Ecological Risk Evaluation and Removal of Emerging Pollutants in Urban Wastewater by a Hollow Fiber Forward Osmosis Membrane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Forward Osmosis Membrane and Experimental Setup
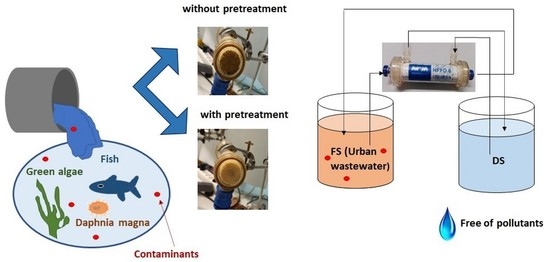
2.2. Urban Wastewater Pretreatment
- Scenario A involved wastewater centrifuged at 10,000 rpm (revolutions per minute) for ten minutes and then filtered through a filter with 0.7 μm pores. The final characteristics of the urban wastewater obtained after this pretreatment and used as the FS for the FO process were 82.42 mgO2/L in COD, 0.89 g/Kg in TS, and 0.35 g/Kg in VS.
- Scenario B involved centrifuging wastewater at 10,000 rpm for ten minutes without filtering it. The final characteristics of the urban wastewater with this pretreatment, which were used as the FS for the FO process, were 146.15 mgO2/L in COD, 0.79 g/Kg in TS, and 0.36 g/Kg in VS.
- Scenario C involved using wastewater directly as the FS in an FO procedure without carrying out any pretreatment. The characteristics of this FS were those mentioned at the beginning of this section.
2.3. Experiments with Different DS Chemicals and with Different Concentrations of NaCl
2.4. Emerging Contaminants in Urban Wastewater
Ecological Risk Assessment of CECs
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Different Urban Wastewater Pretreatments
3.2. Effect of Different DS
3.3. Effect of Different NaCl Concentration as Draw Solution
3.4. Recovery of Organic Matter in the Forward Osmosis Process
3.5. Contaminants of Emerging of Concern (CECs)
3.5.1. CECs in Urban Wastewater
3.5.2. Ecological Risks and CECS in Wastewater
3.5.3. Concentration and Recovery of CECs
3.5.4. Ecological Risk of CECs after FO
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guerra-Rodríguez, S.; Oulego, P.; Rodríguez, E.; Singh, D.N.; Rodríguez-Chueca, J. Towards the Implementation of Circular Economy in the Wastewater Sector: Challenges and Opportunities. Water 2020, 12, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Toja, Y.; Vázquez-Rowe, I.; Amores, M.J.; Termes-Rifé, M.; Marín-Navarro, D.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G. Benchmarking Wastewater Treatment Plants under an Eco-Efficiency Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.L.; Stadler, L.B.; Love, N.G.; Skerlos, S.J.; Raskin, L. Perspectives on Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor Treatment of Domestic Wastewater: A Critical Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Burton, F.L.; Stensel, H.D. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse, 4th ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ozgun, H.; Dereli, R.K.; Ersahin, M.E.; Kinaci, C.; Spanjers, H.; van Lier, J.B. A Review of Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactors for Municipal Wastewater Treatment: Integration Options, Limitations and Expectations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikosana, M.L.; Sikhwivhilu, K.; Moutloali, R.; Madyira, D.M. Municipal Wastewater Treatment Technologies: A Review. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 35, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gu, Y.; Cao, C.; Zhang, J.; Ng, J.W.; Tang, C. Performance of a Submerged Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor with Forward Osmosis Membrane for Low-Strength Wastewater Treatment. Water Res. 2014, 50, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blandin, G.; Ferrari, F.; Lesage, G.; Le-Clech, P.; Héran, M.; Martinez-Lladó, X. Forward Osmosis as Concentration Process: Review of Opportunities and Challenges. Membranes 2020, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.; Hai, F.I.; Price, W.E.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. Assessing the integration of forward osmosis and anaerobic digestion for simultaneous wastewater treatment and resource recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 260, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.J.; Hai, F.I.; Price, W.E.; Drewes, J.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Forward osmosis as a platform for resource recovery from municipal wastewater—A critical assessment of the literature. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Ning, Z.; Wang, D.K.; da Costa, J.C.D. Processing Municipal Wastewaters by Forward Osmosis Using CTA Membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansari, A.J.; Hai, F.I.