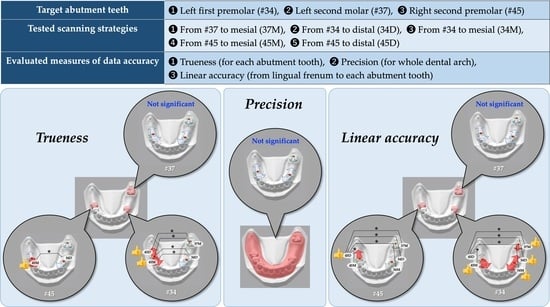
Effect of Scanning Origin Location on Data Accuracy of Abutment Teeth Region in Digital Impression Acquired Using Intraoral Scanner for Removable Partial Denture: A Preliminary In Vitro Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reference Model
2.2. Digital Data Acquired Using a High-Accuracy Industrial Scanner (Reference Data)
2.3. Scanning Strategies for Digital Data Acquisition Using an Intraoral Scanner (IOS Data)
2.4. General Trueness (TG), Local Trueness (TL), and Precision
2.5. Linear Accuracy
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Virard, F.; Venet, L.; Richert, R.; Pfeffer, D.; Viguié, G.; Bienfait, A.; Farges, J.C.; Ducret, M. Manufacturing of an immediate removable partial denture with an intraoral scanner and CAD-CAM technology: A case report. BMC Oral Health 2018, 18, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, H.; Taniguchi, A.; Tanaka, S.; Baba, K. Novel fully digital workflow for removable partial denture fabrication. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2020, 64, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fueki, K.; Inamochi, Y.; Wada, J.; Arai, Y.; Takaichi, A.; Murakami, N.; Ueno, T.; Wakabayashi, N. A systematic review of digital removable partial dentures. Part I: Clinical evidence, digital impression, and maxillomandibular relationship record. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2020, 66, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, A.B.; Evans, J.L.; Robb, N.D. A technical and clinical digital approach to the altered cast technique with an intraoral scanner and polyvinyl siloxane impression material. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayama, H.; Fueki, K.; Wadachi, J.; Wakabayashi, N. Trueness and precision of digital impressions obtained using an intraoral scanner with different head size in the partially edentulous mandible. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2018, 62, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Amelya, A.; Shin, Y.; Shim, J.S. Accuracy of intraoral digital impressions using an artificial landmark. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, T.; Tasaka, A.; Wadachi, J.; Yamashita, S. A new proposal for improving the accuracy of intraoral scanning for partially edentulous residual ridge. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoenix, R.D.; Cagna, D.R.; DeFreest, C.F. Stewart’s Clinical Removable Partial Prosthodontics, 4th ed.; Quintessence Publishing Co., Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA, 2008; p. 490. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Yun, J.H.; Han, J.S.; Yeo, I.L.; Yoon, H.I. Repeatability of Intraoral Scanners for Complete Arch Scan of Partially Edentulous Dentitions: An In Vitro Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diker, B.; Tak, Ö. Accuracy of Digital Impressions Obtained Using Six Intraoral Scanners in Partially Edentulous Dentitions and the Effect of Scanning Sequence. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2021, 34, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO/DIS 5725-1; Accuracy (Trueness and Precision) of Measurement Methods and Results—Part 1: General Principles and Definitions. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/69418.html (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Andriessen, F.S.; Rijkens, D.R.; van der Meer, W.J.; Wismeijer, D.W. Applicability and accuracy of an intraoral scanner for scanning multiple implants in edentulous mandibles: A pilot study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 111, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.C.; Park, J.M.; Moon, H.S. Effects of Scanning Strategy and Scanner Type on the Accuracy of Intraoral Scans: A New Approach for Assessing the Accuracy of Scanned Data. J. Prosthodont. 2020, 29, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, Z.; Simon, B.; Mennito, A.; Evans, Z.; Renne, W.; Vág, J. Comparing the trueness of seven intraoral scanners and a physical impression on dentate human maxilla by a novel method. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakamoto, K.; Wada, J.; Arai, Y.; Hayama, H.; Ishioka, Y.; Kim, E.; Kazama, R.; Toyoshima, Y.; Wakabayashi, N. Effect of abutment tooth location on the accuracy of digital impressions obtained using an intraoral scanner for removable partial dentures. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2022. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Dold, P.; Bone, M.C.; Flohr, M.; Preuss, R.; Joyce, T.J.; Deehan, D.; Holland, J. Validation of an optical system to measure acetabular shell deformation in cadavers. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2014, 228, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthardt, R.G.; Koch, R.; Rudolph, H.; Walter, M.H. Qualitative computer aided evaluation of dental impressions in vivo. Dent. Mater. 2006, 22, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.G.; Lee, K.M. Comparison of the accuracy of intraoral scans between complete-arch scan and quadrant scan. Prog. Orthod. 2020, 21, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, K.; Lee, K.B. Effect of Tooth Types on the Accuracy of Dental 3D Scanners: An In Vitro Study. Materials 2020, 13, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, N.; Abbasi, M.S.; Haider, S.; Ahmed, N.; Habib, S.R.; Altamash, S.; Zafar, M.S.; Alam, M.K. Fit Accuracy of Removable Partial Denture Frameworks Fabricated with CAD/CAM, Rapid Prototyping, and Conventional Techniques: A Systematic Review. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 3194433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Cho, Y.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Chang, M. Full-arch accuracy of five intraoral scanners: In vivo analysis of trueness and precision. Korean J. Orthod. 2021, 51, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinak, C.F.; Draughn, R.A. Linear dimensional changes in addition curing silicone impression materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1982, 47, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, L.; Meiga, S.; Brigagão, V.; Street, A. Impact of different scanning strategies on the accuracy of two current intraoral scanning systems in complete-arch impressions: An in vitro study. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2019, 22, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stefanelli, L.V.; Franchina, A.; Pranno, A.; Pellegrino, G.; Ferri, A.; Pranno, N.; Di Carlo, S.; De Angelis, F. Use of Intraoral Scanners for Full Dental Arches: Could Different Strategies or Overlapping Software Affect Accuracy? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, A.; Chen, Y.W.; Hayashi, J.; Sadr, A. Accuracy of CAD/CAM Digital Impressions with Different Intraoral Scanner Parameters. Sensors 2020, 20, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giménez, B.; Özcan, M.; Martínez-Rus, F.; Pradíes, G. Accuracy of a digital impression system based on active wavefront sampling technology for implants considering operator experience, implant angulation, and depth. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, e54–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Variable | TG | TL | Linear Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scanning strategy | <0.001 * | 0.032 * | <0.001 * |
| Target abutment tooth | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, E.-Y.; Wada, J.; Sakamoto, K.; Ishioka, Y.; Arai, Y.; Murakami, N.; Yamazaki, T.; Hayama, H.; Utsumi, M.; Inukai, S.; et al. Effect of Scanning Origin Location on Data Accuracy of Abutment Teeth Region in Digital Impression Acquired Using Intraoral Scanner for Removable Partial Denture: A Preliminary In Vitro Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7392. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247392
Kim E-Y, Wada J, Sakamoto K, Ishioka Y, Arai Y, Murakami N, Yamazaki T, Hayama H, Utsumi M, Inukai S, et al. Effect of Scanning Origin Location on Data Accuracy of Abutment Teeth Region in Digital Impression Acquired Using Intraoral Scanner for Removable Partial Denture: A Preliminary In Vitro Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(24):7392. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247392
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Eung-Yeol, Junichiro Wada, Kazuki Sakamoto, Yurika Ishioka, Yuki Arai, Natsuko Murakami, Toshiki Yamazaki, Hironari Hayama, Miona Utsumi, Shusuke Inukai, and et al. 2022. "Effect of Scanning Origin Location on Data Accuracy of Abutment Teeth Region in Digital Impression Acquired Using Intraoral Scanner for Removable Partial Denture: A Preliminary In Vitro Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 24: 7392. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247392
APA StyleKim, E. -Y., Wada, J., Sakamoto, K., Ishioka, Y., Arai, Y., Murakami, N., Yamazaki, T., Hayama, H., Utsumi, M., Inukai, S., & Wakabayashi, N. (2022). Effect of Scanning Origin Location on Data Accuracy of Abutment Teeth Region in Digital Impression Acquired Using Intraoral Scanner for Removable Partial Denture: A Preliminary In Vitro Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(24), 7392. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247392