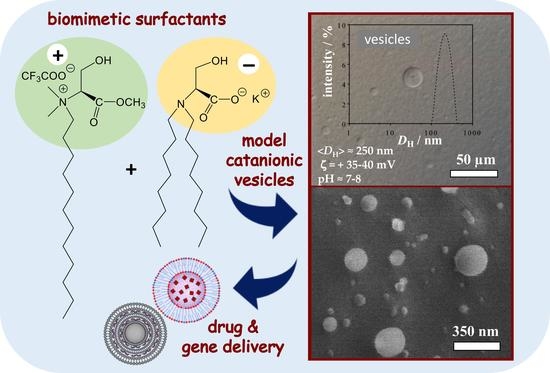
Model Catanionic Vesicles from Biomimetic Serine-Based Surfactants: Effect of the Combination of Chain Lengths on Vesicle Properties and Vesicle-to-Micelle Transition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Video-Enhanced Light Microscopy (VELM)
2.4. Cryo-Scanning Electron Microscopy (Cryo-SEM)
2.5. Dynamic (DLS) and Electrophoretic (ELS) Light Scattering
2.6. Surface Tension
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Behavior and Aggregate Structure for the Catanionic Mixtures
3.2. Vesicle Characterization: Size, Charge, and pH
3.3. Critical Aggregation Concentrations
3.4. Discussion
3.4.1. Vesicle Formation and Vesicle/Micelle Transition
3.4.2. Vesicle Stabilization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, Y.H.M.; Boxer, S.G. Model membrane systems and their applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2007, 11, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquardt, D.; Geier, B.; Pabst, G. Asymmetric Lipid Membranes: Towards More Realistic Model Systems. Membranes 2015, 5, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschi, S.; Ward, T.R.; Meier, W.P.; Mueller, D.J.; Fotiadis, D. Synthetic Biology: Bottom-Up Assembly of Molecular Systems. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 16294–16328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmsten, M. Soft drug delivery systems. Soft Matter 2006, 2, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohvo-Rekila, H.; Ramstedt, B.; Leppimaki, P.; Slotte, J.P. Cholesterol interactions with phospholipids in membranes. Prog. Lipid Res. 2002, 41, 66–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Honeywell-Nguyen, P.L.; Gooris, G.S.; Ponec, M. Structure of the skin barrier and its modulation by vesicular formulations. Prog. Lipid Res. 2003, 42, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, T.K.; Grinkova, Y.V.; Bayburt, T.H.; Denisov, I.G.; Zolnerciks, J.K.; Atkins, W.M.; Sligar, S.G. Reconstitution of Membrane Proteins in Phospholipid Bilayer Nanodiscs. In Methods in Enzymology; Liposomes, Pt F; Duzgunes, N., Ed.; Elsevier Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; Volume 464, pp. 211–231. [Google Scholar]
- Batrakova, E.V.; Kabanov, A.V. Pluronic block copolymers: Evolution of drug delivery concept from inert nanocarriers to biological response modifiers. J. Control. Release 2008, 130, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, E.F.; Regev, O.; Khan, A.; Lindman, B. Self-organization of double-chained and pseudodouble-chained surfactants: Counterion and geometry effects. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 100–102, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šegota, S.; Težak, D.u.i. Spontaneous formation of vesicles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 121, 51–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonietti, M.; Förster, S. Vesicles and Liposomes: A Self-Assembly Principle Beyond Lipids. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaler, E.; Murthy, A.; Rodriguez, B.; Zasadzinski, J. Spontaneous vesicle formation in aqueous mixtures of single-tailed surfactants. Science 1989, 245, 1371–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, E.F. Size and Stability of Catanionic Vesicles: Effects of Formation Path, Sonication, and Aging. Langmuir 2000, 16, 4798–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondre, C.; Caillet, C. Properties of the amphiphilic films in mixed cationic/anionic vesicles: A comprehensive view from a literature analysis. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 93, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Marques, E.F. Synergism and polymorphism in mixed surfactant systems. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 4, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, R.O.; Marques, E.F.; Gomes, P.; Falcao, S.; Soderman, O. Self-assembly in a catanionic mixture with an aminoacid-derived surfactant: From mixed micelles to spontaneous vesicles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 18158–18165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Bai, G.Y.; Marques, E.F.; Yan, H.K. Phase behavior and thermodynamics of a mixture of cationic gemini and anionic surfactant. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 5294–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.R.A.; Silva, B.F.B.; Marques, E.F. Chain length mismatch and packing effects on the thermotropic phase behavior of salt-free catanionic surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 405, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.F.B.; Marques, E.F.; Olsson, U. Aqueous phase behavior of salt-free catanionic surfactants: The influence of solubility mismatch on spontaneous curvature and balance of forces. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.F.B.; Marques, E.F.; Olsson, U.; Pons, R. Headgroup Effects on the Unusual Lamellar-Lamellar Coexistence and Vesicle-to-Micelle Transition of Salt-Free Catanionic Amphiphiles. Langmuir 2010, 26, 3058–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manghisi, N.; Leggio, C.; Jover, A.; Meijide, F.; Pavel, N.V.; Soto Tellini, V.H.; Vazquez Tato, J.; Agostino, R.G.; Galantini, L. Catanionic tubules with tunable charge. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2010, 49, 6604–6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Hoffmann, H. Self-assembled structures in excess and salt-free catanionic surfactant solutions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 9, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokela, P.; Jonsson, B.; Khan, A. Phase-equilibria of catanionic surfactant water-systems. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 3291–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaler, E.W.; Herrington, K.L.; Murthy, A.K.; Zasadzinski, J.A.N. Phase behavior and structures of mixtures of anionic and cationic surfactants. J. Phys. Chem. 1992, 96, 6698–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, E.F.; Regev, O.; Khan, A.; Miguel, M.D.; Lindman, B. Vesicle formation and general phase behavior in the catanionic mixture SDS-DDAB-water. The anionic-rich side. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 6746–6758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Dey, J. Interaction of sodium N-lauroylsarcosinate with N-alkylpyridinium chloride surfactants: Spontaneous formation of pH-responsive, stable vesicles in aqueous mixtures. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 358, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, P.; Funari, S.S.; La Mesa, C.; Mariani, P.; Ortore, M.G.; Sinibaldi, R.; Spinozzi, F. Multi-to Unilamellar Transitions in Catanionic Vesicles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 8056–8060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.G.; do Vale, M.L.; Marques, E.F. Size, charge, and stability of fully serine-based catanionic vesicles: Towards versatile biocompatible nanocarriers. Chemistry 2015, 21, 4092–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagnoli, S.; Alderete, L.S.; Luna, M.A.; Agostini, E.; Falcone, R.D.; Niebylski, A.M.; Correa, N.M. Catanionic nanocarriers as a potential vehicle for insulin delivery. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2020, 188, 110759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves Lopes, R.C.F.; Silvestre, O.F.; Faria, A.R.; do Vale, M.L.C.; Marques, E.F.; Nieder, J.B. Surface charge tunable catanionic vesicles based on serine-derived surfactants as efficient nanocarriers for the delivery of the anticancer drug doxorubicin. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 5932–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauroy, C.; Castagnos, P.; Orio, J.; Blache, M.-C.; Rico-Lattes, I.; Teissié, J.; Rols, M.-P.; Blanzat, M. Versatile Cellular Uptake Mediated by Catanionic Vesicles: Simultaneous Spontaneous Membrane Fusion and Endocytosis. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Ambade, B.; Ray, A. Stable Catanionic Vesicles as Drug Delivery Vehicle. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2013, 5, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Liu, C.; Lv, J.; kumar deb, D.; Qiao, W. Enhanced intercellular release of anticancer drug by using nano-sized catanionic vesicles of doxorubicin hydrochloride and gemini surfactants. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 259, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, V.V.; Nagarsenker, M.S. Catanionic systems in nanotherapeutics—Biophysical aspects and novel trends in drug delivery applications. J. Control. Release 2017, 266, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramer, T.; Dew, N.; Edsman, K. Pharmaceutical applications for catanionic mixtures. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 1319–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, R.S.; Lindman, B.; Miguel, M.G. DNA Interaction with Catanionic Vesicles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 12600–12607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.; Miguel Mda, G.; Lindman, B. DNA encapsulation by biocompatible catanionic vesicles. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2007, 312, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Chen, J.; Feng, L.; Dong, S.; Hao, J. Loading capacity and interaction of DNA binding on catanionic vesicles with different cationic surfactants. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 9143–9152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Bai, X.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, L. C12mimBr Ionic Liquid/SDS Vesicle Formation and Use As Template for the Synthesis of Hollow Silica Spheres. Langmuir 2010, 26, 11726–11731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentze, H.P.; Raghavan, S.R.; McKelvey, C.A.; Kaler, E.W. Silica hollow spheres by templating of catanionic vesicles. Langmuir 2003, 19, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.-H.; Yeh, L.-H.; Liao, P.