Peptide Dose and/or Structure in Vaccines as a Determinant of T Cell Responses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
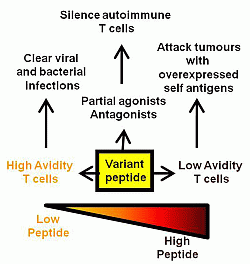
2. Peptide Dose

3. Peptide Structure
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paran, N.; Sutter, G. Smallpox vaccines: New formulations and revised strategies for vaccination. Hum. Vaccin 2009, 5, 824–831. [Google Scholar]
- Lauring, A.S.; Jones, J.O.; Andino, R. Rationalizing the development of live attenuated virus vaccines. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, M.F.; Kalinke, U.; Althage, A.; Freer, G.; Burkhart, C.; Roost, H.; Aguet, M.; Hengartner, H.; Zinkernagel, R.M. The role of antibody concentration and avidity in antiviral protection. Science 1997, 276, 2024–2027. [Google Scholar]
- Perrin, H.; Canderan, G.; Sekaly, R.P.; Trautmann, L. New approaches to design HIV-1 T-cell vaccines. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2010, 5, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, H.L. HIV/AIDS vaccines: 2007. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 82, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, E.R.; Pape, K.A.; Loh, D.Y.; Jenkins, M.K. Visualization of peptide-specific T cell immunity and peripheral tolerance induction in vivo. Immunity 1994, 1, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, A.; Koernig, S.; Silva, A.; Drane, D.; Maraskovsky, E.; Morelli, A.B. Combination of adjuvants: The future of vaccine design. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2013, 12, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riese, P.; Schulze, K.; Ebensen, T.; Prochnow, B.; Guzman, C.A. Vaccine adjuvants: Key tools for innovative vaccine design. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 2562–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, M.F.; Jennings, G.T. Vaccine delivery: A matter of size, geometry, kinetics and molecular patterns. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia-Pinto, J.F.; Csaba, N.; Alonso, M.J. Vaccine delivery carriers: Insights and future perspectives. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 440, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, M.; Krebs, S.J.; Haigwood, N.L.; de Berardinis, P. Delivery strategies for novel vaccine formulations. World J. Virol. 2012, 1, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, S.D.; Shin, H.; Haining, W.N.; Zou, T.; Workman, C.J.; Polley, A.; Betts, M.R.; Freeman, G.J.; Vignali, D.A.; Wherry, E.J. Coregulation of CD8+ T cell exhaustion by multiple inhibitory receptors during chronic viral infection. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, D.L.; Wherry, E.J.; Masopust, D.; Zhu, B.; Allison, J.P.; Sharpe, A.H.; Freeman, G.J.; Ahmed, R. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature 2006, 439, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskophidis, D.; Lechner, F.; Pircher, H.; Zinkernagel, R.M. Virus persistence in acutely infected immunocompetent mice by exhaustion of antiviral cytotoxic effector T cells. Nature 1993, 362, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradin, G.; Etlinger, H.M.; Chiller, J.M. Lymphocyte specificity to protein antigens. I. Characterization of the antigen-induced in vitro T cell-dependent proliferative response with lymph node cells from primed mice. J. Immunol. 1977, 119, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander-Miller, M.A.; Leggatt, G.R.; Sarin, A.; Berzofsky, J.A. Role of antigen, CD8, and cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) avidity in high dose antigen induction of apoptosis of effector CTL. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 184, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valkenburg, S.A.; Gras, S.; Guillonneau, C.; la Gruta, N.L.; Thomas, P.G.; Purcell, A.W.; Rossjohn, J.; Doherty, P.C.; Turner, S.J.; Kedzierska, K. Protective efficacy of cross-reactive CD8+ T cells recognising mutant viral epitopes depends on peptide-MHC-I structural interactions and T cell activation threshold. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchison, N.A. Induction of immunological paralysis in two zones of dosage. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1964, 161, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parish, C.R.; Liew, F.Y. Immune response to chemically modified flagellin. 3. Enhanced cell-mediated immunity during high and low zone antibody tolerance to flagellin. J. Exp. Med. 1972, 135, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorse, G.J.; Keitel, W.; Keyserling, H.; Taylor, D.N.; Lock, M.; Alves, K.; Kenner, J.; Deans, L.; Gurwith, M. Immunogenicity and tolerance of ascending doses of a recombinant protective antigen (rPA102) anthrax vaccine: A randomized, double-blinded, controlled, multicenter trial. Vaccine 2006, 24, 5950–5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirima, S.B.; Tiono, A.B.; Ouedraogo, A.; Diarra, A.; Ouedraogo, A.L.; Yaro, J.B.; Ouedraogo, E.; Gansane, A.; Bougouma, E.C.; Konate, A.T.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the malaria vaccine candidate MSP3 long synthetic peptide in 12–24 months-old Burkinabe Children. PLoS One 2009, 4, e7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treanor, J.J.; Taylor, D.N.; Tussey, L.; Hay, C.; Nolan, C.; Fitzgerald, T.; Liu, G.; Kavita, U.; Song, L.; Dark, I.