The Liver Can Deliver: Utility of Hepatic Function Tests as Predictors of Outcome in COVID-19, Influenza and RSV Infections
Abstract
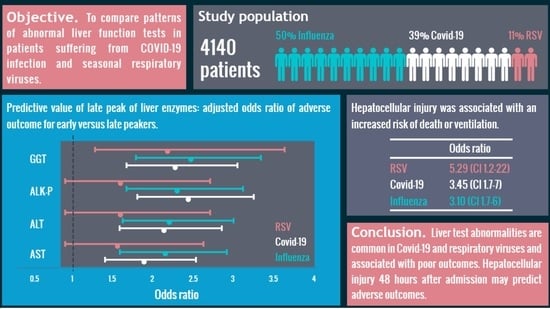
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Microbiology
2.5. Liver Test Parameters and Abnormalities
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Liver Function Abnormalities
3.2. Correlation with Clinical Outcome
3.3. Temporal Pattern of Liver Enzymes and Prognostic Value
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alqahtani, S.A.; Schattenberg, J.M. Liver injury in COVID-19: The current evidence. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020, 8, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, P.P.; Meyerowitz, E.A.; Reinus, Z.; Daidone, M.; Gustafson, J.; Kim, A.Y.; Schaefer, E.; Chung, R.T. Liver Biochemistries in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19. Hepatology 2021, 73, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgonje, A.R.; Abdulle, A.E.; Timens, W.; Hillebrands, J.L.; Navis, G.J.; Gordijn, S.J.; Bolling, M.C.; Dijkstra, G.; Voors, A.A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). J. Pathol. 2020, 251, 228–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paizis, G.; Tikellis, C.; Cooper, M.E.; Schembri, J.M.; Lew, R.A.; Smith, I.A.; Shaw, T.; Warner, F.J.; Zuilli, A.; Burrell, L.M.; et al. Chronic liver injury in rats and humans upregulates the novel enzyme angiotensin converting enzyme 2. Gut 2005, 54, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Cheng, X.; Yang, J.; Tian, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, J. Clinical Features of COVID-19-Related Liver Functional Abnormality. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.L.; Rapkiewicz, A.; Maghsoodi-Deerwester, M.; Gupta, M.; Cao, W.; Palaia, T.; Zhou, J.; Ram, B.; Vo, D.; Rafiee, B.; et al. Pathological findings in the postmortem liver of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Hum. Pathol. 2020, 109, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, B.; Kubes, P. Innate Immune Cell Trafficking and Function During Sterile Inflammation of the Liver. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effenberger, M.; Grander, C.; Grabherr, F.; Griesmacher, A.; Ploner, T.; Hartig, F.; Bellmann-Weiler, R.; Joannidis, M.; Zoller, H.; Weiss, G.; et al. Systemic inflammation as fuel for acute liver injury in COVID-19. Dig. Liver Dis. 2021, 53, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Hossain, K. Liver injury in severe COVID-19 infection: Current insights and challenges. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 14, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, J.R.; Mack, C.L.; O’Connor, J.A.; Narkewicz, M.R.; Mengshol, S.; Sokol, R.J. Acute hepatitis and liver failure associated with influenza A infection in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 43, 536–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papic, N.; Pangercic, A.; Vargovic, M.; Barsic, B.; Vince, A.; Kuzman, I. Liver involvement during influenza infection: Perspective on the 2009 influenza pandemic. Influ. Other Respir. Viruses 2011, 6, e2–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafran, N.; Issachar, A.; Shochat, T.; Shafran, I.H.; Bursztyn, M.; Shlomai, A. Abnormal liver tests in patients with SARS-CoV-2 or influenza—Prognostic similarities and temporal disparities. JHEP Rep. Innov. Hepatol. 2021, 3, 100258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.K.; Akl, E.A.; Duda, S.; Solo, K.; Yaacoub, S.; Schünemann, H.J.; COVID-19 Systematic Urgent Review Group Effort (SURGE) Study Authors. Physical distancing, face masks, and eye protection to prevent person-to-person transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2020, 395, 1973–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Quinn, J.; Pinsky, B.; Shah, N.H.; Brown, I. Rates of Co-infection Between SARS-CoV-2 and Other Respiratory Pathogens. JAMA 2020, 323, 2085–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Zhang, T.; Lyu, Y.; Lai, S.; Dai, P.; Zheng, J.; Yang, W.; Zhou, X.; Feng, L. The Incoming Influenza Season—China, the United Kingdom, and the United States, 2021-2022. China CDC Wkly. 2021, 3, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Liu, L.; Zhao, M.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, Q. Liver impairment in COVID-19 patients: A retrospective analysis of 115 cases from a single centre in Wuhan city, China. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, A.; Van De Peppel, I.P.; Bodewes, F.A.; Moshage, H.; Fantin, A.; Farinati, F.; Fiorotto, R.; Jonker, J.W.; Strazzabosco, M.; Verkade, H.J.; et al. Abnormal Liver Function Tests in Patients With COVID-19: Relevance and Potential Pathogenesis. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1864–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhut, M.; Thorburn, K. Hepatitis associated with severe respiratory syncytial virus-positive lower respiratory tract infection. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhut, M.; Thorburn, K.; Ahmed, T. Transaminase levels in ventilated children with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Intensiv. Care Med. 2004, 30, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal, D.; Wunderli, W.; Meurmann, O.; Briner, J.; Hirsig, J. Isolation of respiratory syncytial virus from liver tissue and extrahepatic biliary atresia material. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 22, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, M.M.; Barraza, L.H.; LaSota, E.D.; Sobieszczyk, M.E.; Pereira, M.R.; Zheng, E.X.; Fox, A.N.; Zucker, J.; Verna, E.C. Acute Liver Injury in COVID-19: Prevalence and Association with Clinical Outcomes in a Large U.S. Cohort. Hepatology 2020, 72, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fislová, T.; Gocník, M.; Sládková, T.; Ďurmanová, V.; Rajčáni, J.; Varečková, E.; Mucha, V.; Kostolanský, F. Multiorgan distribution of human influenza A virus strains observed in a mouse model. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polakos, N.K.; Cornejo, J.C.; Murray, D.A.; Wright, K.O.; Treanor, J.J.; Crispe, I.N.; Topham, D.J.; Pierce, R.H. Kupffer cell-dependent hepatitis occurs during influenza infection. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florescu, D.F.; Kalil, A.C. The complex link between influenza and severe sepsis. Virulence 2014, 5, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, S.A.; Hagan, R.S.; Hayden, F.G.; Fischer, W.A. The hidden burden of influenza: A review of the extra-pulmonary complications of influenza infection. Influ. Other Respir. Viruses 2017, 11, 372–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Chen, A.; Ravindran, N.; To, C.; Thuluvath, P.J. Gastrointestinal and Liver Manifestations of COVID-19. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2020, 10, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Lin, F.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Xu, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection of the liver directly contributes to hepatic impairment in patients with COVID-19. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M.F.; Guerra, M.T.; Hundt, M.A.; Ciarleglio, M.M.; Pinto, R.A.d.A.; Dutra, B.G.; Xavier, M.S.; Lacerda, M.V.G.; Ferreira, A.J.; Wanderley, D.C.; et al. Correlation Between Clinical and Pathological Findings of Liver Injury in 27 Patients With Lethal COVID-19 Infections in Brazil. Hepatol. Commun. 2021, 6, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-L.; Chen, K.-T.; Lai, S.-K.; Kuo, H.-W.; Su, I.-J.; Lin, R.S.; Sung, F.-C. Hematological and biochemical factors predicting SARS fatality in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2006, 105, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idalsoaga, F.; Ayares, G.; Arab, J.P.; Díaz, L.A. COVID-19 and Indirect Liver Injury: A Narrative Synthesis of the Evidence. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2021, 9, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Immunotherapeutic implications of IL-6 blockade for cytokine storm. Immunotherapy 2016, 8, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoh, A.K.; Bishburg, E.; Grinberg, S.; Nagarakanti, S. Tocilizumab use in COVID-19-associated pneumonia. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, M.; Safadi, R.; Mader, R. Hepatotoxicity of tocilizumab and anakinra in rheumatoid arthritis: Management decisions. Clin. Pharmacol. Adv. Appl. 2011, 3, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anger, F.; Wiegering, A.; Wagner, J.; Lock, J.; Baur, J.; Haug, L.; Schmalzing, M.; Geier, A.; Löb, S.; Klein, I. Toxic drug-induced liver failure during therapy of rheumatoid arthritis with tocilizumab subcutaneously: A case report. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1628–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Qin, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, X.; Cai, J.; Lin, L.; Ouyang, S.; et al. Longitudinal Association Between Markers of Liver Injury and Mortality in COVID-19 in China. Hepatology 2020, 72, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, F.M.; Islam, M.M. Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Mortality Among COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis. J. Community Health 2020, 45, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanislav, C.; Kostev, K. Fewer non-COVID-19 respiratory tract infections and gastrointestinal infections during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, L.; Zhang, D.; Xu, J.; Dai, H.; Tang, N.; Su, X.; Cao, B. SARS-CoV-2 and viral sepsis: Observations and hypotheses. Lancet 2020, 395, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| COVID-19 (n = 1624) | Influenza (n = 2056) | RSV (n = 460) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) * | 69 (55–81) | 74 (58–83) | 79 (69–86) | p < 0.001 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index * | 4 (2–6) | 4 (2–6) | 5 (4–7) | p < 0.001 |
| Vital Signs | ||||
| O2 Saturation (%) * | 96 (93–98) | 97 (93–99) | 96 (93–99) | p < 0.005 |
| Heart Rate at Admission (beats/min) * | 87 (77–99) | 92 (80–106) | 88 (77–103) | p < 0.001 |
| Body Temperature (°C) * | 37.4 (36.8–38) | 37.1 (36.7–37.8) | 37.1 (36.7–37.8) | p < 0.001 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) * | 135 (120–150) | 135 (117–152) | 140 (123–160) | p < 0.01 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) * | 75 (66–84) | 74 (64–83) | 74 (65–87) | p < 0.05 |
| CRP (mg/L) * | 69.9 (20.34–142.96) | 48.79 (21.11–113.7) | 51 (20.05–112.36) | p < 0.001 |
| Baseline Liver Enzymes | ||||
| ALT (U/L) * | 24 (15–39) | 22 (15–33) | 20 (13–29) | p < 0.001 |
| AST (U/L) * | 32 (23–49) | 30 (22–45) | 26 (19–35) | p < 0.001 |
| ALK (U/L) * | 70 (55–91) | 69 (55–90) | 75 (60–98) | p < 0.001 |
| GGT (U/L) * | 33 (20–66) | 27 (16–53) | 29 (18–60) | p < 0.001 |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) * | 0.41 (0.26–0.62) | 0.33 (0.2–0.51) | 0.36 (0.23–0.55) | p < 0.001 |
| Maximal Liver Enzymes | ||||
| ALT (U/L) * | 32 (20–62) | 26 (18–44) | 24.5 (16–40) | p < 0.001 |
| AST (U/L) * | 40 (26–69) | 34 (24–54) | 30 (22–44) | p < 0.001 |
| ALK (U/L) * | 79 (61–108) | 74 (58–102) | 83 (64–109) | p < 0.001 |
| GGT (U/L) * | 44 (24–99) | 34 (19–70) | 42 (21–88) | p < 0.001 |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) * | 0.60 (0.42–0.85) | 0.48 (0.3–0.7) | 0.48 (0.31–0.71) | p < 0.001 |
| Hepatocellular Injury (%) X | 3.08 | 2.48 | 1.74 | p = 0.24 |
| Cholestatic Injury (%) X | 29.13 | 19.75 | 23.48 | p < 0.001 |
| Mix Injury (%) X | 11.45 | 6.42 | 8.26 | p < 0.001 |
| Outcomes | ||||
| Death (%) | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.14 | p < 0.001 |
| Mechanical Ventilation (%) | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.08 | p < 0.001 |
| Length of Hospital Stay (days) * | 5 (2–10) | 4 (2–9) | 5 (3–12) | p < 0.001 |
| COVID-19 | Influenza | RSV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | p Value | OR | p Value | OR | p Value | |
| Mixed | 2.83 | <0.001 | 3.3 | <0.001 | 3.33 | 0.019 |
| Cholestatic | 2.05 | <0.001 | 1.7 | 0.002 | 1.57 | 0.13 |
| Hepatocellular | 3.45 | <0.001 | 3.1 | <0.001 | 5.29 | 0.023 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ritter, E.; Shusterman, E.; Prozan, L.; Kehat, O.; Weiss Meilik, A.; Shibolet, O.; Ablin, J.N. The Liver Can Deliver: Utility of Hepatic Function Tests as Predictors of Outcome in COVID-19, Influenza and RSV Infections. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3335. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093335
Ritter E, Shusterman E, Prozan L, Kehat O, Weiss Meilik A, Shibolet O, Ablin JN. The Liver Can Deliver: Utility of Hepatic Function Tests as Predictors of Outcome in COVID-19, Influenza and RSV Infections. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(9):3335. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093335
Chicago/Turabian StyleRitter, Einat, Eden Shusterman, Lior Prozan, Orli Kehat, Ahuva Weiss Meilik, Oren Shibolet, and Jacob Nadav Ablin. 2023. "The Liver Can Deliver: Utility of Hepatic Function Tests as Predictors of Outcome in COVID-19, Influenza and RSV Infections" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 9: 3335. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093335
APA StyleRitter, E., Shusterman, E., Prozan, L., Kehat, O., Weiss Meilik, A., Shibolet, O., & Ablin, J. N. (2023). The Liver Can Deliver: Utility of Hepatic Function Tests as Predictors of Outcome in COVID-19, Influenza and RSV Infections. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(9), 3335. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093335