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Factors governing the pre-concentration of wastewater using forward osmosis for subsequent resource recovery. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, F.; Pijuan, M.; Rodriguez-Roda, I.; Blandin, G. Exploring submerged forward osmosis for water recovery and pre-concentration of wastewater before anaerobic digestion: A pilot scale study. Membranes 2019, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Tang, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z. A pilot-scale forward osmosis membrane system for concentrating low-strength municipal wastewater: Performance and implications. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bao, X.; Wu, Q.; Tian, J.; Shi, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, B.; Guo, Y.; Shu, S.; et al. Fouling mechanism of forward osmosis membrane in domestic wastewater concentration: Role of substrate structures. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutchmiah, K.; Cornelissen, E.R.; Harmsen, D.J.H.; Post, J.W.; Lampi, K.; Ramaekers, H.; Rietveld, L.C.; Roest, K. Water recovery from sewage using forward osmosis. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Nghiem, L.D.; Price, W.E.; Elimelech, M. A forward osmosis-membrane distillation hybrid process for direct sewer mining: System performance and limitations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13486–13493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.; Son, M.; Choi, H. Integrating Seawater Desalination and Wastewater Reclamation Forward Osmosis Process Using Thin-Film Composite Mixed Matrix Membrane with Functionalized Carbon Nanotube Blended Polyethersulfone Support Layer. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chou, S.; Wang, R.; Shi, L.; Fang, W.; Chaitra, G.; Tang, C.Y.; Torres, J.; Hu, X.; Fane, A.G. Nature Gives the Best Solution for Desalination: Aquaporin-Based Hollow Fiber Composite Membrane with Superior Performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 494, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lateef, S.K.; Soh, B.Z.; Kimura, K. Direct Membrane Filtration of Municipal Wastewater with Chemically Enhanced Backwash for Recovery of Organic Matter. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 150, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- She, Q.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G.; Tang, C.Y. Membrane Fouling in Osmotically Driven Membrane Processes: A Review. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 201–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilli, A.; Cath, T.Y.; Childress, A.E. Selection of Inorganic-Based Draw Solutions for Forward Osmosis Applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.J.; Hai, F.I.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Selection of Forward Osmosis Draw Solutes for Subsequent Integration with Anaerobic Treatment to Facilitate Resource Recovery from Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 191, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alaswad, S.O.; Al-Aibi, S.; Alpay, E.; Sharif, A.O. Efficiency of Organic Draw Solutions in a Forward Osmosis Process Using Nano-Filtration Flat Sheet Membrane. J. Chem. Eng. Process Technol. 2018, 9, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Q.; Su, J.; Amy, G.L.; Chung, T.S. Exploration of Polyelectrolytes as Draw Solutes in Forward Osmosis Processes. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Ling, M.; Chung, T.S. Draw Solutions for Forward Osmosis Processes: Developments, Challenges, and Prospects for the Future. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 442, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Chu, K.H.; Her, N.; Im, J.; Park, Y.G.; Cho, J.; Sarp, S.; Jang, A.; Jang, M.; Yoon, Y. Organic Fouling and Reverse Solute Selectivity in Forward Osmosis: Role of Working Temperature and Inorganic Draw Solutions. Desalination 2016, 389, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutchmiah, K.; Lauber, L.; Roest, K.; Harmsen, D.J.H.; Post, J.W.; Rietveld, L.C.; van Lier, J.B.; Cornelissen, E.R. Zwitterions as Alternative Draw Solutions in Forward Osmosis for Application in Wastewater Reclamation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 460, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernacka, E.; Jaroszek, H.; Turek, M.; Dydo, P.; Czechowicz, D.; Mitko, K. Application of Waste Glycerol as a Draw Solution for Forward Osmosis. Membranes 2021, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valladares Linares, R.; Li, Z.; Sarp, S.; Bucs, S.S.; Amy, G.