Triple-Layer Nanocomposite Membrane Prepared by Electrospinning Based on Modified PES with Carbon Nanotubes for Membrane Distillation Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
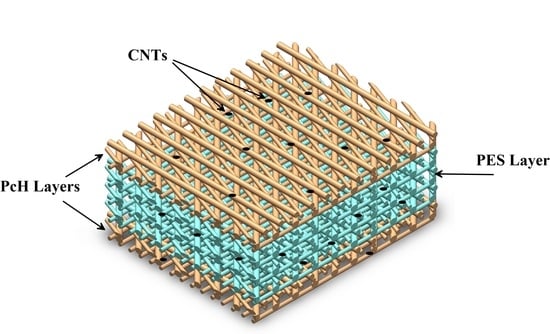
2.2. Membrane Preparation
2.3. Membrane Characterization
2.3.1. Membrane and Nanofiber Morphology
2.3.2. Liquid Entry Pressure (LEP)
2.3.3. Membrane Morphology
2.3.4. Static Water Contact Angle
2.3.5. Membrane Thickness
2.4. Membrane Distillation (MD) Cell Design
2.5. Membrane Distillation Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimal Concentration of the Carbon Nanotubes Content
3.2. Membrane Characterization
3.2.1. SEM and TEM Observation
3.2.2. Water Contact Angle Measurement
3.2.3. Membrane Thickness, Porosity, LEP, and Average Fiber and Pore Diameters Measurements
3.3. Membrane Distillation Performance Evaluation
3.3.1. Effect of Feed Water Temperature
3.3.2. Effect of Feed Water Flow Rate
3.3.3. Effect of Salt Concentration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Acevedo, L.; Uche, J.; Del-Amo, A.J.W. Improving the distillate prediction of a membrane distillation unit in a trigeneration scheme by using artificial neural networks. Water 2018, 10, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosegrant, M.W.; Cai, X.; Cline, S.A. Global Water Outlook to 2025; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Darwish, N.; Hilal, N.J.D. Membrane distillation: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2012, 287, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drioli, E.; Ali, A.; Macedonio, F.J.D. Membrane distillation: Recent developments and perspectives. Desalination 2015, 356, 56–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M.; García-Payo, M.C.; García-Fernández, L.; Contreras-Martínez, J. Dual-layered electrospun nanofibrous membranes for membrane distillation. Desalination 2018, 426, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, L.F.; Lawler, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Marrot, B.; Moulin, P.J.W. Reverse osmosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2317–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, G.; Al-Obaidi, M.; Manenti, F.; Mujtaba, I.M.J.D. Performance analysis of hybrid system of multi effect distillation and reverse osmosis for seawater desalination via modelling and simulation. Desalination 2018, 448, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Shazly, A.; Al-Zahrani, A.; Alhamed, Y.; Nosier, S.J.D. Productivity intensification of humidification—Dehumidification desalination unit by using pulsed water flow regime. Desalination 2012, 293, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Okamura, R.; Ishigami, T.; Hasegawa, S.; Kato, N.; Matsuyama, H.J.W. The effect of membrane material and surface pore size on the fouling properties of submerged membranes. Water 2016, 8, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mi, B.; Elimelech, M.J.J. Organic fouling of forward osmosis membranes: Fouling reversibility and cleaning without chemical reagents. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 348, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijing, L.D.; Woo, Y.C.; Choi, J.-S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.-H.; Shon, H.K. Fouling and its control in membrane distillation—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 215–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alklaibi, A.M.; Lior, N.J.D. Membrane-distillation desalination: Status and potential. Desalination 2005, 171, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, L.M.; Dumée, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.-D.; Duke, M.; Gomez, J.; Gray, S.J.W. Advances in membrane distillation for water desalination and purification applications. Water 2013, 5, 94–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khayet, M.J. Membranes and theoretical modeling of membrane distillation: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 164, 56–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.S.; El-shazly, A.H.; Nady, N.; Elmarghany, M.R.; Shouman, M.A.; Sabry, M.N. 3-D numerical investigation on commercial PTFE membranes for membrane distillation: Effect of inlet conditions on heat and mass transfer. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2019, 13, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonyadi, S.; Chung, T.S. Flux enhancement in membrane distillation by fabrication of dual layer hydrophilic—Hydrophobic hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 306, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Loh, C.-H.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Electrospun superhydrophobic membranes with unique structures for membrane distillation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16035–16048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qtaishat, M.; Khayet, M.; Matsuura, T.J. Novel porous composite hydrophobic/hydrophilic polysulfone membranes for desalination by direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 341, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Marghany, M.R.; El-Shazly, A.H.; Salem, M.S.A.; Sabry, M.N.; Nady, N. Novel Membrane Suitable for Membrane Distillation: Effect of Mixed Nanofillers on the Membrane Performance. Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 801, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.S.A.; El-Shazly, A.H.; El-Marghany, M.R.; Sabry, M.N.; Nady, N. Effect of Adding Functionalized Graphene on the Performance of PVDF Membrane in Direct Contact Membrane Distillation. Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 801, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Dong, X.; Chen, M.; Zhu, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, F.; Dong, Y.J.M. Fabrication and water treatment application of carbon nanotubes (CNTs)-based composite membranes: A review. Membranes 2017, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashraf, A.; Salih, H.; Nam, S.; Dastgheib, S.A.J.C. Robust carbon nanotube membranes directly grown on Hastelloy substrates and their potential application for membrane distillation. Carbon 2016, 106, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasrabadi, A.T.; Foroutan, M.J.D. Ion-separation and water-purification using single-walled carbon nanotube electrodes. Desalination 2011, 277, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, Z.Z.; Sagadevan, S.; Johan, R.B.; Shah, S.T.; Adebesi, A.; Md, S.I.; Rafique, R.F. A review on electrochemically modified carbon nanotubes (CNTs) membrane for desalination and purification of water. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 102001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.-K.; Jiao, L.; Lin, S.; Ji, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.J.D. Superhydrophobic electrospun nanofiber membrane coated by carbon nanotubes network for membrane distillation. Desalination 2018, 437, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Ali, M.E.; Hamid, S.B.A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Chowdhury, Z.Z. Carbon nanotube membranes for water purification: A bright future in water desalination. Desalination 2014, 336, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaper, S.; Abdel-Karim, A.; Faki, B.; Luque-Alled, J.M.; Alberto, M.; Vijayaraghavan, A.; Holmes, S.M.; Szekely, G.; Badawy, M.I.; Shokri, N.J. Flux-enhanced PVDF mixed matrix membranes incorporating APTS-functionalized graphene oxide for membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragunath, S.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Carbon nanotube immobilized membrane with controlled nanotube incorporation via phase inversion polymerization for membrane distillation based desalination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 194, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Bhadra, M.; Mitra, S. Enhanced desalination via functionalized carbon nanotube immobilized membrane in direct contact membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 136, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, M.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Flux enhancement in direct contact membrane distillation by implementing carbon nanotube immobilized PTFE membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 161, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.S.; El-Shazly, A.H.; Nady, N.; Elmarghany, M.R.; Sabry, M.N. PES/PVDF blend membrane and its composite with graphene nanoplates: Preparation, characterization, and water desalination via membrane distillation. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 166, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.C.; Tijing, L.D.; Shim, W.-G.; Choi, J.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; He, T.; Drioli, E.; Shon, H.K. Water desalination using graphene-enhanced electrospun nanofiber membrane via air gap membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-J.; An, A.K.; Hadi, P.; Lee, S.; Woo, Y.C.; Shon, H.K. Advanced multi-nozzle electrospun functionalized titanium dioxide/polyvinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene (TiO2/PVDF-HFP) composite membranes for direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.J. Fabrication of hydrophobic flat sheet and hollow fiber membranes from PVDF and PVDF-CTFE for membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Veen, S.; Nady, N.; Franssen, M.C.; Zuilhof, H.; Boom, R.M.; Abee, T.; Schroën, K.J. Listeria monocytogenes repellence by enzymatically modified PES surfaces. J. Appl. Polym. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nady, N.; Franssen, M.; Zuilhof, H.; Boom, R.; Schroën, K.J.W. Enzymatic modification of polyethersulfone membranes. Water 2012, 4, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, K.