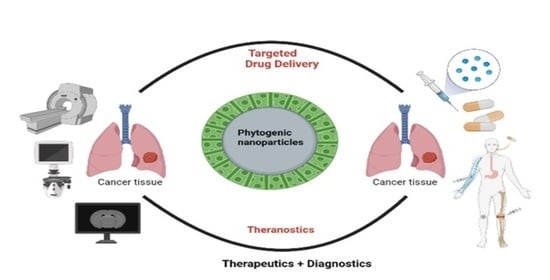
Bio-Inspired Smart Nanoparticles in Enhanced Cancer Theranostics and Targeted Drug Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Phytogenic Nanoparticles in Oncology—“Phyto-Nano-Oncology”
3. Synthesis of Plant-Based Nanoparticles
Key Factors in the Synthesis of Plant-Based Nanoparticles
4. Drug Encapsulation in Plant-Based Nanoparticles
5. Plant-Based Nanoparticles in Enhanced Cancer Imaging and Diagnosis
6. Targeted Drug Delivery Using Phytogenic Nanoparticles
7. Insights on Different Cancer Pathways Targeted by Plant-Based Nanoparticles
8. Limitations of Plant-Based Metallic Nanoparticles
9. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chakraborty, S.; Rahman, T. The difficulties in cancer treatment. Ecancermedicalscience 2012, 6, ed16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chithrani, B.D.; Ghazani, A.A.; Chan, W.C.W. Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Xing, Y.; Kim, G.J.; Simons, J.W. Nanotechnology applications in cancer. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 7, 257–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Liu, B.; Gao, J. The application of nanoparticles in diagnosis and theranostics of gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 368, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, Z.A.; Roslan, M.A.; Yahya, R.; Wan Sulaiman, W.Y.; Puteh, R. Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its larvicidal property against fourth instar larvae of Aedes aegypti. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H. Current trends in sensors based on conducting polymer nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2013, 3, 524–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arshad, R.; Kiani, M.H.; Rahdar, A.; Sargazi, S.; Barani, M.; Shojaei, S.; Bilal, M.; Kumar, D.; Pandey, S. Nano-Based Theranostic Platforms for Breast Cancer: A Review of Latest Advancements. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökcsen Tosun, N.; Kaplan, O.; Türkekul, I.; Gökçe, I.; Özgr, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Schizophyllum commune and Geopora sumneriana extracts and evaluation of their anticancer and antimicrobial activities. Part. Sci. Technol. 2021, 40, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burducsel, A.C.; Gherasim, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogoantua, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Biomedical Applications of Silver Nanoparticles: An Up-to-Date Overview. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uzair, B.; Liaqat, A.; Iqbal, H.; Menaa, B.; Razzaq, A.; Thiripuranathar, G.; Fatima Rana, N.; Menaa, F. Green and cost-effective synthesis of metallic nanoparticles by algae: Safe methods for translational medicine. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Nagraik, R.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, G.; Pandey, S.; Azizov, S.; Chauhan, P.K.; Kumar, D. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Ficus palmata: Antioxidant, antibacterial and antidiabetic studies. Results Chem. 2022, 4, 100509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, K.S.; Almalki, W.H.; Makeen, H.A.; Albratty, M.; Meraya, A.M.; Nagraik, R.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, D.; Chellappan, D.K.; Singh, S.K.; et al. Role of Medicinal plant-derived Nutraceuticals as a potential target for the treatment of breast cancer. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 19, e14387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesinghe, U.; Thiripuranathar, G.; Menaa, F.; Iqbal, H.; Razzaq, A.; Almukhlifi, H. Green synthesis, structural characterization and photocatalytic applications of ZnO nanoconjugates using Heliotropium indicum. Catalysts 2021, 11, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Amatya, R.; Hwang, S.; Lee, S.; Min, K.A.; Shin, M.C. BSA-silver nanoparticles: A potential multimodal therapeutics for conventional and photothermal treatment of skin cancer. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regassa, H.; Sourirajan, A.; Kumar, V.; Pandey, S.; Kumar, D.; Dev, K. A Review of Medicinal Plants of the Himalayas with Anti-Proliferative Activity for the Treatment of Various Cancers. Cancers 2022, 14, 3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.; Norbert, C.C.; Acharyya, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Kathirvel, M.; Patra, C.R. Biosynthesized silver nanoparticles for cancer therapy and in vivo bioimaging. Cancers 2021, 13, 6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.L.; Giraud, S.; Bialecki, A.; Moustaoui, H.; de La Chapelle, M.L.; Spadavecchia, J. Green extraction of endemic plants to synthesize gold nanoparticles for theranostic applications. Front. Lab. Med. 2017, 1, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, S.; Chow, J.C.L. Gold nanoparticles for drug delivery and cancer therapy. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F. Tumor microenvironment-responsive intelligent nanoplatforms for cancer theranostics. Nano Today 2020, 32, 100851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Vinothkumar, B.; Prashanthi, S.; Bangal, P.R.; Sreedhar, B.; Patra, C.R. Potential therapeutic and diagnostic applications of one-step in situ biosynthesized gold nanoconjugates (2-in-1 system) in cancer treatment. RSC Adv. 2013, 7, 2318–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.; Sathy, B.N.; Mony, U.; Koyakutty, M.; Nair, S.V.; Menon, D. Biocompatible magnetite/gold nanohybrid contrast agents via green chemistry for MRI and CT bioimaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. CRC 675—Current trends in phytosynthesis of metal nanoparticles. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2008, 28, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, N.; Zhou, C.; Chu, Z.; Chen, L.; Jia, N. Barley leaves mediated biosynthesis of Au nanomaterials as a potential contrast agent for computed tomography imaging. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2021, 64, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celia, C. Anticancer activity of liposomal bergamot essential oil (BEO) on human neuroblastoma cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, K.; Yu, W.; Sanders, B.G. Vitamin E and breast cancer. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 3458S–3462S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McNeil, S.E. Nanoparticle therapeutics: A personal perspective. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotech. 2009, 1, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutradhar, K.B.; Amin, M. Nanotechnology in cancer drug delivery and selective targeting. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 939378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.; Wang, X. Plant-derived natural products as leads to antitumor drugs. Plant Sci. Today 2014, 12, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.W.; Dalton, W.S.; Mosley, K.; Dorr, R.T.; Salmon, S.E. Combination chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, adriamycin, and dexamethasone (CVAD) plus oral quinine and verapamil in patients with advanced breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1997, 42, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.Z.; Siddiqui, F.A. Nanomedicine and drug delivery: A mini review. Int. Nano Lett. 2014, 4, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyam, J.; Labhasetwar, V. Biodegradable nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery to cells and tissue. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthold, D.R. Treatment of hormone-refractory prostate cancer with docetaxel or mitoxantrone: Relationships between prostate-specific antigen, pain, and quality of life response and survival in the TAX-327 study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2763–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yadav, V.R.; Prasad, S.; Sung, B.; Kannappan, R.; Aggarwal, B.B. Targeting inflammatory pathways by triterpenoids for prevention and treatment of cancer. Toxins 2010, 10, 2428–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiyaboonchai, W.; Tungpradit, W.; Plianbangchang, P. Formulation and characterization of curcuminoids loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 337, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Aseh, A. Rios CN Aggarwal BB Mathur AB Int. J. Nanomed. 2009, 4, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barreto, A.C.H. Magnetic nanosystem for cancer therapy using Oncocalyxone A, an antitomour secondary metabolite isolated from a Brazilian plant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 18269–18283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Van Kuiken, M.E.; Iyer, L.H.; Harikumar, K.B.; Sung, B. Molecular targets of nutraceuticals derived from dietary spices: Potential role in suppression of inflammation and tumorigenesis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009, 284, 825–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddiqui, I.A. Introducing nanochemoprevention as a novel approach for cancer control: Proof of principle with green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Cancer Res. 2009, 12, 1712–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nair, H.B.; Yadav, V.R.; Kannappan, R.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Delivery of antiinflammatory nutraceuticals by nanoparticles for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganeshkumar, M.; Sathishkumar, M.; Ponrasu, T.; Dinesh, M.G.; Suguna, L. Spontaneous ultra fast synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Punica granatum for cancer targeted drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 106, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Randhawa, J.K. High melting lipid-based approach for drug delivery: Solid lipid nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1842–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, G.M.; Dringen, R.; Robinson, S.R. Zinc stimulates the production of toxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibits glutathione reductase in astrocytes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y. Cytotoxic effects of ZnO hierarchical architectures on RSC96 Schwann cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mu, L.; Sprando, R.L. Application of nanotechnology in cosmetics. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 1746–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Herdade, A.M.; Guerra, C.; Peixoto, D.; Pereira-Silva, M.; Zeinali, M.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F.; Paranhos, A.; Veiga, F. Plant-mediated green synthesis of metal-based nanoparticles for dermopharmaceutical and cosmetic applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 15, 120311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, S.M.; Assadpoor, E.; He, Y.; Bhandari, B. Encapsulation efficiency of food flavours and oils during spray drying. Dry. Technol. 2008, 26, 816–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Srivastava, S.; Ghosh, S.; Khare, S.K. Phytochemical delivery through nanocarriers: A review. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 197, 111389. [Google Scholar]
- Prietto, L.; Pinto, V.Z.; El Halal, S.L.M.; de Morais, M.G.; Costa, J.A.V.; Lim, L.T.; Dias, A.R.G.; Zavareze, E.D.R. Ultrafine fibers of zein and anthocyanins as natural pH indicator. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 98, 2735–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Du, X.; Cui, D.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, G. Improvement of stability of blueberry anthocyanins by carboxymethyl starch/xanthan gum combinations microencapsulation. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 91, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.D.C.G.; de Barros, F.A.R.; Perrone, Í.T.; Viana, K.W.C.; Tavares, G.M.; Stephani, R.; Stringheta, P.C. Microencapsulation by atomization of the mixture of phenolic extracts. Powder Technol. 2019, 343, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriola, N.D.A.; Chater, P.I.; Wilcox, M.; Lucini, L.; Rocchetti, G.; Dalmina, M.; Pearson, J.P.; Amboni, R.D.D.M.C. Encapsulation of stevia rebaudiana Bertoni aqueous crude extracts by ionic gelation–Effects of alginate blends and gelling solutions on the polyphenolic profile. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Mundo, J.L.M.; McClements, D.J. Protection of anthocyanin-rich extract from pH-induced color changes using water-in-oil-in-water emulsions. J.Food Eng. 2019, 254, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.-S. Physiological significance of metallothionein in oxidative stress. Yakugaku Zasshi J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 127, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franklin, N.M.; Rogers, N.J.; Apte, S.C.; Batley, G.E.; Gadd, G.E.; Casey, P.S. Comparative toxicity of nanoparticulate ZnO, bulk ZnO, and ZnCl2 to a freshwater microalga (Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata): The importance of particle solubility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8484–8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, J.W.; Weber, P.K.; Martin, M.C.; Gilbert, B.; Hutcheon, I.D.; Banfield, J.F. Extracellular proteins limit the dispersal of biogenic nanoparticles. Science 2007, 316, 1600–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saqr, A. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles by using green machinery: Characterization and in vitro toxicity. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 801. [Google Scholar]
- Manikandan, R. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using ethanolic petals extract of Rosa indica and characterization of its antibacterial, anticancer and anti-inflammatory activities. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 138, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, R.; Nakkala, J.R.; Sadras, S.R. Catalytic and biological activities of green silver nanoparticles synthesized from Plumeria alba (frangipani) flower extract. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 51, 216–225. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, N.J.; Vali, D.N.; Rani, M.; Rani, S.S. Evaluation of antioxidant, antibacterial and cytotoxic effects of green synthesized silver nanoparticles by Piper longum fruit. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 34, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.P.; Ngabire, D.; Thi, H.H.P.; Kim, M.D.; Kim, G.-D. Eco-friendly synthesis of gold nanoparticles and evaluation of their cytotoxic activity on cancer cells. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukundan, D.; Mohankumar, R.; Vasanthakumari, R. Comparative study of synthesized silver and gold nanoparticles using leaves extract of Bauhinia tomentosa Linn and their anticancer efficacy. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2017, 40, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, E.E.; John Poonga, P.R.; Panicker, S.G. Characterization and in vitro studies on anticancer, antioxidant activity against colon cancer cell line of gold nanoparticles capped with Cassia tora SM leaf extract. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gautam, P.K.; Kumar, S.; Tomar, M.S.; Singh, R.K.; Acharya, A. Biologically synthesized gold nanoparticles using Ocimum sanctum (Tulsi leaf extract) induced anti-tumor response in a T cell daltons lymphoma. J. Cell Sci. Ther. 2017, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, R.; Rashidipour, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using extract of oak fruit hull (Jaft): Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxic effect on MCF-7 cells. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2015, 2015, 846743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P. Facile bio-synthesis of gold nanoparticles by using extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa and evaluation of its cytotoxicity against U87 glioblastoma cells under hyperglycemic condition. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 105, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Ledwani, L.; Bhatnagar, N. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Rheum emodi roots extract. New Front. Chem. 2015, 24, 121. [Google Scholar]
- Jeyaraj, M. Biogenic silver nanoparticles for cancer treatment: An experimental report. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 106, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramar, M. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Solanum trilobatum fruits extract and its antibacterial, cytotoxic activity against human breast cancer cell MCF 7. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 140, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S. Potential theranostics application of bio-synthesized silver nanoparticles (4-in-1 system). Theranostics 2014, 4, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, J.L. Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 366, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.D.; Gopal, K. Plant-mediated biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanisaadi, M.; Bonjar, G.H.S.; Rahdar, A.; Pandey, S.; Hosseinipour, A.; Abdolshahi, R. Environmentally safe biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using plant water extracts. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepeur, S. Nanotechnology: Technical Basics and Applications; Vincentz Network GmbH & Co KG.: Hanover, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vlamidis, Y.; Voliani, V. Bringing again noble metal nanoparticles to the forefront of cancer therapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, M.A.; Mishra, A.; Benson, D.J. Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2006, 51, 427–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezadoost, M.H.; Kumleh, H.; Ghasempour, A. Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction in breast cancer, skin cancer and glioblastoma cells by plant extracts. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 5131–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, B.A.; Nader, M.M.; El-Saadony, M.T. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by Serratia marcescens ssp sakuensis and its antibacterial application against some pathogenic bacteria. J. Agric. Chem. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sharipov, M.; Turaev, A.; Azizov, S.; Azizov, I.; Makhado, E.; Rahdar, A.; Kumar, D.; Pandey, S. Polymer-Based Hybrid Nanoarchitectures for Cancer Therapy Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thovhogi, N.; Diallo, A.; Gurib-Fakim, A.; Maaza, M. Nanoparticles green synthesis by Hibiscus sabdariffa flower extract: Main physical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 647, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooti, W. Effective medicinal plant in cancer treatment, part 2: Review study. J. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 22, 982–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dan, N. Antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy: Chemistry to clinical implications. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: A green expertise. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abbasi, B.A.; Iqbal, J.; Mahmood, T.; Ahmad, R.; Kanwal, S.; Afridi, S. Plant-mediated synthesis of nickel oxide nanoparticles (NiO) via Geranium wallichianum: Characterization and different biological applications. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 0850a7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.C.; Lin, S.; Wang, P.C.; Sridhar, R. Techniques for physicochemical characterization of nanomaterials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 711–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, S.Z.M. Carbon nanotube—Liposome complexes in hydrogels for controlled drug delivery via near-infrared laser stimulation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 4, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W. Application of Multifunctional Nanomaterials Combined with Sports Rehabilitation Training in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2021, 216, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Shegokar, R. Metal Nanoparticles in Pharma; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–493. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, R.; Das, J.; Lalhlenmawia, H.; Tonk, R.; Singh, L.; Kumar, D. Chapter 38—Targeting cancer using phytoconstituents-based drug delivery. In Advanced Drug Delivery Systems in the Management of Cancer; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 499–508. [Google Scholar]