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Forward Osmosis Niches in Seawater Desalination and Wastewater Reuse. Water Res. 2014, 66, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulied, M.; al Momani, F.; Khraisheh, M.; Bhosale, R.; Al Nouss, A. Influence of Draw Solution Type and Properties on the Performance of Forward Osmosis Process: Energy Consumption and Sustainable Water Reuse. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Luo, W.; Guo, H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Tang, C.Y.; Gray, S.R. Trace Organic Contaminant Rejection by Aquaporin Forward Osmosis Membrane: Transport Mechanisms and Membrane Stability. Water Res. 2018, 132, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Chu, K.H.; Al-Hamadani, Y.A.J.; Park, C.M.; Jang, M.; Kim, D.H.; Yu, M.; Heo, J.; Yoon, Y. Removal of Contaminants of Emerging Concern by Membranes in Water and Wastewater: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 896–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Rangabhashiyam, S.; Verma, P.; Singh, P.; Devi, P.; Kumar, P.; Hussain, C.M.; Gaurav, G.K.; Kumar, K.S. Environmental and Health Impacts of Contaminants of Emerging Concerns: Recent Treatment Challenges and Approaches. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosset, A.; Polomé, P.; Perrodin, Y. Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment of Micropollutants from Treated Urban Wastewater Effluents for Watercourses at a Territorial Scale: Application and Comparison of Two Approaches. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 224, 113437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, E.; Volschenk, M.; Brocker, L.; Wolfaardt, G.M. A Two-Year Study of Emerging Micro-Pollutants and Drugs of Abuse in Two Western Cape Wastewater Treatment Works (South Africa). Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Galvis, E.A.; Botero-Coy, A.M.; Martínez-Pachón, D.; Moncayo-Lasso, A.; Ibáñez, M.; Hernández, F.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Degradation of Seventeen Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Municipal Wastewater Effluents by Sonochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes. Water Res. 2019, 154, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Guzmán, C.; Ulloa-Sánchez, S.; Mora, K.; Helena-Bustos, R.; Lopez-Barrera, E.; Alvarez, J.; Rodriguez-Pinzón, M. Emerging Pollutants in the Urban Water Cycle in Latin America: A Review of the Current Literature. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 237, 408–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda-Marquez, J.J.; Levchuk, I.; Fernández Ibañez, P.; Sillanpää, M. A Critical Review on Application of Photocatalysis for Toxicity Reduction of Real Wastewaters. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Valladares Linares, R.; Bucs, S.; Fortunato, L.; Hélix-Nielsen, C.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Ghaffour, N.; Leiknes, T.O.; Amy, G. Aquaporin Based Biomimetic Membrane in Forward Osmosis: Chemical Cleaning Resistance and Practical Operation. Desalination 2017, 420, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamanca, M.; López-Serna, R.; Palacio, L.; Hernández, A.; Prádanos, P.; Peña, M. Study of the Rejection of Contaminants of Emerging Concern by a Biomimetic Aquaporin Hollow Fiber Forward Osmosis Membrane. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gao, B.; Jang, A.; Shon, H.k.; Yue, Q. Municipal Wastewater Treatment by Forward Osmosis Using Seawater Concentrate as Draw Solution. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blandin, G.; Rosselló, B.; Monsalvo, V.M.; Batlle-Vilanova, P.; Viñas, J.M.; Rogalla, F.; Comas, J. Volatile Fatty Acids Concentration in Real Wastewater by Forward Osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 575, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2000/60/ec of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2000, 327, 1–72.
