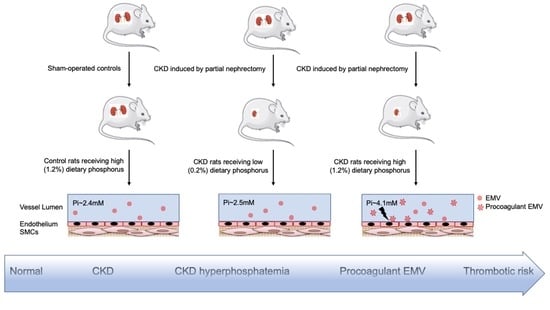
Hyperphosphatemia Drives Procoagulant Microvesicle Generation in the Rat Partial Nephrectomy Model of CKD
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rat Partial Nephrectomy Model of CKD
2.2. Blood and Urine Biochemistry
2.3. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.4. Thrombin Generation Assay (TGA) Using Calibrated Automated Thrombography
2.5. Immunoblotting
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Contribution of Hyperphosphatemia to Pro-Coagulant MV Load in CKD
4.2. Role of Endothelial Versus Platelet-Derived MVs
4.3. Clinical Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henry, R.M.A.; Kostense, P.J.; Bos, G.; Dekker, J.M.; Nijpels, G.; Heine, R.J.; Bouter, L.M.; Stehouwer, C.D.A. Mild renal insufficiency is associated with increased cardiovascular mortality: The Hoorn Study. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1402–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London, G.M.; Guérin, A.P.; Marchais, S.J.; Métivier, F.; Pannier, B.; Adda, H. Arterial media calcification in end-stage renal disease: Impact on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2003, 18, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blacher, J.; Guerin, A.P.; Pannier, B.; Marchais, S.J.; London, G.M. Arterial Calcifications, Arterial Stiffness, and Cardiovascular Risk in End-Stage Renal Disease. Hypertension 2001, 38, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jono, S.; McKee, M.D.; Murry, C.E.; Shioi, A.; Nishizawa, Y.; Mori, K.; Morii, H.; Giachelli, C.M. Phosphate Regulation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Calcification. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, E10–E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, X.; Nie, L.; Liu, C.; Xiong, J.; He, T.; Xu, X.; Yu, Y.; et al. High phosphate-induced downregulation of PPARgamma contributes to CKD-associated vascular calcification. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2018, 114, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, J.L.; Joannides, A.J.; Skepper, J.N.; McNair, R.; Schurgers, L.J.; Proudfoot, D.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Weissberg, P.L.; Shanahan, C.M. Human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Undergo Vesicle-Mediated Calcification in Response to Changes in Extracellular Calcium and Phosphate Concentrations: A Potential Mechanism for Accelerated Vascular Calcification in ESRD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 2857–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giachelli, C.M.; Jono, S.; Shioi, A.; Nishizawa, Y.; Mori, K.; Morii, H. Vascular calcification and inorganic phosphate. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 38, S34–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatopolsky, E.; Brown, A.; Dusso, A. Pathogenesis of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1999, 73, S14–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abbasian, N.; Burton, J.O.; Herbert, K.E.; Tregunna, B.-E.; Brown, J.R.; Ghaderi-Najafabadi, M.; Brunskill, N.J.; Goodall, A.H.; Bevington, A. Hyperphosphatemia, Phosphoprotein Phosphatases, and Microparticle Release in Vascular Endothelial Cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2152–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbasian, N.; Bevington, A.; Burton, J.O.; Herbert, K.E.; Goodall, A.H.; Brunskill, N.J. Inorganic Phosphate (Pi) Signaling in Endothelial Cells: A Molecular Basis for Generation of Endothelial Microvesicles in Uraemic Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco, G.S.; Hausberg, M.; Hillebrand, U.; Rustemeyer, P.; Wittkowski, W.; Lang, D.; Pavenstädt, H. Increased inorganic phosphate induces human endothelial cell apoptosis in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2008, 294, F1381–F1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marco, G.S.; König, M.; Stock, C.; Wiesinger, A.; Hillebrand, U.; Reiermann, S.; Reuter, S.; Amler, S.; Köhler, G.; Buck, F.; et al. High phosphate directly affects endothelial function by downregulating annexin II. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shuto, E.; Taketani, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Harada, N.; Isshiki, M.; Sato, M.; Nashiki, K.; Amo, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Higashi, Y.; et al. Dietary Phosphorus Acutely Impairs Endothelial Function. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burton, J.O.; Hamali, H.A.; Singh, R.; Abbasian, N.; Parsons, R.; Patel, A.K.; Goodall, A.H.; Brunskill, N.J. Elevated Levels of Procoagulant Plasma Microvesicles in Dialysis Patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amabile, N.; Guérin, A.P.; Leroyer, A.; Mallat, Z.; Nguyen, C.; Boddaert, J.; London, G.M.; Tedgui, A.; Boulanger, C.M. Circulating Endothelial Microparticles Are Associated with Vascular Dysfunction in Patients with End-Stage Renal Failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3381–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mörtberg, J.; Lundwall, K.; Mobarrez, F.; Wallén, H.; Jacobson, S.H.; Spaak, J. Increased concentrations of platelet- and endothelial-derived microparticles in patients with myocardial infarction and reduced renal function- a descriptive study. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, N.S.; Chantrathammachart, P.; Moody, P.W.; Chang, J.-Y. Membrane microparticles in VTE and cancer. Thromb. Res. 2010, 125, S80–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, S.; Abbasian, N.; Burton, J.O.; Stover, C.M. Microparticles and their Roles in Inflammation: A Review. Open Immunol. J. 2013, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neves, K.-R.; Graciolli, F.-G.; Dos Reis, L.M.; Graciolli, R.-G.; Neves, C.-L.; Magalhães, A.-O.; Custódio, M.-R.; Batista, D.-G.; Jorgetti, V.; Moysés, R.M.; et al. Vascular calcification: Contribution of parathyroid hormone in renal failure. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nuhu, F.; Seymour, A.