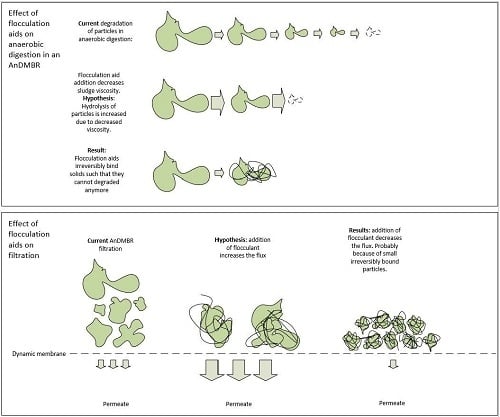
Impact of Coagulant and Flocculant Addition to an Anaerobic Dynamic Membrane Bioreactor (AnDMBR) Treating Waste-Activated Sludge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. AnDMBR Setup and Operation
2.2. FA Selection and Addition
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Performance of the Conventional Sludge Digester and the AnDMBR (Period 1 and 2)
3.2. FA Selection
3.3. Performance of the AnMBR with FAs dosing (Period 3)
4. Discussion
4.1. Digestion Performance in Period 2
4.2. Digester Performance in Period 3
4.3. Filtration Performance and Nutrients in Period 2 and 3
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Lier, J.B. High-rate anaerobic wastewater treatment: Diversifying from end-of-the-pipe treatment to resource-oriented conversion techniques. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Sarkar, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Choi, H.; Bhattacharjee, C. Remediation of antiseptic components in wastewater by photocatalysis using TiO2 nanoparticles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 3012–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Chakraborty, S.; Roy, M. Arsenic Separation by a Membrane-Integrated Hybrid Treatment System: Modeling, Simulation, and Techno-Economic Evaluation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzeminski, P.; Leverette, L.; Malamis, S.; Katsou, E. Membrane bioreactors—A review on recent developments in energy reduction, fouling control, novel configurations, LCA and market prospects. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 527, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, H.; Azócar, L.; Torres, A.; Lopes, S.I.C.; Jeison, D. Use of flocculants for increasing permeate flux in anaerobic membrane bioreactors. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 2237–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooijman, G.; de Kreuk, M.; van Lier, J.B. Influence of chemically enhanced primary treatment on anaerobic digestion and dewaterability of waste sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 2017. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Dartois, A.; Singh, J.; Kaur, L.; Singh, H. Influence of guar gum on the in vitro starch digestibility-rheological and Microstructural characteristics. Food Biophys. 2010, 5, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.A.; Ferguson, J.F. Solubilization of particulate organic carbon during the acid phase of anaerobic digestion. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1981, 53, 352–366. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, C.P.; Lee, D.J.; Chang, B.V.; You, C.H.; Liao, C.S.; Tay, J.H. Anaerobic digestion of polyelectrolyte flocculated waste activated sludge. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Song, Z.; Wen, X.; Huang, X. Using polyaluminum chloride and polyacrylamide to control membrane fouling in a cross-flow anaerobic membrane bioreactor. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 479, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meabe, E.; Déléris, S.; Soroa, S.; Sancho, L. Performance of anaerobic membrane bioreactor for sewage sludge treatment: Mesophilic and thermophilic processes. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 446, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeison, D.; Días, I.; van Lier, J.B. Anaerobic membrane bioreactors: Are membranes really necessary? Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 11, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.; Arnot, T.C.; Mattia, D. A review of reverse osmosis membrane materials for desalination—Development to date and future potential. J. Memb. Sci. 2011, 370, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersahin, M.E.; Ozgun, H.; Tao, Y.; van Lier, J.B. Applicability of dynamic membrane technology in anaerobic membrane bioreactors. Water Res. 2014, 48, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, J.T.; Goodman, G.L.; Pariroo, A.; Huang, J.; Goodman, L. The Blinding of Sludges during Filtration The blinding of sludges. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1988, 60, 206–214. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. Available online: https://www.mwa.co.th/download/file_upload/SMWW_1000-3000.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2017).
