Changes in Acid Herbicide Concentrations in Urban Streams after a Cosmetic Pesticides Ban
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Monitoring Sites

2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Laboratory Analyses
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Detection
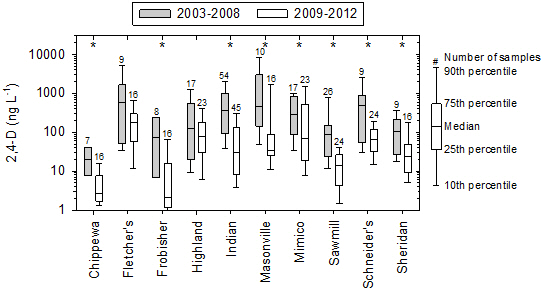
3.2. Temporal Changes
3.3. Land Use Influences



| Stream | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°W) | Area (km2) | Urban (%) | Agriculture (%) | Golf Course (%) | Population Density (km km2) | Road Density (km km−2) | Stream Density (km km2) | Mean Flow (m3 s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chippewa | 46.300 | −79.461 | 40.2 | 38 | 0 | 1.2 | 463 | 4.0 | 1.2 | 0.6 |
| Fletcher’s | 43.659 | −79.741 | 31.2 | 58 | 38 | 0 | 2,799 | 4.1 | 2.5 | n/a |
| Frobisher | 46.484 | −80.936 | 4.4 | 35 | 0 | 0 | 869 | 5.0 | 0.6 | n/a |
| Highland | 43.779 | −79.191 | 74.8 | 89 | 0 | 0 | 3,945 | 9.2 | 0.8 | 1.2 |
| Indian | 43.316 | −79.811 | 22.3 | 73 | 4 | 1.7 | 1,466 | 8.2 | 3.2 | n/a |
| Masonville | 43.018 | −81.268 | 1.4 | 69 | 0 | 0 | 1,815 | 5.1 | 2.6 | n/a |
| Mimico | 43.646 | −79.517 | 60.0 | 96 | 0 | 1.6 | 1,525 | 7.8 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| Sawmill | 45.390 | −75.676 | 21.6 | 71 | 0 | 0 | 1,766 | 8.8 | 1.4 | 0.3 |
| Schneider’s | 43.438 | −80.473 | 30.1 | 91 | 4 | 0 | 2,739 | 8.9 | 0.9 | 0.4 |
| Sheridan | 43.516 | −79.615 | 8.3 | 97 | 0 | 0 | 1,784 | 10.0 | 0.6 | n/a |
| Variable | Equation | r2 a | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| log102,4-Dpre-ban | −1.65 + 1.21log10(population density) | 0.46 | 6.8 | 0.03 |
| log10dicambapre-ban | −2.31 + 1.07log10(population density) + 0.97log10(stream density) | 0.36, 0.63 | 5.9 | 0.03 |
| log10mecoproppre-ban | −1.31 + 1.03log10(population density) | 0.40 | 5.3 | 0.05 |
| log102,4-Dpost-ban | −7.04 + 1.60log10(population density) + 0.77log10(%golf + 1) − 2.09log10(road density) + 2.67log10(% urban) +0.20log10(%agriculture + 1) | 0.74, 0.87, 0.93, 0.98, 0.99 | 165 | <0.001 |
| log10dicambapost-ban | −5.78 + 3.28log10(%urban) + 0.55log10(% agriculture+1) | 0.63, 0.83 | 17.6 | 0.002 |
| log10mecoproppost-ban | −3.71 + 1.51log10(population density) + 1.03log10(%golf + 1) + 0.26log10(%agriculture + 1) | 0.65, 0.85, 0.93 | 27.9 | <0.001 |
3.4. Herbicide Ratios
4. Discussion
4.1. Detection
4.2. Sources
4.3. Influence of Pesticides Regulation
4.4. Influence on Aquatic Ecosystems
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Supporting Information Available
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skark, C.; Zullei-Seibert, N.; Willme, U.; Gatzemann, U.; Schlett, C. Contribution of non-agricultural pesticides to pesticide load in surface water. Pest Manag. Sci. 2004, 60, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.S.; Capel, P.D.; Larson, S.J. Comparison of pesticide use in eight U.S. urban streams. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2000, 19, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.J.; Bode, R.W. Pesticides in surface water runoff in south-eastern New York State: Seasonal and stormflow effects on concentrations. Pest Manag. Sci. 2004, 60, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliom, R.J.; Barbash, J.E.; Crawford, C.G.; Hamilton, P.A.; Martin, J.D.; Nakagaki, N.; Nowell, L.H.; Scott, J.C.; Stackelberg, P.E.; Thelin, G.P.; et al. The Quality of Our Nation’s Waters—Pesticides in the Nation’s Streams and Ground Water, 1992–2001; Circular 1291; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sprague, L.A.; Nowell, L.H. Comparison of pesticide concentrations in streams at low flow in six metropolitan areas of the United States. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchoud, H.; Farrugia, F.; Mouchel, J.M. Pesticide uses and transfers in urbanized catchments. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, K.E.; Hunter, D.H.; Wachal, D. Chlorpyrifos in surface waters before and after a federally mandated ban. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, K.E.; Hunter, D.H.; Wachal, D. Diazinon in surface waters before and after a federally-mandated ban. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 350, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.J.; Ator, S.W.; Nystrom, E.A. Temporal changes in surface-water insecticide concentrations after the phaseout of diazinon and chlorpyrifos. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4246–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesticide Product Information System. Available online: http://app.ene.gov.on.ca/pepsis/ (accessed on 14 January 2010).
