Assessment of Dye-Absorbed Eggshell Membrane Composites as Solid Polymer Electrolyte of Fuel Cells
Abstract
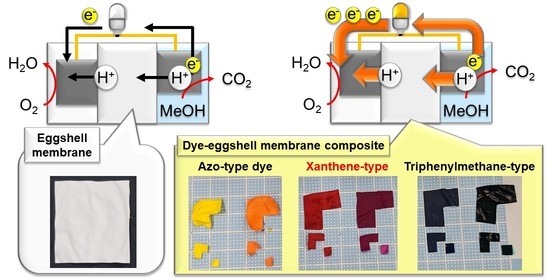
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Dye–ESM Composites
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Equipped with Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX) Characterization
2.4. Proton Conductivity Measurement of Dye–ESM Composites
2.5. I–V Performance of the Fuel Cells
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, C.; Negro, E.; Vezzù, K.; Pagot, G.; Cavinato, G.; Nale, A.; Bang, Y.H.; Di Noto, V. Hybrid inorganic-organic proton-conducting membranes based on SPEEK doped with WO3 nanoparticles for application in vanadium redox flow batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 309, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Vinothkannan, M.; Song, M.H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, H.-K.; Yoo, D.J. Amine functionalized carbon nanotube (ACNT) filled in sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) membrane: Effects of ACNT in improving polymer electrolyte fuel cell performance under reduced relative humidity. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 188, 107890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, R.K.; Thombre, S.B.; Shrivastava, N.K. A critical review of the current collector for passive direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2015, 285, 510–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarudin, S.K.; Achmad, F.; Daud, W.R.W. Overview on the application of direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC) for portable electronic devices. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 6902–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Faghri, A.; Xu, C. Structural optimization of the direct methanol fuel cell passively fed with a high-concentration methanol solution. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 8202–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinzel, A.; Barragán, V. A review of the state-of-the-art of the methanol crossover in direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 1999, 84, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, W.; Li, Y. An overview of the proton conductivity of nafion membranes through a statistical analysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 504, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbinati, O. A Direct Methanol Fuel Cell. J. Chem. Educ. 2002, 79, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurau, B.; Smotkin, E.S. Methanol crossover in direct methanol fuel cells: A link between power and energy density. J. Power Sources 2002, 112, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radenahmad, N.; Afif, A.; Petra, P.I.; Rahman, S.M.; Eriksson, S.-G.; Azad, A.K. Proton-conducting electrolytes for direct methanol and direct urea fuel cells—A state-of-the-art review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.K.; Pitchumani, S.; Sridhar, P.; Shukla, A.K. Nafion and modified-Nafion membranes for polymer electrolyte fuel cells: An overview. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2009, 32, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M.; Witek-Krowiak, A. Agricultural Waste Peels as Versatile Biomass for Water Purification—A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 244–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Khodaiyan, F.; Yarmand, M.S. Optimization of microwave assisted extraction of pectin from sour orange peel and its physicochemical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 140, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanifuji, N.; Shimizu, T.; Yoshikawa, H.; Tanaka, M.; Nishio, K.; Ida, K.; Shimizu, A.; Hasebe, Y. Assessment of Eggshell Membrane as a New Type of Proton-Conductive Membrane in Fuel Cells. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 12637–12642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arami, M.; Limaee, N.Y.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Evaluation of the adsorption kinetics and equilibrium for the potential removal of acid dyes using a biosorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 139, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.; Yang, J.; Lai, C.; Cheng, Y.; Lin, C.; Yeh, C. Characterization and adsorption properties of eggshells and eggshell membrane. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şişmanoğlu, T.; Pozan, G. Adsorption of congo red from aqueous solution using various TiO2 nanoparticles. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 13318–13333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfikar, M.A.; Mariske, E.D.; Djajanti, S.D. Adsorption of Lignosulfonate Compounds Using Powdered Eggshell. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2012, 34, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Belay, K.; Hayelom, A. Removal of Methyl Orange from Aqueous Solutions Using Thermally Treated Egg Shell (Locally Available and Low Cost Biosorbent). Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. 2014, 8, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, S.; Chakraborty, J.; Parmar, V.S.; Bera, S.P.; Ganguli, N.; Konar, S. Channel-Assisted Proton Conduction Behavior in Hydroxyl-Rich Lanthanide-Based Magnetic Metal–Organic Frameworks. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 4956–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, K.K.; Charan, C.; Shahi, V.K.; Mitra, K.; Ray, B.; Rana, D.; Maiti, P. Functionalized poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanohybrid for superior fuel cell membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 481, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, M.; Meng, Y.; Hay, A. Synthesis and characterization of poly(arylene ether)s containing triphenylmethane moieties for proton exchange membrane. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosu, M.; Mitachi, K.; Yang, J.; Pershing, E.V.; Horowitz, B.D.; Wachter, E.A.; Lacey, J.W.; Ji, Y.; Rodrigues, D.J. Antibacterial Activity of Pharmaceutical-Grade Rose Bengal: An Application of a Synthetic Dye in Antibacterial Therapies. Molecules 2022, 27, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.J.; Litster, S. In Situ, ionic conductivity measurement of ionomer/binder-free Pt catalyst under fuel cell operating condition. ECS Trans. 2013, 58, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.; de Sá, A.I.; Teixeira, A.P.S.; Ortiz-Martínez, V.; Ortiz, A.; Ortiz, I.; Rangel, C. New modified Nafion-bisphosphonic acid composite membranes for enhanced proton conductivity and PEMFC performance. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 17562–17571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, Y.; Ekdunge, P.; Simonsson, D. Proton Conductivity of Nafion 117 as Measured by a Four-Electrode AC Impedance Method. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, M. An infrared study of water in perfluorosulfonate (Nafion) membranes. Can. J. Chem. 1980, 58, 1495–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostroverkh, A.; Johánek, V.; Dubau, M.; Kúš, P.; Khalakhan, I.; Šmíd, B.; Fiala, R.; Václavů, M.; Ostroverkh, Y.; Matolín, V. Optimization of Ionomer-Free Ultra-Low Loading Pt Catalyst for Anode/Cathode of PEMFC via Magnetron Sputtering. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 19344–19356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Zeng, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Li, S.; Guo, W.; Gao, Y.; Pan, M. Magnetron sputtering a high-performance catalyst for ultra-low-Pt loading PEMFCs. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 815, 152374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostroverkh, A.; Dubau, M.; Peter, K.; Haviar, S.; Václavů, M.; Šmíd, B.; Fiala, R.; Yakovlev, Y.; Ostroverkh, Y.; Johánek, V. Durable Ultra-Low-Platinum Ionomer-Free Anode Catalyst for Hydrogen Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 4641–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanifuji, N.; Shimizu, T.; Ida, K.; Nishio, K.; Tanaka, M.; Tsukaguchi, Y.; Tsubouchi, K.; Shimizu, A.; Hino, E.-i.; Date, Y.; et al. Assessment of Dye-Absorbed Eggshell Membrane Composites as Solid Polymer Electrolyte of Fuel Cells. Membranes 2023, 13, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010115
Tanifuji N, Shimizu T, Ida K, Nishio K, Tanaka M, Tsukaguchi Y, Tsubouchi K, Shimizu A, Hino E-i, Date Y, et al. Assessment of Dye-Absorbed Eggshell Membrane Composites as Solid Polymer Electrolyte of Fuel Cells. Membranes. 2023; 13(1):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010115
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanifuji, Naoki, Takeshi Shimizu, Kentaro Ida, Kosuke Nishio, Miki Tanaka, Yuta Tsukaguchi, Kentaro Tsubouchi, Akihiro Shimizu, Ei-ichi Hino, Yusuke Date, and et al. 2023. "Assessment of Dye-Absorbed Eggshell Membrane Composites as Solid Polymer Electrolyte of Fuel Cells" Membranes 13, no. 1: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010115
APA StyleTanifuji, N., Shimizu, T., Ida, K., Nishio, K., Tanaka, M., Tsukaguchi, Y., Tsubouchi, K., Shimizu, A., Hino, E. -i., Date, Y., Aoki, K., & Yoshikawa, H. (2023). Assessment of Dye-Absorbed Eggshell Membrane Composites as Solid Polymer Electrolyte of Fuel Cells. Membranes, 13(1), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010115