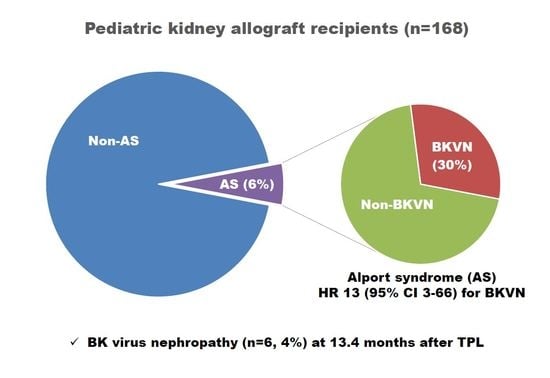
Higher Incidence of BK Virus Nephropathy in Pediatric Kidney Allograft Recipients with Alport Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population and Ethics
2.2. Immunosuppression
2.3. BK Viremia and BKVN
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Risk Factors for BKVN and BK Viremia
3.2. Clinical Course of BKVN
3.3. Alport Syndrome and BKVN
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reploeg, M.D.; Storch, G.A.; Clifford, D.B. BK virus: A clinical review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Randhawa, P. BK polyomavirus in solid organ transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randhawa, P.; Brennan, D.C. BK virus infection in transplant recipients: An overview and update. Am. J. Transplant. 2006, 6, 2000–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, J.; Van Ranst, M.; Snoeck, R.; Beuselinck, K.; Lerut, E.; Van Damme-Lombaerts, R. Polyomavirus infection in pediatric renal transplant recipients: Evaluation using a quantitative real-time PCR technique. Pediatr. Transplant. 2004, 8, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Steiger, J. Polyomavirus BK. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Brennan, D.C.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Ginevri, F.; Gordon, J.; Limaye, A.P.; Mihatsch, M.J.; Nickeleit, V.; Ramos, E.; Randhawa, P.; et al. Polyomavirus-associated nephropathy in renal transplantation: Interdisciplinary analyses and recommendations. Transplantation 2005, 79, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acott, P.D.; Hirsch, H.H. BK virus infection, replication, and diseases in pediatric kidney transplantation. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2007, 22, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, J.M.; Dharnidharka, V.R.; Talley, L.; Martz, K.; McDonald, R.A. BK virus nephropathy in pediatric renal transplant recipients: An analysis of the North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies (NAPRTCS) registry. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, E.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Papadimitriou, J.C.; Hamze, O.; Fink, J.C.; Klassen, D.K.; Drachenberg, R.C.; Wiland, A.; Wali, R.; Cangro, C.B.; et al. Clinical course of polyoma virus nephropathy in 67 renal transplant patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 2145–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disease, K. Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) transplant work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the care of kidney transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 3, S1–S155. [Google Scholar]
- Almeras, C.; Vetromile, F.; Garrigue, V.; Szwarc, I.; Foulongne, V.; Mourad, G. Monthly screening for BK viremia is an effective strategy to prevent BK virus nephropathy in renal transplant recipients. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2011, 13, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawinski, D.; Goral, S. BK virus infection: An update on diagnosis and treatment. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.M.; McDonald, R.A.; Finn, L.S.; Healey, P.J.; Davis, C.L.; Limaye, A.P. Polyomavirus nephropathy in pediatric kidney transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2004, 4, 2109–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drachenberg, R.C.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Papadimitriou, J.C.; Ramos, E.; Fink, J.C.; Wali, R.; Weir, M.R.; Cangro, C.B.; Klassen, D.K.; Khaled, A. Morphological spectrum of polyoma virus disease in renal allografts: Diagnostic accuracy of urine cytology. Am. J. Transplant. 2001, 1, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabardi, S.; Waikar, S.S.; Martin, S.; Roberts, K.; Chen, J.; Borgi, L.; Sheashaa, H.; Dyer, C.; Malek, S.K.; Tullius, S.G. Evaluation of fluoroquinolones for the prevention of BK viremia after renal transplantation. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginevri, F.; Azzi, A.; Hirsch, H.H.; Basso, S.; Fontana, I.; Cioni, M.; Bodaghi, S.; Salotti, V.; Rinieri, A.; Botti, G. Prospective monitoring of polyomavirus BK replication and impact of pre-emptive intervention in pediatric kidney recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 2727–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, H.H. BK virus: Opportunity makes a pathogen. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginevri, F.; De Santis, R.; Comoli, P.; Pastorino, N.; Rossi, C.; Botti, G.; Fontana, I.; Nocera, A.; Cardillo, M.; Ciardi, M.R. Polyomavirus BK infection in pediatric kidney-allograft recipients: A single-center analysis of incidence, risk factors, and novel therapeutic approaches. Transplantation 2003, 75, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruegel, J.; Rubel, D.; Gross, O. Alport syndrome—insights from basic and clinical research. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013, 9, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallett, A.; Tang, W.; Clayton, P.A.; Stevenson, S.; McDonald, S.P.; Hawley, C.M.; Badve, S.V.; Boudville, N.; Brown, F.G.; Campbell, S.B. End-stage kidney disease due to Alport syndrome: Outcomes in 296 consecutive Australia and New Zealand Dialysis and Transplant Registry cases. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 2277–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidet, L.; Gubler, M.C. The renal lesions of Alport syndrome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagaaij, E.L.; Cramer-Knijnenburg, G.F.; van Kemenade, F.J.; van Es, L.A.; Bruijn, J.A.; van Krieken, J.H. Endothelial cell chimerism after renal transplantation and vascular rejection. Lancet 2001, 357, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeras, C.; Foulongne, V.; Garrigue, V.; Szwarc, I.; Vetromile, F.; Segondy, M.; Mourad, G. Does reduction in immunosuppression in viremic patients prevent BK virus nephropathy in de novo renal transplant recipients? A prospective study. Transplantation 2008, 85, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, E.R.; Bresnahan, B.A.; Cohen, E.P.; Lu, N.; Orentas, R.J.; Vasudev, B.; Hariharan, S. Successful treatment of BK viremia using reduction in immunosuppression without antiviral therapy. Transplantation 2008, 85, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, P.; Senanayake, S.; Sujeet, K.; Medipalli, R.; Zhu, Y.R.; Johnson, C.P.; Hariharan, S. Management and outcome of BK viremia in renal transplant recipients: A prospective single-center study. Transplantation 2012, 94, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wali, R.K.; Drachenberg, C.; Hirsch, H.H.; Papadimitriou, J.; Nahar, A.; Mohanlal, V.; Brisco, M.A.; Bartlett, S.T.; Weir, M.R.; Ramos, E. BK virus-associated nephropathy in renal allograft recipients: Rescue therapy by sirolimus-based immunosuppression. Transplantation 2004, 78, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | BKVN (n = 6) | Non-BKVN (n = 162) | Total (n = 168) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, M:F | 3:3 | 98:64 | 101:67 | 0.684 |
| Recipient age at transplant, years | 13.9 (7.7–18.9) | 13.2 (1.5–19.9) | 13.3 (1.5–19.9) | 0.587 |
| Primary kidney disease | ||||
| Glomerulopathy | 5 (83.3) | 85 (52.5) | 90 (53.6) | 0.282 |
| CAKUT | 0 | 36 (22.2) | 36 (21.4) | |
| Other | 1 | 41 (25.3) | 42 (25.0) | |
| Alport syndrome | 3 (50.0) | 7 (4.3) | 10 (6.0) | 0.003 |
| Donor type | ||||
| Deceased donor | 3 (50.0) | 63 (38.9) | 66 (39.3) | 0.681 |
| Living donor | 3 (50.0) | 99 (61.1) | 102 (60.7) | |
| Recipient age at transplant, years | ||||
| 0 to <7 | 0 | 28 (17.3) | 28 (16.7) | 0.285 |
| 7 to <13 | 2 (33.3) | 52 (32.1) | 54 (32.1) | |
| ≥13 | 4 (66.7) | 82 (50.6) | 86 (51.2) | |
| HLA mismatch | ||||
| 0–2 | 0 | 35 (21.6) | 35 (20.8) | 0.578 |