-M.; Bhandari, S. Impact of Intravenous Iron on Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Function in Experimental Chronic Kidney Disease. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambrose, A.R.; Alsahli, M.A.; Kurmani, S.A.; Goodall, A.H. Comparison of the release of microRNAs and extracellular vesicles from platelets in response to different agonists. Platelets 2018, 29, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.J.; González, E.A. Prevention and Control of Phosphate Retention/Hyperphosphatemia in CKD-MBD: What Is Normal, When to Start, and How to Treat? Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dursun, I.; Poyrazoglu, H.M.; Gunduz, Z.; Ulger, H.; Yykylmaz, A.; Dusunsel, R.; Patyroglu, T.; Gurgoze, M. The relationship between circulating endothelial microparticles and arterial stiffness and atherosclerosis in children with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2511–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jalal, D.; Renner, B.; Laskowski, J.; Stites, E.; Cooper, J.; Valente, K.; You, Z.; Perrenoud, L.; Le Quintrec, M.; Muhamed, I.; et al. Endothelial Microparticles and Systemic Complement Activation in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e007818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erdbrügger, U.; Le, T.H. Extracellular Vesicles in Renal Diseases: More than Novel Biomarkers? J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mege, D.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Ouaissi, M.; Robert, S.; Sielezneff, I.; Sastre, B.; Dignat-George, F.; Dubois, C. The origin and concentration of circulating microparticles differ according to cancer type and evolution: A prospective single-center study. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Challa, A.; Noorwali, A.; Bevington, A.; Russell, R.G.G. Cellular phosphate metabolism in patients receiving bisphosphonate therapy. Bone 1986, 7, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanakit, K.; Cushman, M.; Stehman-Breen, C.; Heckbert, S.R.; Folsom, A.R. Chronic kidney disease increases risk for venous thromboembolism. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valdivielso, J.M.; Rodríguez-Puyol, D.; Pascual, J.; Barrios, C.; Bermúdez-López, M.; Sánchez-Niño, M.D.; Pérez-Fernández, M.; Ortiz, A. Atherosclerosis in Chronic Kidney Disease: More, Less, or Just Different? Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 1938–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, A.; Wu, T.; Zeng, C.; Rakheja, D.; Zhu, J.; Ye, T.; Hutcheson, J.; Vaziri, N.D.; Liu, Z.; Mohan, C.; et al. Adverse Effects of Simulated Hyper- and Hypo-Phosphatemia on Endothelial Cell Function and Viability. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, G.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhai, F.; Kok, F.J.; Yang, X. Phytate intake and molar ratios of phytate to zinc, iron and calcium in the diets of people in China. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khokhar, S.; Fenwick, G.R. Phytate content of Indian foods and intakes by vegetarian Indians of Hisar Region, Haryana State. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 2440–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, R.A.; Mehta, O. Phosphorus and Potassium Content of Enhanced Meat and Poultry Products: Implications for Patients Who Receive Dialysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1370–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, R.A.; Mehta, O. Dietary Phosphorus Restriction in Dialysis Patients: Potential Impact of Processed Meat, Poultry, and Fish Products as Protein Sources. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 54, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, C.; Sayre, S.S.; León, J.B.; Machekano, R.; Love, T.E.; Porter, D.; Marbury, M.; Sehgal, A.R. Effect of Food Additives on Hyperphosphatemia Among Patients With End-stage Renal Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. JAMA 2009, 301, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakova, T.; Ix, J.H.; Sprague, S.M.; Raphael, K.L.; Fried, L.; Gassman, J.J.; Raj, D.; Cheung, A.K.; Kusek, J.W.; Flessner, M.F.; et al. Rationale and Approaches to Phosphate and Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 Reduction in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2328–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, E.; Yamamoto, H.; Yamanaka-Okumura, H.; Taketani, Y. Dietary phosphorus in bone health and quality of life. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.W.; Nolte, J.V.; Gaber, A.O.; Suki, W.N. Association of dietary phosphate and serum phosphorus concentration by levels of kidney function. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbasian, N.; Goodall, A.H.; Burton, J.O.; Bursnall, D.; Bevington, A.; Brunskill, N.J. Hyperphosphatemia Drives Procoagulant Microvesicle Generation in the Rat Partial Nephrectomy Model of CKD. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3534. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113534
Abbasian N, Goodall AH, Burton JO, Bursnall D, Bevington A, Brunskill NJ. Hyperphosphatemia Drives Procoagulant Microvesicle Generation in the Rat Partial Nephrectomy Model of CKD. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(11):3534. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113534
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbasian, Nima, Alison H. Goodall, James O. Burton, Debbie Bursnall, Alan Bevington, and Nigel J. Brunskill. 2020. "Hyperphosphatemia Drives Procoagulant Microvesicle Generation in the Rat Partial Nephrectomy Model of CKD" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 11: 3534. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113534
APA StyleAbbasian, N., Goodall, A. H., Burton, J. O., Bursnall, D., Bevington, A., & Brunskill, N. J. (2020). Hyperphosphatemia Drives Procoagulant Microvesicle Generation in the Rat Partial Nephrectomy Model of CKD. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(11), 3534. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113534