Modeling and Simulation of the Simultaneous Absorption/Stripping of CO2 with Potassium Glycinate Solution in Membrane Contactor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
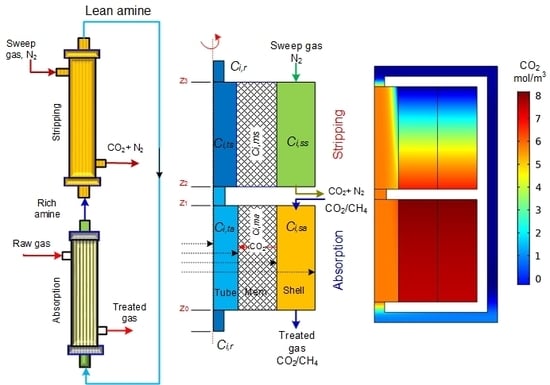
2. Model Development
2.1. Absorption
2.1.1. Hollow Fiber Lumen
2.1.2. Membrane Layer
2.1.3. Shell of the Module
2.2. Stripping
2.2.1. Hollow Fiber Lumen
2.2.2. Membrane Layer
2.2.3. Shell of the Module
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahim, N.A.; Ghasem, N.; Al-Marzouqi, M. Stripping of CO2 from different aqueous solvents using PVDF hollow fiber membrane contacting process. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2014, 21, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Chen, B.H. Review of CO2 absorption using chemical solvents in hollow fiber membrane contactors. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 41, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, N.A.; Ghasem, N.; Al-Marzouqi, M. Absorption of CO2 from natural gas using different amino acid salt solutions and regeneration using hollow fiber membrane contactors. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 26, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Lin, S.Z. Optimization in the absorption and desorption of CO2 using sodium glycinate solution. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalilpour, R.; Mumford, K.; Zhai, H.; Abbas, A.; Stevens, G.; Rubin, E.S. Membrane-based carbon capture from flue gas: a review. J Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Holst, J.; Versteeg, G.F.; Brilman, D.W.F.; Hogendoorn, J.A. Kinetic study of CO2 with various amino acid salts in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Thomsen, K. Kinetics of absorption of carbon dioxide into aqueous potassium salt of proline. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2012, 8, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Yang, Y.N.; Bian, Y.; Zhao, Y. Kinetics of CO2 Absorption into Aqueous Basic Amino Acid Salt: Potassium Salt of Lysine Solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2054–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Song, H.J.; Maken, S.; Park, J.W. Kinetics of CO2 absorption in aqueous sodium glycinate solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portugal, A.F.; Sousa, J.M.; Magalhães, F.D.; Mendes, A. Solubility of carbon dioxide in aqueous solutions of amino acid salts. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosadegh-Sedghi, S.; Rodrigue, D.; Brisson, J.; Iliuta, M.C.; Mavroudi, M.; Kaldis, S.P.; Sakellaropoulos, G.P.; Mosadegh-Sedghi, S.; Rodrigue, D.; Brisson, J.; et al. Wetting phenomenon in membrane contactors – Causes and prevention. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 332–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ren, S.; Han, J.; Chen, A. CO2 absorption into aqueous potassium salts of lysine and proline: Density, viscosity and solubility of CO2. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2015, 399, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosadegh-Sedghi, S.; Félix, S.; Mendes, A. Determination of CO2 Absorption Kinetics in Amino Acid Salts Solutions Using Membrane Contactors. Int. J. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2017, 4, 8–18. [Google Scholar]
- Simons, K.; Brilman, W.; Mengers, H.; Nijmeijer, K.; Wessling, M. Kinetics of CO2 absorption in aqueous sarcosine salt solutions: Influence of concentration, temperature, and CO2 loading. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 9693–9702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanganeh, K.E.; Shafeen, A.; Salvador, C. CO2 Capture and Development of an Advanced Pilot-Scale Cryogenic Separation and Compression Unit. Energy Procedia 2009, 1, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakhjiri, A.T.; Heydarinasab, A.; Bakhtiari, O.; Mohammadi, T. Modeling and simulation of CO2 separation from CO2/CH4 gaseous mixture using potassium glycinate, potassium argininate and sodium hydroxide liquid absorbents in the hollow fiber membrane contactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1500–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demontigny, D.; Tontiwachwuthikul, P.; Chakma, A. Comparing the absorption performance of packed columns and membrane contactors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 5726–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoor, S.; Sirkar, K.K. Gas Absorption Studies in Microporous Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1993, 32, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasem, N.; Al-Marzouqi, M. Modeling and experimental study of carbon dioxide absorption in a flat sheet membrane contactor. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2017, 3, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.G.; Hua, A.C.; Xu, Z.W.; Li, J.T.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhao, Y.L.; Pan, C. CO2 capture by membrane absorption coupling process: Experiments and coupling process evaluation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 431, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, X. Experimental studies on carbon dioxide absorption using potassium carbonate solutions with amino acid salts. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 219, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, R.; Khulbe, K.C.C.; Ismail, A.F.F.; Matsuura, T. Characterization of PVDF hollow fiber membrane for CO2 stripping by atomic force microscopy analysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 109, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Bian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Li, H. CO2 absorption using aqueous potassium lysinate solutions: Vapor―Liquid equilibrium data and modelling. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2017, 115, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourizadeh, A.; Ismail, A.F. CO2 stripping from water through porous PVDF hollow fiber membrane contactor. Desalination 2011, 273, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbari-Sisakht, M.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Emadzadeh, D.; Padaki, M.; Ismail, A.F. Study on CO2 stripping from water through novel surface modified PVDF hollow fiber membrane contactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 246, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemifard, S.A.; Ahmadi, H.; Ismail, A.F.; Moarefian, A.; Abdullah, M.S. The effect of heat treatment on hollow fiber membrane contactor for CO2 stripping. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 223, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, S.; Rahimpour, M.R.; Mehdipour, M. Removal of carbon dioxide by aqueous amino acid salts using hollow fiber membrane contactors. J. Co2 Util. 2016, 16, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvinder, K.M.S.; Zabiri, H.; Taqvi, S.A.; Ramasamy, M.; Isa, F.; Rozali, N.E.M.; Suleman, H.; Maulud, A.; Shariff, A.M. An overview on control strategies for CO2 capture using absorption/stripping system. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 147, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Cui, Q.; Xu, L.; Tu, T.; He, Q. Reducing CO2 regeneration heat requirement through waste heat recovery from hot stripping gas using nanoporous ceramic membrane. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2019, 82, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, F.; Wilson, I.; Lewis, C.; Rochelle, G. Effective Gas/Liquid Contact Area of Packing for CO2 absoprtion/stripping. In Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies; Elsevier Science Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; ISBN 9780080447049. [Google Scholar]
- Naim, R.; Ismail, A.F. Effect of polymer concentration on the structure and performance of PEI hollow fiber membrane contactor for CO2 stripping. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250–251, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakeri, G.; Ismail, A.F.; Shariaty-Niassar, M.; Matsuura, T. Effect of polymer concentration on the structure and performance of polyetherimide hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 363, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Rees, R.J.; Conway, W.; Puxty, G.; Yang, Q.; Winkler, D.A. Computational Modeling and Simulation of CO2 Capture by Aqueous Amines. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9524–9593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohrabi, M.R.; Marjani, A.; Moradi, S.; Davallo, M.; Shirazian, S. Mathematical modeling and numerical simulation of CO2 transport through hollow-fiber membranes. Appl. Math. Model. 2011, 35, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, F.J.; Hernández, M.R.; Catalá, L.; Marcilla, A. Estimation of CO2 stripping/CO2 microalgae consumption ratios in a bubble column photobioreactor using the analysis of the pH profiles. Application to Nannochloropsis oculata microalgae culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 119, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, S.; Mousavi, S.M.; Danesh, S.; Banazadeh, H. Modeling and simulation of CO2 removal from power plant flue gas by PG solution in a hollow fiber membrane contactor. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2011, 42, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchan, P.; Narku-Tetteh, J.; Saiwan, C.; Idem, R.; Supap, T. Effect of number of amine groups in aqueous polyamine solution on carbon dioxide (CO2) capture activities. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 184, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajilary, N.; Rezakazemi, M. CFD modeling of CO2 capture by water-based nanofluids using hollow fiber membrane contactor. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2018, 77, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happel, J. Viscous flow relative to arrays of cylinders. Aiche J. 1959, 5, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasem, N. Modeling and Simulation of the Absorption of CO2 and NO2 from a Gas Mixture in a Membrane Contactor. Processes 2019, 7, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qazi, S.; Gómez-Coma, L.; Albo, J.; Druon-Bocquet, S.; Irabien, A.; Sanchez-Marcano, J. CO2 capture in a hollow fiber membrane contactor coupled with ionic liquid: Influence of membrane wetting and process parameters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 233, 115986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasem, N. Chemical absorption of CO2 enhanced by nanoparticles using a membrane contactor: Modeling and simulation. Membranes 2019, 9, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fougerit, V.; Pozzobon, V.; Pareau, D.; Théoleyre, M.-A.; Stambouli, M. Experimental and numerical investigation binary mixture mass transfer in a gas―Liquid membrane contactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ju, S. Numerical simulation and analysis of CO2 removal in a polypropylene hollow fiber membrane contactor. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2014, 256840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wickramasinghe, S.R.; Semmens, M.J.; Cussler, E.L. Mass transfer in various hollow fiber geometries. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 69, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, K.A.; Svendsen, H.F. CO2 absorption with membrane contactors vs. packed absorbers- Challenges and opportunities in post combustion capture and natural gas sweetening. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Inner hollow fiber diameter (mm) | 0.42 |
| Outer hollow fiber diameter (mm) | 1.10 |
| Number of fibers | 15 |
| Inner surface area (m2) | |
| Outer diameter of module (mm) | 8.0 |
| Effective length module (mm) | 260 |
| Parameters | Value | Ref. |
| Reversible reaction rate constant, (1/s) | 3.4 × 103exp(−2800/T) | calculated |
| Diffusivity of CO2 in shell side, (m2/s) | 8.3 × 10−10 × T1.75 | [40] |
| Diffusion of CO2 in tube side, (m2/s) | 1.5 × 10−6 × exp(−2119/T) | [36] |
| Diffusivity of CO2 in membrane, | × ε/τ | [41] |
| Porosity, ε | 0.4 | Measured |
| Tortuosity, τ | (2 − ε)/ε | [42] |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghasem, N. Modeling and Simulation of the Simultaneous Absorption/Stripping of CO2 with Potassium Glycinate Solution in Membrane Contactor. Membranes 2020, 10, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10040072
Ghasem N. Modeling and Simulation of the Simultaneous Absorption/Stripping of CO2 with Potassium Glycinate Solution in Membrane Contactor. Membranes. 2020; 10(4):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10040072
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhasem, Nayef. 2020. "Modeling and Simulation of the Simultaneous Absorption/Stripping of CO2 with Potassium Glycinate Solution in Membrane Contactor" Membranes 10, no. 4: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10040072
APA StyleGhasem, N. (2020). Modeling and Simulation of the Simultaneous Absorption/Stripping of CO2 with Potassium Glycinate Solution in Membrane Contactor. Membranes, 10(4), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10040072