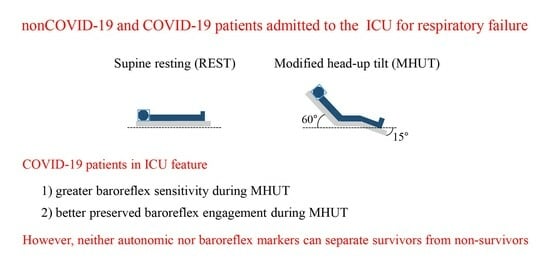
Autonomic Function and Baroreflex Control in COVID-19 Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Protocol
2.2. Extraction of Beat-to-Beat Variability Series
2.3. Frequency Domain Markers of the Autonomic Function
2.4. Frequency Domain Indexes of the Baroreflex Control
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Autonomic Control of Non-COVID-19 and COVID-19 Patients Admitted to the ICU for Respiratory Failure
4.2. Baroreflex Control of Non-COVID-19 and COVID-19 Patients Admitted to the ICU for Respiratory Failure
4.3. Association of Autonomic Markers of Non-COVID-19 and COVID-19 Patients Admitted to the ICU for Respiratory Failure with Mortality
4.4. Association of Baroreflex Control Markers of Non-COVID-19 and COVID-19 Patients Admitted to the ICU for Respiratory Failure with Mortality
4.5. Limitations of the Study and Future Developments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aragón-Benedí, C.; Oliver-Forniés, P.; Galluccio, F.; Altinpulluk, E.Y.; Ergonenc, T.; El Sayed Allam, A.; Salazar, C.; Fajardo-Pérez, M. Is the heart rate variability monitoring using the analgesia nociception index a predictor of illness severity and mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19? A pilot study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249128. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, M.S.; Mayer, C.; Fischer, M.; Kluge, S.; Roedl, K.; Gerloff, C.; Czorlich, P.; Thomall, G.; Schulze zur Wiesch, J.; Schweingruber, N. Clinical surrogates of dysautonomia predict lethal outcome in COVID-19 on intensive care unit. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2023, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phua, J.; Weng, L.; Ling, L.; Egi, M.; Lim, C.-M.; Divatia, J.V.; Shrestha, B.R.; Arabi, Y.M.; Ng, J.; Gomersall, C.D.; et al. Intensive care management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Challenges and recommendations. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzerini, P.E.; Boutjdir, M.; Capecchi, P.L. COVID-19, Arrhythmic risk, and inflammation: Mind the gap! Circulation 2020, 142, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasselli, G.; Greco, M.; Zanella, A.; Albano, G.; Antonelli, M.; Bellani, G.; Bonanomi, E.; Cabrini, L.; Carlesso, E.; Castelli, G.; et al. Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 in intensive care units in Lombardy, Italy. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.A.; Fossali, T.; Pandolfi, L.; Carsana, L.; Ottolina, D.; Frangipane, V.; Rech, R.; Tosoni, A.; Lopez, G.; Agarossi, A.; et al. Hypoalbuminemia in COVID-19: Assessing the hypothesis for underlying pulmonary capillary leakage. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 289, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasty, F.; García, G.; Dávila, C.H.; Wittels, S.H.; Hendricks, S.; Chong, S. Heart rate variability as a possible predictive marker for acute inflammatory response in COVID-19 patients. Mil. Med. 2021, 186, e34–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mol, M.B.A.; Strous, M.T.A.; van Osch, F.H.M.; Vogelaar, F.J.; Barten, D.G.; Farchi, M.; Foudraine, N.A.; Gidron, Y. Heart-rate-variability (HRV), predicts outcomes in COVID-19. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.B.; June, C.H. Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19. Science 2020, 368, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Huang, S.; Yin, L. The cytokine storm and COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, B.E.; Sundman, E.; Terrando, N.; Eriksson, L.I.; Olofsson, P.S. Neural control of inflammation. Anesthesiology 2016, 124, 1174–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlov, V.A.; Tracey, K.J. The vagus nerve and the inflammatory reflex—Linking immunity and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matschke, J.