Recovery of Aromatics from Orange Juice Evaporator Condensate Streams by Reverse Osmosis
Abstract
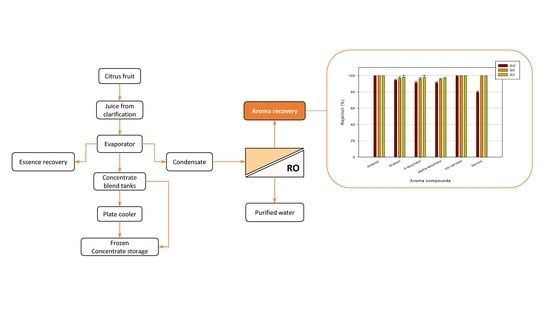
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Solutions and Reactants
2.2. Reverse Osmosis Equipment and Procedures
2.3. Analytical Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of TMP and Feed Flowrate on Permeate Flux
3.2. Effect of VCR on Permeate Flux
3.3. Retention of Aroma Compounds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braddock, R.J. By-products of citrus fruits. Food Technol. 1995, 49, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Anagnostopoulou, M.A.; Kefalas, P.; Papageorgiou, V.P.; Assimopoulou, A.N.; Boskou, D. Radical scavenging activity of various extracts and fractions of sweet orange peel (Citrus sinensis). Food Chem. 2006, 94, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-López, J.; Fernández-Ginés, J.M.; Aleson-Carbonell, L.; Sendra, E.; Sayas-Barberá, E.; Pérez-Alvarez, J.A. Application of functional citrus by-products to meat products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, H.T. Citrus juices. In Cleaner Production Series. Sucos Cítricos (Serie P+L); Company of Environmental Sanitation Technology: São Paulo, Brazil, 2005; Available online: https://www.crq4.org.br/downloads/sucos_citricos.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2020).
- Belletti, N.; Ndagijimana, M.; Sisto, C.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Lanciotti, R.; Gardini, F. Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of citrus essences on Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6932–6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X. Isolation and biological activities of decanal, linalool, valencene, and octanal from sweet orange oil. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, C1156–C1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dastager, S.G. Aroma compounds. In Biotechnology for Agro-Industrial Residues Utilization; Pandey, A., Nigam, P.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 105–128. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, R.G. Aroma Biotechnology; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, A.L.A.; Paterniani, J.E.S.; Viotto, L.A.; Tocchini, R.P.; Morgano, M.A.; Junqueira, V.C.A.; Padula, M. Bottled water production using the condensed water from a concentrated orange juice plant. J. Water Process Eng. 2015, 6, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destefano, D. Recovering Water from Fruit-by Extracting the Juice, Concentrating it by Removing Water and Collecting the Water. US Patent 5534274-A, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Aroujalian, A.; Raisi, A. Recovery of volatile aroma components from orange juice by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 303, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudot, A.; Souchon, I.; Marin, M. Total permeate pressure influence on the selectivity of the pervaporation of aroma compounds. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 158, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diban, N.; Urtiaga, A.; Ortiz, I. Recovery of key components of bilberry aroma using a commercial pervaporation membrane. Desalination 2008, 224, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, R.; Sanz, M.T.; Beltrán, S. Concentration by pervaporation of brown crab volatile compounds from dilute model solutions: Evaluation of PDMS membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, C.C.; Ribeiro, C.P.; Nobrega, R.; Borges, C.P. Pervaporation recovery of volatile aroma compounds from fruit juices. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 274, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagger-Jørgensen, R.; Meyer, A.S.; Varming, C.; Jonsson, G. Recovery of volatile aroma compounds from black currant juice by vacuum membrane distillation. J. Food. Eng. 2004, 64, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagger-Jørgensen, R.; Meyer, A.S.; Pinelo, M.; Varming, C.; Jonsson, G. Recovery of volatile fruit juice aroma compounds by membrane technology: Sweeping gas versus vacuum membrane distillation. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2012, 11, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diban, N.; Voinea, O.C.; Urtiaga, A.; Ortiz, I. Vacuum membrane distillation of the main pear aroma compound: Experimental study and mass transfer modelling. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, S.A.; Riera, F.A.; Álvarez, R.; Coca, J. Permeation of apple aroma compounds in reverse osmosis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 1998, 14, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, S.A.; Riera, F.A.; Álvarez, R.; Coca, J. Prediction of flux and aroma compounds rejection in a reverse osmosis concentration of apple juice model solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 4295–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozderović, A.; Moslavac, T. Apple juice aroma concentration from evaporator condensate by reverse osmosis—I. Influence of process parameters on retention and final aroma concentration. Acta Aliment. 1999, 28, 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Iborra, I.M.; Alcaina, I.M.; Álvarez, S. Membrane processes in juice production. In Juice Processing: Quality, Safety and Value-Added Opportunities; Falguera, V., Ibarz, A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 265–300. [Google Scholar]
