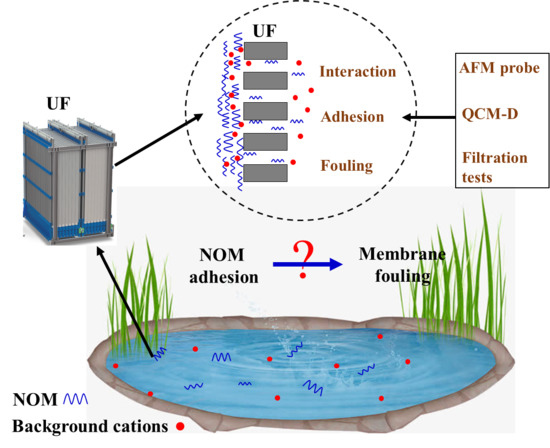
Impacts of Natural Organic Matter Adhesion on Irreversible Membrane Fouling during Surface Water Treatment Using Ultrafiltration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Water and Natural Organic Matter (NOM) Extraction
2.2. Membranes and Experimental Setup
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of NOM in Surface Water
3.2. Effects of Background Cations on Interfacial Interactions between the NOM and Membrane Surface
3.3. Effects of Background Cations on NOM Adhesion onto the Ultrafiltration (UF) Membrane Surface
3.4. Effects of Background Cations on the Rejection of NOM by UF
3.5. Effects of Background Cations on Membrane Fouling Caused by NOM
3.6. Morphological Characterization of Fouled Membranes by NOM
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacangelo, J.G.; Trussell, R.R.; Watson, M. Role of membrane technology in drinking water treatment in the United States. Desalination 1997, 113, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wen, G.; Li, S.; Chang, H.; Shao, S.; Huang, T.; Li, G.; Liang, H. Effect of pre-oxidation on low pressure membrane (LPM) for water and wastewater treatment: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, H.; Kimura, K.; Higuchi, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Ding, Q.; Hafuka, A. Tracking inorganic foulants irreversibly accumulated on low-pressure membranes for treating surface water. Water Res. 2015, 87, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Lou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, G.; Liao, B.-Q.; Shen, L.; Lin, H. Effects of surface morphology on alginate adhesion: Molecular insights into membrane fouling based on XDLVO and DFT analysis. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Lee, N.; Young, T.; Gary, A.; Lozier, J.C.; Jacangelo, J.G. Natural organic matter fouling of low-pressure, hollow-fiber membranes: Effects of NOM source and hydrodynamic conditions. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3823–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wu, C.; Yu, H.; Gao, S.; Li, G.; Cui, F.; Qu, F. Applying ultraviolet/persulfate (UV/PS) pre-oxidation for controlling ultrafiltration membrane fouling by natural organic matter (NOM) in surface water. Water Res. 2018, 132, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Wu, M.; Cheng, J.; Lin, H.; He, Y. Different fouling propensities of loosely and tightly bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) and the related fouling mechanisms in a membrane bioreactor. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, F.; Meng, F.; Liao, B.-Q.; Hong, H.; Cheng, J.; Gao, W. A critical review of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) in membrane bioreactors: Characteristics, roles in membrane fouling and control strategies. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 460, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Qu, F.; Liang, H.; Yu, H.; Pang, H.; Rong, H.; Fan, G.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Effect of biopolymers and humic substances on gypsum scaling and membrane wetting during membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 617, 118638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamse, A.; Lipreau, C.; Li, S.; Heijman, B. Removal of divalent cations reduces fouling of ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 323, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listiarini, K.; Chun, W.; Sun, D.D.; Leckie, J.O. Fouling mechanism and resistance analyses of systems containing sodium alginate, calcium, alum and their combination in dead-end fouling of nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 344, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Jia, H.; Cui, Z.; Yang, G. Role of ionic strength on protein fouling during ultrafiltration by synchronized UV–vis spectroscopy and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.-Y.; Ernst, M.; Cui, F.; Jekel, M. Effect of different cations on UF membrane fouling by NOM fractions. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Hong, H.-C.; Lin, H.; Shen, L.; Yu, H.; Ma, G.; Cheng, J.; Liao, B. Mechanistic insights into alginate fouling caused by calcium ions based on terahertz time-domain spectra analyses and DFT calculations. Water Res. 2018, 129, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Liang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Li, G. Ultrafiltration membrane fouling by extracellular organic matters (EOM) of Microcystis aeruginosa in stationary phase: Influences of interfacial characteristics of foulants and fouling mechanisms. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.