
| Apigenin-O-hexuronide | 112.8 a ± 0.1 | 6.8 c ± 0.1 | 3.8 e ± 0.1 | 6.1 d ± 0.1 | 3.5 ef ± 0.1 | 9.8 b ± 0.1 | 3.8 e ± 0.1 | 6.1 d ± 0.1 | 3.1 f ± 0.1 | 1.4 g ± 0.1 | -h | -h | |||||
| Phenolic terpene | |||||||||||||||||
| Carvacrol | -c | -c | -c | -c | -c | -c | -c | -c | -c | -c | 2221.6 a ± 2.5 | 1374.7 b ± 5.0 | |||||
| Bioactivities | Sh | Usa | Msa | Lsa | Ua | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ta 1 | Ta 2 | Ta 3 | Ta 4 | Ta 5 | Ta 6 | Ta 7 | Ta 8 | Ta 9 | Ta 10 | Ta 11 | Ta 12 | ||||||
| Antioxidant activity | |||||||||||||||||
| DPPH• (µg/mL) | 42.7 c ± 2.5 | 54.5 b ± 2.1 | 52.3 b ± 1.4 | 22.7 fg ± 0.9 | 37.8 d ± 0.6 | 40.7 cd± 1.0 | 26.6 f ± 1.4 | 68.8 a ± 1.0 | 32.4 e ± 1.0 | 19.9 g ± 1.1 | 8.9 h ± 0.1 | 10.3 h ± 0.4 | |||||
| β-carotene (mg/mL) | 1.43 e ± 0.0 | 1.50 d ± 0.1 | 1.81 a ± 0.0 | 1.04 h ± 0.0 | 1.35 f ± 0.3 | 1.60 b ± 0.0 | 1.13 g ± 0.0 | 1.60 b ± 0.0 | 1.53 c ± 0.1 | 0.40 i ± 0.0 | 0.03 k ± 0.0 | 0.06 j ± 0.0 | |||||
| FRAP (mmolFe2+/L) | 2 f ± 0.0 | 1.2 gh ± 0.0 | 0.3 i ± 0.01 | 4.8 d ± 0.0 | 6.8 c ± 0.0 | 1.8 fg ± 0.0 | 5.1 d ± 0.0 | 1.0 hi ± 0.0 | 4.0 e ± 0.0 | 6.5 c ± 0.05 | 16.7 b ± 0.1 | 20.6 a ± 0.2 | |||||
| Anti-acetylcholinesterase (mg/mL) | 1.0 ef ± 0.0 | 1.3 e ± 0.1 | 3.0 a ± 0.1 | 0.7 g ± 0.0 | 2.3 b ± 0.1 | 0.9 f ± 0.1 | 2.1 c ± 0.1 | 1.0 ef ± 0.0 | 1.6 d ± 0.1 | 1.2 e ± 0.0 | 0.2 hi ± 0.0 | 0.1 i ± 0.0 | |||||
| Bacteria | Ta 11 | Ta 12 | Gentamicin | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC | Inh Zone | MIC | MBC | Inh Zone | MIC | MBC | |||
| Gram-negative | |||||||||
| E. coli | 10,536 | 14.5 a ± 0.0 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 13.0 b ± 0.0 | 1.4 | - | 18.0 ± 0.0 | |
| P. aeruginosa | 9027 | 10.0 a ± 0.5 | 1.4 | - | 9.0 a ± 0.0 | 1.4 | - | 12.0 ± 0.0 | |
| K. pneumoniae | 10,031 | 10.5 a ± 0.5 | 1.4 | - | 10.0 a ± 0.0 | 1.4 | - | 17.0 ± 0.0 | |
| Gram-positive | |||||||||
| S. aureus | 6538 | 11.5 a ± 0.5 | 1.4 | - | 10.0 a ± 0.0 | 1.4 | - | 21.0 ± 0.0 | |
| B. cereus | 11,778 | 13.5 a ± 0.5 | 1.4 | - | 11.0 a ± 0.5 | 1.4 | - | 17.0 ± 0.0 | |
| S. epidermis | 12,228 | 12.0 a ± 0.0 | 1.4 | - | 10.5 b ± 0.0 | 1.4 | - | 27.0 ± 0.5 | |
| S. feacalis | 10,541 | 14.0 a ± 0.0 | 1.4 | - | 13.0 a ± 0.5 | 1.4 | - | 12.0 ± 0.0 | |
| Compounds | Antioxidant Activity | Anti-AChE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPPH• | β-Carotene | FRAP | Anti-AChE | |||
| Total phenols | −0.81 ** | −0,94 ** | 0.96 ** | −0,64 * | ||
| Flavonoids | −0.72 ** | −0.69 * | 0.70 * | −0.37 ns | ||
| Phenolic acids | ||||||
| Rosmarinic acid | −0.83 ** | −0.76 ** | 0.54 ns | −0.42 ns | ||
| Caffeoyl rosmarinic acid | −0.72 ** | −0.77 ** | 0.67 * | −0.20 ns | ||
| Flavanones | ||||||
| Eriodictyol hexoside | 0.20 ns | 0.40 ns | −0.22 ns | 0.37 ns | ||
| Eriodictyol | −0.58 * | −0.68 * | 0.78 ** | −0.54 ns | ||
| Flavones | ||||||
| Apigenin-C-di-hexoside | −0.38 ns | −0.31 ns | 0.39 ns | −0.07 ns | ||
| Apigenin-O-hexuronide | 0.19 ns | 0.22 ns | −0.26 ns | −0.08 ns | ||
| Luteolin-O-hexuronide | −0.18 ns | 0.15 ns | −0.11 ns | 0.23 ns | ||
| Kaempferol-O-hexuronide | −0.77 ** | −0.76 ** | 0.78 ** | −0.58 * | ||
| Kaempferol-O-hexoside | 0.04 ns | 0.33 ns | −0.14 ns | 0.44 ns | ||
| Phenolic terpene | ||||||
| Carvacrol | −0.63 * | −0.79 ** | 0.87 ** | −0.60 * | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaouadi, R.; Silva, A.M.S.; Boussaid, M.; Yahia, I.B.H.; Cardoso, S.M.; Zaouali, Y. Differentiation of Phenolic Composition Among Tunisian Thymus algeriensis Boiss. et Reut. (Lamiaceae) Populations: Correlation to Bioactive Activities. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8110515
Jaouadi R, Silva AMS, Boussaid M, Yahia IBH, Cardoso SM, Zaouali Y. Differentiation of Phenolic Composition Among Tunisian Thymus algeriensis Boiss. et Reut. (Lamiaceae) Populations: Correlation to Bioactive Activities. Antioxidants. 2019; 8(11):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8110515
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaouadi, Rym, Artur M. S. Silva, Mohamed Boussaid, Imen B. H. Yahia, Susana M. Cardoso, and Yosr Zaouali. 2019. "Differentiation of Phenolic Composition Among Tunisian Thymus algeriensis Boiss. et Reut. (Lamiaceae) Populations: Correlation to Bioactive Activities" Antioxidants 8, no. 11: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8110515
APA StyleJaouadi, R., Silva, A. M. S., Boussaid, M., Yahia, I. B. H., Cardoso, S. M., & Zaouali, Y. (2019). Differentiation of Phenolic Composition Among Tunisian Thymus algeriensis Boiss. et Reut. (Lamiaceae) Populations: Correlation to Bioactive Activities. Antioxidants, 8(11), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8110515