Efficient Recovery of Organic Matter from Municipal Wastewater by a High-Rate Membrane Bioreactor Equipped with Flat-Sheet Ceramic Membranes
Abstract
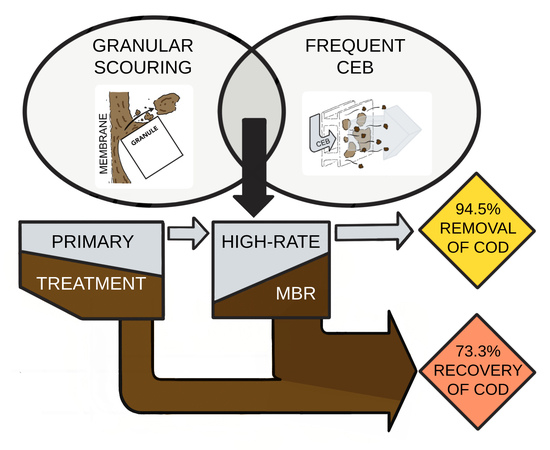
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Experimental Conditions
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Assessments of Membrane Fouling
2.5. Fractionation of Concentrate and Bioflocculation Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effectiveness of the Combination of Granular Scouring and CEB with Various Concentrations of NaClO (Run 1)
3.1.1. Fouling Evolution in Run 1
3.1.2. Analysis of Fouling Resistance in Run 1
3.1.3. Bioflocculation in Run 1
3.2. Longer Operation of the HR-MBR (Run 2)
3.2.1. Fouling Evolution in Run 2
3.2.2. Carbon Recovery and Effluent Quality Achieved by the HR-MBR
3.2.3. Comparison with Other Reported HR-MBRs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maktabifard, M.; Zaborowska, E.; Makinia, J. Achieving Energy Neutrality in Wastewater Treatment Plants through Energy Savings and Enhancing Renewable Energy Production. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio Technol. 2018, 17, 655–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jimenez, J.; Miller, M.; Bott, C.; Murthy, S.; De Clippeleir, H.; Wett, B. High-Rate Activated Sludge System for Carbon Management—Evaluation of Crucial Process Mechanisms and Design Parameters. Water Res. 2015, 87, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Lu, D.; Phua, K.; Yan, W.; Le, C.; Tao, G.; Zhou, Y. Organics Transformation and Energy Production Potential in a High Rate A- Stage System: A Demo-Scale Study. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 295, 122300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho, I.; Lopez-Palau, S.; Arespacochaga, N.; Cortina, J.L. New Concepts on Carbon Redirection in Wastewater Treatment Plants: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, H.; Batstone, D.J.; Mouiche, M.; Hu, S.; Keller, J. Nutrient Removal and Energy Recovery from High-Rate Activated Sludge Processes—Impact of Sludge Age. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanyeti, I.; Temmink, H.; Remy, M.; Zwijnenburg, A. Feasibility of Bioflocculation in a High-Loaded Membrane Bioreactor for Improved Energy Recovery from Sewage. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabia, G.; Ferraris, M.; Spagni, A. Effect of Solid Retention Time on Sludge Filterability and Biomass Activity: Long-Term Experiment on a Pilot-Scale Membrane Bioreactor Treating Municipal Wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 221, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, L.; Temmink, H.; Zwijnenburg, A.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M. High Loaded MBRs for Organic Matter Recovery Fromsewage: Effect of Solids Retention Time on Bioflocculation and on the Role of Extracellular Polymers. Water Res. 2014, 56, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, L.H.; Temmink, H.; Zeeman, G.; Buisman, C.J.N. Bioflocculation of Grey Water for Improved Energy Recovery within Decentralized Sanitation Concepts. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9065–9070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Xu, X.; Yang, F. High-Rate Contact Stabilization Process-Coupled Membrane Bioreactor for Maximal Recovery of Organics from Municipal Wastewater. Water 2018, 10, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimura, K.; Uchida, H. Intensive Membrane Cleaning for MBRs Equipped with Flat-Sheet Ceramic Membranes: Controlling Negative Effects of Chemical Reagents Used for Membrane Cleaning. Water Res. 2019, 150, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninomiya, Y.; Kimura, K.; Sato, T.; Kakuda, T.; Kaneda, M.; Hafuka, A.; Tsuchiya, T. High-Flux Operation of MBRs with Ceramic Flat-Sheet Membranes Made Possible by Intensive Membrane Cleaning: Tests with Real Domestic Wastewater under Low-Temperature Conditions. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Kimura, K.; Wang, Q.; Han, X. Membrane Cleaning in Membrane Bioreactors: A Review. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 468, 276–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apha, A. WEF Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; Baird, R.B., Eaton, A.D., Rice, E.W., Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-087553-287-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, K.; Honoki, D.; Sato, T. Effective Physical Cleaning and Adequate Membrane Flux for Direct Membrane Filtration (DMF) of Municipal Wastewater: Up-Concentration of Organic Matter for Efficient Energy Recovery. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 181, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweity, A.; Ying, W.; Ali-Shtayeh, M.S.; Yang, F.; Bick, A.; Oron, G.; Herzberg, M. Relation between EPS Adherence, Viscoelastic Properties, and MBR Operation: Biofouling Study with QCM-D. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6430–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.B.; Zhang, Z. Ceramic Membrane Technology for Water and Wastewater Treatment: A Critical Review of Performance, Full-Scale Applications, Membrane Fouling and Prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K.; Itokawa, H.; Hashimoto, T. Demonstration of Energy-Saving Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, S.J. The Status of Industrial and Municipal Effluent Treatment with Membrane Bioreactor Technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 305, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Cheng, F.; Liu, Y. Ceramic Membrane Fouling by Dissolved Organic Matter Generated during On-Line Chemical Cleaning with Ozone in MBR. Water Res. 2018, 146, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, L.; Temmink, H.; Zwijnenburg, A.