- Hernando, M.D.; Mezcua, M.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; Barceló, D. Environmental Risk Assessment of Pharmaceutical Residues in Wastewater Effluents, Surface Waters and Sediments. Talanta 2006, 69, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matamoros, V.; Rodríguez, Y.; Albaigés, J. A Comparative Assessment of Intensive and Extensive Wastewater Treatment Technologies for Removing Emerging Contaminants in Small Communities. Water Res. 2016, 88, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, W.R.; Calvo, J.I.A. Hernández. Steps of membrane blocking in flux decline during protein microfiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 101, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.A.; Stokes, R.H. Electrolite Solution, 2nd ed.; Dover Books on Chemistry Series: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Special Student Edition, 75th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, L. The Osmotic Pressure of Concentrated Solutions and the Laws of the Perfect Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1908, 30, 668–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castaldi, M.; D’Errico, G.; Paduano, L.; Vitalgliano, V. Transport Properties of the Binary System Glucose−Water at 25 °C. A Velocity Correlation Study. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1998, 43, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Online, R.; Nghiem, L.; Schaefer, A.; Elimelech, M. Role of electrostatic interactions in the retention of pharmaceutically active contaminants by a loose nanofiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 286, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolfram Research, Inc. Wolfram|Alpha Notebook Edition; Wolfram: Champaign, IL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, N.H.; Gin, K.Y.H. Occurrence and Removal of Pharmaceuticals, Hormones, Personal Care Products, and Endocrine Disrupters in a Full-Scale Water Reclamation Plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.; Hooda, P.S.; Barker, J.; Barton, S.; Swinden, J. Occurrence, Fate and Transformation of Emerging Contaminants in Water: An Overarching Review of the Field. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ata, R.; Tore, G.Y.; Shah, M.P. Emerging Technologies for Treatment of Antibiotic Residues from Wastewater Influent/Effluent for Sustainable Environment: A Case Study with NFC-Doped Titania Immobilized on Polystyrene as an Efficient Technology. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hube, S.; Wu, B. Mitigation of Emerging Pollutants and Pathogens in Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Processes: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, G.; Chen, H.; Srinivasa Raghavan, D.S.; Ting, Y.P. Removal Behaviors of Antibiotics in a Hybrid Microfiltration-Forward Osmotic Membrane Bioreactor for Real Municipal Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Patterson-Fortin, L.; Boutros, J.; Smith, R.; Goss, G.G. Removal of Biological Effects of Organic Pollutants in Municipal Wastewater by a Novel Advanced Oxidation System. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalecka, B.; Strods, M.; Cacivkins, P.; Ziverte, E.; Rajarao, G.K.; Juhna, T. Removal of Pharmaceutical Compounds from Municipal Wastewater by Bioaugmentation with Fungi: An Emerging Strategy Using Fluidized Bed Pelleted Bioreactor. Environ. Adv. 2021, 5, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcal, J.; Bishop, T.; Hofman, J.; Shen, J. From Pollutant Removal to Resource Recovery: A Bibliometric Analysis of Municipal Wastewater Research in Europe. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Meng, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; He, B.; Zhao, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Wang, T. Which Type of Pollutants Need to Be Controlled with Priority in Wastewater Treatment Plants: Traditional or Emerging Pollutants? Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiest, L.; Gosset, A.; Fildier, A.; Libert, C.; Hervé, M.; Sibeud, E.; Giroud, B.; Vulliet, E.; Bastide, T.; Polomé, P.; et al. Occurrence and Removal of Emerging Pollutants in Urban Sewage Treatment Plants Using LC-QToF-MS Suspect Screening and Quantification. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, P.R.; Zhang, T.C.; Bhunia, P.; Surampalli, R.Y. Treatment Technologies for Emerging Contaminants in Wastewater Treatment Plants: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, V.K.; Saidulu, D.; Majumder, A.; Srivastava, A.; Gupta, B.; Gupta, A.K. Emerging Contaminants in Wastewater: A Critical Review on Occurrence, Existing Legislations, Risk Assessment, and Sustainable Treatment Alternatives. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansch, C.; Sharon, D.; Rockwell, S.D.; Jow, P.C.Y.; Leo, A.; Steller, E.E. Substituent constants for correlation analysis. J. Med. Chem. 1977, 20, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.I.C.; Cooney, C.L.; Dunnill, P.; Humphrey, A.E.; Heden, C.-G. Fermentation and Enzyme Technology. Prep. Biochem. 1980, 9, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosset, A.; Wiest, L.; Fildier, A.; Libert, C.; Giroud, B.; Hammada, M.; Hervé, M.; Sibeud, E.; Vulliet, E.; Polomé, P.; et al. Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment of Contaminants of Emerging Concern Identified by “Suspect Screening” from Urban Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents at a Territorial Scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Serna, R.; Postigo, C.; Blanco, J.; Pérez, S.; Ginebreda, A.; de Alda, M.L.; Petrović, M.; Munné, A.; Barceló, D. Assessing the Effects of Tertiary Treated Wastewater Reuse on the Presence Emerging Contaminants in a Mediterranean River (Llobregat, NE Spain). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1000–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, E.O.; Santos, L.V.S.; Lange, L.C. Prioritization and Environmental Risk Assessment of Pharmaceuticals Mixtures from Brazilian Surface Waters. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Wang, B.; Fu, C.; Dong, R.; Huang, J.; Deng, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, G. Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) in Urban and Suburban Rivers of Beijing, China: Occurrence, Source Apportionment and Potential Ecological Risk. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 2016, 18, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.J.; Park, J.; Lee, M.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, K. Ecological hazard assessment of major veterinary benzimidazoles: Acute and chronic toxicities to aquatic microbes and invertebrates. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 2221–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagil, M.; Białk-Bielińska, A.; Puckowski, A.; Wychodnik, K.; Maszkowska, J.; Mulkiewicz, E.; Kumirska, J.; Stepnowski, P.; Stolte, S. Toxicity of Anthelmintic Drugs (Fenbendazole and Flubendazole) to Aquatic Organisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 2566–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.; Fu, L.; Tang, B.; Bin, L.; Li, P.; Huang, S.; Fu, F. Occurrence, Ecotoxicological Risks of Sulfonamides and Their Acetylated Metabolites in the Typical Wastewater Treatment Plants and Receiving Rivers at the Pearl River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; An, S.; Jho, E.H.; Bae, S.; Choi, Y.; Choe, J.K. Exploring Reductive Degradation of Fluorinated Pharmaceuticals Using Al2O3-Supported Pt-Group Metallic Catalysts: Catalytic Reactivity, Reaction Pathways, and Toxicity Assessment. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visca Palermo, M. Emerging Pollutants Removal in Wastewater Treatment Plants: A Review and Their Implications in a River Basin in Uruguay. This Research Is Done for the Partial Fulfilment of Requirements for the Master of Science Degree at the UNESCO-IHE Institute for Water Education, Delft, The Netherlands. 2017. Available online: https://saniup.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/UWS-SE-CALI-2017-17-Mercedes-Visca-Palermo_EXAM-VERSION.pdf (accessed on 22 December 2021).
- Camargo, M.A.F.; Camargo, C.A.C.M. Effects of Caffeine on the Organism—Literature Review. Open Access Libr. J. 2019, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigueto, C.V.T.; Nazari, M.T.; de Souza, C.F.; Cadore, J.S.; Brião, V.B.; Piccin, J.S. Alternative Techniques for Caffeine Removal from Wastewater: An Overview of Opportunities and Challenges. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 35, 101231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Analytes | Analytes | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Penicillin | 27 | Clarithromycin |
| 2 | Oxytetracycline | 28 | Erythromycin |
| 3 | Doxycycline | 29 | Naproxen |
| 4 | Tetracycline | 30 | Clofibrate |
| 5 | Marbofloxacin | 31 | Levofloxacin |
| 6 | Enrofloxacin | 32 | Norfloxacin |
| 7 | Danofloxacin | 33 | 1,4-Benzoquinone |
| 8 | Sulfadiazine | 34 | Atorvastatin |
| 9 | Sulfathiazole | 35 | Atenolol |
| 10 | Sulfamethizole | 36 | Caffeine |
| 11 | Sulfadimidine | 37 | Atrazine |
| 12 | Sulfamethoxazole | 38 | N, N-diethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET) |
