Therapeutic Potential of Capsaicin against Cyclophosphamide-Induced Liver Damage
Abstract
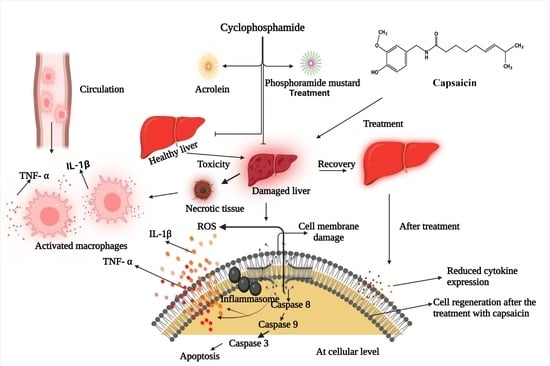
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Kits, and Drugs
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Assessment of Liver Function
2.4. Assessment of Oxidative Stress
2.5. Assessment of Cytokines and Apoptosis Markers
2.6. Histopathological Assessment
2.7. Protein Assessment
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Capsaicin on Liver Function and Morphology
3.2. Effect of Capsaicin on Oxidative Stress
3.3. Effect of Capsaicin on Inflammatory Cytokine and Apoptotic Markers
3.4. Effects of Capsaicin on Liver Histology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdul Razak, R.N.H.A.; Ismail, F.; Isa, M.L.M.; Wahab, A.Y.A.; Muhammad, H.; Ramli, R.; Ismail, R.A.S. R Ameliorative effects of Aquilaria malaccensis leaves aqueous extract on reproductive toxicity induced by cyclopshosphamide in male rat. Malays J. Med. Sci. 2019, 26, 44–57. [Google Scholar]
- Petri, M. Cyclophosphamide: New approaches for systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2004, 13, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokrzadeh, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Naghshvar, F.; Chabra, A.; Jafarinejhad, M. Prophylactic Efficacy of Melatonin on Cyclophosphamide-Induced Liver Toxicity in Mice. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 470425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai-Turton, M.; Luong, B.T.; Tan, Y.; Luderer, U. Cyclophosphamide-induced apoptosis in COV434 human granulosa cells involves oxidative stress and glutathione depletion. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 98, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mok, C.C.; Wong, W.M.; Shek, T.W.; Ho, C.T.; Lau, C.S.; Lai, C.L. Cumulative hepatotoxicity induced by continuous low-dose cyclophosphamide therapy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 845–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeelani, R.; Khan, S.N.; Shaeib, F.; Kohan-Ghadr, H.R.; Aldhaheri, S.R.; Najafi, T.; Thakur, M.; Morris, R.; Abu-Soud, H.M. Cyclophosphamide and acrolein induced oxidative stress leading to deterioration of metaphase II mouse oocyte quality. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 110, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, A.; Yaman, S.; Appak, S.; Gunes, S. Hematoprotective effect of Seleno-L methionine on cyclophosphamide toxicity in rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 32, 424–428. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrecht, S.; Kiebist, J.; König, R.; Thiessen, M.; Schmidtke, K.-U.; Kammerer, S.; Küpper, J.-H.; Scheibner, K. Synthesis of cyclophosphamide metabolites by a peroxygenase from Marasmius rotula for toxicological studies on human cancer cells. AMB Expr. 2020, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Long, M.H.; Wu, J.; Wang, M.M.; Li, X.Y.; Shen, H.; Xu, J.-D.; Zhou, L.; Fang, Z.-J.; Luo, Y.; et al. Ginseng alleviates cyclophosphamide-induced hepatotoxicity via reversing disordered homeostasis of glutathione and bile acid. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tohamy, A.F.; Hussein, S.; Moussa, I.M.; Rizk, H.; Daghash, S.; Alsubki, R.A.; Mubarak, A.S.; Alshammari, H.O.; Al-Maary, K.S.; Hemeg, H.A. Lucrative antioxidant effect of metformin against cyclophosphamide induced nephrotoxicity. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2755–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, W.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S.; Yue, N.; Ye, D.; Zhu, Y.; Tao, R.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, A.; et al. Antioxidative and Energy Metabolism-Improving Effects of Maca Polysaccharide on Cyclophosphamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity Mice via Metabolomic Analysis and Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheweita, S.A.; El-Hosseiny, L.S.; Nashashibi, M.A. Protective Effects of Essential Oils as Natural Antioxidants against Hepatotoxicity Induced by Cyclophosphamide in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.H.; Edfawy, M.; Mansour, A.; Hamed, A.A. Antioxidant and anti apoptotic effects of Capsaicin against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2012, 28, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, B.