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M. Effect of Dissolved Oxygen Concentration on the Bioflocculation Process in High Loaded MBRs. Water Res. 2014, 66, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Hou, B.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Song, L.; Zhang, H. Effects of NaClO Shock on MBR Performance under Continuous Operating Conditions. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.L.; Niessen, W.; Sørensen, N.B.; Hansen, S.H.; Jørgensen, M.K.; Nielsen, P.H. Sludge Fractionation as a Method to Study and Predict Fouling in MBR Systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 194, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuda, T.; Iwasaki, H.; Huang, X.; Kimura, K. Intensive Monitoring of Sludge Filterability of a Pilot-Scale Membrane Bioreactor Treating Municipal Wastewater for Better Interpretation of Fouling. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuda, T.; Iwasaki, H.; Kimura, K. Fouling Potential of Lipopolysaccharides Released at Low Temperatures in MBRs. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, K.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Huang, X. Current State and Challenges of Full-Scale Membrane Bioreactor Applications: A Critical Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wett, B.; Aichinger, P.; Hell, M.; Andersen, M.; Wellym, L.; Fukuzaki, Y.; Cao, Y.S.; Tao, G.; Jimenez, J.; Takacs, I.; et al. Operational and Structural A-Stage Improvements for High-Rate Carbon Removal. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1983–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerburg, F.A.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Roume, H.; Seuntjens, D.; Pieper, D.H.; Jauregui, R.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Boon, N. High-Rate Activated Sludge Communities Have a Distinctly Different Structure Compared to Low-Rate Sludge Communities, and Are Less Sensitive towards Environmental and Operational Variables. Water Res. 2016, 100, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hube, S.; Eskafi, M.; Hrafnkelsdóttir, K.F.; Bjarnadóttir, B.; Bjarnadóttir, M.Á.; Axelsdóttir, S.; Wu, B. Direct Membrane Filtration for Wastewater Treatment and Resource Recovery: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emaminejad, S.A.; Avval, S.S.; Bonakdarpour, B. Gaining Deeper Insights into the Bioflocculation Process Occurring in a High Loaded Membrane Bioreactor Used for the Treatment of Synthetic Greywater. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, L.; Lu, W. High Loaded Bioflocculation Membrane Reactor of Novel Structure for Organic Matter Recovery from Sewage: Effect of Temperature on Bioflocculation and Membrane Fouling. Water 2020, 12, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Reference | Membrane Type | Feedwater | Volume (L) | SRT (days)/HRT (hours) | MLVSS (mg/L) | COD Removal | Net Flux (Gross Flux) a (LMH) | Fouling Rate (kPa/d) | Carbon Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dai et al., 2018 [10] | Hollow-fiber polysulfone of 0.1 μm pores, 0.34 m2 (Dalian, China) | Screened and degritted WWTP influent with 441 ± 33 mg-COD/L | 5.0 | 0.5/1.2 | 612 ± 122 | Around 80% | 11.0 (11.0) | 4.5 b | 47.9% |
| Emaminejad et al., 2019 [30] | Flat sheet chlorinated polyethylene of 0.4 μm pores, 0.11 m2 (Kubota Co., Osaka, Japan) | Synthetic greywater with 387 ± 33 mg-COD/L | 5.5 | 0.5/1.5 | 1297 ± 31 | 87% | 25.0 (33.3) | N/A | 54.3% |
| Wan et al., 2020 [31] | Hollow-fiber ultrafiltration polyvinylidene fluoride of 0.03 μm pores, 0.28 m2 (Tianjin, China) | Screened and degritted WWTP influent with 247 ± 21 mg-COD/L | 1.7 | 0.6/1.0 | N/A | 86–89% | 4.8 (6.0) | 2.8–11.5 b | 65.1–67.1% |
| This Study | Flat sheet alumina ceramic of 0.1 μm pores, 0.2 m2 (Meidensha, Tokyo, Japan) | Effluent of the primary sedimentation basin with 209 ± 46 mg-COD/L | 8.4 | 0.5/1.6 | 404 ± 108 | 94% c | 20.0 (25.0) | 1.3 | 58.9% (73.3% d) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rocco, M.J.; Hafuka, A.; Tsuchiya, T.; Kimura, K. Efficient Recovery of Organic Matter from Municipal Wastewater by a High-Rate Membrane Bioreactor Equipped with Flat-Sheet Ceramic Membranes. Membranes 2023, 13, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030300
Rocco MJ, Hafuka A, Tsuchiya T, Kimura K. Efficient Recovery of Organic Matter from Municipal Wastewater by a High-Rate Membrane Bioreactor Equipped with Flat-Sheet Ceramic Membranes. Membranes. 2023; 13(3):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030300
Chicago/Turabian StyleRocco, Michael Joseph, Akira Hafuka, Toru Tsuchiya, and Katsuki Kimura. 2023. "Efficient Recovery of Organic Matter from Municipal Wastewater by a High-Rate Membrane Bioreactor Equipped with Flat-Sheet Ceramic Membranes" Membranes 13, no. 3: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030300
APA StyleRocco, M. J., Hafuka, A., Tsuchiya, T., & Kimura, K. (2023). Efficient Recovery of Organic Matter from Municipal Wastewater by a High-Rate Membrane Bioreactor Equipped with Flat-Sheet Ceramic Membranes. Membranes, 13(3), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030300