Urban Saturated Power Load Analysis Based on a Novel Combined Forecasting Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Basic Principle of CFM for Saturated Power Load Analysis
2.1. Basic Principle of the Logistic Curve Model

2.2. Basic Principle of the Multi-Dimensional Saturated Power Load Forecasting Model (MSPLF)
2.3. Basic Principle of the CFM
- (1)
- Initialization parameters.The maximum iteration number maxgen, the population size sizepop, the initial fruit fly swarm location (X_axis, Y_axis), and the random flight distance range FR are determined first.
- (2)
- Evolution starts.Set i = 1, gen = 0, and give the random flight direction rand() and the flight distance for food finding for an individual fruit fly i. In the hybrid forecasting model, two variables (X(i,:), Y(i,:)) are employed to represent the flight distance for food finding for an individual fruit fly i, and set X(i,:) = X_axis + 20*rand() − 10, Y(i,:) = Y_axis + 20*rand() − 10, respectively.
- (3)
- Preliminary calculations.Update the coordinate (X(i,:), Y(i,:)) of the i-th fly fruit, calculate the distance Disti of the fruit fly i to the origin, and then calculate the smell concentration judgment value Si. In the hybrid forecasting model, (D(i,1), D(i,2)) is employed to represent Disti, and set D(i,1) = (X(i,1)2 + Y(i,1)2)0.5, D(i,2) = (X(i,2)2 + Y(i,2)2)0.5, respectively. Similarly, (S(i,1), S(i,2)) is used to represent Si in the hybrid forecasting model, and set S(i,1) = 1/D(i,1), S(i,2) = 1/D(i,2), respectively. Then, input Si into the hybrid forecasting model for power load forecasting. In the hybrid forecasting model, the parameters [w1, w2] are represented by [S(i,1), S(i,2)], and we set w1 = S(i,1) and w2 = S(i,2), respectively. According to the power load forecasting result, the smell concentration Smelli (also called the fitness function value) can be calculated. The Smelli is employed by Equation (12), which measures the deviations between the forecasting values and actual values.where n is the number of forecasting periods; is the actual value at period i; and denotes the forecasting value of the logistic curve model and MSPLF model at period i, respectively; and and are the weight of the logistic curve model and MSPLF model in the hybrid model, respectively.
- (4)
- Population iteration.Set i = i + 1 and repeat (3). When i equals the population size, find and keep the minimum smell concentration value among the fruit fly swarm, and update (X_axis, Y_axis) and Smellbest.
- (5)
- Offspring generation.Generate the offspring generation, and input the offspring into the hybrid forecasting model and calculate the smell concentration value again. Set gen = gen + 1.
- (6)
- Circulation stops.When gen reaches the max iterative number, the stop criterion is satisfied and the optimal parameters and of CFM are obtained. Otherwise, go back to (3).

3. Forecasting Performance Test of Proposed CFM

3.1. Forecasting Result of the Logistic Curve Model

| Year | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual maximum power load (104 kW) | 1461 | 1576 | 1698 | 1827 | 1962 | 2104 | 2252 |
3.2. Forecasting Result of the MSPLF Model
| Year | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual maximum power load (104 kW) | 1383 | 1567 | 1763 | 1968 | 2235 | 2541 | 2830 |
3.3. Forecasting Result of the CFM

| Year | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual maximum power load (104 kW) | 1426 | 1572 | 1727 | 1890 | 2083 | 2298 | 2508 |
3.4. Comparison of Forecasting Results


4. Empirical Analysis of Saturated Power Load
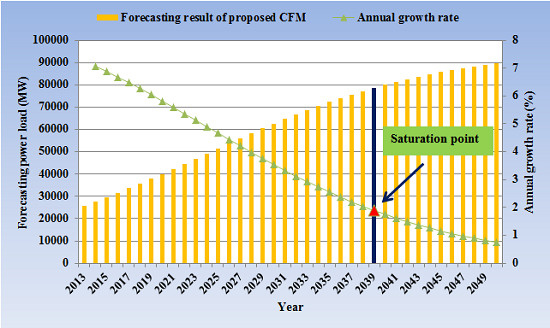
4.1. Forecasting Result for Power Load from 2013 to 2050