- Hunter, C.; McGee, B. Survey of Pesticide Use in Ontario, 1993; Ontario Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Struger, J.; Fletcher, T. Occurrence of lawn care and agricultural pesticides in the Don River and Humber River watersheds (1998–2002). J. Great Lakes Res. 2007, 33, 887–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glozier, N.E.; Struger, J.; Cessna, A.J.; Gledhill, M.; Rondeau, M.; Ernst, W.R.; Sekela, M.A.; Cagampan, S.J.; Sverko, E.; Murphy, C.; et al. Occurrence of glyphosate and acidic herbicides in select urban rivers and streams in Canada, 2007. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 19, 821–834. [Google Scholar]
- HYDAT Database. Available online: http://www.ec.gc.ca/rhc-wsc/ (accessed on 11 August 2013).
- Final Evaluation of Toronto’s Pesticide Bylaw and Summary of New Provincial Pesticide Regulation. Available online: http://www.toronto.ca/legdocs/mmis/2009/hl/bgrd/backgroundfile-21099.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2014).
- Woudneh, M.B.; Sekela, M.; Tuominen, T.; Gledhill, M. Isotope dilution high-resolution gas chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry method for analysis of selected acidic herbicides in surface water. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1133, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, D.B.; Cessna, A.J.; Sverko, E.; Glozier, N.E. Pesticides in surface drinking-water supplies of the northern Great Plains. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woudneh, M.B.; Ou, Z.; Sekela, M.; Tuominen, T.; Gledhill, M. Pesticide multiresidues in waters of the Lower Fraser Valley, British Columbia, Canada. Part II. Groundwater. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life. Available online: http://ceqg-rcqe.ccme.ca/ (accessed on 12 March 2014).
- Proposed EQS for Water Framework Directive Annex VIII Substances: Mecoprop. Available online: http://a0768b4a8a31e106d8b0-50dc802554eb38a24458b98ff72d550b.r19.cf3.rackcdn.com/scho1110bteo-e-e.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2014).
- Helsel, D.R.; Hirsch, R.M. Statistical Methods in Water Resources, Techniques of Water Resources Investigations of the United States Geological Survey; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, R.P.; Baker, D.B. Pesticide concentration patterns in agricultural drainage networks in the Lake Erie Basin. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1993, 12, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, C.G. Factors affecting pesticide occurrence and transport in a large midwestern river basin. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosin, M.C.; Calderon, M.J.; Real, M.; Cornejo, J. Impact of herbicides uses in olive groves on waters of the Guadalquivir river basin (southern Spain). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 164, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Households and the Environment Survey, 1994, 2006, 2007, 2009. Available online: http://www.statcan.gc.ca/ (accessed on 22 August 2013).
- Battaglin, W.; Fairchild, J. Potential toxicity of pesticides measured in midwestern streams to aquatic organisms. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Laetz, C.A.; Baldwin, D.H.; Collier, T.K.; Hebert, V.; Stark, J.D.; Scholz, N.L. The synergistic toxicity of pesticide mixtures: Implications for risk assessment and the conservation of endangered Pacific salmon. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, K.B.; Sekela, M.A.; Cobbler, C.E.; Xhabija, B.; Gledhill, M.; Ananvoranich, S.; Zieleinski, B.S. Evidence for behavioral preference toward environmental concentrations of urban-use herbicides in a model adult fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 2046–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Todd, A.; Struger, J. Changes in Acid Herbicide Concentrations in Urban Streams after a Cosmetic Pesticides Ban. Challenges 2014, 5, 138-151. https://doi.org/10.3390/challe5010138
Todd A, Struger J. Changes in Acid Herbicide Concentrations in Urban Streams after a Cosmetic Pesticides Ban. Challenges. 2014; 5(1):138-151. https://doi.org/10.3390/challe5010138
Chicago/Turabian StyleTodd, Aaron, and John Struger. 2014. "Changes in Acid Herbicide Concentrations in Urban Streams after a Cosmetic Pesticides Ban" Challenges 5, no. 1: 138-151. https://doi.org/10.3390/challe5010138
APA StyleTodd, A., & Struger, J. (2014). Changes in Acid Herbicide Concentrations in Urban Streams after a Cosmetic Pesticides Ban. Challenges, 5(1), 138-151. https://doi.org/10.3390/challe5010138