Picosecond Laser-Induced Hierarchical Periodic Near- and Deep-Subwavelength Ripples on Stainless-Steel Surfaces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of Hierarchical Periodic Near-Subwavelength Ripples (NSRs) and Deep-Subwavelength Ripples (DSRs)
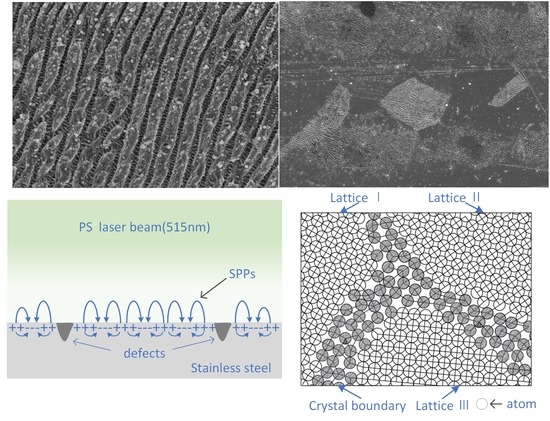
3.2. Lattice Orientation of Grains as a Factor in the ps Laser-Induced Hierarchical Periodic NSRs and DSRs
3.3. Mechanism for the Picosecond (ps) Laser-Induced Hierarchical Periodic NSRs and DSRs
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The peak power density of incident laser makes a decisive role in the light–matter interaction which leads to the generation of hierarchical periodic NSRs and DSRs. The DSRs can be independently generated at a relatively low peak power density, whereas the generation of NSRs needs much higher peak power density and are accompanied by DSRs in the valleys of the NSRs. The orientation of the periodic DSRs is perpendicular to that of the periodic NSRs, which was always found to be perpendicular to the polarization of the incident laser and coincides with the laser-induced SPPs.
- (2)
- The formation of the DSRs at low peak power density has a conformance with the metallic grain structures, and preferentially occurs in the interior of the grains that have low surface atomic planar densities. Moreover, the spatial period of the NSRs is determined by the peak power density absorption and the material intrinsic thermo-physical properties.
- (3)
- A qualitative explanation based on SPP-modulated periodic coulomb explosion is proposed for the formation mechanism of hierarchical periodic NSRs and DSRs. During a picosecond laser pulse duration, the photon-absorbed free electrons’ motion initiates the locally non-thermal phase change coulomb explosion and results in the subsequent coulomb explosion chain that forms the DSRs. The laser electric field (TM wave)-induced constraint on SPPs’ propagation along the metallic surface makes the free electron concentration increase and a strong coulomb explosion chain occurs that forms the NSRs with orientation vertical to the laser polarization direction.
- (4)
- The preparation of large-area hierarchical periodic NSRs and DSRs was implemented by a line-by-line laser scanning process within which either the incident laser power or scanning speed can be used as the control variable. The spatial periods of the obtained NSRs and DSRs were 356 ± 17 nm and 58 ± 15 nm, respectively.