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Bhattacharayay, D.; De, A.K. Capsaicin, a unique antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, analgesic compound with antifungal activity against dermatophytes. Med. Sci. Res. 1996, 24, 669–670. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Bai, Y.; Gao, M. Hepatoprotective effect of Capsaicin against concanavalin A-induced hepatic injury via inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 3029–3038. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Li, S.; Meng, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Suonan, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shen, Q.; Liao, X.; Xue, Y. Capsaicin Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis in ApoE-/-Mice via Remodeling Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyagbemi, A.A.; Omobowale, O.T.; Asenuga, E.R.; Akinleye, A.S.; Ogunsanwo, R.O.; Saba, A.B. Cyclophosphamide-induced Hepatotoxicity in Wistar Rats: The Modulatory Role of Gallic Acid as a Hepatoprotective and Chemopreventive Phytochemical. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Pelt, L.F. Ketamine and xylazine for surgical anesthesia in rats. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1977, 171, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Utley, H.G.; Bernheim, F.; Hochstein, P. Effect of sulfhydryl reagent on peroxidation in microsome. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1967, 260, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jollow, D.J.; Mitchell, J.R.; Zampaglione, N.; Gillette, J.R. Bromobenzene-induced liver necrosis. Protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3,4-bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmacology 1974, 11, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claiborne, A. Catalase activity. In CRC Handbook of Methods for Oxygen Radical Research; Greenwald, R.A., Ed.; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1985; pp. 283–284. [Google Scholar]
- Tevens, M.J.; Obrosova, I.; Cao, X.; Van Huysen, C.; Greene, D.A. Effects of DL-alpha-lipoic acid on peripheral nerve conduction, blood flow, energy metabolism, and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alam, M.F.; Khan, G.; Safhi, M.M.; Alshahrani, S.; Siddiqui, R.; Moni, S.S.; Anwer, T. Thymoquinone Ameliorates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Swiss Albino Mice by Modulating Oxidative Damage and Cellular Inflammation. Cardiol. Res. Pr. 2018, 2018, 1483041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alam, M.F.; Safhi, M.M.; Anwer, T.; Siddiqui, R.; Khan, G.; Moni, S.S. Therapeutic potential of Vanillylacetone against CCl4 induced hepatotoxicity by suppressing the serum marker, oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokines and apoptosis in Swiss albino mice. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2018, 105, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avraham, Y.; Zolotarev, O.; Grigoriadis, N.C.; Poutahidis, T.; Magen, I.; Vorobiav, L.; Zimmer, A.; Ilan, Y.; Mechoulam, R.; Berry, E.M. Cannabinoids and capsaicin improve liver function following thioacetamide-induced acute injury in mice. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 3047–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, B.F. Comparison of the mutagenicity and teratogenicity of cyclophosphamide and its active metabolites, 4-hydroxycyclophosphamide, phosphoramide mustard, and acrolein. Cancer Res. 1982, 42, 3016–3021. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spielmann, H.; Jacob-Müller, U. Investigation on cyclophosphamide treatment during the preimplantation period. II. In vitro studies on the effects of cyclophosphamide and its metabolites 4-OH-cyclophosphamide, phosphoramide mustard, and acrolein on blastulation of four-cell and eight-cell mouse embryos and on their subsequent development during implantation. Teratology 1981, 23, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.M.; Mohammed, H.A.; Faris, T.M.; Hassan, A.S.; Mohamed, H.B.; El Dosoky, M.I.; Aboubakr, E.M. Nano-Structured Lipid Carrier-Based Oral Glutathione Formulation Mediates Renoprotection against Cyclophosphamide-Induced Nephrotoxicity, and Improves Oral Bioavailability of Glutathione Confirmed through RP-HPLC Micellar Liquid Chromatography. Molecules 2021, 26, 7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muratori, L.; Ferrari, R.; Muratori, P.; Granito, A.; Bianchi, F.B. Acute icteric hepatitis induced by a short course of low-dose cyclophosphamide in a patient with lupus nephritis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2005, 50, 2364–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.M. Stimulation of cyclophosphamide-induced pulmonary microsomal lipid peroxidation by oxygen. Toxicology 1987, 45, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Valle, V.; Chávez-Tapia, N.C.; Uribe, M.; Méndez-Sánchez, N. Role of oxidative stress and molecular changes in liver fibrosis: A review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 4850–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winterbourn, C.C. Are free radicals involved in thiol-based redox signaling? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 80, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, L.; Price, L.T.; Whitney, P.L. Possible mechanism for late gestational development of the antioxidant enzymes in the fetal rat lung. Biol. Neonate 1996, 70, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabra, A.; Shokrzadeh, M.; Naghshvar, F.; Salehi, F.; Ahmadi, A. Melatonin ameliorates oxidative stress and reproductive toxicity induced by cyclophosphamide in male mice. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocahan, S.; Dogan, Z.; Erdemli, E.; Taskin, E. Protective Effect of Quercetin Against Oxidative Stress-induced Toxicity Associated With Doxorubicin and Cyclophosphamide in Rat Kidney and Liver Tissue. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 11, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Temel, Y.; Kucukler, S.; Yıldırım, S.; Caglayan, C.; Kandemir, F.M. Protective effect of chrysin on cyclophosphamide-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity via the inhibition of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, J.J.; Witmer, C.M.; Witz, G. Nephrotoxicity of the 1:1 acrolein-glutathione adduct in the rat. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1992, 117, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, S.; Devaki, T.; Manohar, B.M.; Babu, M.S. Effect of squalene on cyclophosphamide-induced toxicity. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 364, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, M.; Yildiz, S.C.; Demir, C.; Şahin, İ.K.; Teksoy, Ö.; Ayhanci, A. Hepato-preventive and anti-apoptotic role of boric acid against liver injury induced by cyclophosphamide. Trace Elements Med. Biol. 2019, 53, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiri, Y.A. Probucol attenuates cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative apoptosis, p53 and Bax signal expression in rat cardiac tissues. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2010, 3, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iqubal, A.; Syed, M.; Ali, J.; Najmi, A.K.; Haque, M.M. Nerolidol protects the liver against cyclophosphamide-induced hepatic inflammation, apoptosis, and fibrosis via modulation of Nrf2, NF-κB p65, and caspase-3 signaling molecules in Swiss albino mice. BioFactors 2020, 46, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aladaileh, S.H.; Abukhalil, M.H.; Saghir, S.A.M.; Hanieh, H.; Alfwuaires, M.A.; Almaiman, A.A.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Mahmoud, A.M. Galangin Activates Nrf2 Signaling and Attenuates Oxidative Damage, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in a Rat Model of Cyclophosphamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ALHaithloul, H.; Alotaibi, M.F.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Elgebaly, H.; Mahmoud, A.M. Olea europaea leaf extract up-regulates Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 signaling and attenuates cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rat kidney. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.F.; Alshahrani, S.; Alamira, E.A.; Alhazmi, M.A.; Anwer, T.; Khan, G.; Khan, A.; Tanweer, K.T.; Moni, S.S. Nephroprotective effects of 4-4(hydroxyl-3 methoxyphenyl)-2-butane against sodium tellurite induced acute kidney dysfunction by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in rats. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonova, P.P.; Gallucci, R.M.; Hulderman, T. The role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in liver toxicity, inflammation, and fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2001, 177, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Jiang, J.; Jing, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, X.; Hou, X.; Gao, L.; Wei, L. The concentration of tumor necrosis factor-α determines its protective or damaging effect on liver injury by regulating Yap activity. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lutz, A.; Sanwald, J.; Thomas, M.; Feuer, R.; Sawodny, O.; Ederer, M.; Borner, C.; Humar, M.; Merfort, I. Interleukin-1β Enhances FasL-Induced Caspase-3/-7 Activity without Increasing Apoptosis in Primary Mouse Hepatocytes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alqahtani, S.; Mahmoud, A.M. Gamma-Glutamylcysteine Ethyl Ester Protects against Cyclophosphamide-Induced Liver Injury and Hematologic Alterations via Upregulation of PPARγ and Attenuation of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4016209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caglayan, C.; Temel, Y.; Kandemir, F.M.; Yildirim, S.; Kucukler, S. Naringin protects against cyclophosphamide-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity through modulation of oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, autophagy, and DNA damage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 20968–20984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Groups | AST (U/L) | ALT (U/L) | ALP(U/L) | BLI (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CONT | 45.5 ± 3.27 | 27.83 ± 4.26 | 113.33 ± 5.82 | 1.225 ± 0.27 |
| CPM-200 | 97.16 ± 4.71 a | 77.66 ± 2.88 a | 383.66 ± 4.50 a | 2.4 ± 0.32 a |
| CPS-20 | 46.83 ± 5.64 b | 34.33 ± 4.13 b | 123.33 ± 4.55 b | 1.30 ± 0.09 b |
| CPS10 + CPM200 | 85.16 ± 7.01 c | 62.33 ± 5.01 c | 257.5 ± 4.76 c | 2.25 ± 0.19 c |
| CPS20 + CPM200 | 57 ± 4.20 d | 38.66 ± 4.55 d | 128.5 ± 5.47 d | 1.32 ± 0.15 d |
| Groups | Body Weight (g) | Liver Weight (g) | LW/BW(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CONT | 222.60 ± 3.78 | 5.41 ± 0.11 | 2.43 ± 0.09 |
| CPM-200 | 187.60 ± 11.34 a | 8.98 ± 0.06 a | 4.80 ± 0.30 a |
| CPS20 | 218.60 ± 2.30 ns | 5.25 ± 0.13 ns | 2.40 ± 0.07 ns |
| CPS10 + CPM200 | 197.20 ± 6.90 b | 8.48 ± 0.40 b | 4.30 ± 0.25 b |
| CPS20 + CPM200 | 216.80 ± 4.21 c | 6.21 ± 0.266 c | 2.86 ± 0.10 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alam, M.F.; Ajeibi, A.O.; Safhi, M.H.; Alabdly, A.J.A.; Alshahrani, S.; Rashid, H.; Qadri, M.; Jali, A.M.; Alqahtani, S.; Nomier, Y.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Capsaicin against Cyclophosphamide-Induced Liver Damage. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030911
Alam MF, Ajeibi AO, Safhi MH, Alabdly AJA, Alshahrani S, Rashid H, Qadri M, Jali AM, Alqahtani S, Nomier Y, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Capsaicin against Cyclophosphamide-Induced Liver Damage. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(3):911. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030911
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlam, Mohammad Firoz, Ahmed O. Ajeibi, Majed H. Safhi, Ahmad J. A. Alabdly, Saeed Alshahrani, Hina Rashid, Marwa Qadri, Abdulmajeed M. Jali, Saud Alqahtani, Yousra Nomier, and et al. 2023. "Therapeutic Potential of Capsaicin against Cyclophosphamide-Induced Liver Damage" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 3: 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030911
APA StyleAlam, M. F., Ajeibi, A. O., Safhi, M. H., Alabdly, A. J. A., Alshahrani, S., Rashid, H., Qadri, M., Jali, A. M., Alqahtani, S., Nomier, Y., Moni, S. S., Khalid, M., & Anwer, T. (2023). Therapeutic Potential of Capsaicin against Cyclophosphamide-Induced Liver Damage. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(3), 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030911