The Efficacy and Safety of Single-Strain Probiotic Formulations Containing Bifidobacterium lactis or Bacillus coagulans in Adult Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome—A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Three-Arm Interventional Trial
Abstract
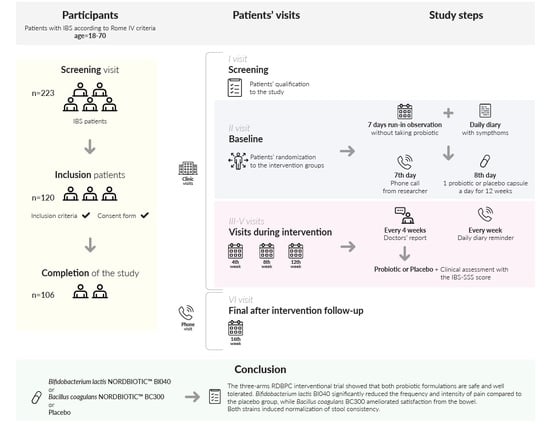
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.1.1. Patient Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.1.2. Intervention
2.1.3. The Study Protocol
2.1.4. Outcome Definitions
2.2. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. The Effect of Probiotic Supplementation on the IBS-SSS Score
3.3. The Effect of Probiotic Intervention on Clinical Improvement
3.4. The Effect of Intervention on Secondary Outcomes
3.5. Safety and Adverse Events
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ford, A.C.; Lacy, B.E.; Talley, N.J. Irritable bowel syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2566–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Canavan, C.; West, J.; Card, T. The epidemiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 6, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sperber, A.D.; Bangdiwala, S.I.; Drossman, D.A.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Imren, M.; Tack, J.; Whitehead, W.E.; Dumitrascu, D.L.; Fang, X.; Fukudo, S.; et al. Worldwide prevalence and burden of functional gastrointestinal disorders, results of Rome Foundation global study. Gastroenterology 2020, 160, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivinus-Nébot, M.; Frin-Mathy, G.; Bzioueche, H.; Dainese, R.; Bernard, G.; Anty, R.; Filippi, J.; Saint-Paul, M.C.; Tulic, M.K.; Verhasselt, V.; et al. Functional bowel symptoms in quiescent inflammatory bowel diseases: Role of epithelial barrier disruption and low-grade inflammation. Gut 2014, 63, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moloney, R.D.; Johnson, A.C.; O’Mahony, S.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Cryan, J.F. Stress and the microbiota-gut-brain axis in visceral pain: Relevance to irritable bowel syndrome. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2016, 22, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzydło-Radomańska, B.; Cukrowska, B. How to recognize and treat small intestinal bacterial overgrowth? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, B.; Patel, D.; Shah, H.; Hanna, K.S.; Kaur, H.; Alazzeh, M.S.; Thandavaram, A.; Channar, A.; Purohit, A.; Venugopal, S. The Role of gut-microbiota in the pathophysiology and therapy of irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review. Cureus 2022, 14, e28064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, A.; Baker, F.A.; Mahamid, M.; Sbeit, W.; Khoury, T. The evolving role of gut microbiota in the management of irritable bowel syndrome: An overview of the current knowledge. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll, I.M.; Ringel-Kulka, T.; Siddle, J.P.; Ringel, Y. Alterations in composition and diversity of the intestinal microbiota in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerckhoffs, A.P.; Samsom, M.; van der Rest, M.E.; de Vogel, J.; Knol, J.; Ben-Amor, K.; Akkermans, L.M.A. Lower bifidobacteria counts in both duodenal mucosa-associated and fecal microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 2887–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.N.; Wu, H.