- (5)
- Further theoretical calculation and simulation are needed to verify the qualitative explanation and find routes to improve continuity and strict directionality of the hierarchical periodic NSRs and DSRs. The potential applications such as wettability, tribology, structural color are promising since the laser-scanning preparation method is simple and precisely controllable.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonse, J.; Hohm, S.; Kirner, S.V.; Rosenfeld, A.; Kruger, J. Laser-induced periodic surface structures—A scientific evergreen. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2016, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, F.A.; Kunz, C.; Graf, S. Bio-Inspired Functional Surfaces Based on Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures. Materials 2016, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Zhao, F.L.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, N.S.; Xu, Z.Z. Origin of Laser-Induced Near-Subwavelength Ripples: Interference between Surface Plasmons and Incident Laser. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 4062–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shugaev, M.V.; Gnilitskyi, I.; Bulgakova, N.M.; Zhigilei, L.V. Mechanism of single-pulse ablative generation of laser-induced periodic surface structures. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 205429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurevich, E.L. Mechanisms of femtosecond LIPSS formation induced by periodic surface temperature modulation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 374, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnilitskyi, I.; Derrien, T.J.; Levy, Y.; Bulgakova, N.M.; Mocek, T.; Orazi, L. High-speed manufacturing of highly regular femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures: Physical origin of regularity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuentes-Edfuf, Y.; Garcia-Lechuga, M.; Puerto, D.; Florian, C.; Garcia-Leis, A.; Sanchez-Cortes, S.; Solis, J.; Siegel, J. Coherent scatter-controlled phase-change grating structures in silicon using femtosecond laser pulses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivas, J.J.J.; He, S.; Song, Z.; Rubano, A.; Vecchione, A.; Paparo, D.; Marrucci, L.; Bruzzese, R.; Amoruso, S. Femtosecond laser surface structuring of silicon with Gaussian and optical vortex beams. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 418, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhao, F.L.; Jia, T.Q.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, N.S.; Xu, Z.Z. A uniform 290 nm periodic square structure on ZnO fabricated by two-beam femtosecond laser ablation. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 505301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, C.; Liu, K.; Zhou, Q. Periodic structures on germanium induced by high repetition rate femtosecond laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 101, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, N.; Xu, Z. Mechanisms of ultrafast laser-induced deep-subwavelength gratings on graphite and diamond. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 125436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipe, J.E.; Young, J.F.; Preston, J.S.; van Driel, H.M. Laser-induced periodic surface structure. I. Theory. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 27, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.F.; Preston, J.S.; van Driel, H.M.; Sipe, J.E. Laser-induced periodic surface structure. II. Experiments on Ge, Si, Al, and brass. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 27, 1155–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, J.; Varlamova, O.; Costache, F. Femtosecond laser induced nanostructure formation: Self-organization control parameters. Appl. Phys. A 2008, 92, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, J.; Varlamova, O.; Uhlig, S.; Varlamov, S.; Bestehorn, M. On the physics of self-organized nanostructure formation upon femtosecond laser ablation. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 117, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Yuan, Y.; Lu, Y. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic structure adjustments based on electron dynamics control: From subwavelength ripples to double-grating structures. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 3743–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Réal, V. Femtosecond laser-induced ultra-fine nanostructures on silicon surface. Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 3330–3338. [Google Scholar]
- Gemini, L.; Hashida, M.; Miyasaka, Y.; Inoue, S.; Limpouch, J.; Mocek, T.; Sakabe, S. Periodic surface structures on titanium self-organized upon double femtosecond pulse exposures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 336, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Baba, M.; Suzuki, M.; Ganeev, R.A.; Kuroda, H.; Qiu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; Xu, Z. Fabrication of two-dimensional periodic nanostructures by two-beam interference of femtosecond pulses. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 1874–1878. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, T.Q.; Chen, H.X.; Huang, M.; Zhao, F.L.; Qiu, J.R.; Li, R.X.; Xu, Z.Z.; He, X.K.; Zhang, J.; Kuroda, H. Formation of nanogratings on the surface of a ZnSe crystal irradiated by femtosecond laser pulses. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 125429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, J.; Varlamova, O.; Varlamov, S.; Bestehorn, M. The role of asymmetric excitation in self-organized nanostructure formation upon femtosecond laser ablation. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 104, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayats, A.V.; Smolyaninov, I.I.; Maradudin, A.A. Nano-optics of surface plasmon polaritons. Phys. Rep. 2005, 408, 131–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudenko, A.; Mauclair, C.; Garrelie, F.; Stoian, R.; Colombier, J.P. Self-organization of surfaces on the nanoscale by topography-mediated selection of quasi-cylindrical and plasmonic waves. Nanophotonics 2019, 8, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Krüger, J.; Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures. J. Laser Appl. 2012, 24, 042006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Q.D.; Cao, X.W.; Buividas, R.; Wang, X.; Juodkazis, S.; Sun, H.B. Plasmonic nano-printing: Large-area nanoscale energy deposition for efficient surface texturing. Light Sci. Appl. 2017, 6, e17112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J. On the role of surface plasmon polaritons in the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures upon irradiation of silicon by femtosecond-laser pulses. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 104910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Ye, Y.; Jia, B.; Li, Y.; Ding, R.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X. Polarization and fluence effects in femtosecond laser induced micro/nano structures on stainless steel with antireflection property. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 425, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Han, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, A.; Lu, Y. Femtosecond laser-induced cross-periodic structures on a crystalline silicon surface under low pulse number irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 326, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, S.; Podagatlapalli, G.K.; Vendamani, V.S.; Nageswara Rao, S.V.S.; Pathak, A.P.; Tewari, S.P.; Venugopal Rao, S. Femtosecond Ablation of Silicon in Acetone: Tunable Photoluminescence from Generated Nanoparticles and Fabrication of Surface Nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 7139–7151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, T.J.Y.; Koter, R.; Krüger, J.; Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Bonse, J. Plasmonic formation mechanism of periodic 100-nm-structures upon femtosecond laser irradiation of silicon in water. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 074902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.S.; Ahmed, F.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, M.S.; Jun, M.B.G. Colorizing stainless steel surface by femtosecond laser induced micro/nano-structures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 7771–7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, J.M.; Garcia-Giron, A.; Penchev, P.; Dimov, S. Triangular Laser-Induced submicron textures for functionalising stainless steel surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 440, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurevich, E.L.; Gurevich, S.V. Laser Induced Periodic Surface Structures induced by surface plasmons coupled via roughness. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 302, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.; Ni, J.; Qiao, L.; Huang, M.; Bellouard, Y.; Sugioka, K.; Cheng, Y. High-fidelity visualization of formation of volume nanogratings in porous glass by femtosecond laser irradiation. Optica 2015, 2, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, S.; Varlamova, O.; Reif, J.; Bestehorn, M.; Varlamov, S.; Mollabashi, M.; Madanipour, K.; Ratzke, M. Birth of periodic Micro/Nano structures on 316L stainless steel surface following femtosecond laser irradiation; single and multi scanning study. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 104, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Nivas, J.J.J.; Anoop, K.K.; Vecchione, A.; Hu, M.; Bruzzese, R.; Amoruso, S. Surface structures induced by ultrashort laser pulses: Formation mechanisms of ripples and grooves. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 353, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichstädt, J.; Römer, G.R.B.E.; Huis in ‘t Veld, A.J. Determination of irradiation parameters for laser-induced periodic surface structures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 264, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buividas, R.; Rosa, L.; Šliupas, R.; Kudrius, T.; Šlekys, G.; Datsyuk, V.; Juodkazis, S. Mechanism of fine ripple formation on surfaces of (semi)transparent materials via a half-wavelength cavity feedback. Nanotechnology 2010, 22, 055304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, F.; Tian, D.; Li, H.; Liu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, A.; Jin, M. Possible evidence of Coulomb explosion in the femtosecond laser ablation of metal at low laser fluence. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 355, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, S.A. Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 49–74. [Google Scholar]











© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, S.; Zhu, D.; Xue, W.; Liu, W.; Cao, Y. Picosecond Laser-Induced Hierarchical Periodic Near- and Deep-Subwavelength Ripples on Stainless-Steel Surfaces. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010062
Ding S, Zhu D, Xue W, Liu W, Cao Y. Picosecond Laser-Induced Hierarchical Periodic Near- and Deep-Subwavelength Ripples on Stainless-Steel Surfaces. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(1):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010062
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Shijie, Dehua Zhu, Wei Xue, Wenwen Liu, and Yu Cao. 2020. "Picosecond Laser-Induced Hierarchical Periodic Near- and Deep-Subwavelength Ripples on Stainless-Steel Surfaces" Nanomaterials 10, no. 1: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010062
APA StyleDing, S., Zhu, D., Xue, W., Liu, W., & Cao, Y. (2020). Picosecond Laser-Induced Hierarchical Periodic Near- and Deep-Subwavelength Ripples on Stainless-Steel Surfaces. Nanomaterials, 10(1), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010062