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Formation of functional polyethersulfone electrospun membrane for water purification by mixed solvent and oxidation processes. Polymer 2009, 50, 2893–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, Z. Improved antifouling properties of polyethersulfone membrane by blending the amphiphilic surface modifier with crosslinked hydrophobic segments. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 486, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nady, N.J.M. PES surface modification using green chemistry: New generation of antifouling membranes. Membranes 2016, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdallah, H.; Moustafa, A.F.; AlAnezi, A.A.; El-Sayed, H.E.M. Performance of a newly developed titanium oxide nanotubes/polyethersulfone blend membrane for water desalination using vacuum membrane distillation. Desalination 2014, 346, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Lin, D.; Ding, C.; Wang, D.; Wang, J. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun superhydrophobic PVDF-HFP/SiNPs hybrid membrane for membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 189, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas, P.; Khayet, M.; García-Payo, M.C.; Gil, L. Self-sustained electro-spun polysulfone nano-fibrous membranes and their surface modification by interfacial polymerization for micro- and ultra-filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 138, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, A.K.; Guo, J.; Lee, E.-J.; Jeong, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Leiknes, T. PDMS/PVDF hybrid electrospun membrane with superhydrophobic property and drop impact dynamics for dyeing wastewater treatment using membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 525, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elmarghany, M.R.; El-Shazly, A.H.; Salem, M.S.; Sabry, M.N.; Nady, N. Thermal analysis evaluation of direct contact membrane distillation system. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2019, 13, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essalhi, M.; Khayet, M. Self-sustained webs of polyvinylidene fluoride electrospun nanofibers at different electrospinning times: 1. Desalination by direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 433, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalia, B.S.; Guillen-Burrieza, E.; Arafat, H.A.; Hashaikeh, R. Fabrication and characterization of polyvinylidenefluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene (PVDF-HFP) electrospun membranes for direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, H.; Feldman, E.; Guzman, P.; Cole, J.; Wei, Q.; Chu, B.; Alkhudhiri, A.; Alrasheed, R.; Hsiao, B.S. Electrospun polystyrene nanofibrous membranes for direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 515, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimpour, A.; Madaeni, S.S.; Mansourpanah, Y. Fabrication of polyethersulfone (PES) membranes with nano-porous surface using potassium perchlorate (KClO4) as an additive in the casting solution. Desalination 2010, 258, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eykens, L.; De Sitter, K.; Stoops, L.; Dotremont, C.; Pinoy, L.; Van der Bruggen, B. Development of polyethersulfone phase-inversion membranes for membrane distillation using oleophobic coatings. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegarpanah, A.; Mortaheb, H.R. Surface treatment of polyethersulfone membranes for applying in desalination by direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2016, 377, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos Mierzwa, J.; Vecitis, C.D.; Carvalho, J.; Arieta, V.; Verlage, M. Anion dopant effects on the structure and performance of polyethersulfone membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 421–422, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; McCutcheon, J.R.; Rahaman, M.S. A high flux polyvinyl acetate-coated electrospun nylon 6/SiO2 composite microfiltration membrane for the separation of oil-in-water emulsion with improved antifouling performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, J.H.; Hrapovic, S.; Wang, D.; Bensebaa, F.; Simard, B.J. Solubilization of Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes by 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane Towards the Fabrication of Electrochemical Biosensors with Promoted Electron Transfer. Electroanalysis 2004, 16, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, R.; Hill, G.J. Equations for vapour pressure versus temperature: Derivation and use of the Antoine equation on a hand-held programmable calculator. Br. J. Anaesth. 