| 13 | Tylosin | 9 | Ciprofloxacin |
| 14 | Tiamulin | 40 | 17-α-Ethynylestradiol |
| 15 | Apramycin | 41 | Crotamiton |
| 16 | Trimethoprim | 42 | Estrone |
| 17 | Florfenicol | 43 | Ethyl Paraben |
| 18 | Fenbendazole | 44 | Propyl Paraben |
| 19 | Dexametasone | 45 | Diclofenac Sodium Salt |
| 20 | Progesterone | 46 | Ibuprofen |
| 21 | Methyl paraben | 47 | Salicylic acid |
| 22 | Carbamazepine | 48 | Clofibric acid |
| 23 | Propanolol | 49 | Triclosan |
| 24 | Sulfapyridine | 50 | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid |
| 25 | Metronidazole | 51 | Gemfibrozil |
| 26 | Ofloxacin |
| K (min−1) | (L/m2h) | (g/m2h) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario A | 0.010 ± 0.002 | 8.2 ± 0.7 | 0.67 ± 0.05 |
| Scenario B | 0.033 ± 0.002 | 6.6 ± 0.5 | 0.59 ± 0.05 |
| Scenario C | 0.111 ± 0.008 | 5.1 ± 0.4 | 0.75 ± 0.06 |
| Analytes | Concentration (ng/L) | Analytes | Concentration (ng/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penicillin G | <MLD | Naproxen | 1864.5 |
| Oxytetracycline | <MLD | Clarithromycin | 83.2 |
| Doxycycline | <MLQ | Erythromycin | <MLQ |
| Tetracycline | <MLD | Clofibrate | <MLD |
| Marbofloxacin | <MLD | Levofloxacin | 111.76 |
| Enrofloxacin | <MLQ | Norfloxacin | <MLD |
| Danofloxacin | <MLD | 1,4-Benzoquinone | <MLD |
| Sulfadiazine | <MLD | Atorvastatin | 36.68 |
| Sulfathiazole | <MLD | Atenolol | 316.37 |
| Sulfamethizole | <MLD | Caffeine | 14,210.9 |
| Sulfadimidine | <MLD | Atrazine | <MLQ |
| Sulfamethoxazole | 218.05 | DEET | 72.44 |
| Tylosin | <MLD | Ciprofloxacin | 257.21 |
| Tiamulin | <MLQ | 17-α-Ethynylestradiol | <MLD |
| Apramycin | <MLD | Crotamiton | <MLD |
| Trimethoprim | 93.54 | Estrone | <MLD |
| Florfenicol | <MLD | Ethyl Paraben | <MLD |
| Fenbendazole | 11.09 | Propyl Paraben | <MLD |
| Dexametasone | <MLD | Diclofenac Sodium Salt | 680.91 |
| Progesterone | <MLD | Ibuprofen | 5322.55 |
| Methyl paraben | 117.83 | Salicylic acid | <MLD |
| Carbamazepine | 28.76 | Clofibric acid | <MLQ |
| Propanolol | <MLQ | Triclosan | <MLD |
| Sulfapyridine | 11.05 | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | <MLD |
| Metronidazole | <MLD | Gemfibrozil | 540.49 |
| Ofloxacin | 85.92 |
| ANALYTES | RQ Daphnia | RQ Fish | RQ Green Algae |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfamethoxazole | 0.01 | 0.00 | 8.08 |
| Diclofenac | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.05 |
| Naproxen | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Ibuprofen | 0.59 | 0.13 | 1.33 |
| Gemfibrozil | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.06 |
| Atorvastatin | 0.43 | 0.41 | 016 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0.00 | 0.00 | 51.44 |
| Ofloxacin | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Carbamazepine | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Caffeine | 32.30 | 0.20 | 0.09 |
| DEET | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Fenbendazole | 0.67 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| Methylparaben | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Sulfapyridine | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Levofloxacin | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Clarithromycin | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 |
| Atenolol | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.15 |
| Trimethoprim | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salamanca, M.; López-Serna, R.; Palacio, L.; Hernandez, A.; Prádanos, P.; Peña, M. Ecological Risk Evaluation and Removal of Emerging Pollutants in Urban Wastewater by a Hollow Fiber Forward Osmosis Membrane. Membranes 2022, 12, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030293
Salamanca M, López-Serna R, Palacio L, Hernandez A, Prádanos P, Peña M. Ecological Risk Evaluation and Removal of Emerging Pollutants in Urban Wastewater by a Hollow Fiber Forward Osmosis Membrane. Membranes. 2022; 12(3):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030293
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalamanca, Mónica, Rebeca López-Serna, Laura Palacio, Antonio Hernandez, Pedro Prádanos, and Mar Peña. 2022. "Ecological Risk Evaluation and Removal of Emerging Pollutants in Urban Wastewater by a Hollow Fiber Forward Osmosis Membrane" Membranes 12, no. 3: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030293
APA StyleSalamanca, M., López-Serna, R., Palacio, L., Hernandez, A., Prádanos, P., & Peña, M. (2022). Ecological Risk Evaluation and Removal of Emerging Pollutants in Urban Wastewater by a Hollow Fiber Forward Osmosis Membrane. Membranes, 12(3), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030293