From the Reef to the Ocean: Revealing the Acoustic Range of the Biophony of a Coral Reef (Moorea Island, French Polynesia)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Analyses
2.3. Benthic Invertebrate Sounds
2.4. Fish Sounds
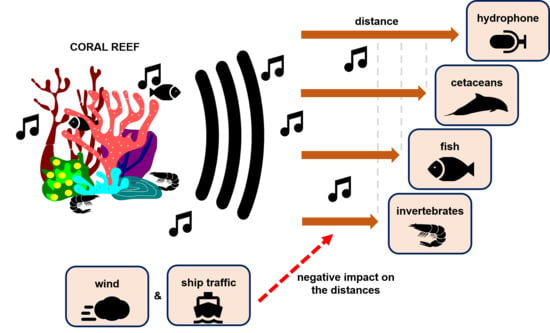
2.5. Propagation Distances of Reef Sounds
2.6. Comparisons with Audiograms
3. Results
3.1. Benthic Invertebrate Sounds
3.2. Fish Sounds
3.3. Propagation Distances of Reef Sounds
3.4. Comparisons with Audiograms: Fish
3.5. Comparisons with Audiograms: Cetaceans
3.6. Comparisons with Audiograms: Invertebrates
4. Discussion
4.1. Diel Pattern
4.2. Propagation Distances
4.3. Wind and Anthropogenic Noise
4.4. Comparisons with Audiograms
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krause, B. Anatomy of the soundscape: Evolving perspectives. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2008, 56, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Pijanowski, B.C.; Farina, A.; Gage, S.H.; Dumyahn, S.L.; Krause, B.L. What is soundscape ecology? An introduction and overview of an emerging new science. Landsc. Ecol. 2011, 26, 1213–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rountree, R.A.; Grant Gilmore, R.; Goudey, C.A.; Hawkins, A.D.; Luczkovich, J.J.; Mann, D.A. Listening to Fish: Applications of Passive Acoustics to Fisheries Science. Fisheries 2006, 31, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquereau, L.; Grall, J.; Chauvaud, L.; Gervaise, C.; Clavier, J.; Jolivet, A.; Di Iorio, L. Sound production and associated behaviours of benthic invertebrates from a coastal habitat in the north-east Atlantic. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart-Smith, R.D.; Bates, A.E.; Lefcheck, J.S.; Duffy, J.E.; Baker, S.C.; Thomson, R.J.; Stuart-Smith, J.F.; Hill, N.A.; Kininmonth, S.J.; Airoldi, L.; et al. Integrating abundance and functional traits reveals new global hotspots of fish diversity. Nature 2013, 501, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobel, P.S.; Kaatz, I.M.; Rice, A.N. Acoustical behavior of coral reef fishes. In Reproduction and Sexuality in Marine Fishes; Cole, K.S., Ed.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 307–348. [Google Scholar]
- Bertucci, F.; Maratrat, K.; Berthe, C.; Besson, M.; Guerra, A.S.; Raick, X.; Lerouvreur, F.; Lecchini, D.; Parmentier, E. Local sonic activity reveals potential partitioning in a coral reef fish community. Oecologia 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.W.L.; Banks, K. The acoustics of the snapping shrimp Synalpheus parneomeris in Kaneohe Bay. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staaterman, E.; Rice, A.N.; Mann, D.A.; Paris, C.B. Soundscapes from a Tropical Eastern Pacific reef and a Caribbean Sea reef. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leis, J.; Sweatman, H.; Reader, S. What the Pelagic Stages of Coral Reef Fishes Are Doing out in Blue Water: Daytime Field Observations of Larval Behavioural Capabilities. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1996, 47, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobutzki, I.C.; Bellwood, D.R. Nocturnal orientation to reefs by late pelagic stage coral reef fishes. Coral Reefs 1998, 17, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrberg, A.A.; Fuiman, L.A. The Sensory World of Coral Reef Fishes. In Coral Reef Fishes; Elsevier Science: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 123–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.A.; Casper, B.M.; Boyle, K.S.; Tricas, T.C. On the attraction of larval fishes to reef sounds. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 338, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, B.F.; Penrose, J.D. The Puerulus Stage of the Spiny (Rock) Lobster and its Ability to Locate the Coast; Western Australian Institute of Technology, School of Physics and Geosciences: Perth, Australia, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, K.J.; Higgs, D.M.; Cato, D.H.; Leis, J.M. Auditory sensitivity in settlement-stage larvae of coral reef fishes. Coral Reefs 2010, 29, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilges, K.; Potty, G.; Freeman, S.; Freeman, L.; Van Uffelen, L. Measurements and models of acoustic transmission loss on two Hawaiian coral reefs. In Proceedings of the Meetings on Acoustics 178ASA, San Diego, CA, USA, 2–6 December 2019; Volume 39, p. 070005. [Google Scholar]
