Systematic Study of the Impact of Pulsed Electric Field Parameters (Pulse/Pause Duration and Frequency) on ED Performances during Acid Whey Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acid Whey
2.2. Electrodialytic Configuration
2.3. Protocol
2.4. Analyses
2.5. Total Solids and Ash Contents
2.6. Mineral Concentration
2.7. Organic Acid Concentration
2.8. pH
2.9. Conductivity
2.10. Global System Resistance
2.11. Relative Energy Consumption (REC)
2.12. Membrane Mineral Concentration
2.13. Statistical Analyses
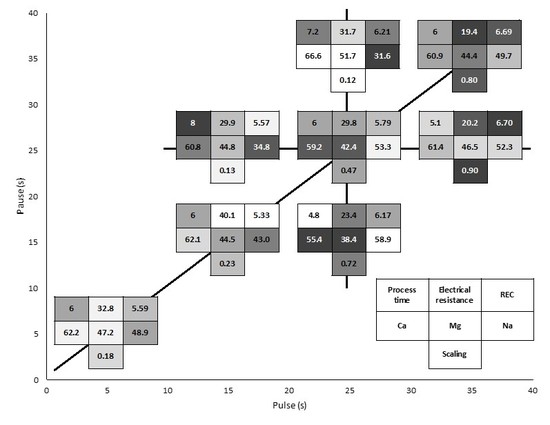
3. Results
3.1. Whey and Recovery Solution Analysis
3.1.1. Lactate Migration
3.1.2. pH
3.1.3. Conductivity and Mineral Concentrations
3.2. Global System Resistance and Relative Energy Consumption
3.3. Membrane Analysis
3.3.1. Membrane Photographs
3.3.2. Mineral Content
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prazeres, A.R.; Carvalho, F.; Rivas, J. Cheese whey management: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 110, 48–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakali, E.; Petrotos, K.; Allessandro, A.D. A review on whey composition and the methods used for its utilization for food and pharmaceutical products. Proceedings of 6th International Conference on Simulation and Modelling in Food and Bio Industries, Bragança, Portugal, 24–26 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ganju, S.; Gogate, P.R. A review on approaches for efficient recovery of whey proteins from dairy industry effluents. J. Food Eng. 2017, 215, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrapala, J.; Duke, M.C.; Gray, S.R.; Zisu, B.; Weeks, M.; Palmer, M.; Vasiljevic, T. Properties of acid whey as a function of pH and temperature. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 4352–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, M.; Langrish, T. Effect of lactic acid in-process crystallization of lactose/protein powders during spray drying. J. Food Eng. 2014, 137, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrapala, J.; Vasiljevic, T. Properties of spray dried lactose powders influenced by presence of lactic acid and calcium. J. Food Eng. 2017, 198, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Q.; Eschbach, F.I.I.; Weeks, M.; Gras, S.L.; Kentish, S.E. Removal of lactic acid from acid whey using electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 158, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrapala, J.; Chen, G.Q.; Kezia, K.; Bowman, E.G.; Vasiljevic, T.; Kentish, S.E. Removal of lactate from acid whey using nanofiltration. J. Food Eng. 2016, 177, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bédas, M.; Tanguy, G.; Dolivet, A.; Méjean, S.; Gaucheron, F.; Garric, G.; Senard, G.; Jeantet, R.; Schuck, P. Nanofiltration of lactic acid whey prior to spray drying: Scaling up to a semi-industrial scale. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 79, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufton, G.; Mikhaylin, S.; Gaaloul, S.; Bazinet, L. How electrodialysis configuration influences acid whey deacidification and membrane scaling. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balster, J.; Krupenko, O.; Pünt, I.; Stamatialis, D.F.; Wessling, M. Preparation and characterisation of monovalent ion selective cation exchange membranes based on sulphonated poly(ether ether ketone). J. Memb. Sci. 2005, 263, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Bribiesca, E.; Pourcelly, G.; Bazinet, L. Nature identification and morphology characterization of anion-exchange membrane fouling during conventional electrodialysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 308, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufton, G.; Mikhaylin, S.; Gaaloul, S.; Bazinet, L. Positive impact of pulsed electric field on lactic acid removal, demineralization and membrane scaling during acid whey electrodialysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, Y.; Seno, M. Concentration polarization and water dissociation in ion-exchange membrane electrodialysis. Mechanism of water dissociation. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1986, 82, 2065–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, M.A.; Gil, V.