-Q.; Hao, X.-D.; Wang, Z.; Song, X.; Iritani, E.; Katagiri, N. Membrane recovery of alginate in an aqueous solution by the addition of calcium ions: Analyses of resistance reduction and fouling mechanism. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 535, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Winters, H.; Liu, Y. Ultrafiltration behaviors of alginate blocks at various calcium concentrations. Water Res. 2015, 83, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Bligh, M.W.; Kinsela, A.S.; Wang, Y.; Waite, T.D. Calcium-mediated polysaccharide gel formation and breakage: Impact on membrane foulant hydraulic properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, H.; Shen, L.; Liao, B.-Q.; Wu, X.; Li, R. Effect of calcium ions on fouling properties of alginate solution and its mechanisms. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 525, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Xiao, K.; Shen, Y.; Huang, X. A new perspective on the effect of complexation between calcium and alginate on fouling during nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 82, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, L.; Wu, G.; Wang, J.; Lv, Y.; Liu, T. A comparison of the roles of Ca2+ and Mg2+ on membrane fouling with humic acid: Are there any differences or similarities? J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 545, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Mu, Y.; Yu, H.-Q. Differences in the colloid properties of sodium alginate and polysaccharides in extracellular polymeric substances with regard to membrane fouling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 535, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.D.; Kamanyi, J.; Heijman, B.G.; Amy, G. Colloidal organic matter fouling of UF membranes: Role of NOM composition & size. Desalination 2008, 220, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Qu, F.; Liang, H.; Van Der Bruggen, B.; Cheng, X.; Yu, H.; Xu, G.; Li, G. Microcystis aeruginosa -laden surface water treatment using ultrafiltration: Membrane fouling, cell integrity and extracellular organic matter rejection. Water Res. 2017, 112, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Liang, H.; Zhou, J.; Nan, J.; Shao, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. Ultrafiltration membrane fouling caused by extracellular organic matter (EOM) from Microcystis aeruginosa: Effects of membrane pore size and surface hydrophobicity. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 449, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, B.; Qu, F.; Ding, A.; Liang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, G. Control of ultrafiltration membrane fouling caused by algal extracellular organic matter (EOM) using enhanced Al coagulation with permanganate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 172, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Yan, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Liang, H.; Yu, H.; He, J.; Li, G. A pilot study of hybrid biological activated carbon (BAC) filtration-ultrafiltration process for water supply in rural areas: Role of BAC pretreatment in alleviating membrane fouling. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Qu, F.; Sun, L.; Liang, H.; Han, Z.; Chang, H.; Shao, S.; Li, G. Relationship between soluble microbial products (SMP) and effluent organic matter (EfOM): Characterized by fluorescence excitation emission matrix coupled with parallel factor analysis. Chemosphere 2015, 121, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Qu, F.; Zhang, X.; Shao, S.; Rong, H.; Liang, H.; Wiesner, M.; Ma, J. Development of correlation spectroscopy (COS) method for analyzing fluorescence excitation emission matrix (EEM): A case study of effluent organic matter (EfOM) ozonation. Chemosphere 2019, 228, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Wang, L.; Zhu, M.; Deng, D.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Lv, Y. Effect of Hydration Forces on Protein Fouling of Ultrafiltration Membranes: The Role of Protein Charge, Hydrated Ion Species, and Membrane Hydrophilicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, M.; Keith, H. Forces between Colloid Particles in Natural Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 3303–3308. [Google Scholar]