- Stevick, P.; McConnell, B.; Hammond, P. Patterns of Movement. In Marine Mammal Biology: An Evolutionary Approach; Hoelzel, A.R., Ed.; Blackwell: Malden, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 185–216. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.A.; Prieto, R.; Magalhães, S.; Seabra, M.I.; Santos, R.S.; Hammond, P.S. Ranging patterns of bottlenose dolphins living in oceanic waters: Implications for population structure. Mar. Biol. 2008, 156, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Opzeeland, I.; Slabbekoorn, H. Importance of Underwater Sounds for Migration of Fish and Aquatic Mammals. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer Nature: London, UK, 2012; Volume 730, pp. 357–359. [Google Scholar]
- Crane, N.L.; Lashkari, K. Sound production of gray whales, Eschrichtius robustus, along their migration route: A new approach to signal analysis. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 100, 1878–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann Nichole, A. An Investigation of the Roles of Geomagnetic and Acoustic Cues in Whale Navigation and Orientation, Joint Program in Oceanography/Applied Ocean Science and Engineering; Department of Biology, Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA; The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution: Falmouth, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- van den Thillart, G.; Dufour, S.; Rankin, J.C. Spawning Migration of the European Eel; van den Thillart, G., Dufour, S., Rankin, J.C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; ISBN 978-1-4020-9094-3. [Google Scholar]
- Leis, J.M.; McCormick, M.I. The Biology, Behavior, and Ecology of the Pelagic, Larval Stage of Coral Reef Fishes. Coral Reef Fishes 2002, 1, 171–199. [Google Scholar]
- Shanks, A.L. Pelagic Larval Duration and Dispersal Distance Revisited. Biol. Bull. 2009, 216, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nozais, C.; Duchêne, J.C.; Bhaud, M. Control of position in the water column by the larvae of Poecilochaetus serpens, (Polychaeta): The importance of mucus secretion. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 1997, 210, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.D.; Meekan, M.G.; Jeffs, A.; Montgomery, J.C.; McCauley, R.D. Settlement-stage coral reef fish prefer the higher-frequency invertebrate-generated audible component of reef noise. Anim. Behav. 2008, 75, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, P.; Berenshtein, I.; Besson, M.; Roux, N.; Parmentier, E.; Lecchini, D. From the ocean to a reef habitat: How do the larvae of coral reef fishes find their way home? State Art Latest Adv. 2015, 65, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Havel, L.N.; Fuiman, L.A. Depth Preference of Settling Red Drum (Sciaenops ocellatus) Larvae in Relation to Benthic Habitat Color and Water-Column Depth. Estuaries Coasts 2017, 40, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixson, D.L.; Jones, G.P.; Munday, P.L.; Pratchett, M.S.; Srinivasan, M.; Planes, S.; Thorrold, S.R. Terrestrial chemical cues help coral reef fish larvae locate settlement habitat surrounding islands. Ecol. Evol. 2011, 1, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixson, D.L.; Jones, G.P.; Munday, P.L.; Planes, S.; Pratchett, M.S.; Srinivasan, M.; Syms, C.; Thorrold, S.R. Coral reef fish smell leaves to find island homes. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 275, 2831–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, G.; Atema, J.; Kingsford, M.J.; Black, K.P.; Miller-sims, V. Smelling home can prevent dispersal of reef fish larvae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lecchini, D.; Mills, S.C.; Brié, C.; Maurin, R.; Banaigs, B. Ecological determinants and sensory mechanisms in habitat selection of crustacean postlarvae. Behav. Ecol. 2010, 21, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecchini, D.; Planes, S.; Galzin, R. Experimental assessment of sensory modalities of coral-reef fish larvae in the recognition of their settlement habitat. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2005, 58, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leis, J.M.; Carson-Ewart, B.M. Complex behaviour by coral-reef fish larvae in open-water and near-reef pelagic environments. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1998, 53, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leis, J.M.; Carson-Ewart, B.M. In situ swimming and settlement behaviour of larvae of an Indo-Pacific coral-reef fish, the coral trout Plectropomus leopardus (Pisces: Serranidae). Mar. Biol. 1999, 134, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecchini, D.; Peyrusse, K.; Lanyon, R.G.; Lecellier, G. Importance of visual cues of conspecifics and predators during the habitat selection of coral reef fish larvae. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2014, 337, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeij, M.J.A.; Marhaver, K.L.; Huijbers, C.M.; Nagelkerken, I.; Simpson, S.D. Coral larvae move toward reef sounds. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lillis, A.; Bohnenstiehl, D.; Peters, J.W.; Eggleston, D. Variation in habitat soundscape characteristics influences settlement of a reef-building coral. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apprill, A.; Lillis, A.; Suca, J.J.; Llopiz, J.K.; Mooney, T.A.; Becker, C. Soundscapes influence the settlement of the common Caribbean coral Porites astreoides irrespective of light conditions. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 181358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lillis, A.; Eggleston, D.B.; Bohnenstiehl, D.R. Oyster larvae settle in response to habitat-associated underwater sounds. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eggleston, D.B.; Lillis, A.; Bohnenstiehl, D.R. Soundscapes and Larval Settlement: Larval Bivalve Responses to Habitat-Associated Underwater Sounds. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life II; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa, I.A.; Green, B.S.; Gardner, C.; Hesse, J.; Stanley, J.A.; Jeffs, A.G. Reef sound as an orientation cue for shoreward migration by pueruli of the rock lobster, Jasus edwardsii. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, C.A.; Jeffs, A.G.; Montgomery, J.C. Directional swimming behavior by five species of crab postlarvae in response to reef sound. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2007, 80, 369–378. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffs, A.; Tolimieri, N.; Montgomery, J.C. Crabs on cue for the coast: The use of underwater sound for orientation by pelagic crab stages. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2003, 54, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, C.A.; Tindle, C.T.; Montgomery, J.C.; Jeffs, A.G. Modelling a reef as an extended sound source increases the predicted range at which reef noise may be heard by fish larvae. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 438, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simpson, S.D.; Meekan, M.; Montgomery, J.; McCauley, R.; Jeffs, A. Homeward sound. Science 2005, 308, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolimieri, N.; Jeffs, A.; Montgomery, J.C. Ambient sound as a cue for navigation by the pelagic larvae of reel fishes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 207, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leis, J.M.; Carson-Ewart, B.M.; Cato, D.H. Sound detection in situ by the larvae of a coral-reef damselfish (Pomacentridae). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 232, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leis, J.M.; Carson-Ewart, B.M.; Hay, A.C.; Cato, D.H. Coral-reef sounds enable nocturnal navigation by some reef-fish larvae in some places and at some times. J. Fish. Biol. 2003, 63, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, E.; Berten, L.; Rigo, P.; Aubrun, F.; Nedelec, S.L.; Simpson, S.D.; Lecchini, D. The influence of various reef sounds on coral-fish larvae behaviour. J. Fish. Biol. 2015, 86, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lossent, J.; Di Iorio, L.; Valentini-Poirier, C.; Boissery, P.; Gervaise, C. Mapping the diversity of spectral shapes discriminates between adjacent benthic biophonies. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 585, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervaise, C.; Lossent, J.; Valentini-Poirier, C.A.; Boissery, P.; Noel, C.; Di Iorio, L. Three-dimensional mapping of the benthic invertebrates biophony with a compact four-hydrophones array. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council, N.R. Ocean Noise and Marine Mammals; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kinda, G.B.; Simard, Y.; Gervaise, C.; Mars, J.I.; Fortier, L. Under-ice ambient noise in Eastern Beaufort Sea, Canadian Arctic, and its relation to environmental forcing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenz, G.M. Acoustic Ambient Noise in the Ocean: Spectra and Sources. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1962, 34, 1936–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervaise, C.; Simard, Y.; Roy, N.; Kinda, B.; Ménard, N. Shipping noise in whale habitat: Characteristics, sources, budget, and impact on belugas in Saguenay–St. Lawrence Marine Park hub. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cato, D.H. Marine biological choruses observed in tropical waters near Australia. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1978, 64, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iorio, L.; Raick, X.; Parmentier, E.; Boissery, P.; Valentini-Poirier, C.-A.; Gervaise, C. ‘Posidonia meadows calling’: A ubiquitous fish sound with monitoring potential. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 4, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ainslie, M.A.; McColm, J.G. A simplified formula for viscous and chemical absorption in sea water. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 103, 1671–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelec, S.L.; Campbell, J.; Radford, A.N.; Simpson, S.D.; Merchant, N.D. Particle motion: The missing link in underwater acoustic ecology. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egner, S.A.; Mann, D.A. Auditory sensitivity of sergeant major damselfish Abudefduf saxatilis from post-settlement juvenile to adult. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 285, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yost, W.A. Fundamentals of Hearing; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000; ISBN 9780127756950. [Google Scholar]
- Zwicker, E.; Flottorp, G.; Stevens, S.S. Critical Band Width in Loudness Summation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1957, 29, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.J.; Higgs, D.M.; Belanger, A.J.; Leis, J.M. Auditory and olfactory abilities of pre-settlement larvae and post-settlement juveniles of a coral reef damselfish (Pisces: Pomacentridae). Mar. Biol. 2005, 147, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.J.; Higgs, D.M.; Leis, J.M. Ontogenetic and interspecific variation in hearing ability in marine fish larvae. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 424, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, K.A.; Nachtigall, P.E.; Mooney, T.A.; Supin, A.Y.; Yuen, M.M.L. A Portable System for the Evaluation of the Auditory Capabilities of Marine Mammals. Aquat. Mamm. 2007, 33, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, T.N. Ontogenetic changes in the auditory sensitivity of damselfishes (pomacentridae). J. Comp. Physiol. A Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 1996, 179, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.J.; Higgs, D.M.; Belanger, A.J.; Leis, J.M. Auditory and olfactory abilities of larvae of the Indo-Pacific coral trout Plectropomus leopardus (Lacepède) at settlement. J. Fish. Biol. 2008, 72, 2543–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colleye, O.; Kéver, L.; Lecchini, D.; Berten, L.; Parmentier, E. Auditory evoked potential audiograms in post-settlement stage individuals of coral reef fishes. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2016, 483, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J.C.; Jeffs, A.; Simpson, S.D.; Meekan, M.; Tindle, C. Sound as an Orientation Cue for the Pelagic Larvae of Reef Fishes and Decapod Crustaceans. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2006, 51, 143–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, C.A.; Montgomery, J.C.; Caiger, P.; Higgs, D.M. Pressure and particle motion detection thresholds in fish: A re-examination of salient auditory cues in teleosts. J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 215, 3429–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wysocki, L.E.; Codarin, A.; Ladich, F.; Picciulin, M. Sound pressure and particle acceleration audiograms in three marine fish species from the Adriatic Sea. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 126, 2100–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chapman, C.J.; Sand, O. Field studies of hearing in two species of flatfish Pleuronectes platessa (L.) and Limanda limanda (L.) (family pleuronectidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1974, 47, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacini, A.F.; Nachtigall, P.E.; Quintos, C.T.; Schofield, T.D.; Look, D.A.; Levine, G.A.; Turner, J.P. Audiogram of a stranded Blainville’s beaked whale (Mesoplodon densirostris) measured using auditory evoked potentials. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 2409–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greenhow, D.R.; Brodsky, M.C.; Lingenfelser, R.G.; Mann, D.A. Hearing threshold measurements of five stranded short-finned pilot whales (Globicephala macrorhynchus). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 135, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastelein, R.A.; Hagedoorn, M.; Au, W.W.L.; de Haan, D. Audiogram of a striped dolphin (Stenella coeruleoalba). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 113, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houser, D.S.; Helweg, D.A.; Moore, P.W.B. A bandpass filter-bank model of auditory sensitivity in the humpback whale. Aquat. Mamm. 2001, 27, 82–91. [Google Scholar]
- Randall Hughes, A.; Mann, D.A.; Kimbro, D.L. Predatory fish sounds can alter crab foraging behaviour and influence bivalve abundance. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breithaupt, T.; Tautz, J. Vibration sensitivity of the crayfish statocyst. Naturwissenschaften 1988, 75, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, J.M.; Findlay, M.M.; Moate, R.M.; Yan, H.Y. The hearing abilities of the prawn Palaemon serratus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2005, 140, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.Y.; Yan, H.Y.; Chung, W.S.; Shiao, J.C.; Hwang, P.P. Acoustically evoked potentials in two cephalopods inferred using the auditory brainstem response (ABR) approach. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2009, 153, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, T.A.; Al, E. Sound detection b the longfin squid (Loligo pealeii) studied with auditory evoked potentials: Sensitivity to low-frequency particle motion and not pressure. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 3748–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Budelmann, B.U.; Bleckmann, H. A lateral line analogue in cephalopods: Water waves generate microphonic potentials in the epidermal head lines of Sepia and Lolliguncula. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1988, 164, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piercy, J.J.B.; Codling, E.A.; Hill, A.J.; Smith, D.J.; Simpson, S.D. Habitat quality affects sound production and likely distance of detection on coral reefs. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 516, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertucci, F.; Parmentier, E.; Berten, L.; Brooker, R.M.; Lecchini, D. Temporal and spatial comparisons of underwater sound signatures of different reef habitats in Moorea Island, French Polynesia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, M.B.; Mooney, T.A. Coral reef soundscapes may not be detectable far from the reef. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, J.A.; Radford, C.A.; Jeffs, A.G. Behavioural response thresholds in New Zealand crab megalopae to ambient underwater sound. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holles, S.H.; Simpson, S.D.; Radford, A.N.; Berten, L.; Lecchini, D. Boat noise disrupts orientation behaviour in a coral reef fish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 485, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simpson, S.D.; Radford, A.N.; Holles, S.; Ferarri, M.C.O.; Chivers, D.P.; Mccormick, M.I.; Meekan, M.G. Small-boat noise impacts natural settlement behavior of coral reef fish larvae. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life II; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 875, pp. 1041–1048. ISBN 978-1-4939-2980-1. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, S.E.; Clarke, J.T. Potential impact of offshore human activities on gray whales. J. Cetacean Res. Manag. 2002, 4, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, C.; Jeffs, A.; Tindle, C.; Montgomery, J.C. Resonating sea urchin skeletons create coastal choruses. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 362, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fay, R.R. The goldfish ear codes the axis of acoustic particle motion in three dimensions. Science 1984, 225, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horodysky, A.Z.; Brill, R.W.; Fine, M.L.; Musick, J.A.; Latour, R.J. Acoustic pressure and particle motion thresholds in six sciaenid fishes. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 1504–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Norris, K.S. Some observations on the migration and orientation of marine mammals. In Animal Orientation and Navigation, Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh Annual Biology Colloquium, Corvallis, OR, USA, 6–7 May 1966; Storm, R.M., Ed.; Oregon State University Press: Corvallis, OR, USA, 1966; pp. 101–125. [Google Scholar]