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a recombinant hemagglutinin influenza-flagellin fusion vaccine (VAX125) in healthy young adults. Vaccine 2010, 28, 8268–8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangartner, L.; Zinkernagel, R.M.; Hengartner, H. Antiviral antibody responses: The two extremes of a wide spectrum. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.J.; Janetzki, S.; Schaed, S.; Panageas, K.S.; Wang, S.; Williams, L.; Meyers, M.; Butterworth, L.; Livingston, P.O.; Chapman, P.B.; et al. Evaluation of CD8+ T-cell frequencies by the elispot assay in healthy individuals and in patients with metastatic melanoma immunized with tyrosinase peptide. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 87, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciani, F.; Sanders, M.T.; Oveissi, S.; Pang, K.C.; Chen, W. Increasing viral dose causes a reversal in CD8+ T cell immunodominance during primary influenza infection due to differences in antigen presentation, T cell avidity, and precursor numbers. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrani, A.; Verdaguer, J.; Serra, P.; Tafuro, S.; Tan, R.; Santamaria, P. Progression of autoimmune diabetes driven by avidity maturation of a T-cell population. Nature 2000, 406, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slifka, M.K.; Whitton, J.L. Functional avidity maturation of CD8+ T cells without selection of higher affinity TCR. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Essen, M.R.; Kongsbak, M.; Geisler, C. Mechanisms behind functional avidity maturation in T cells. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, T.M.; Bieler, J.G.; Edidin, M.; Schneck, J.P. Increased TCR avidity after T cell activation: A mechanism for sensing low-density antigen. Immunity 2001, 14, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Kersh, E.N.; Kaech, S.M.; Onami, T.M.; Moran, M.; Wherry, E.J.; Miceli, M.C.; Ahmed, R. TCR signal transduction in antigen-specific memory CD8 T cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5455–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, R.A.; Corse, E.; Allison, J.P. TCR ligand density and affinity determine peripheral induction of FoxP3 in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander-Miller, M.A.; Leggatt, G.R.; Berzofsky, J.A. Selective expansion of high- or low-avidity cytotoxic T lymphocytes and efficacy for adoptive immunotherapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 4102–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlik, C.; Dadaglio, G.; Saron, M.F.; Deriaud, E.; Rojas, M.; Casal, S.I.; Leclerc, C. In vivo induction of a high-avidity, high-frequency cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response is associated with antiviral protective immunity. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 5769–5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, M.H.; Forcier, T.; McAndrew, E.; Gonzalez, M.; Chen, H.; Juelg, B.; Walker, B.D.; Irvine, D.J. High avidity CD8+ T cells efficiently eliminate motile HIV-infected targets and execute a locally focused program of anti-viral function. PLoS One 2014, 9, e87873. [Google Scholar]
- Neveu, B.; Debeaupuis, E.; Echasserieau, K.; le Moullac-Vaidye, B.; Gassin, M.; Jegou, L.; Decalf, J.; Albert, M.; Ferry, N.; Gournay, J.; et al. Selection of high-avidity CD8 T cells correlates with control of hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2008, 48, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander-Miller, M.A.; Derby, M.A.; Sarin, A.; Henkart, P.A.; Berzofsky, J.A. Supraoptimal peptide-major histocompatibility complex causes a decrease in BC1-2 levels and allows tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor II-mediated apoptosis of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar]
- Derby, M.A.; Snyder, J.T.; Tse, R.; Alexander-Miller, M.A.; Berzofsky, J.A. An abrupt and concordant initiation of apoptosis: Antigen-dependent death of CD8+ CTL. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 2951–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertelt, J.M.; Johanns, T.M.; Mysz, M.A.; Nanton, M.R.; Rowe, J.H.; Aguilera, M.N.; Way, S.S. Selective culling of high avidity antigen-specific CD4+ T cells after virulent salmonella infection. Immunology 2011, 134, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molldrem, J.J.; Lee, P.P.; Kant, S.; Wieder, E.; Jiang, W.; Lu, S.; Wang, C.; Davis, M.M. Chronic myelogenous leukemia shapes host immunity by selective deletion of high-avidity leukemia-specific T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.J.; Kreuwel, H.T.; Fleck, S.; Levitsky, H.I.; Pardoll, D.M.; Sherman, L.A. Activation of low avidity CTL specific for a self epitope results in tumor rejection but not autoimmunity. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 643–651. [Google Scholar]
- Cawthon, A.G.; Lu, H.; Alexander-Miller, M.A. Peptide requirement for CTL activation reflects the sensitivity to CD3 engagement: Correlation with CD8αβ versus CD8αα expression. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 2577–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroger, C.J.; Alexander-Miller, M.A. Dose-dependent modulation of CD8 and functional avidity as a result of peptide encounter. Immunology 2007, 122, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawthon, A.G.; Alexander-Miller, M.A. Optimal colocalization of TCR and CD8 as a novel mechanism for the control of functional avidity. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 3492–3498. [Google Scholar]