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Hagel, C.; Sperhake, J.P.; Schroder, A.S.; Edler, C.; Mushumba, H.; Fitzek, A.; Allweiss, L.; Dandri, M.; et al. Neuropathology of patients with COVID-19 in Germany: A post-mortem case series. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heming, M.; Li, X.; Rauber, S.; Mausberg, A.K.; Börsch, A.-L.; Hartlehnert, M.; Singhal, A.; Lu, I.-N.; Fleischer, M.; Szepanowski, F.; et al. Neurological manifestations of COVID-19 feature T cell exhaustion and dedifferentiated monocytes in cerebrospinal fluid. Immunity 2021, 54, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlow, J.; Viale, J.-P.; Annat, G.; Hughson, R.; Quintin, L. Spontaneous cardiac baroreflex in humans. Comparison with drug-induced responses. Hypertension 1995, 25, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stute, N.L.; Stickford, J.L.; Province, V.M.; Augenreich, M.A.; Ratchford, S.M.; Stickford, A.S.L. COVID-19 is getting on our nerves: Sympathetic neural activity and haemodynamics in young adults recovering from SARS-CoV-2. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 4269–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, P.; Nabeel, P.M.; Raj, K.V.; Soneja, M.; Chandran, D.S.; Joseph, J.; Wig, N.; Jaryal, A.K.; Thijssen, D.; Deepak, K.K. Baroreflex sensitivity is impaired in survivors of mild COVID-19 at 3–6 months of clinical recovery; association with carotid artery stiffness. Physiol. Rep. 2023, 11, e15845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scala, I.; Rizzo, P.A.; Bellavia, S.; Brunetti, V.; Colò, F.; Broccolini, A.; Della Marca, G.; Calabresi, P.; Luigetti, M.; Frisullo, G. Autonomic dysfunction during acute SARS-CoV-2 infection: A systematic review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yu, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Hu, H.; Zhou, L.; et al. Alteration of autonomic nervous system is associated with severity and outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 630038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.B.; Neves, V.R.; Barros, M.C.; Gambassi, B.B.; Schwingel, P.A.; Sobral-Filho, D.C. Autonomic dysfunction in COVID-19 patients receiving mechanical ventilation: A cross-sectional study. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2023, 141, e2022513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, A.; Colombo, R.; Marchi, A.; Bari, V.; De Maria, B.; Ranuzzi, G.; Guzzetti, S.; Fossali, T.; Raimondi, F. Association between autonomic control indexes and mortality in subjects admitted to intensive care unit. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rovere, M.T.; Porta, A.; Schwartz, P.J. Autonomic control of the heart and its clinical impact. A personal perspective. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, P.; Taylor, E.W. Toward understanding respiratory sinus arrhythmia: Relations to cardiac vagal tone, evolution and biobehavioral functions. Biol. Psychol. 2007, 74, 263–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagani, M.; Montano, N.; Porta, A.; Malliani, A.; Abboud, F.M.; Birkett, C.; Somers, V.K. Relationship between spectral components of cardiovascular variabilities and direct measures of muscle sympathetic nerve activity in humans. Circulation 1997, 95, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi, A.; Bari, V.; De Maria, B.; Esler, M.; Lambert, E.; Baumert, M.; Porta, A. Calibrated variability of muscle sympathetic nerve activity during graded head-up tilt in humans and its link with noradrenaline data and cardiovascular rhythms. Am. J. Physiol. 2016, 310, R1134–R1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laude, D.; Elghozi, J.-L.; Girard, A.; Bellard, E.; Bouhaddi, M.; Castiglioni, P.; Cerutti, C.; Cividjian, A.; Di Rienzo, M.; Fortrat, J.-O.; et al. Comparison of various techniques used to estimate spontaneous baroreflex sensitivity (the EuroBaVar study). Am. J. Physiol. 