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Shen, X.Z.; Liu, T. Altered molecular signature of intestinal microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome patients compared with healthy controls: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Liang, L.; Deng, H.; Guo, J.; Shu, H.; Zhang, L. Efficacy and safety of probiotics in irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ford, A.C.; Harris, L.A.; Lacy, B.E.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Moayyedi, P. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The efficacy of prebiotics, probiotics, synbiotics and antibiotics in irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 1044–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asha, M.Z.; Khalil, S.F.H. Efficacy and safety of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2020, 20, e13–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skrzydło-Radomańska, B.; Prozorow-Król, B.; Cichoż-Lach, H.; Majsiak, E.; Bierła, J.B.; Kanarek, E.; Sowińska, A.; Cukrowska, B. The effectiveness and safety of multi-strain probiotic preparation in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized controlled study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrzydło-Radomańska, B.; Prozorow-Król, B.; Cichoż-Lach, H.; Majsiak, E.; Bierła, J.B.; Kosikowski, W.; Szczerbiński, M.; Gantzel, J.; Cukrowska, B. The effectiveness of synbiotic preparation containing Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium probiotic strains and short chain fructooligosaccharides in patients with diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome-a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, F.; Duan, L. Efficacy of Probiotics for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 1, 859967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mearin, F.; Lacy, B.E.; Chang, L.; Chey, W.D.; Lembo, A.J.; Simren, M.; Spiller, R. Bowel disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1393–1407. [Google Scholar]
- Riegler, G.; Esposito, I. Bristol scale stool form: A still valid help in medical practice and clinical research. Tech. Coloproctol. 2001, 5, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.Y.; Morris, J.; Whorwell, P.J. The irritable bowel severity scoring system: A simple method of monitoring irritable bowel syndrome and its progress. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 11, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, C.R.; Tang, B.; Shi, Y.Z.; Peng, W.Y.; Ye, K.; Tao, Q.F.; Yu, S.G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, M. Low FODMAP diet and probiotics in irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review with network meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 9, 853011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martoni, C.J.; Srivastava, S.; Leyer, G.J. Lactobacillus acidophilus DDS-1 and Bifidobacterium lactis UABla-12 improve abdominal pain severity and symptomology in irritable bowel syndrome: Randomized controlled trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madempudi, R.S.; Ahire, J.J.; Neelamraju, J.; Tripathi, A.; Nanal, S. Randomized clinical trial: The effect of probiotic Bacillus coagulans Unique IS2 vs. placebo on the symptoms management of irritable bowel syndrome in adults. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.K.; Maity, C. Efficacy and safety of Bacillus coagulans LBSC in irritable bowel syndrome: A prospective, interventional, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study [CONSORT Compliant]. Medicine 2021, 100, e23641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeed, M.; Nagabhushanam, K.; Arumugam, S.; Majeed, S.; Ali, F. Bacillus coagulans MTCC 5856 for the management of major depression with irritable bowel syndrome: A randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled, multi-centre, pilot clinical study. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Schoot, A.; Helander, C.; Whelan, K.; Dimidi, E. Probiotics and synbiotics in chronic constipation in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 2759–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, R.; Basson, A.R.; Wearsh, P.; Cominelli, F.; Rodriguez-Palacios, A. Validity of food additive maltodextrin as placebo and effects on human gut physiology: Systematic review of placebo-controlled clinical trials. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 2853, Erratum in Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Control Group (n = 39) N (%) or Mean ± SD | Bifidobacterium lactis NORDBIOTIC™ BI040 Group (n = 33) n (%) or Mean ± SD | Bacillus coagulans NORDBIOTIC™ BC300 Group (n = 34) n (%) or Mean ± SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Female | 33 (84.6%) | 21 (63.6%) | 23 (67.4%) |
| Male | 6 (15.4%) | 11 (33.3%) | 11 (32.6%) |
| Age in years | 39.5 ± 13.8 | 40.8 ± 13.2 | 39.0 ± 17.0 |
| Height (m) | 1.68 ± 0.08 | 1.70 ± 0.13 | 1.69 ± 0.1 |
| Body weight (kg) | 67.0 ± 15.6 | 74.0 ± 16.9 | 70.8 ± 13.9 |
| BMI | 23.5 ± 4.2 | 25.7 ± 5.5 | 24.6 ± 4.5 |
| IBS type | |||
| IBS-D | 12 (30.8%) | 12 (36.4%) | 17 (50.0%) |
| IBS-C | 4 (10.3%) | 7 (21.2%) | 4 (11.7%) |
| IBS-M | 23 (58.9%) | 14 (42.4%) | 12 (35.3%) |
| IBS severity * | |||
| Moderate | 9 (23.1%) | 10 (30.3%) | 8 (23.5%) |
| Severe | 30 (76.9%) | 23 (69.7%) | 26 (76.5%) |
| Total IBS-SSS score | 349.7 ± 58.0 | 344.4 ± 63.9 | 335.8 ± 65.1 |
| Groups | Baseline | 4 Weeks of Intervention | 8 Weeks of Intervention | 12 Weeks of Intervention | Follow-up after the End of Intervention (16 Weeks) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p-Value between Groups | Mean ± SD | p Value between Groups | Mean ± SD | p-Value between Groups | Mean ± SD | p-Value between Groups | |
| IBS-SSS total score | |||||||||
| Placebo (P) | 349.7 ± 58.0 | 277.6 ± 72.2 | Bl vs. P: NS | 224.7 ± 77.7 | BI vs. P: NS | 180.5 ± 81.9 | BI vs. P: NS | 236.3 ± 97.4 | BI vs. P: NS |
| Bifidobacterium lactis BI040 (BI) | 344.4 ± 63.9 | 241.1 ± 69.2 | BC vs. P: NS | 214.5 ± 80.2 | BC vs. P: NS | 167.8 ± 85.8 | BC vs. P: NS | 196.4 ± 89.6 | BC vs. P: NS |
| Bacillus coagulans BC300 (BC) | 335.8 ± 65.1 | 248.1 ± 89.8 | Bl vs. BC: NS | 212.7 ± 90.2 | BI vs. BC: NS | 184.2 ± 97.4 | BI vs. BC: NS | 192.8 ± 88.1 | BI vs. BC: NS |
| IBS-SSS1 score (the intensity of pain) | |||||||||
| Placebo (P) | 55.1 ± 19.2 | 39.1 ± 18.0 | BI vs. P: NS | 31.4 ± 17.9 | BI vs. P: NS | 24.4 ± 16.7 | BI vs. P: NS | 37.8 ± 19.8 | * BI vs. P: 0.026 |
| Bifidobacterium lactis BI040 (BI) | 47.7 ± 17.0 | 29.6 ± 13.2 | BC vs. P: NS | 26.5 ± 14.0 | BC vs. P: NS | 22.7 ± 17.0 | BC vs. P: NS | 25.0 ± 19.4 | BC vs. P: NS |