-W.; Chou, T.-H. Characterization and in vitro biocompatibility of catanionic assemblies formed with oppositely charged dicetyl amphiphiles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 126, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, C.; Andreozzi, P.; La Mesa, C.; Risuleo, G. Biological activity of SDS-CTAB cat-anionic vesicles in cultured cells and assessment of their cytotoxicity ending in apoptosis. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 78, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachy, N.; Touraud, D.; Heilmann, J.; Kunz, W. Determining the cytotoxicity of catanionic surfactant mixtures on HeLa cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 70, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, R.O.; Marques, E.F.; Silva, S.G.; do Vale, M.L.; Gomes, P.; Araujo, M.J.; Rodriguez-Borges, J.E.; Infante, M.R.; Garcia, M.T.; Ribosa, I.; et al. Physicochemical and toxicological properties of novel amino acid-based amphiphiles and their spontaneously formed catanionic vesicles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 72, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, J.H.; Jan, M.S.; Chang, C.H.; Chiu, H.W.; Li, C.T. Cytotoxicity characterization of catanionic vesicles in RAW 264.7 murine macrophage-like cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2005, 41, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinazo, A.; Pons, R.; Marques, A.; Farfan, M.; da Silva, A.; Perez, L. Biocompatible Catanionic Vesicles from Arginine-Based Surfactants: A New Strategy to Tune the Antimicrobial Activity and Cytotoxicity of Vesicular Systems. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.S.; Pereira, C.; Borges, E.; do Vale, M.L.; Gomes, A.C.; Marques, E.F. Formation of catanionic vesicles by threonine-derived surfactants and gemini surfactants based on conventional or serine-derived headgroups: Designing versatile and cytocompatible nanocarriers. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 7099–7110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante, M.R.; Pérez, L.; Pinazo, A.; Clapés, P.; Morán, M.C.; Angelet, M.; García, M.T.; PilarVinardell, M. Amino Acid-Based Surfactants. C. R. Chimie 2004, 7, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consola, S.; Blanzat, M.; Perez, E.; Garrigues, J.C.; Bordat, P.; Rico-Lattes, I. Design of original bioactive formulations based on sugar-surfactant/non-steroidal anti-inflammatory catanionic self-assemblies: A new way of dermal drug delivery. Chem. A Eur. J. 2007, 13, 3039–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Gregorio, M.C.; Severoni, E.; Travaglini, L.; Gubitosi, M.; Sennato, S.; Mura, F.; Redondo-Gómez, C.; Jover, A.; Pavel, N.V.; Galantini, L. Bile acid derivative-based catanionic mixtures: Versatile tools for superficial charge modulation of supramolecular lamellae and nanotubes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 18957–18968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanzat, M.; Perez, E.; Rico-Lattes, I.; Prome, D.; Prome, J.C.; Lattes, A. New catanionic glycolipids. 1. Synthesis, characterization, and biological activity of double-chain and gemini catanionic analogues of galactosylceramide (gal beta(1)cer). Langmuir 1999, 15, 6163–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dew, N.; Bramer, T.; Edsman, K. Catanionic aggregates formed from drugs and lauric or capric acids enable prolonged release from gels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 323, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, M.C.; Pinazo, A.; Perez, L.; Clapes, P.; Angelet, M.; Garcia, M.T.; Vinardell, M.P.; Infante, M.R. “Green” amino acid-based surfactants. Green Chem. 2004, 6, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, L.; Pinazo, A.; Pons, R.; Infante, M.R. Gemini surfactants from natural amino acids. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2014, 205, 134–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.G.; Alves, C.; Cardoso, A.M.S.; Jurado, A.S.; de Lima, M.C.P.; Vale, M.L.C.; Marques, E.F. Synthesis of Gemini Surfactants and Evaluation of Their Interfacial and Cytotoxic Properties: Exploring the Multifunctionality of Serine as Headgroup. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 1758–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.G.; Fernandes, R.F.; Marques, E.F.; do Vale, M.L.C. Serine-Based Bis-quat Gemini Surfactants: Synthesis and Micellization Properties. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, T.; Sakato, A.; Tsuchiya, K.; Ohkubo, T.; Sakai, H.; Abe, M.; Esumi, K. Adsorption and Aggregation Properties of Amino Acid-Based N-alkyl Cysteine Monomeric and N,N-dialkyl Cystine Gemini Surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 308, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.S.; Lo, M.; Araújo, M.J.; Marques, E.F. Temperature-responsive self-assembled nanostructures from lysine-based surfactants with high chain length asymmetry: From tubules and helical ribbons to micelles and vesicles. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 3700–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.G.; Rodriguez-Borges, J.E.; Marques, E.F.; do Vale, M.L.C. Towards novel efficient monomeric surfactants based on serine, tyrosine and 4-hydroxyproline: Synthesis and micellization properties. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 4156–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.G.; Oliveira, I.S.; do Vale, M.L.C.; Marques, E.F. Serine-based gemini surfactants with different spacer linkages: From self-assembly to DNA compaction. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 9352–9361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and zeta potential—What they are and what they are not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, P.A.; Rana, S.; Verma, G. Making Sense of Brownian Motion: Colloid Characterization by Dynamic Light Scattering. Langmuir 2015, 31, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safran, S.A.; Pincus, P.; Andelman, D. Theory of spontaneous vesicle formation in surfactant mixtures. Science 1990, 248, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villeneuve, M.; Kaneshina, S.; Imae, T.; Aratono, M. Vesicle-micelle equilibrium of anionic and cationic surfactant mixture studied by surface tension. Langmuir 1999, 15, 2029–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillo, I.; Penfold, J.; Tucker, I.; Cousin, F. Spontaneous Formation of Nanovesicles in Mixtures of Nonionic and Dialkyl Chain Cationic Surfactants Studied by Surface Tension and SANS. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3932–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israelachvili, J.N.; Mitchell, D.J.; Ninham, B.W. Theory of self-assembly of hydrocarbon amphiphiles into micelles and bilayers. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1976, 72, 1525–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington, K.L.; Kaler, E.W.; Miller, D.D.; Zasadzinski, J.A.; Chiruvolu, S. Phase-Behavior Of Aqueous Mixtures Of Dodecyltrimethylammonium Bromide (DTAB) And Sodium Dodecyl-Sulfate (SDS). J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 13792–13802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, E.F.; Brito, R.O.; Silva, S.G.; Rodriguez-Borges, J.E.; do Vale, M.L.; Gomes, P.; Araujo, M.J.; Soderman, O. Spontaneous vesicle formation in catanionic mixtures of amino acid-based surfactants: Chain length symmetry effects. Langmuir 2008, 24, 11009–11017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.T.; Coldren, B.; Zasadzinski, J.A.; Iampietro, D.J.; Kaler, E.W. The origins of stability of spontaneous vesicles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasic, D.D.; Joannic, R.; Keller, B.C.; Frederik, P.M.; Auvray, L. Spontaneous Vesiculation. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 89–90, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| System | xmSer | pH | cac/mmol·dm−3 | γcac/mN·m−1 | as/nm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8-8Ser | 0 | 12.0 (1) | 0.25 ± 0.04 | 23.6 | 1.2 ± 0.1 (ns = 1) 0.6 ± 0.1 (ns = 2) |
| 12Ser | 1 | 5.3 | 3.0 ± 0.1 (2) | 30.2 | 0.56 ± 0.05 |
| 12Ser/8-8Ser | 0.50 | 9.8 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 25.2 | - |
| 12Ser/8-8Ser | 0.80 | 7.0 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 27.1 | - |
| 10-10Ser | 0 | 12.0 (1) | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 23.2 | 1.2 ± 0.1 (ns = 1) 0.6 ± 0.1 (ns = 2) |
| 14Ser | 1 | 4.6 | 1.2 ± 0.1 (2) | 32.9 | 0.55 ± 0.06 |
| 14Ser/10-10Ser | 0.50 | 9.2 | 0.20 ± 0.04 | 32.2 | - |
| 14Ser/10-10Ser | 0.80 | 5.8 | 0.49 ± 0.02 | 32.5 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, I.S.; Silva, S.G.; do Vale, M.L.; Marques, E.F. Model Catanionic Vesicles from Biomimetic Serine-Based Surfactants: Effect of the Combination of Chain Lengths on Vesicle Properties and Vesicle-to-Micelle Transition. Membranes 2023, 13, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020178
Oliveira IS, Silva SG, do Vale ML, Marques EF. Model Catanionic Vesicles from Biomimetic Serine-Based Surfactants: Effect of the Combination of Chain Lengths on Vesicle Properties and Vesicle-to-Micelle Transition. Membranes. 2023; 13(2):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020178
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Isabel S., Sandra G. Silva, Maria Luísa do Vale, and Eduardo F. Marques. 2023. "Model Catanionic Vesicles from Biomimetic Serine-Based Surfactants: Effect of the Combination of Chain Lengths on Vesicle Properties and Vesicle-to-Micelle Transition" Membranes 13, no. 2: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020178
APA StyleOliveira, I. S., Silva, S. G., do Vale, M. L., & Marques, E. F. (2023). Model Catanionic Vesicles from Biomimetic Serine-Based Surfactants: Effect of the Combination of Chain Lengths on Vesicle Properties and Vesicle-to-Micelle Transition. Membranes, 13(2), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020178