2004, 286, R226–R231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korach, M.; Sharshar, T.; Jarrin, I.; Fouillot, J.P.; Raphaël, J.C.; Gajdos, P.; Annane, D. Cardiac variability in critically ill adults: Influence of sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontet, J.; Contreras, P.; Curbelo, A.; Medina, J.; Noveri, S.; Bentancourt, S.; Migliaro, E.R. Heart rate variability as early marker of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in septic patients. J. Crit. Care 2003, 18, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrara, M.; Bollen Pinto, B.; Baselli, G.; Bendjelid, K.; Ferrario, M. Baroreflex sensitivity and blood pressure variability can help in understanding the different response to therapy during acute phase of septic shock. Shock 2018, 50, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi, A.; Colombo, R.; Guzzetti, S.; Bari, V.; Bassani, T.; Raimondi, F.; Porta, A. Characterization of the cardiovascular control during modified head-up tilt test in healthy adult humans. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 2013, 179, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelpi, F.; Bari, V.; Cairo, B.; De Maria, B.; Cornara, N.; Colombo, R.; Porta, A. Derangement of cardiovascular regulatory mechanisms in COVID-19 patients in intensive care unit and its association with mortality. Comput. Cardiol. 2022, 49, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.C.; Jung, C.W. Vital Recorder-a free research tool for automatic recording of high-resolution time-synchronised physiological data from multiple anaesthesia devices. Sci. Rep. 2018, 24, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, A.; Baselli, G.; Lombardi, F.; Cerutti, S.; Antolini, R.; Del Greco, M.; Ravelli, F.; Nollo, G. Performance assessment of standard algorithms for dynamic RT interval measurement: Comparison between RTapex and RTend approach. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1998, 36, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baselli, G.; Porta, A.; Rimoldi, O.; Pagani, M.; Cerutti, S. Spectral decomposition in multichannel recordings based on multivariate parametric identification. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1997, 44, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical novel identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Heart rate variability: Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Circulation 1996, 93, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeranz, B.; Macaulay, R.J.; Caudill, M.A.; Kutz, I.; Adam, D.; Gordon, D.; Kilborn, K.M.; Barger, A.C.; Shannon, D.C.; Cohen, R.J.; et al. Assessment of autonomic function in humans by heart rate spectral analysis. Am. J. Physiol. 1985, 248, H151–H153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, A.; Bari, V.; Bassani, T.; Marchi, A.; Pistuddi, V.; Ranucci, M. Model-based causal closed loop approach to the estimate of baroreflex sensitivity during propofol anesthesia in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 115, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, A.; Baselli, G.; Rimoldi, O.; Malliani, A.; Pagani, M. Assessing baroreflex gain from spontaneous variability in conscious dogs: Role of causality and respiration. Am. J. Physiol. 2000, 279, H2558–H2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinna, G.D.; Porta, A.; Maestri, R.; De Maria, B.; Dalla Vecchia, L.A.; La Rovere, M.T. Different estimation methods of spontaneous baroreflex sensitivity have different predictive value in heart failure patients. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 1666–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krstacic, A.; Krstacic, G.; Gamberger, D. The influence of corticosteroids on heart rate variability in acute cervical spinal cord injury. Acta Clin. Croat. 2016, 55, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montano, N.; Gnecchi-Ruscone, T.; Porta, A.; Lombardi, F.; Pagani, M.; Malliani, A. Power spectrum analysis of heart rate variability to assess the changes in sympatho-vagal balance during graded orthostatic tilt. Circulation 1994, 90, 1826–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, W.H.; Hoag, J.B.; Crossman, A.A.; Kuusela, T.A.; Tahvanainen, K.U.O.; Eckberg, D.L. Human responses to upright tilt: A window on central autonomic integration. J. Physiol. 