- Au, W.W.L.; Hastings, M.C. Principles of Marine Bioacoustics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-387-78364-2. [Google Scholar]








| Band (kHz) | Feature | Equation | R2 | Value at 1 m | Value at 10 km | Δ Night |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (dB re 1 µPa) | ||||||
| 3.5–5.5 | ANL | y = −8.99 log10x + 121.97 | 0.85 | 121.97 | 86.01 | 7.92 |
| SPL | y = −10.01 log10x + 147.23 | 0.83 | 147.23 | 107.19 | 6.81 | |
| 6–8 | ANL | y = −10.22 log10x + 121.79 | 0.88 | 121.79 | 80.91 | 6.73 |
| SPL | y = −11.13 log10x + 146.72 | 0.84 | 146.72 | 102.20 | 5.60 | |
| 10–13 | ANL | y = −13.84 log10x + 130.29 | 0.94 | 130.29 | 74.93 | 6.22 |
| SPL | y = −14.50 log10x + 155.64 | 0.93 | 155.64 | 97.64 | 5.72 | |
| 14–17 | ANL | y = −16.42 log10x + 135.74 | 0.96 | 135.74 | 70.06 | 6.24 |
| SPL | y = −16.80 log10x + 160.45 | 0.95 | 160.45 | 93.25 | 5.71 | |
| Distance from the Reef Crest (km) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day | Night | ||||||||||
| Band (kHz) | Feature | 0 kn | 3 kn | 6 kn | 9 kn | 12 kn | 0 kn | 3 kn | 6 kn | 9 kn | 12 kn |
| 3.5–5.5 | ANL | 65 | 39 | 28 | 20 | 13 | 90 | 65 | 54 | 46 | 39 |
| SPL | 134 | 108 | 97 | 90 | 82 | 156 | 130 | 120 | 111 | 104 | |
| SPL–10 | 101 | 75 | 65 | 56 | 50 | 123 | 97 | 87 | 79 | 72 | |
| γANL | 59 | 33 | 22 | 15 | 8.4 | 81 | 55 | 45 | 36 | 30 | |
| γQ0.50 | 54 | 28 | 18 | 9.8 | 6.0 | 76 | 50 | 39 | 31 | 24 | |
| γQ0.90 | 71 | 46 | 35 | 27 | 20 | 92 | 66 | 56 | 47 | 40 | |
| 6–8 | ANL | 43 | 26 | 19 | 13 | < 10 | 58 | 40 | 33 | 28 | 23 |
| SPL | 90 | 72 | 65 | 60 | 55 | 102 | 84 | 77 | 72 | 67 | |
| SPL–10 | 68 | 50 | 43 | 38 | 33 | 80 | 63 | 55 | 50 | 45 | |
| γANL | 40 | 22 | 15 | 9.7 | 7.0 | 52 | 35 | 27 | 22 | 17 | |
| γQ0.50 | 36 | 19 | 12 | 6.1 | 4.4 | 48 | 31 | 24 | 18 | 14 | |
| γQ0.90 | 48 | 30 | 23 | 18 | 13 | 59 | 42 | 35 | 29 | 25 | |
| 10–13 | ANL | 23 | 14 | <10 | <10 | <10 | 31 | 21 | 17 | 14 | 12 |
| SPL | 50 | 41 | 37 | 34 | 31 | 57 | 48 | 44 | 41 | 38 | |
| SPL–10 | 38 | 29 | 25 | 22 | 19 | 45 | 36 | 32 | 29 | 26 | |
| γANL | 21 | 12 | 7.5 | 5.0 | 3.5 | 28 | 18 | 15 | 12 | <10 | |
| γQ0.50 | 19 | 10 | 5.9 | 4.0 | 2.8 | 26 | 17 | 13 | <10 | <10 | |
| γQ0.90 | 26 | 16 | 13 | 9.6 | 6.9 | 32 | 23 | 19 | 16 | 14 | |
| 14–17 | ANL | 16 | 10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | 21 | 15 | 13 | 11 | <10 |
| SPL | 34 | 28 | 26 | 24 | 22 | 38 | 32 | 30 | 28 | 26 | |
| SPL–10 | 26 | 20 | 18 | 16 | 14 | 31 | 25 | 22 | 20 | 19 | |
| γANL | 15 | 9.0 | 5.7 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 20 | 14 | 11 | <10 | <10 | |
| γQ0.50 | 14 | 7.4 | 4.7 | 3.3 | 2.5 | 19 | 13 | 10 | <10 | <10 | |
| γQ0.90 | 19 | 13 | 10 | 7.5 | 5.6 | 23 | 17 | 14 | 13 | 11 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raick, X.; Di Iorio, L.; Gervaise, C.; Lossent, J.; Lecchini, D.; Parmentier, É. From the Reef to the Ocean: Revealing the Acoustic Range of the Biophony of a Coral Reef (Moorea Island, French Polynesia). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040420
Raick X, Di Iorio L, Gervaise C, Lossent J, Lecchini D, Parmentier É. From the Reef to the Ocean: Revealing the Acoustic Range of the Biophony of a Coral Reef (Moorea Island, French Polynesia). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(4):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040420
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaick, Xavier, Lucia Di Iorio, Cédric Gervaise, Julie Lossent, David Lecchini, and Éric Parmentier. 2021. "From the Reef to the Ocean: Revealing the Acoustic Range of the Biophony of a Coral Reef (Moorea Island, French Polynesia)" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 4: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040420
APA StyleRaick, X., Di Iorio, L., Gervaise, C., Lossent, J., Lecchini, D., & Parmentier, É. (2021). From the Reef to the Ocean: Revealing the Acoustic Range of the Biophony of a Coral Reef (Moorea Island, French Polynesia). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(4), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040420