- Hodge, J.W.; Chakraborty, M.; Kudo-Saito, C.; Garnett, C.T.; Schlom, J. Multiple costimulatory modalities enhance CTL avidity. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 5994–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Hodge, J.W.; Ahlers, J.D.; Burke, D.S.; Schlom, J.; Berzofsky, J.A. Selective induction of high avidity CTL by altering the balance of signals from APC. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 2523–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Perera, L.P.; Burke, D.S.; Waldmann, T.A.; Berzofsky, J.A. IL-15/IL-15ralpha-mediated avidity maturation of memory CD8+ T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15154–15159. [Google Scholar]
- Amoah, S.; Yammani, R.D.; Grayson, J.M.; Alexander-Miller, M.A. Changes in functional but not structural avidity during differentiation of CD8+ effector cells in vivo after virus infection. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroger, C.J.; Alexander-Miller, M.A. Cutting edge: CD8+ T cell clones possess the potential to differentiate into both high- and low-avidity effector cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 748–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeh, H.J., 3rd; Perry-Lalley, D.; Dudley, M.E.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Yang, J.C. High avidity CTLs for two self-antigens demonstrate superior in vitro and in vivo antitumor efficacy. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 989–994. [Google Scholar]
- Derby, M.; Alexander-Miller, M.; Tse, R.; Berzofsky, J. High-avidity CTL exploit two complementary mechanisms to provide better protection against viral infection than low-avidity CTL. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 1690–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander-Miller, M.A. Differential expansion and survival of high and low avidity cytotoxic T cell populations during the immune response to a viral infection. Cell. Immunol. 2000, 201, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroger, C.J.; Amoah, S.; Alexander-Miller, M.A. Cutting edge: Dendritic cells prime a high avidity CTL response independent of the level of presented antigen. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5784–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, T.N.; Mullins, D.W.; Engelhard, V.H. Antigen density presented by dendritic cells in vivo differentially affects the number and avidity of primary, memory, and recall CD8+ T cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 1822–1829. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, S.E.; Harty, J.T. Quantitation of CD8+ T cell expansion, memory, and protective immunity after immunization with peptide-coated dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 4936–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochenderfer, J.N.; Chien, C.D.; Simpson, J.L.; Gress, R.E. Maximizing CD8+ T cell responses elicited by peptide vaccines containing CPG oligodeoxynucleotides. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 124, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggatt, G.R.; Narayan, S.; Fernando, G.J.; Frazer, I.H. Changes to peptide structure, not concentration, contribute to expansion of the lowest avidity cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 76, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, S.; Choyce, A.; Fernando, G.J.; Leggatt, G.R. Secondary immunisation with high-dose heterologous peptide leads to CD8 T cell populations with reduced functional avidity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, T.N.; Mullins, D.W.; Colella, T.A.; Engelhard, V.H. Manipulation of avidity to improve effectiveness of adoptively transferred CD8+ T cells for melanoma immunotherapy in human MHC class I-transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 5824–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, K.R.; McMahan, R.H.; Kemmler, C.B.; Kappler, J.W.; Slansky, J.E. Peptide vaccines prevent tumor growth by activating T cells that respond to native tumor antigens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4652–4657. [Google Scholar]
- Fazilleau, N.; McHeyzer-Williams, L.J.; Rosen, H.; McHeyzer-Williams, M.G. The function of follicular helper T cells is regulated by the strength of T cell antigen receptor binding. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.M.; Mylin, L.M.; Thompson, M.M.; Schell, T.D. Modification of a tumor antigen determinant to improve peptide/MHC stability is associated with increased immunogenicity and cross-priming a larger fraction of CD8+ T cells. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 5549–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babatz, J.; Rollig, C.; Lobel, B.; Folprecht, G.; Haack, M.; Gunther, H.; Kohne, C.H.; Ehninger, G.; Schmitz, M.; Bornhauser, M. Induction of cellular immune responses against carcinoembryonic antigen in patients with metastatic tumors after vaccination with altered peptide ligand-loaded dendritic cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2006, 55, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overwijk, W.W.; Tsung, A.; Irvine, K.R.; Parkhurst, M.R.; Goletz, T.J.; Tsung, K.; Carroll, M.W.; Liu, C.; Moss, B.; Rosenberg, S.A.; et al. Gp100/pmel 17 is a murine tumor rejection antigen: Induction of “self”-reactive, tumoricidal T cells using high-affinity, altered peptide ligand. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, L.B.; Greer, J.M.; Sobel, R.A.; Lees, M.B.; Kuchroo, V.K. An altered peptide ligand mediates immune deviation and prevents autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Immunity 1995, 3, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielekova, B.; Goodwin, B.; Richert, N.; Cortese, I.; Kondo, T.; Afshar, G.; Gran, B.; Eaton, J.; Antel, J.; Frank, J.A.; et al. Encephalitogenic potential of the myelin basic protein peptide (amino acids 83–99) in multiple sclerosis: Results of a phase II clinical trial with an altered peptide ligand. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappos, L.; Comi, G.; Panitch, H.; Oger, J.; Antel, J.; Conlon, P.; Steinman, L. Induction of a non-encephalitogenic type 2 T helper-cell autoimmune response in multiple sclerosis after administration of an altered peptide ligand in a placebo-controlled, randomized phase II trial. The altered peptide ligand in relapsing MS study group. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezzi, G.; Scotet, E.; Scheidegger, D.; Lanzavecchia, A. The interplay between the duration of TCR and cytokine signaling determines T cell polarization. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 4092–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Bhardwaj, V.; Soares, L.; Alexander, J.; Sette, A.; Sercarz, E. Major histocompatibility complex binding affinity of an antigenic determinant is crucial for the differential secretion of interleukin 4/5 or interferon gamma by T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9510–9514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, K.; Chodisetti, S.B.; Rai, P.K.; Maurya, S.K.; Amir, M.; Sheikh, J.A.; Agrewala, J.N. Decision-making critical amino acids: Role in designing peptide vaccines for eliciting Th1 and Th2 immune response. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evavold, B.D.; Allen, P.M. Separation of IL-4 production from th cell proliferation by an altered T cell receptor ligand. Science 1991, 252, 1308–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Katsara, M.; Minigo, G.; Plebanski, M.; Apostolopoulos, V. The good, the bad and the ugly: How altered peptide ligands modulate immunity. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2008, 8, 1873–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaft, N.; Coccoris, M.; Drexhage, J.; Knoop, C.; de Vries, I.J.; Adema, G.J.; Debets, R. An altered gp100 peptide ligand with decreased binding by TCR and CD8α dissects T cell cytotoxicity from production of cytokines and activation of NFAT. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridkis-Hareli, M.; Reinherz, E.L. New approaches to eliciting protective immunity through T cell repertoire manipulation: The concept of thymic vaccination. Med. Immunol. 2004, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fridkis-Hareli, M.; Reche, P.A.; Reinherz, E.L. Peptide variants of viral CTL epitopes mediate positive selection and emigration of Ag-specific thymocytes in vivo. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Southwood, S.; Arrhenius, T.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Grey, H.M.; Sette, A.; Ishioka, G.Y. T cell receptor antagonist peptides are highly effective inhibitors of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Eur. J. Immunol. 1994, 24, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanami, K.; Matsumoto, I.; Yoshiga, Y.; Inoue, A.; Kondo, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Minami, R.; Hayashi, T.; Goto, D.; et al. Altered peptide ligands inhibit arthritis induced by glucose-6-phosphate isomerase peptide. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silano, M.; Vincentini, O.; de Vincenzi, M. Toxic, immunostimulatory and antagonist gluten peptides in celiac disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silano, M.; Vincentini, O.; Iapello, A.; Mancini, E.; de Vincenzi, M. Antagonist peptides of the gliadin T-cell stimulatory sequences: A therapeutic strategy for celiac disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 42, S191–S192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruna, B.V.; Ben-David, H.; Sela, M.; Mozes, E. A dual altered peptide ligand down-regulates myasthenogenic T cell responses and reverses experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis via up-regulation of Fas-FasL-mediated apoptosis. Immunology 2006, 118, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, A.G.; Sette, A.; Grey, H.M. Inhibition of antigen presentation in vitro and in vivo by MHC antagonist peptides. Int. Rev. Immunol. 1990, 6, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Leggatt, G.R. Peptide Dose and/or Structure in Vaccines as a Determinant of T Cell Responses. Vaccines 2014, 2, 537-548. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines2030537
Leggatt GR. Peptide Dose and/or Structure in Vaccines as a Determinant of T Cell Responses. Vaccines. 2014; 2(3):537-548. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines2030537
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeggatt, Graham R. 2014. "Peptide Dose and/or Structure in Vaccines as a Determinant of T Cell Responses" Vaccines 2, no. 3: 537-548. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines2030537
APA StyleLeggatt, G. R. (2014). Peptide Dose and/or Structure in Vaccines as a Determinant of T Cell Responses. Vaccines, 2(3), 537-548. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines2030537