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Dammak, L.; Kononenko, N.A.; Larchet, C.; Grande, D.; Nikonenko, V.V. Mitigation of membrane scaling in electrodialysis by electroconvection enhancement, pH adjustment and pulsed electric field application. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 549, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casademont, C.; Sistat, P.; Ruiz, B.; Pourcelly, G.; Bazinet, L. Electrodialysis of model salt solution containing whey proteins: Enhancement by pulsed electric field and modified cell configuration. J. Memb. Sci. 2009, 328, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes-Araya, N.; Pourcelly, G.; Bazinet, L. Impact of pulsed electric field on electrodialysis process performance and membrane fouling during consecutive demineralization of a model salt solution containing a high magnesium/calcium ratio. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemay, N.; Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. Voltage spike and electroconvective vortices generation during electrodialysis under pulsed electric field: Impact on demineralization process efficiency and energy consumption. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 52, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchuk, N.A.; Koopal, L.K.; Gonzalez-Caballero, F. Intensification of electrodialysis by applying a non-stationary electric field. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 176, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistat, P.; Huguet, P.; Ruiz, B.; Pourcelly, G.; Mareev, S.A.; Nikonenko, V.V. Effect of pulsed electric field on electrodialysis of a NaCl solution in sub-limiting current regime. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 164, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gésan-Guiziou, G. 6 Integrated membrane operations in whey processing. In Integrated Membrane Operations; A Cassano, DE GRUYTER: Berlin, Gemany; Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.G.; Moon, S.H.; Chang, Y.K.; Yoo, I.K.; Chang, H.N. Lactic acid recovery using two-stage electrodialysis and its modelling. J. Memb. Sci. 1998, 145, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, D.A.; Brown, J.H. Limiting Current in Electrodialysis Cells. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1959, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, P.; Ortiz, J.M.; Richards, B.S.; Schäfer, A.I. Electrodialytic removal of NaCl from water: Impacts of using pulsed electric potential on ion transport and water dissociation phenomena. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 435, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simons, R. Water splitting in ion exchange membranes. Electrochim. Acta 1985, 30, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; He, Q.; Ma, G.; Wang, H.; Nirmalakhandan, N.; Xu, P. Selective separation of mono- and di-valent cations in electrodialysis during brackish water desalination: Bench and pilot-scale studies. Desalination 2018, 428, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Walker, W.S.; Lawler, D.F. Competitive separation of di- vs. mono-valent cations in electrodialysis: Effects of the boundary layer properties. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2042–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galizia, M.; Benedetti, F.M.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B.D. Monovalent and divalent ion sorption in a cation exchange membrane based on cross-linked poly (p-styrene sulfonate-co-divinylbenzene). J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 535, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdaous, L.; Malériat, J.P.; Schlumpf, J.P.; Quéméneur, F. Transfer of monovalent and divalent cations in salt solutions by electrodialysis. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 931–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Miao, M.; Pan, J.; Sotto, A.; Shen, J.; Gao, C.; van der Bruggen, B. Separation of divalent ions from seawater concentrate to enhance the purity of coarse salt by electrodialysis with monovalent-selective membranes. Desalination 2017, 411, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Moon, S.H.; Tsai, S.P. Effects of pulsed electric fields on membrane fouling in electrodialysis of NaC1 solution containing humate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2002, 27, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylin, S.; Nikonenko, V.; Pourcelly, G.; Bazinet, L. Intensification of demineralization process and decrease in scaling by application of pulsed electric field with short pulse/pause conditions. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 468, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes-Araya, N.; Pourcelly, G.; Bazinet, L. Water splitting proton-barriers for mineral membrane fouling control and their optimization by accurate pulsed modes of electrodialysis. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 447, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, S.; Chen, G.Q.; Freeman, B.; Suarez, F.; Freckleton, A.; Bathurst, K.; Kentish, S.E. Fouling and in-situ cleaning of ion-exchange membranes during the electrodialysis of fresh acid and sweet whey. J. Food Eng. 2019, 246, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Amorphous calcium (ortho)phosphates. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 4457–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cifuentes-Araya, N.; Pourcelly, G.; Bazinet, L. Multistep mineral fouling growth on a cation-exchange membrane ruled by gradual sieving effects of magnesium and carbonate ions and its delay by pulsed modes of electrodialysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 372, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Characteristics | Unit | Acid Whey | Acid Whey from First Studies | Values Reported in the Literature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total solids | g/L | 57.5 ± 2.6 | 57.2 ± 1.5–59.8 ± 4.2 | 50.0–70.0 |
| Lactose | g/L | 36.7 ± 1.1 | 34.9 ± 1.0–41.2 ± 0.9 | 38.0–49.0 |
| Minerals | g/L | 6.1 ± 0.4 | 5.1 ± 1.1–6.9 ± 0.1 | 4.7–7.5 |
| P | g/L | 0.68 ± 0.03 | 0.55 ± 0.01–0.76 ± 0.02 | 0.44–0.90 |
| Ca | g/L | 0.93 ± 0.05 | 0.86 ± 0.02–1.08 ± 0.02 | 0.43–1.60 |
| K | g/L | 1.42 ± 0.04 | 1.26 ± 0.05–1.65 ± 0.03 | 1.28–1.82 |
| Mg | g/L | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 0.09 ± 0.00–0.10 ± 0.00 | 0.09–0.19 |
| Na | g/L | 0.43 ± 0.02 | 0.39 ± 0.03–0.53 ± 0.02 | 0.40–0.61 |
| Lactate | g/L | 7.67 ± 0.37 | 7.00 ± 0.14–7.12 ± 0.11 | 5.18–8.00 |
| Ratio Lactate/Lactose | - | 0.21 | 0.17–0.20 | 0.12–0.15 |
| pH | - | 4.4 | 4.4–4.6 | 4.0–4.6 |
| Conductivity | mS/cm | 7.81 ± 0.14 | 7.05 ± 0.24–7.09 ± 0.35 | 8.27 ± 0.42 |
| Condition | Energy Consumption (Wh/g) |
|---|---|
| 35 s/25 s | 6.7 ± 1.0 |
| 35 s/35 s | 6.7 ± 1.1 |
| 25 s/35 s | 6.2 ± 1.3 |
| 25 s/15 s | 6.2 ± 0.7 |
| 25 s/25 s | 5.8 ± 0.3 |
| 5 s/5 s | 5.6 ± 0.8 |
| 15 s/25 s | 5.6 ± 0.3 |
| 15 s/15 s | 5.3 ± 0.4 |
| Condition | Cumulative Mineral Content (g/100 g of Membrane) |
|---|---|
| 35 s/25 s | 0.90 ± 0.45 * |
| 35 s/35 s | 0.80 ± 0.47 * |
| 25s/15 s | 0.72 ± 0.08 * |
| 25 s/25 s | 0.47 ± 0.13 |
| 15 s/15 s | 0.23 ± 0.04 |
| 5 s/5 s | 0.18 ± 0.11 |
| 15 s/25 s | 0.13 ± 0.08 |
| 25 s/35 s | 0.12 ± 0.06 |
| Before ED | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dufton, G.; Mikhaylin, S.; Gaaloul, S.; Bazinet, L. Systematic Study of the Impact of Pulsed Electric Field Parameters (Pulse/Pause Duration and Frequency) on ED Performances during Acid Whey Treatment. Membranes 2020, 10, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10010014
Dufton G, Mikhaylin S, Gaaloul S, Bazinet L. Systematic Study of the Impact of Pulsed Electric Field Parameters (Pulse/Pause Duration and Frequency) on ED Performances during Acid Whey Treatment. Membranes. 2020; 10(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleDufton, Guillaume, Sergey Mikhaylin, Sami Gaaloul, and Laurent Bazinet. 2020. "Systematic Study of the Impact of Pulsed Electric Field Parameters (Pulse/Pause Duration and Frequency) on ED Performances during Acid Whey Treatment" Membranes 10, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10010014
APA StyleDufton, G., Mikhaylin, S., Gaaloul, S., & Bazinet, L. (2020). Systematic Study of the Impact of Pulsed Electric Field Parameters (Pulse/Pause Duration and Frequency) on ED Performances during Acid Whey Treatment. Membranes, 10(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10010014