1978, 50, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Warsinger, D.M.; Duke, M.C.; Matsuura, T.; Samhaber, W.M. Wetting phenomena in membrane distillation: Mechanisms, reversal, and prevention. Water Res. 2018, 139, 329–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souhaimi, M.K.; Matsuura, T. Membrane Distillation: Principles and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa, A.; Ahmad, H.; Antar, M.; Laoui, T.; Khayet, M.J.D. Experimental and theoretical investigations on water desalination using direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2017, 404, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gethard, K.; Sae-Khow, O.; Mitra, S. Water Desalination Using Carbon-Nanotube-Enhanced Membrane Distillation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balis, E.; Sapalidis, A.; Pilatos, G.; Kouvelos, E.; Athanasekou, C.; Veziri, C.; Boutikos, P.; Beltsios, K.; Romanos, G.J. Enhancement of vapor flux and salt rejection efficiency induced by low cost-high purity MWCNTs in upscaled PVDF and PVDF-HFP hollow fiber modules for membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol 2019, 224, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Feng, C.; Han, H.; Hua, X.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, J.; Cheng, P.; Du, W.; Wang, X.J.D. High permeation flux polypropylene/ethylene vinyl acetate co-blending membranes via thermally induced phase separation for vacuum membrane distillation desalination. Desalination 2016, 394, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Ye, Y.; Mansouri, J.; Chen, V.J. Crystallization behavior of salts during membrane distillation with hydrophobic and superhydrophobic capillary membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 473, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Jiang, L.Y.; Hu, B.J. Fabrication of novel PVDF/P (VDF-co-HFP) blend hollow fiber membranes for DCMD. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 566, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.S.; Deb, C.K.; Chang, H.M.; Chen, S.S.; Ganesapillai, M.J. Crosslinked PVDF-HFP-based hydrophobic membranes incorporated with CNF for enhanced stability and permeability in membrane distillation. J. Appl. Polym. 2019, 136, 48021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Membrane Code | PES wt.% | PcH wt.% | CNTs wt.% |
|---|---|---|---|
| PES | 23 | - | - |
| PcH | - | 15 | - |
| PES/CNTs | 23 | - | 0.5 |
| PcH/CNTs | - | 15 | 0.5 |
| PcH-PES-PcH/CNTs | 23 | 15 | 0.5 |
| Membrane Code | Membrane Thickness (µm) | Porosity ε (%) | LEP * (bar) | Average Fiber Diameter (µm) | Average Pore Diameter (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PES | 112 ± 2.1 | 92 ± 1.6 | NA | 0.342 ± 0.06 | 0.79 ± 0.05 |
| PcH | 108 ± 2.3 | 87 ± 1.5 | 1.7 | 0.366 ± 0.04 | 0.67 ± 0.05 |
| PES/CNTs | 104 ± 1.9 | 89 ± 2.0 | NA | 0.334 ± 0.05 | 0.63 ± 0.03 |
| PcH/CNTs | 92 ± 2.3 | 86 ± 2.1 | 1.8 | 0.338 ± 0.04 | 0.56 ± 0.04 |
| PcH -PES-PcH/CNTs | 107 ± 2.8 | 91 ± 1.8 | 1.8 | 0.343 ± 0.05 | 0.55 ± 0.03 |
| Polymer | Membrane Characteristics | Feed Concen. | Tfeed (°C) | Temperature (°C) | Flux (kg/m2h) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silica-PVDF composite, electrospinning | Contact angle 156.3° | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 60 | 20 | 18.1 | [17] |
| PcH-CNTs | Contact angle 91.65° | 3 wt.% mixed salts | 74 | 56 | 0.6–1 | [60] |
| PVDF-based membranes, electrospinning | Contact angle 128°–154° | 1–3.5 wt.% NaCl | 50–80 | 17–24 | 4.28 | [61] |
| TiO2 and fluoro-silane compound coating on PTFE | Average pore diameter: 0.25 μm | Up to 10 wt.% NaCl | 60 | 25 | 4–6 | [62] |
| PVDF-PcH | contact angle: 96.4° | 5 wt.% NaCl solution | 80 | 17 | 9 | [63] |
| PcH-CNF | contact angle: 115° | 3 wt.% NaCl | 70 | 20 | 7-8 | [64] |
| PcH-PES-PcH/CNTs composite membrane | Porosity: 91 ± 1.8%; contact angle:144° ± 2° | 1–3.5 wt.% NaCl solution | 35–65 | 20-25 | 8.4–22.2 | This study |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elmarghany, M.R.; H. El-Shazly, A.; Rajabzadeh, S.; S. Salem, M.; A. Shouman, M.; Nabil Sabry, M.; Matsuyama, H.; Nady, N. Triple-Layer Nanocomposite Membrane Prepared by Electrospinning Based on Modified PES with Carbon Nanotubes for Membrane Distillation Applications. Membranes 2020, 10, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10010015
Elmarghany MR, H. El-Shazly A, Rajabzadeh S, S. Salem M, A. Shouman M, Nabil Sabry M, Matsuyama H, Nady N. Triple-Layer Nanocomposite Membrane Prepared by Electrospinning Based on Modified PES with Carbon Nanotubes for Membrane Distillation Applications. Membranes. 2020; 10(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleElmarghany, Mohamed R., Ahmed H. El-Shazly, Saeid Rajabzadeh, Mohamed S. Salem, Mahmoud A. Shouman, Mohamed Nabil Sabry, Hideto Matsuyama, and Norhan Nady. 2020. "Triple-Layer Nanocomposite Membrane Prepared by Electrospinning Based on Modified PES with Carbon Nanotubes for Membrane Distillation Applications" Membranes 10, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10010015
APA StyleElmarghany, M. R., H. El-Shazly, A., Rajabzadeh, S., S. Salem, M., A. Shouman, M., Nabil Sabry, M., Matsuyama, H., & Nady, N. (2020). Triple-Layer Nanocomposite Membrane Prepared by Electrospinning Based on Modified PES with Carbon Nanotubes for Membrane Distillation Applications. Membranes, 10(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10010015