| 3–4 | 6 (100) | 112 (69.1) | 118 (70.2) | |
| 5–6 | 0 | 15 (9.3) | 15 (8.9) | |
| Acute cellular rejection | 4/6 (66.7) | 95/151 (62.9) | 99/157 (63.1) | 1.000 |
| Immunosuppression | ||||
| MMF | 6 | 162 | 168 | 1.000 |
| Tac | 6 | 161 (99.4) | 167 (99.4) | 1.000 |
| BSX | 6 | 131 (80.9) | 137 (81.5) | 0.594 |
| ATG | 0 | 9 (5.6) | 9 (5.4) | 1.000 |
| Transplant year | ||||
| 2001–2008 | 0 | 47 (29.0) | 47 (28.0) | 0.187 |
| 2009–2015 | 6 | 115 (71.0) | 121 (72.0) | |
| CMV infection | 3/5 (60) | 60/131 (45.8) | 63/136 (46.3) | 0.663 |
| EBV infection | 1/4 (25) | 70/132 (53.0) | 71/136 (52.2) | 0.348 |
| Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia | 0 | 6 (3.7) | 6 (3.6) | 1.000 |
| PTLD | 0 | 8 (4.9) | 8 (4.8) | 1.000 |
| Comorbidity | ||||
| Hypertension | 2 (33.3) | 27 (16.7) | 29 (17.3) | 0.277 |
| Cardiovascular disease 1 | 0 | 8 (4.9) | 8 (4.8) | 1.000 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0 | 9 (5.6) | 9 (5.4) | 1.000 |
| Dyslipidemia | 0 | 10 (6.2) | 10 (6.0) | 1.000 |
| Neurological disorder 2 | 0 | 14 (8.6) | 14 (8.3) | 1.000 |
| Liver disease 3 | 1 (16.7) | 7 (4.3) | 8 (4.8) | 0.257 |
| Cancer except PTLD | 0 | 1 (0.6) | 1(0.6) | 1.000 |
| Mortality | 0 | 2 (1.2) | 2 (1.2) | 1.000 |
| Factors | Univariate | Multivariate 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Alport syndrome | <0.001 | 13.204 (2.662–65.502) | 0.002 |
| HLA mismatch ≥3 | 0.206 | NS | 0.984 |
| Basiliximab | 0.224 | NS | 0.975 |
| Transplant year, 2009–2015 | 0.108 | NS | 0.976 |
| Patient No. | Sex/Age at BKVN (yr) | Primary Disease | Transplant Year/Donor Type | Onset of Viremia after KT | Initial Level 1 (Copies/mL) | Peak Level 2 (Copies/mL) | Biopsy Grade | Treatment | Follow up after BKVN | Time to Viremia Clearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F/8.0 | ATN | 2009/D | 1.5 mo | 16,924 | 10,165,852 | B1 | Reduction of IS, IVIG, leflunomide | 8.3 yr | 89.9 mo |
| 2 | F/20.6 | Alport | 2010/D | 60.3 mo | 289,699 | 289,699 | B3 | Reduction of IS, IVIG, leflunomide | 3.0 yr | No |
| 3 | M/13.1 | Alport | 2010/L | 24.0 mo | 41,914 | 41,914 | B1 | Reduction of IS, IVIG, leflunomide | 6.4 yr | No |
| 4 | M/15.0 | Alport | 2014/L | 15.9 mo | 68,919 | 2,266,980 | B1 | Reduction of IS, IVIG, leflunomide, ciprofloxacin, cidofovir | 2.2 yr | No |
| 5 | F/16.8 | FSGS | 2014/L | 4.6 mo | 51,102 | 322,854 | ND | Reduction of IS, leflunomide, ciprofloxacin | 3.8 yr | 16.6 mo |
| 6 | M/19.5 | FSGS | 2015/D | 6.0 mo | 25,555 | 62,481 | ND | Reduction of IS, leflunomide | 2.4 yr | 20.5 mo |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, Y.H.; Hyun, H.S.; Park, E.; Moon, K.C.; Min, S.-I.; Ha, J.; Ha, I.-S.; Cheong, H.I.; Ahn, Y.H.; Kang, H.G. Higher Incidence of BK Virus Nephropathy in Pediatric Kidney Allograft Recipients with Alport Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040491
Cho YH, Hyun HS, Park E, Moon KC, Min S-I, Ha J, Ha I-S, Cheong HI, Ahn YH, Kang HG. Higher Incidence of BK Virus Nephropathy in Pediatric Kidney Allograft Recipients with Alport Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(4):491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040491
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Young Hoon, Hye Sun Hyun, Eujin Park, Kyung Chul Moon, Sang-Il Min, Jongwon Ha, Il-Soo Ha, Hae Il Cheong, Yo Han Ahn, and Hee Gyung Kang. 2019. "Higher Incidence of BK Virus Nephropathy in Pediatric Kidney Allograft Recipients with Alport Syndrome" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 4: 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040491
APA StyleCho, Y. H., Hyun, H. S., Park, E., Moon, K. C., Min, S. -I., Ha, J., Ha, I. -S., Cheong, H. I., Ahn, Y. H., & Kang, H. G. (2019). Higher Incidence of BK Virus Nephropathy in Pediatric Kidney Allograft Recipients with Alport Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(4), 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040491