1999, 517, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlan, R.; Porta, A.; Costa, F.; Tank, J.; Baker, L.; Schiavi, R.; Robertson, D.; Malliani, A.; Mosqueda-Garcia, R. Oscillatory patterns in sympathetic neural discharge and cardiovascular variables during orthostatic stimulus. Circulation 2000, 101, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Maria, B.; Dalla Vecchia, L.A.; Bari, V.; Cairo, B.; Gelpi, F.; Perego, F.; Takahashi, A.C.M.; Milan-Mattos, J.C.; Minatel, V.; Rehder-Santos, P.; et al. The degree of engagement of cardiac and sympathetic arms of the baroreflex does not depend on the absolute value and sign of arterial pressure variations. Physiol. Meas. 2023, 44, 114002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, A.; Faes, L.; Nollo, G.; Bari, V.; Marchi, A.; De Maria, B.; Takahashi, A.C.M.; Catai, A.M. Conditional self-entropy and conditional joint transfer entropy in heart period variability during graded postural challenge. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, A.; Takahashi, A.C.M.; Catai, A.M. Cardiovascular coupling during graded postural challenge: Comparison between linear tools and joint symbolic analysis. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2016, 20, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Maria, B.; Bari, V.; Cairo, B.; Vaini, E.; Esler, M.; Lambert, E.; Baumert, M.; Cerutti, S.; Dalla Vecchia, L.; Porta, A. Characterization of the asymmetry of the cardiac and sympathetic arms of the baroreflex from spontaneous variability during incremental head-up tilt. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, J.; Rupprecht, S.; Künstler, E.C.S.; Hoyer, D. Heart rate variability as a marker and predictor of inflammation, nosocomial infection, and sepsis—A systematic review. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 2023, 249, 103116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.A.; Lopez, G.; Nebuloni, M.; Ottolina, D.; Montomoli, J.; Carsana, L.; Fossali, T.; Castelli, A.; Rech, R.; Cogliati, C.; et al. Lung histopathologic clusters in severe COVID-19: A link between clinical picture and tissue damage. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranucci, M.; Porta, A.; Bari, V.; Pistuddi, V.; La Rovere, M.T. Baroreflex sensitivity and outcomes following coronary surgery. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, A.; Di Rienzo, M.; Wessel, N.; Kurths, J. Addressing the complexity of cardiovascular regulation. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, A.; De Maria, B.; Bari, V.; Marchi, A.; Faes, L. Are nonlinear model-free conditional entropy approaches for the assessment of cardiac control complexity superior to the linear model-based one? IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modra, L.; Higgins, A.; Vithanage, R.; Abeygunawardana, V.; Bailey, M.; Bellomo, R. Sex differences in illness severity and mortality among adult intensive care patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Crit. Care 2021, 65, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Variable | Non-COVID-19 (n = 33) | COVID-19 (n = 17) |
|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | 59.9 ± 11.9 | 62.5 ± 9.8 |
| Gender [male] | 23 (70) | 14 (82) |
| BMI [kg·m−2] | 27.1 ± 4.9 | 28.3 ± 2.6 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 29 (88) | 16 (94) |
| Administration of catecholamines | 17 (52) | 8 (46) |
| Sedation | 29 (88) | 16 (94) |
| Steroids | 10 (30) | 16 (94) * |
| Septic shock | 6 (18) | 0 (0) |
| SOFA score | 8.2 ± 3.4 | 9.5 ± 3.1 |
| RASS score | −3.5 ± 1.6 | −4.7 ± 1.2 * |
| LOS in ICU [days] | 10.5 ± 8.1 | 18.8 ± 12.1 * |
| Intra-ICU mortality | 6 (18) | 11 (65) * |
| Variable | SURV (n = 25) | Non-SURV (n = 8) |