- Brockmann, M.; Seyfried, C.F. Sludge activity and cross-flow microfiltration—A non-beneficial relationship. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 34, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, K.H.; Lee, C.H. Membrane fouling mechanisms in the membrane-coupled anaerobic bioreactor. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghyoot, W.R.; Verstraete, W.H. Coupling Membrane Filtration to Anaerobic Primary Sludge Digestion. Environ. Technol. 1997, 18, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghyoot, W.; Verstreate, W. Anaerobic digestion of primary sludge from chemical pre-precipitation. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, R.; Masse, D.I.; Singh, G. A critical review on inhibition of anaerobic digestion process by excess ammonia. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, E.; Almirall, M.; Mtnez-Almela, J.; Palatsi, J.; Flotats, X. Feasibility study of the anaerobic digestion of dewatered pig slurry by means of polyacrylamide. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huyskens, C.; de Wever, H.; Fovet, Y.; Wegmann, U.; Diels, L.; Lenaerts, S. Screening of novel MBR fouling reducers: Benchmarking with known fouling reducers and evaluation of their mechanism of action. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 95, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Liao, B.; Chen, J.; Gao, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Lu, X. New insights into membrane fouling in a submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor based on characterization of cake sludge and bulk sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2373–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmitwalli, T.A.; Soellner, J.; de Keizer, A.; Bruning, H.; Zeeman, G.; Lettinga, G. Biodegradability and change of physical characteristics of particles during anaerobic digestion of domestic sewage. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, R. The role of polymer adsorption kinetics in flocculation. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 146, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.L.; Raudenbush, D.L.; Dentel, S.K. Aerobic and anaerobic biodegradability of a flocculant polymer. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hwang, B.K.; Lee, W.N.; Park, P.K.; Lee, C.H.; Chang, I.S. Effect of membrane fouling reducer on cake structure and membrane permeability in membrane bioreactor. J. Memb. Sci. 2007, 288, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Period | Period | Reactor Operation | Substrate | Hydraulic Retention Time (Days) | Solids Retention Time (Days) | Flocculation Aid Addition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period 1 | 0–86 | Conventional anaerobic digester | WAS | 24 | 24 | – |
| Period 2 | 86–303 | AnDMBR | WAS | 18 | 24 | – |
| Period 3 | 303–386 | AnDMBR | WAS | 18 | 24 | Calfloc 1502 + FeCl3 |
| Parameter | Unit | Average Value |
|---|---|---|
| Total Solids | g·L−1 | 48.2 ± 1.7 |
| Total Volatile Solids | g·L−1 | 34.9 ± 1.0 |
| Total Suspended Solids | g·L−1 | 45.6 ± 1.6 |
| Volatile Suspended Solid | g·L−1 | 33.9 ± 1.0 |
| Total chemical oxygen demand | g·L−1 | 50.1 ± 3.2 |
| Total Nitrogen | mg·L−1 | 2490 ± 0.515 |
| Total Phosphorus | mg·L−1 | 2435 ± 0.149 |
| Product | Characteristics | Charge |
|---|---|---|
| Calfloc L1408 | Branched, cationic, emulsion | Medium |
| Calfloc L111 | Branched, cationic, emulsion | Medium |
| Calfloc L1401 LMW | N.A. | Medium/high |
| Calfloc P1502 | Linear, cationic, powder | High |
| Calfloc LS1423 | Polyamine | Medium |
| Nalco 71305 | Acryl-amide based | High |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kooijman, G.; Lopes, W.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, H.; De Kreuk, M.; Spanjers, H.; Van Lier, J. Impact of Coagulant and Flocculant Addition to an Anaerobic Dynamic Membrane Bioreactor (AnDMBR) Treating Waste-Activated Sludge. Membranes 2017, 7, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7020018
Kooijman G, Lopes W, Zhou Z, Guo H, De Kreuk M, Spanjers H, Van Lier J. Impact of Coagulant and Flocculant Addition to an Anaerobic Dynamic Membrane Bioreactor (AnDMBR) Treating Waste-Activated Sludge. Membranes. 2017; 7(2):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleKooijman, Guido, Wilton Lopes, Zhongbo Zhou, Hongxiao Guo, Merle De Kreuk, Henri Spanjers, and Jules Van Lier. 2017. "Impact of Coagulant and Flocculant Addition to an Anaerobic Dynamic Membrane Bioreactor (AnDMBR) Treating Waste-Activated Sludge" Membranes 7, no. 2: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7020018
APA StyleKooijman, G., Lopes, W., Zhou, Z., Guo, H., De Kreuk, M., Spanjers, H., & Van Lier, J. (2017). Impact of Coagulant and Flocculant Addition to an Anaerobic Dynamic Membrane Bioreactor (AnDMBR) Treating Waste-Activated Sludge. Membranes, 7(2), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7020018