4.2. Saturation Analysis
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The forecasting accuracy of the proposed combined forecasting model in this paper is much higher than that of the single logistic curve model and multi-dimensional saturated power load forecasting model, which indicates the proposed CFM is more suitable for saturated power load analysis;
- (2)
- The annual maximum power load of Hubei Province will reach saturation in 2039, at which time the growth rate of the annual maximum power load will fall to 1.898%, and the annual maximum power load, GDP per capita, SVSG and urbanization rate will reach 78,629.25 MW, 70,561.03 RMB per capita, 51.8% and 78.18%, respectively.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amin, S.M.; Wollenberg, B.F. Toward a smart grid: Power delivery for the 21st century. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2005, 3, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, W.; Yuan, Z. City’s Power Planning Methods at the Stage of Load Saturation and Its Application in Jinan Power Grid. Power Syst. Technol. 2007, 31, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, K.; Li, J.; Zhao, B.; Liu, H. Research on City Saturated Load and its Forecast Methods. Electr. Power Technol. Econ. 2008, 20, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Li, X. City future saturated load forecasting based model of saturated load density. J. Fuzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci. Edition) 2008, 36, 532–536. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, N. Survey of saturated load analysis technology for urban power system and its application. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2014, 34, 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y. Saturated Load Forecasting Based on Per Capita Electricity Consumption and Per Capita Electricity Load. East China Electr. Power 2014, 42, 661–664. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Li, S.; Tan, Y.; Zhao, F.; Hou, F. Improved parametric estimation of logistic model for saturated load forecast. In Proceedings of IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, Shanghai, China, 26–28 March 2012.
- Bai, C. Application of improved GM (1, 1) power model to middle and long term load forecasting. Water Resour. Power 2011, 29, 177–179. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H. Research and application of nonlinear regression correct model in sudden change load forecasting. Math. Pract. Theory 2008, 38, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- He, H. Forecasting the urban saturated load based on the analysis of land-use change. Master’s Thesis, North China Electric Power University, Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Fang, T. The application of per-person electricity consumption method in saturation load forecasting. Power Demand Side Manag. 2012, 14, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Wu, L.; Dai, A.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y. Combined saturation load forecast model based on system dynamics and econometrics. Power Demand Side Manag. 2010, 12, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. The Research of Saturation Load Analysis Techniques and its Application. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, J.M.; Granger, C.W.J. Combination of forecasts. Oper. Res. Q. 1969, 20, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.J.; Shih, K.R. Short-term load forecasting via ARMA model identification including non-Gaussian process considerations. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2003, 18, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, P.F.; Hong, W.C. Forecasting regional electricity load based on recurrent support vector machines with genetic algorithms. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2005, 74, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Youn, H.S.; Kang, Y.C. Short-term load forecasting for special days in anomalous load conditions using neural networks and fuzzy inference method. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2000, 15, 559–565. [Google Scholar]
- Hanmandlu, M.; Chauhan, B.K. Load forecasting using hybrid models. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 26, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.N.; Lee, C.M. Short-term load forecasting using SVR (support vector regression)-based radial basis function neural network with dual extended Kalman filter. Energy 2013, 49, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selakov, A.; Cvijetinović, D.; Milović, L.; Mellon, S.; Bekut, D. Hybrid PSO–SVM method for short-term load forecasting during periods with significant temperature variations in city of Burbank. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 16, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Validity Theory of Combined Forecasting Model and Its Application; Beijing Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lemeshow, S.; Hosmer, D.W. A review of goodness of fit statistics for use in the development of logistic regression models. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1982, 115, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mood, C. Logistic regression: Why we cannot do what we think we can do, and what we can do about it. Eur. Sociol. Rev. 2010, 26, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.; Lee, S. Delineation of landslide hazard areas on Penang Island, Malaysia, by using frequency ratio, logistic regression, and artificial neural network models. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 60, 1037–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.T. A new fruit fly optimization algorithm: Taking the financial distress model as an example. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2012, 26, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, S.; Li, C.; Sun, J. A hybrid annual power load forecasting model based on generalized regression neural network with fruit fly optimization algorithm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2013, 37, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, S.; Zhao, H.; Su, C.; Wang, B. Annual electric load forecasting by a least squares support vector machine with a fruit fly optimization algorithm. Energies 2012, 5, 4430–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ji, F.; Zhou, M. Study on evolutional process of coal industry chain system based on Logistic model. Math. Pract. Theory 2013, 43, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Huang, H.; Liu, J. Fluctuation analysis of China’s business cycle and forecasting of main Macroeconomic indicators. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2007, 24, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Ma, F.; Ma, Y. Logistic curve model for regional economy medium-term and long-term forecast. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. (Inf. Manag. Eng.) 2011, 33, 94–97. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Guo, S.; Xue, W. Urban Saturated Power Load Analysis Based on a Novel Combined Forecasting Model. Information 2015, 6, 69-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/info6010069
Zhao H, Guo S, Xue W. Urban Saturated Power Load Analysis Based on a Novel Combined Forecasting Model. Information. 2015; 6(1):69-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/info6010069
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Huiru, Sen Guo, and Wanlei Xue. 2015. "Urban Saturated Power Load Analysis Based on a Novel Combined Forecasting Model" Information 6, no. 1: 69-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/info6010069
APA StyleZhao, H., Guo, S., & Xue, W. (2015). Urban Saturated Power Load Analysis Based on a Novel Combined Forecasting Model. Information, 6(1), 69-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/info6010069