|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | 61.5 ± 9.9 | 54.7 ± 15.4 |
| Gender [male] | 18 (72) | 5 (62) |
| BMI [kg·m−2] | 27.9 ± 5.2 | 24.8 ± 3.3 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 21 (84) | 8 (100) |
| Administration of catecholamines | 13 (52) | 4 (50) |
| Sedation | 21 (84) | 8 (100) |
| Steroids | 6 (24) | 4 (50) |
| Septic shock | 3 (12) | 3 (37) |
| SOFA score | 8.0 ± 3.4 | 8.6 ± 3.2 |
| RASS score | −3.2 ± 1.7 | −4.4 ± 0.9 |
| LOS in ICU [days] | 16.1 ± 10.8 | 8.7 ± 6.1 |
| Intra-ICU mortality | 0 (0) | 6 (75) * |
| Variable | SURV (n = 6) | Non-SURV (n = 11) |
|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | 57.2 ± 7.3 | 65.5 ± 9.8 |
| Gender [male] | 6 (100) | 8 (73) |
| BMI [kg·m−2] | 28.9 ± 2.5 | 28 ± 2.6 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 6 (100) | 10 (91) |
| Administration of catecholamines | 3 (50) | 5 (45) |
| Sedation | 6 (100) | 10 (91) |
| Steroids | 6 (100) | 10 (91) |
| Septic shock | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| SOFA score | 10.3 ± 2.3 | 9 ± 3.3 |
| RASS score | −4.8 ± 0.2 | −4.5 ± 1.4 |
| LOS in ICU [days] | 15.7 ± 9.8 | 20.5 ± 12.9 |
| Intra-ICU mortality | 0 (0) | 11 (100) * |
| Variable | Non-COVID-19 (n = 33) | COVID-19 (n = 17) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REST | MHUT | REST | MHUT | |
| μHP [ms] | 711 ± 140 | 696 ± 153 | 824 ± 184 * | 819 ± 171 * |
| σ2HP [ms2] | 151 ± 245 | 108 ± 175 | 169 ± 205 | 218 ± 309 |
| HFHP [ms2] | 20 ± 46 | 21 ± 46 | 16 ± 30 | 35 ± 73 |
| μSAP [mmHg] | 127 ± 18 | 118 ± 18 | 115 ± 19 * | 107 ± 21 |
| σ2SAP [mmHg2] | 11 ± 11 | 15 ± 14 | 9 ± 13 | 14 ± 16 |
| LFSAP [mmHg2] | 1.8 ± 4.1 | 0.5 ± 0.9 | 0.2 ± 0.4 | 0.5 ± 1.0 |
| fR [bpm] | 18 ± 4 | 18 ± 5 | 18 ± 5 | 18 ± 4 |
| Variable | SURV (n = 25) | Non-SURV (n = 8) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REST | MHUT | REST | MHUT | |
| μHP [ms] | 726 ± 148 | 716 ± 156 | 666 ± 105 | 635 ± 135 |
| σ2HP [ms2] | 159 ± 265 | 115 ± 191 | 124 ± 183 | 86 ± 118 |
| HFHP [ms2] | 23 ± 52 | 25 ± 51 | 9 ± 15 | 10 ± 21 |
| μSAP [mmHg] | 126 ± 19 | 119 ± 20 | 130 ± 16 | 116 ± 14 |
| σ2SAP [mmHg2] | 11 ± 11 | 13 ± 10 | 12 ± 13 | 22 ± 21 |
| LFSAP [mmHg2] | 1.6 ± 3.9 | 0.5 ± 0.9 | 2.5 ± 5.0 | 0.5 ± 1.0 |
| fR [bpm] | 18 ± 4 | 18 ± 5 | 19 ± 4 | 19 ± 6 |
| Variable | SURV (n = 6) | Non-SURV (n = 11) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REST | MHUT | REST | MHUT | |
| μHP [ms] | 844 ± 242 | 849 ± 242 | 813 ± 156 | 803 ± 128 |
| σ2HP [ms2] | 191 ± 218 | 318 ± 485 | 157 ± 208 | 164 ± 161 |
| HFHP [ms2] | 33 ± 48 | 69 ± 118 | 7 ± 7 | 17 ± 22 |
| μSAP [mmHg] | 106 ± 22 | 106 ± 22 | 120 ± 15 | 108 ± 22 |
| σ2SAP [mmHg2] | 4 ± 4 | 9 ± 5 | 11 ± 16 | 17 ± 19 |
| LFSAP [mmHg2] | 0.3 ± 0.6 | 0.2 ± 0.4 | 0.1 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 1.1 |
| fR [bpm] | 17 ± 1 | 17 ± 1 | 18 ± 5 | 19 ± 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gelpi, F.; Wu, M.A.; Bari, V.; Cairo, B.; De Maria, B.; Fossali, T.; Colombo, R.; Porta, A. Autonomic Function and Baroreflex Control in COVID-19 Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082228
Gelpi F, Wu MA, Bari V, Cairo B, De Maria B, Fossali T, Colombo R, Porta A. Autonomic Function and Baroreflex Control in COVID-19 Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(8):2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082228
Chicago/Turabian StyleGelpi, Francesca, Maddalena Alessandra Wu, Vlasta Bari, Beatrice Cairo, Beatrice De Maria, Tommaso Fossali, Riccardo Colombo, and Alberto Porta. 2024. "Autonomic Function and Baroreflex Control in COVID-19 Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 8: 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082228
APA StyleGelpi, F., Wu, M. A., Bari, V., Cairo, B., De Maria, B., Fossali, T., Colombo, R., & Porta, A. (2024). Autonomic Function and Baroreflex Control in COVID-19 Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(8), 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082228