| Bacillus coagulans BC300 (BC) | 49.3 ± 22.6 | 35.3 ± 21.4 | BI vs. BC: NS | 32.4 ± 20.0 | BI vs. BC: NS | 25.7 ± 19.9 | BI vs. BC: NS | 29.6 ± 22.9 | BI vs. BC: NS |
| IBS-SSS2 score (the frequency of pain) | |||||||||
| Placebo (P) | 70.0 ± 25.1 | 55.4 ± 24.9 | * BI vs. P: 0.013 | 44.1 ± 32.3 | BI vs. P: NS | 33.3 ± 28.9 | BI vs. P: NS | 46.1 ± 30.1 | * BI vs. P: 0.008 |
| Bifidobacterium lactis BI040 (BI) | 68.5 ± 27.3 | 37.6 ± 27.9 | BC vs. P: NS | 33.9 ± 26.0 | BC vs. P: NS | 23.9 ± 24.6 | BC vs. P: NS | 26.1 ± 18.9 | BC vs. P: NS |
| Bacillus coagulans BC300 (BC) | 66.8 ± 26.7 | 49.1 ± 29.7 | BI vs. BC: NS | 42.1 ± 26.7 | BI vs. BC: NS | 33.5 ± 26.8 | BI vs. BC: NS | 39.1 ± 24.3 | * BI vs. BC: 0.042 |
| IBS-SSS3 score (the severity of flatulance) | |||||||||
| Placebo | 69.9 ± 28.2 | 50.0 ± 27.5 | BI vs. P: NS | 41.7 ± 19.3 | BI vs. P: NS | 31.4 ± 19.6 | BI vs. P: NS | 37.8 ± 22.8 | BI vs. P: NS |
| Bifidobacterium lactis BI040 (BI) | 70.4 ± 26.1 | 47.7 ± 24.5 | BC vs. P: NS | 43.9 ± 25.0 | BC vs. P: NS | 31.1 ± 17.7 | BC vs. P: NS | 38.7 ± 24.0 | BC vs. P: NS |
| Bacillus coagulans BC300 (BC) | 67.6 ± 22.6 | 47.1 ± 26.7 | BI vs. BC: NS | 35.3 ± 23.1 | BI vs. BC: NS | 31.6 ± 24.8 | BI vs. BC: NS | 31.1 ± 17.7 | BI vs. BC: NS |
| IBS-SSS4 score (dissatisfaction with bowel habit) | |||||||||
| Placebo (P) | 79.9 ± 16.9 | 68.7 ± 19.5 | BI vs. P: NS | 52.5 ± 18.2 | BI vs. P: NS | 46.6 ± 22.4 | BI vs. P: NS | 59.4 ± 24.4 | BI vs. P: NS |
| Bifidobacterium lactis BI040 (BI) | 81.4 ± 17.2 | 62.1 ± 18.2 | BC vs. P: NS | 56.1 ± 19.5 | BC vs. P: NS | 46.0 ± 20.1 | BC vs. P: NS | 51.2 ± 26.8 | * BC vs. P: 0.044 |
| Bacillus coagulans BC300 (BC) | 80.0 ± 18.9 | 60.3 ± 20.9 | BI vs. BC: NS | 54.4 ± 23.0 | BI vs. BC: NS | 47.6 ± 26.1 | BI vs. BC: NS | 47.0 ± 18.5 | BI vs. P: NS |
| IBS-SSS5 score (quality of life) | |||||||||
| Placebo (P) | 74.7 ± 15.0 | 64.4 ± 15.2 | BI vs. P: NS | 55.0 ± 20.6 | BI vs. P: NS | 44.9 ± 24.6 | BI vs. P: NS | 55.1 ± 26.8 | BI vs. P: NS |
| Bifidobacterium lactis BI040 (BI) | 76.3 ± 17.9 | 64.1 ± 18.6 | BC vs. P: NS | 54.1 ± 24.6 | BC vs. P: NS | 44.0 ± 27.0 | BC vs. P: NS | 55.4 ± 19.9 | BC vs. P: NS |
| Bacillus coagulans BC300 (BC) | 72.1 ± 17.6 | 56.4 ± 23.9 | BI vs. BC: NS | 48.6 ± 27.3 | BI vs. BC: NS | 45.7 ± 28.3 | BI vs. BC: NS | 46.1 ± 24.8 | BI vs. BC: NS |
| Groups | 4 Weeks of Intervention | 8 Weeks of Intervention | 12 Weeks of Intervention | Follow-Up (16 Weeks) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | |
| An improvement in clinical symptoms assessed by total IBS-SSS score | ||||||||
| Bifidobacterium lactis BI040 vs. placebo | NS | 2.4 (0.5–10.9) | NS | 1.1 (0.4–3.2) | NS | 1.2 (04–3.0) | * 0.038 | 3.0 (1.1–8.6) |
| Bacillus coagulans BC300 vs. placebo | NS | 2.7 (0.6–12.1) | NS | 1.2 (0.4–3.4) | NS | 0.8 (0.3–2.1) | * 0.005 | 4.6 (1.5–12.2) |
| An improvement in pain frequency assessed by IBS-SSS2 score | ||||||||
| Bifidobacterium lactis BI040 vs. placebo | * 0.020 | 12.7 (1.5–107.7) | NS | 1.8 (0.6–5.5) | * 0.038 | 3.0 (1.1–8.6) | * 0.010 | 4.3 (1.4–13.0) |
| Bacillus coagulans BC300 vs. placebo | NS | 5.1 (05–47.7) | NS | 0.8 (0.2–2.7) | NS | 1.8 (0.6–5.3) | 0.054 | 3.0 (0.98–9.2) |
| Symptoms | Bifidobacterium lactis NORDBIOTIC™ BI040 Group (BI) n = 23 | Bacillus coagulans NORDBIOTIC™ BC300 Group (BC) n = 27 | Placebo Group (P) n = 33 | OR [95% CI] p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BI vs. P | BC vs. P | ||||