- Wenten, I.G.; Khoiruddin, K. Reverse osmosis applications: Prospect and challenges. Desalination 2016, 391, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, B.; Fukumoto, L.R. Membrane processing of fruit juices and beverages: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2000, 40, 91–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merson, R.L.; Morgan, A.I. Juice concentration by reverse osmosis. Food Technol. 1968, 22, 631–634. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, H.T.; Rao, M.A.; Acree, T.E.; Cunningham, D.G. Reverse osmosis concentration of apple juice: Flux and flavor retention by cellulose acetate and polyamide membranes. J. Food Process Eng. 1987, 9, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, M.J.; Wiley, R.C. Preconcentration of apple juice by reverse osmosis. J. Food Sci. 1983, 48, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, A.; Corcuff, R.; Goulet, C.; Godefroy, S.B.; Doyen, A.; Beaulieu, L. Valorization of snow crab (Chionoecetes opilio) cooking effluents for food applications. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naccarato, A.; Tagarelli, A. Recent applications and newly developed strategies of solid-phase microextraction in contaminant analysis: Through the environment to humans. Separations 2019, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naccarato, A.; Tassone, A.; Moretti, S.; Elliani, R.; Sprovieri, F.; Pirrone, N.; Tagarelli, A. A green approach for organophosphate ester determination in airborne particulate matter: Microwave-assisted extraction using hydroalcoholic mixture coupled with solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2018, 189, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naccarato, A.; Elliani, R.; Cavaliere, B.; Sindona, G.; Tagarelli, A. Development of a fast and simple gas chromatographic protocol based on the combined use of alkyl chloroformate and solid phase microextraction for the assay of polyamines in human urine. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1549, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gionfriddo, E.; Naccarato, A.; Sindona, G.; Tagarelli, A. A reliable solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography–triple quadrupole mass spectrometry method for the assay of selenomethionine and selenomethylselenocysteine in aqueous extracts: Difference between selenized and not-enriched selenium potatoes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 747, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Feudo, G.; Macchione, B.; Naccarato, A.; Sindona, G.; Tagarelli, A. The volatile fraction profiling of fresh tomatoes and triple concentrate tomato pastes as parameter for the determination of geographical origin. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozderović, A.; Moslavac, T.; Pichler, A. Influence of processing parameters and membrane type on permeate flux during solution concentration of different alcohols, esters, and aldehydes by reverse osmosis. J. Food Eng. 2007, 78, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhaya; Mondal, S.; Majumdar, G.C.; De, S. Clarifications of stevia extract using cross flow ultrafiltration and concentration by nanofiltration. Sep. Purof. Technol. 2012, 89, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozderović, A.; Moslavac, T.; Pichler, A. Concentration of aqueous solutions of organic compounds by reverse osmosis II. Influence of transmembrane pressure and membrane type on concentration of different alcohol solutions by reverse osmosis. J. Food Eng. 2006, 77, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte, S.F. The rejection of specific organic compounds by reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 2003, 158, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Compound | Concentration a (µg/L) | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Molecular Formula | Structure | Density (g/cm3) | Water Solubility at 25 °C (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| octanol | 18.3–35.8 | 130.23 | C8H18O |  | 0.8262 | 0.54 |
| α-terpineol | 47.0–77.1 | 154.25 | C10H18O |  | 0.935 | 2.42 |
| terpinen-4-ol | 50.4–97.0 | 154.25 | C10H18O |  | 0.926 | 2.5 |
| cis-carveol | 2.31–3.83 | 152.23 | C12H18O2 |  | 0.958 | 2.82 |
| karvon | 5.41–9.83 | 150.21 | C10H14O |  | - | 1.30 |
| linalool | 44.7–86.5 | 154.25 | C10H18O |  | 0.858 | 1.589 |
| Compound | Membrane Type | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG | SE | SC | ||||||
| Feed | Permeate | Feed | Permeate | Feed | Permeate | |||
| (μg/L) | (μg/L) | (μg/L) | (μg/L) | (μg/L) | (μg/L) | |||
| octanol | 26 ± 2 | n.d. | 18 ± 2 | n.d. | 36 ± 2 | n.d. | ||
| linalool | 72 ± 6 | 4.1 ± 0.4 | 45 ± 5 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 86 ± 3 | 1.6 ± 0.3 | ||
| terpinen-4-ol | 84 ± 4 | 7.2 ± 0.6 | 50 ± 4 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | 97 ± 3 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | ||
| α-terpineol | 77 ± 5 | 6.9 ± 0.5 | 47 ± 6 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | 84 ± 5 | 2.7 ± 0.2 | ||
| cis-carveol | 3.5 ± 0.3 | n.d. | 2.3 ± 0.4 | n.d. | 3.8 ± 0.6 | n.d. | ||
| karvon | 8.7 ± 0.6 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 5.4 ± 0.2 | n.d. | 9.8 ± 0.8 | n.d. | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Destani, F.; Naccarato, A.; Tagarelli, A.; Cassano, A. Recovery of Aromatics from Orange Juice Evaporator Condensate Streams by Reverse Osmosis. Membranes 2020, 10, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050092
Destani F, Naccarato A, Tagarelli A, Cassano A. Recovery of Aromatics from Orange Juice Evaporator Condensate Streams by Reverse Osmosis. Membranes. 2020; 10(5):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050092
Chicago/Turabian StyleDestani, Fitim, Attilio Naccarato, Antonio Tagarelli, and Alfredo Cassano. 2020. "Recovery of Aromatics from Orange Juice Evaporator Condensate Streams by Reverse Osmosis" Membranes 10, no. 5: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050092
APA StyleDestani, F., Naccarato, A., Tagarelli, A., & Cassano, A. (2020). Recovery of Aromatics from Orange Juice Evaporator Condensate Streams by Reverse Osmosis. Membranes, 10(5), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050092