- Motsa, M.M.; Mamba, B.B.; Verliefde, A.R. Combined colloidal and organic fouling of FO membranes: The influence of foulant–foulant interactions and ionic strength. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Wang, L.; Deng, D.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Zhu, M.; Lv, Y. Evaluating the effects of sodium and magnesium on the interaction processes of humic acid and ultrafiltration membrane surfaces. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 526, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Elimelech, M. Organic Fouling and Chemical Cleaning of Nanofiltration Membranes: Measurements and Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4683–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, D.; Chen, X.D.; Mercadé-Prieto, R. Effect of calcium on the fouling of whey protein isolate on stainless steel using QCM-D. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 177, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-F.; He, D.-Q.; Chen, W.; Yu, H.-Q. Probing the roles of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in humic acids-induced ultrafiltration membrane fouling using an integrated approach. Water Res. 2015, 81, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, I.M.; Herzberg, M.; Walker, S.L.; Freger, V. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Attachment on QCM-D Sensors: The Role of Cell and Surface Hydrophobicities. Langmuir 2012, 28, 6396–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrando, D.; Toubiana, D.; Kandiyote, N.S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nejidat, A.; Herzberg, M. Ambivalent role of calcium in the viscoelastic properties of extracellular polymeric substances and the consequent fouling of reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 2018, 429, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, J.; She, Q.; Wan, M.P.; Wang, R.; Chang, V.W.-C.; Tang, C.Y. Role of calcium ions on the removal of haloacetic acids from swimming pool water by nanofiltration: mechanisms and implications. Water Res. 2017, 110, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Lu, Z.; Chen, W. Interaction mechanisms of humic acid combined with calcium ions on membrane fouling at different conditions in an ultrafiltration system. Desalination 2015, 357, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Meng, F.; Lin, A.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tang, C.Y. Monovalent ion-mediated fouling propensity of model proteins during low-pressure membrane filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 152, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Liang, H.; Qu, F.; Li, K.; Chang, H.; Yu, H.; Li, G. Combined influence by humic acid (HA) and powdered activated carbon (PAC) particles on ultrafiltration membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 500, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Wang, L.; Mi, N.; Gao, Z.; Liu, T.; Lv, Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, X.; Yang, Y. Enhancement and Mitigation Mechanisms of Protein Fouling of Ultrafiltration Membranes under Different Ionic Strengths. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6574–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Elimelech, M. Relating Organic Fouling of Reverse Osmosis Membranes to Intermolecular Adhesion Forces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Dempsey, B.A. Effects of wastewater effluent organic materials on fouling in ultrafiltration. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3379–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Yan, Z.; Liu, W.; Shao, S.; Ren, X.; Ren, N.; Li, G.; Liang, H. Effects of manganese dioxides on the ultrafiltration membrane fouling by algal extracellular organic matter. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 153, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, F.; Yang, Z.; Gao, S.; Yu, H.; He, J.; Rong, H.; Tian, J. Impacts of Natural Organic Matter Adhesion on Irreversible Membrane Fouling during Surface Water Treatment Using Ultrafiltration. Membranes 2020, 10, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090238
Qu F, Yang Z, Gao S, Yu H, He J, Rong H, Tian J. Impacts of Natural Organic Matter Adhesion on Irreversible Membrane Fouling during Surface Water Treatment Using Ultrafiltration. Membranes. 2020; 10(9):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090238
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Fangshu, Zhimeng Yang, Shanshan Gao, Huarong Yu, Junguo He, Hongwei Rong, and Jiayu Tian. 2020. "Impacts of Natural Organic Matter Adhesion on Irreversible Membrane Fouling during Surface Water Treatment Using Ultrafiltration" Membranes 10, no. 9: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090238
APA StyleQu, F., Yang, Z., Gao, S., Yu, H., He, J., Rong, H., & Tian, J. (2020). Impacts of Natural Organic Matter Adhesion on Irreversible Membrane Fouling during Surface Water Treatment Using Ultrafiltration. Membranes, 10(9), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090238