| The pain intensity at 5th week of intervention | |||||
| No pain | 4 (17.4%) | 2 (7.4%) | 0 | 15.46 [0.79–302.78] p = 0.07 | NS |
| Severe | 0 | 5 (18.5%) | 0 | NS | NS |
| Moderate | 19 (82.6%) | 20 (74.1%) | 33 (100%) | NS | NS |
| The pain intensity at 9th week of intervention | |||||
| No pain | 5 (21.7%) | 3 (11.1%) | 0 | 19.92 [1.04–380.67] p = 0.047 | NS |
| Severe | 1 (4.3%) | 2 (7.4%) | 2 (6.1%) | NS | NS |
| Moderate | 17 (74.0%) | 22 (81.5%) | 31 (93.9%) | NS | NS |
| The pain intensity at 16th week of the trial (4 weeks after the end of the intervention) | |||||
| No pain | 7 (30.4%) | 2 (7.4%) | 3 (9.1%) | 4.37 [0.99–19.26] p = 0.051 | NS |
| Severe | 1 (4.3%) | 5 (18.5%) | 2 (6.1%) | NS | NS |
| Moderate | 15 (65.2%) | 20 (74.1%) | 28 (84.8%) | NS | NS |
| Type of stool at 6th week of intervention | |||||
| Normal | 12 (52.2%) | 11 (40.7%) | 4 (12.1%) | 7.91 [2.10–29.83] p = 0.002 | 4.98 [1.36–18.23] p = 0.015 |
| Constipation | 7 (30.4%) | 11 (40.7%) | 20 (60.6%) | 0.24 [0.08–0.73] p = 0.01 | NS |
| Diarrhea | 4 (17.4%) | 5 (18.5%) | 9 (27.3%) | NS | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skrzydło-Radomańska, B.; Prozorow-Król, B.; Kurzeja-Mirosław, A.; Cichoż-Lach, H.; Laskowska, K.; Majsiak, E.; Bierła, J.B.; Agnieszka, S.; Cukrowska, B. The Efficacy and Safety of Single-Strain Probiotic Formulations Containing Bifidobacterium lactis or Bacillus coagulans in Adult Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome—A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Three-Arm Interventional Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144838
Skrzydło-Radomańska B, Prozorow-Król B, Kurzeja-Mirosław A, Cichoż-Lach H, Laskowska K, Majsiak E, Bierła JB, Agnieszka S, Cukrowska B. The Efficacy and Safety of Single-Strain Probiotic Formulations Containing Bifidobacterium lactis or Bacillus coagulans in Adult Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome—A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Three-Arm Interventional Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(14):4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144838
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkrzydło-Radomańska, Barbara, Beata Prozorow-Król, Anetta Kurzeja-Mirosław, Halina Cichoż-Lach, Katarzyna Laskowska, Emilia Majsiak, Joanna B. Bierła, Sowińska Agnieszka, and Bożena Cukrowska. 2023. "The Efficacy and Safety of Single-Strain Probiotic Formulations Containing Bifidobacterium lactis or Bacillus coagulans in Adult Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome—A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Three-Arm Interventional Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 14: 4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144838
APA StyleSkrzydło-Radomańska, B., Prozorow-Król, B., Kurzeja-Mirosław, A., Cichoż-Lach, H., Laskowska, K., Majsiak, E., Bierła, J. B., Agnieszka, S., & Cukrowska, B. (2023). The Efficacy and Safety of Single-Strain Probiotic Formulations Containing Bifidobacterium lactis or Bacillus coagulans in Adult Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome—A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Three-Arm Interventional Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(14), 4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144838