Phoenix dactylifera L. Seed Extract Exhibits Antioxidant Effects and Attenuates Melanogenesis in B16F10 Murine Melanoma Cells by Downregulating PKA Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation and Extraction of P. dactylifera Seed Extract
2.3. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) Analysis of P. dactylifera Seed Extract and Ferulic Acid
2.4. DPPH Scavenging Activity Assay
2.5. ABTS+ Scavenging Capacity Assay
2.6. Determination of Total Phenolic Content
2.7. Determination of Reducing Capacity
2.8. Measurement of Iron (II) Ion Chelating Capacity
2.9. Cell Viability Assay
2.10. Measurement of Mushroom Tyrosinase Activity
2.11. Determination of Melanin Content
2.12. Measurement of Intracellular Tyrosinase Activity
2.13. Western Blotting Experiment
2.14. PKA Inhibitor Assay
2.15. Determination of Intracellular ROS Level
2.16. RT-PCR
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. UPLC Analysis of P. dactylifera L. Seed Extract
3.2. Antioxidant Characteristics of P. dactylifera L. Seed Extract
3.3. Cell Viability Assay
3.4. Inhibitory Effects of P. dactylifera L. Seed Extract on Melanogenesis
3.5. P. dactylifera L. seed Extract Inhibits the Expression Levels of Proteins Involved in Melaninogenesis
3.6. P. dactylifera L. Seed Extract Does Not Affect Tyrosinase, TRP1, TRP2, or MITF Gene Expression
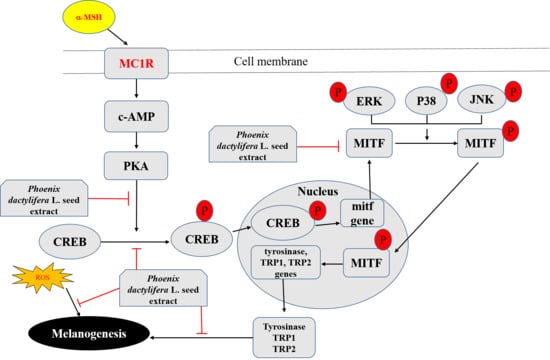
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N.J. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sárdy, M. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in skin ageing. Connect. Tissue Res. 2009, 50, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wlaschek, M.; Briviba, K.; Stricklin, G.P.; Sies, H.; Scharffetter-Kochanek, K. Singlet oxygen may mediate the ultraviolet A-induced synthesis of interstitial collagenase. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1995, 104, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Büyükokuroğlu, M.E.; GülçIn, I.; Oktay, M.; Küfrevioğlu, O.I. In vitro antioxidant properties of dantrolene sodium. Pharmacol. Res. 2001, 44, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülçin, I.; Oktay, M.; Küfrevioğlu, O.I.; Aslan, A. Determination of antioxidant activity of lichen Cetraria islandica (L.) Ach. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 79, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.H.; Liu, P.J.; Lin, K.P.; Chen, P.C. Nutritional supplement therapy improves oxidative stress, immune response, pulmonary function, and quality of life in allergic asthma patients: An open-label pilot study. Altern. Med. Rev. A J. Clin. Ther. 2012, 17, 42–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, N.; Hirose, M.; Fukushima, S.; Tsuda, H.; Shirai, T.; Tatematsu, M. Studies on antioxidants: Their carcinogenic and modifying effects on chemical carcinogenesis. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 1986, 24, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roméro-Graillet, C.; Aberdam, E.; Clément, M.; Ortonne, J.P.; Ballotti, R. Nitric oxide produced by ultraviolet-irradiated keratinocytes stimulates melanogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, M.; Horikoshi, T.; Uchiwa, H.; Miyachi, Y. Up-regulation of tyrosinase gene by nitric oxide in human melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 2000, 13, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.K.; Funasaka, Y.; Slominski, A.; Ermak, G.; Hwang, J.; Pawelek, J.M.; Ichihashi, M. Production and release of proopiomelanocortin (POMC) derived peptides by human melanocytes and keratinocytes in culture: Regulation by ultraviolet B. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1313, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spritz, R.A.; Hearing, V.J., Jr. Genetic disorders of pigmentation. Adv. Hum. Genet. 1994, 22, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.Y.; Sharma, V.K.; Sharma, N. Mushroom tyrosinase: Recent prospects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2837–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briganti, S.; Camera, E.; Picardo, M. Chemical and instrumental approaches to treat hyperpigmentation. Pigment Cell Res. 2003, 16, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funasaka, Y.; Komoto, M.; Ichihashi, M. Depigmenting effect of alpha-tocopheryl ferulate on normal human melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 2000, 13 (Suppl. 8), 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.X.; Wang, Z.J.; Park, D.; Chung, H.Y.; Wang, S.F.; Yan, L.; Yang, J.M.; Qian, G.Y.; Yin, S.J.; Park, Y.D. Effect of hesperetin on tyrosinase: Inhibition kinetics integrated computational simulation study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyden, J.J.; Shergill, B.; Micali, G.; Downie, J.; Wallo, W. Natural options for the management of hyperpigmentation. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. JEADV 2011, 25, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callender, V.D.; St Surin-Lord, S.; Davis, E.C.; Maclin, M. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: Etiologic and therapeutic considerations. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2011, 12, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearing, V.J.; Jiménez, M. Mammalian tyrosinase—The critical regulatory control point in melanocyte pigmentation. Int. J. Biochem. 1987, 19, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Cervantes, C.; Solano, F.; Kobayashi, T.; Urabe, K.; Hearing, V.J.; Lozano, J.A.; García-Borrón, J.C. A new enzymatic function in the melanogenic pathway. The 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid oxidase activity of tyrosinase-related protein-1 (TRP1). J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 17993–18000. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto, K.; Jackson, I.J.; Urabe, K.; Montague, P.M.; Hearing, V.J. A second tyrosinase-related protein, TRP-2, is a melanogenic enzyme termed DOPAchrome tautomerase. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Borrón, J.C.; Sánchez-Laorden, B.L.; Jiménez-Cervantes, C. Melanocortin-1 receptor structure and functional regulation. Pigment Cell Res. 2005, 18, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, C.I.; Setaluri, V. Cyclic AMP (cAMP) signaling in melanocytes and melanoma. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 563, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.E.; Park, S.H.; Oh, S.W.; Yoo, J.A.; Kwon, K.; Park, S.J.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.S.; Cho, J.Y.; Lee, J. Beauvericin inhibits melanogenesis by regulating cAMP/PKA/CREB and LXR-α/p38 MAPK-mediated pathways. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Mello, S.A.; Finlay, G.J.; Baguley, B.C.; Askarian-Amiri, M.E. Signaling Pathways in Melanogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vachtenheim, J.; Borovanský, J. “Transcription physiology” of pigment formation in melanocytes: Central role of MITF. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, T.I.; Yun, J.M.; Park, E.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Lim, J.H. Plumbagin Suppresses α-MSH-Induced Melanogenesis in B16F10 Mouse Melanoma Cells by Inhibiting Tyrosinase Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buscà, R.; Ballotti, R. Cyclic AMP a key messenger in the regulation of skin pigmentation. Pigment Cell Res. 2000, 13, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Hemesath, T.J.; Takemoto, C.M.; Horstmann, M.A.; Wells, A.G.; Price, E.R.; Fisher, D.Z.; Fisher, D.E. c-Kit triggers dual phosphorylations, which couple activation and degradation of the essential melanocyte factor Mi. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 301–312. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, M.M.; Xu, W.; Schwahn, D.J.; Liao, F.; Medrano, E.E. Activation of a cAMP pathway and induction of melanogenesis correlate with association of p16(INK4) and p27(KIP1) to CDKs, loss of E2F-binding activity, and premature senescence of human melanocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 1999, 253, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesiani, D.; Cicconi, R.; Mattei, M.; Bei, R.; Canini, A. Inhibition of Mek 1/2 kinase activity and stimulation of melanogenesis by 5,7-dimethoxycoumarin treatment of melanoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 34, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kim, J.; Hahn, H.G.; Yun, J.; Jeong, H.S.; Yun, H.Y.; Baek, K.J.; Kwon, N.S.; Min, Y.S.; Park, K.C.; et al. KHG26792 Inhibits Melanin Synthesis in Mel-Ab Cells and a Skin Equivalent Model. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Korean Physiol. Soc. Korean Soc. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.S.; Park, S.H.; Kwon, S.B.; Park, E.S.; Huh, C.H.; Youn, S.W.; Park, K.C. Sphingosylphosphorylcholine-induced ERK activation inhibits melanin synthesis in human melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 2006, 19, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Hwang, E.S.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, S.Y.; Kwon, S.B.; Park, K.C. Sphingosine-1-phosphate decreases melanin synthesis via sustained ERK activation and subsequent MITF degradation. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, N.; Dubey, A.; Mishra, R.; Barik, N. Study on antioxidant activity of common dry fruits. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2010, 48, 3316–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Farsi, M.A.; Lee, C.Y. Optimization of phenolics and dietary fibre extraction from date seeds. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasha, I.; Campbell, L.; Lonchamp, J.; Euston, S.R. The major proteins of the seed of the fruit of the date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.): Characterisation and emulsifying properties. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Khalid, N.; Khan, R.S.; Ahmed, H.; Ahmad, A. A review on chemistry and pharmacology of Ajwa date fruit and pit. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 63, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, M.; Bahkali, A.H. Valorization of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) fruit processing by-products and wastes using bioprocess technology—Review. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 20, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Juhaimi, F.; Özcan, M.M.; Adiamo, O.Q.; Alsawmahi, O.N.; Ghafoor, K.; Babiker, E.E. Effect of date varieties on physico-chemical properties, fatty acid composition, tocopherol contents, and phenolic compounds of some date seed and oils. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Al Kiyumi, A.R.; Al Sheidi, M.S.; Al Khusaibi, T.S.; Al Shehhi, N.M.; Alam, T. In vitro inhibitory effects on α-glucosidase and α-amylase level and antioxidant potential of seeds of Phoenix dactylifera L. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habib, H.M.; Ibrahim, W.H. Effect of date seeds on oxidative damage and antioxidant status in vivo. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1674–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, J.S.; Hashim, I.B.; Sharif, F.A. Preliminary analysis and potential uses of date pits in foods. Food Chem. 2002, 76, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theyab, F.; Habib, H.; Othman, A.; Al-Marzooqi, S.; Al-Bawardi, A.; Yasin, J.; Hilary, S.; Souka, U.; Al-Hammadi, S.; Ibrahim, W.; et al. The antioxidant activity of date seed: Preliminary results of a preclinical in vivo study. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2017, 29, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galato, D.; Ckless, K.; Susin, M.F.; Giacomelli, C.; Ribeiro-do-Valle, R.M.; Spinelli, A. Antioxidant capacity of phenolic and related compounds: Correlation among electrochemical, visible spectroscopy methods and structure-antioxidant activity. Redox Rep. Commun. Free Radic. Res. 2001, 6, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyaizu, M. Studies on products of browning reaction—Antioxidative activities of products of browning reaction prepared from glucosamine. Eiyougaku Zasshi 1986, 44, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinis, T.C.; Maderia, V.M.; Almeida, L.M. Action of phenolic derivatives (acetaminophen, salicylate, and 5-aminosalicylate) as inhibitors of membrane lipid peroxidation and as peroxyl radical scavengers. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1994, 315, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, H.; Shiho, O.; Kuroshima, K.; Koyama, M.; Tsukamoto, K. An improved colorimetric assay for interleukin 2. J. Immunol. Methods 1986, 93, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilodeau, M.L.; Greulich, J.D.; Hullinger, R.L.; Bertolotto, C.; Ballotti, R.; Andrisani, O.M. BMP-2 stimulates tyrosinase gene expression and melanogenesis in differentiated melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 2001, 14, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, T.; Kondoh, H.; Hiratsuka, J.; Mishima, Y. Enhanced melanogenesis induced by tyrosinase gene-transfer increases boron-uptake and killing effect of boron neutron capture therapy for amelanotic melanoma. Pigment Cell Res. 1998, 11, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Koo, J.H.; Song, Y.G.; Kwon, K.B.; Lee, J.H.; Sohn, H.S.; Park, B.H.; Jhee, E.C.; Park, J.W. Stimulation of melanogenesis by scoparone in B16 melanoma cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2006, 27, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrant, C.L.; Reid, M.B. Detection of reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species in skeletal muscle. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2001, 55, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasui, H.; Sakurai, H. Age-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species in the skin of live hairless rats exposed to UVA light. Exp. Dermatol. 2003, 12, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Kizawa, K.; Igarashi, S.; Horikoshi, T.; Uchiwa, H.; Miyachi, Y. Suppression of melanogenesis by induction of endogenous intracellular metallothionein in human melanocytes. Exp. Dermatol. 2004, 13, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerit, I. Free radicals and aging of the skin. Birkhäuser 1992, 62, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlaschek, M.; Tantcheva-Poór, I.; Naderi, L.; Ma, W.; Schneider, L.A.; Razi-Wolf, Z.; Schüller, J.; Scharffetter-Kochanek, K. Solar UV irradiation and dermal photoaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2001, 63, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Haley, S.; Perret, J.; Harris, M.; Wilson, J.; Qian, M. Free radical scavenging properties of wheat extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaini, G.; Monzani, E.; Casella, L.; Santagostini, L.; Pagliarin, R. Inhibition of the catecholase activity of biomimetic dinuclear copper complexes by kojic acid. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. JBIC A Publ. Soc. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 5, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldefie-Chézet, F.; Walrand, S.; Moinard, C.; Tridon, A.; Chassagne, J.; Vasson, M.P. Is the neutrophil reactive oxygen species production measured by luminol and lucigenin chemiluminescence intra or extracellular? Comparison with DCFH-DA flow cytometry and cytochrome c reduction. Clin. Chim. Acta; Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2002, 319, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.M.; Schallreuter, K.U. Studies on the reactions between human tyrosinase, superoxide anion, hydrogen peroxide and thiols. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1074, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karg, E.; Odh, G.; Wittbjer, A.; Rosengren, E.; Rorsman, H. Hydrogen peroxide as an inducer of elevated tyrosinase level in melanoma cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1993, 100, 209S–213S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebanks, J.P.; Wickett, R.R.; Boissy, R.E. Mechanisms regulating skin pigmentation: The rise and fall of complexion coloration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 4066–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kameyama, K.; Sakai, C.; Kuge, S.; Nishiyama, S.; Tomita, Y.; Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K.; Hearing, V.J. The expression of tyrosinase, tyrosinase-related proteins 1 and 2 (TRP1 and TRP2), the silver protein, and a melanogenic inhibitor in human melanoma cells of differing melanogenic activities. Pigment Cell Res. 1995, 8, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, C.; Khaled, M.; Fisher, D.E. MITF: Master regulator of melanocyte development and melanoma oncogene. Trends Mol. Med. 2006, 12, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalley, K.; Eisen, T. The involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in the alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)-induced melanogenic and anti-proliferative effects in B16 murine melanoma cells. FEBS Lett. 2000, 476, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.K.; Sarkar, C.; Mallick, S.; Saha, B.; Bera, R.; Bhadra, R. Human placental lipid induces melanogenesis through p38 MAPK in B16F10 mouse melanoma. Pigment Cell Res. 2005, 18, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihashi, M.; Ueda, M.; Budiyanto, A.; Bito, T.; Oka, M.; Fukunaga, M.; Tsuru, K.; Horikawa, T. UV-induced skin damage. Toxicology 2003, 189, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, B.R.; El-Fawal, H.A.; Mousa, S.A. Date (Phoenix dactylifera) Polyphenolics and Other Bioactive Compounds: A Traditional Islamic Remedy’s Potential in Prevention of Cell Damage, Cancer Therapeutics and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 30075–30090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruyama, H.; Kawakami, F.; Lwin, T.T.; Imai, M.; Shamsa, F. Biochemical Characterization of Ferulic Acid and Caffeic Acid Which Effectively Inhibit Melanin Synthesis via Different Mechanisms in B16 Melanoma Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.-C.; Wang, S.-S.; Tsai, T.-C.; Ko, W.-P.; Chang, T.-M. Phoenix dactylifera L. Seed Extract Exhibits Antioxidant Effects and Attenuates Melanogenesis in B16F10 Murine Melanoma Cells by Downregulating PKA Signaling. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121270
Huang H-C, Wang S-S, Tsai T-C, Ko W-P, Chang T-M. Phoenix dactylifera L. Seed Extract Exhibits Antioxidant Effects and Attenuates Melanogenesis in B16F10 Murine Melanoma Cells by Downregulating PKA Signaling. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(12):1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121270
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Huey-Chun, Shr-Shiuan Wang, Tsang-Chi Tsai, Wang-Ping Ko, and Tsong-Min Chang. 2020. "Phoenix dactylifera L. Seed Extract Exhibits Antioxidant Effects and Attenuates Melanogenesis in B16F10 Murine Melanoma Cells by Downregulating PKA Signaling" Antioxidants 9, no. 12: 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121270
APA StyleHuang, H. -C., Wang, S. -S., Tsai, T. -C., Ko, W. -P., & Chang, T. -M. (2020). Phoenix dactylifera L. Seed Extract Exhibits Antioxidant Effects and Attenuates Melanogenesis in B16F10 Murine Melanoma Cells by Downregulating PKA Signaling. Antioxidants, 9(12), 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121270