- Farzin, A.; Etesami, S.A.; Quint, J.; Memic, A.; Tamayol, A. Magnetic nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 1901058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Lee, I.K.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.; Choi, J.Y.; Choi, J.; Hyun, J.W. Silver nanoparticles induce oxidative cell damage in human liver cells through inhibition of reduced glutathione and induction of mitochondria-involved apoptosis. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 201, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.; Ghourchian, H.; Yazdian, F.; Bagherifam, S.; Bekhradnia, S.; Nyström, B. Anti-cancerous effect of albumin coated silver nanoparticles on MDA-MB 231 human breast cancer cell line. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Feng, X.; Gao, L.; Mickymaray, S.; Paramasivam, A.; Abdulaziz Alfaiz, F.; Almasmoum, H.A.; Ghaith, M.M.; Almaimani, R.A.; Aziz Ibrahim, I.A. Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway with copper oxide nanoparticles from Houttuynia cordata plant: Attenuating the proliferation of cervical cancer cells. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2021, 49, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Fu, S.; Zhou, L.; Liang, H.; Fan, M.; Luo, F.; Qian, Z.; Wei, Y. Preparation of curcumin loaded poly (ε-caprolactone)-poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (ε-caprolactone) nanofibers and their in vitro antitumor activity against Glioma 9L cells. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3825–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Li, A.; Jia, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Dai, H.; Li, H. Transferrin modified PEG-PLA-resveratrol conjugates: In vitro and in vivo studies for glioma. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 718, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikshit, P.K.; Kumar, J.; Das, A.K.; Sadhu, S.; Sharma, S.; Singh, S.; Gupta, P.K.; Kim, B.S. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: Applications and limitations. Catalysts 2021, 11, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Plant Name | Part Used | Type of Nanoparticles | Cancer Cell Lines | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benincasa hispida | Fresh peel | Gold (Au) | HeLa cells and normal osteoblast cell lines | [27] |
| Butea monosperma | Leaves | Gold (Au) | Cancer cell lines (B16F10, MCF-7, HNGC2, and A549) | [28] |
| Ocimum sanctum | Leaves | Gold (Au) | Dalton’s lymphoma | [29] |
| Bauhinia tomentosa Linn | Leaves | Gold (Au) | A549, HEp-2, and MCF-7 cells | [30] |
| Cassia tora | Leaves | Gold (Au) | Colon cancer cells | [31] |
| Hibiscus sabdariffa | Leaves | Gold (Au) | U87 cell line | [32] |
| Moringa oleifera | Leaves | Gold (Au) | A549 and SNO cells | [33] |
| Piper longum | Fruit | Silver (Ag) | MCF-7 | [34] |
| Plumeria alba | Flower | Silver (Ag) | COLO-205 | [35] |
| Rosa indica | Petal | Silver (Ag) | HCT 15 | [36] |
| Sesbania grandifloria | Leaves | Silver (Ag) | MCF-7 | [37] |
| Rheum emodi | Root | Silver (Ag) | MCF-7 | [38] |
| Solanum trilobatum | Fruit | Silver (Ag) | MCF-7 | [39] |
| Quercus | Fruit | Silver (Ag) | MCF-7 | [40] |
| Saccharum officinarum | Juice | Zinc (Zn) | MCF-7 | [41] |
| Cannabis sativa | Leaves | Zinc (Zn) | A549 | [42] |
| Catharanthus roseus | Leaves | Zinc (Zn) | MCF-7 | [43] |
| Calotropis gigantea | Leaves | Zinc (Zn) | A549 | [44] |
| Saraca asoca | Flowers | Zinc (Zn) | WEHI-3 cells | [45] |
| Withania somnifera | Leaves | Zinc (Zn) | WEHI-3 cells | [46] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gulia, K.; James, A.; Pandey, S.; Dev, K.; Kumar, D.; Sourirajan, A. Bio-Inspired Smart Nanoparticles in Enhanced Cancer Theranostics and Targeted Drug Delivery. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb13040207
Gulia K, James A, Pandey S, Dev K, Kumar D, Sourirajan A. Bio-Inspired Smart Nanoparticles in Enhanced Cancer Theranostics and Targeted Drug Delivery. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2022; 13(4):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb13040207
Chicago/Turabian StyleGulia, Khushabu, Abija James, Sadanand Pandey, Kamal Dev, Deepak Kumar, and Anuradha Sourirajan. 2022. "Bio-Inspired Smart Nanoparticles in Enhanced Cancer Theranostics and Targeted Drug Delivery" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 13, no. 4: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb13040207
APA StyleGulia, K., James, A., Pandey, S., Dev, K., Kumar, D., & Sourirajan, A. (2022). Bio-Inspired Smart Nanoparticles in Enhanced Cancer Theranostics and Targeted Drug Delivery. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 13(4), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb13040207