Hair Follicle Targeting and Dermal Drug Delivery with Curcumin Drug Nanocrystals—Essential Influence of Excipients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Production and Characterization of Curcumin Nanocrystals with Different Excipients
2.2.2. Ex-Vivo Model for Passive Dermal and Follicular Penetration
Determination of Follicular and Dermal Penetration via Epifluorescence Microscopy
Digital Image Analysis
2.2.3. Determination of Biophysical Skin Properties
2.2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Production and Characterization of Curcumin Nanocrystals with Different Excipients
3.2. Determination of Passive Dermal Penetration
3.2.1. Microscopic Imaging by Inverted Epifluorescence Microscopy
3.2.2. Digital Image Analysis
3.3. Influence on Biophysical Skin Parameters
3.3.1. TEWL
3.3.2. Skin Hydration
3.3.3. Skin Friction
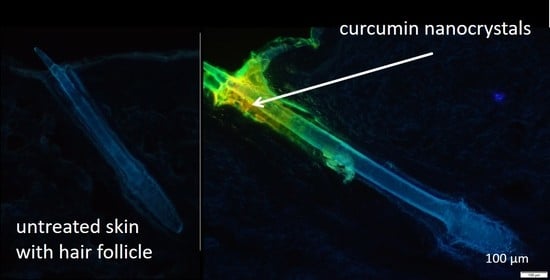
3.4. Determination of Hair Follicle Targeting
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MarketsandMarkets. Topical Drug Delivery Market by Type (Semisolids (Creams, Ointments, Gels, Lotions), Liquids, Solids, Transdermal Products), Route (Dermal, Ophthalmic, Rectal, Vaginal, Nasal), Facility of Use (Homecare, Hospital, Burn Center)—Global Forecast to 2024: Report Code: PH 7545. Available online: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/topical-drug-delivery-market-124871717.html (accessed on 21 August 2020).
- Keck, C.M. Corneotherapie—Pflege und Reparatur der Haut: Präzise, effektiv und nachhaltig. J. Ästhetische Chir. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Prausnitz, M.R. Drug delivery using microneedle patches: Not just for skin. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Tang, J.; Terry, R.N.; Li, S.; Brunie, A.; Callahan, R.L.; Noel, R.K.; Rodríguez, C.A.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Long-acting reversible contraception by effervescent microneedle patch. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Terry, R.N.; Tang, J.; Feng, M.R.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Rapidly separable microneedle patch for the sustained release of a contraceptive. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lademann, J.; Knorr, F.; Richter, H.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Vogt, A.; Antoniou, C.; Sterry, W.; Patzelt, A. Hair follicles—An efficient storage and penetration pathway for topically applied substances. Summary of recent results obtained at the Center of Experimental and Applied Cutaneous Physiology, Charité -Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Germany. Ski. Pharm. Physiol. 2008, 21, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knorr, F.; Lademann, J.; Patzelt, A.; Sterry, W.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Vogt, A. Follicular transport route--research progress and future perspectives. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 71, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume-Peytavi, U.; Massoudy, L.; Patzelt, A.; Lademann, J.; Dietz, E.; Rasulev, U.; Garcia Bartels, N. Follicular and percutaneous penetration pathways of topically applied minoxidil foam. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 76, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knorr, F.; Patzelt, A.; Darvin, M.E.; Lehr, C.-M.; Schäfer, U.; Gruber, A.D.; Ostrowski, A.; Lademann, J. Penetration of topically applied nanocarriers into the hair follicles of dog and rat dorsal skin and porcine ear skin. Vet. Derm. 2016, 27, 256-e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzelt, A.; Richter, H.; Knorr, F.; Schäfer, U.; Lehr, C.-M.; Dähne, L.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Selective follicular targeting by modification of the particle sizes. J. Control. Release 2011, 150, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke, M.; Patzelt, A.; Knorr, F.; Lademann, J.; Netz, R.R. Ratchet effect for nanoparticle transport in hair follicles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 116, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelikh, O.; Eckert, R.W.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Keck, C.M. Hair follicle targeting with curcumin nanocrystals: Influence of the formulation properties on the penetration efficacy. J. Control. Release 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, R.W.; Hartmann, S.F.; Keck, C.M. From lab-bench to large-scale production: Low energy nanomilling bridges the gap. In Proceedings of the Controlled Release Society: Virtual Annual Meeting, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 29 June–2 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, G.B.; Keck, C.M.; Müller, R.H. Simple low-cost miniaturization approach for pharmaceutical nanocrystals production. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 501, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lademann, J.; Richter, H.; Meinke, M.; Sterry, W.; Patzelt, A. Which skin model is the most appropriate for the investigation of topically applied substances into the hair follicles? Ski. Pharm. Physiol. 2010, 23, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelikh, O.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Keck, C.M. Dermal penetration analysis of curcumin in an ex-vivo porcine ear model using epifluorescence microscopy and digital image processing. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasband, W.S. ImageJ: Image Processing and Analysis in Java; Astrophysics Source Code Library, Michigan Technological University: Houghton, MI, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Guiet, R.; Burri, O.; Seitz, A. Open Source Tools for Biological Image Analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2040, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honari, G.; Maibach, H. (Eds.) Chapter 1—Skin Structure and Function. In Applied Dermatotoxicology; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 1–10. ISBN 978-0-12-420130-9. [Google Scholar]
- JASP Team. JASP; Version 0.13.1; University of Amsterdam: Amsterdam, The Netherlanbds, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dinno, A. Nonparametric pairwise multiple comparisons in independent groups using Dunn’s test. Stata J. 2015, 15, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keck, C.M. Particle size analysis of nanocrystals: Improved analysis method. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 390, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, C.M. Cyclosporine Nanosuspensions: Optimised Size Characterisation & Oral Formulations. Ph.D. Thesis, Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V.; Pathak, K. Effect of hydrogen bond formation/replacement on solubility characteristics, gastric permeation and pharmacokinetics of curcumin by application of powder solution technology. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 600–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelikh, O.; Stahr, P.-L.; Huang, J.; Gerst, M.; Scholz, P.; Dietrich, H.; Geisel, N.; Keck, C.M. Nanocrystals for improved dermal drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 128, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, T.; Talukder, M.M.U. Chemical Enhancer: A Simplistic Way to Modulate Barrier Function of the Stratum Corneum. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 8, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pham, Q.D.; Björklund, S.; Engblom, J.; Topgaard, D.; Sparr, E. Chemical penetration enhancers in stratum corneum—Relation between molecular effects and barrier function. J. Control. Release 2016, 232, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Björklund, S.; Andersson, J.M.; Pham, Q.D.; Nowacka, A.; Topgaard, D.; Sparr, E. Stratum corneum molecular mobility in the presence of natural moisturizers. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 4535–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, M.E. Skin penetration enhancers. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 447, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrer, V.; Alonso, C.; Pont, M.; Zanuy, M.; Córdoba, M.; Espinosa, S.; Barba, C.; Oliver, M.A.; Martí, M.; Coderch, L. Effect of propylene glycol on the skin penetration of drugs. Arch. Derm. Res. 2020, 312, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.W.; Maibach, H.I. (Eds.) Percutaneous Penetration Enhancers; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; ISBN 0849326052. [Google Scholar]
- Trottet, L.; Merly, C.; Mirza, M.; Hadgraft, J.; Davis, A.F. Effect of finite doses of propylene glycol on enhancement of in vitro percutaneous permeation of loperamide hydrochloride. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 274, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.B.; Smith, E.W. The role of percutaneous penetration enhancers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1996, 18, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.; Hadgraft, J.; Lane, M.E. The influence of volatile solvents on transport across model membranes and human skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 435, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, R.M.; Herkenne, C.; Guy, R.H.; Hadgraft, J.; Oliveira, G.; Lane, M.E. Influence of ethanol on the solubility, ionization and permeation characteristics of ibuprofen in silicone and human skin. Ski. Pharm. Physiol. 2009, 22, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara-Bergstrom, T.; Knutson, K.; DeNoble, L.J.; Goates, C.Y. Percutaneous absorption enhancement of an ionic molecule by ethanol-water systems in human skin. Pharm. Res. 1990, 7, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommannan, D.; Potts, R.O.; Guy, R.H. Examination of the effect of ethanol on human stratum corneum in vivo using infrared spectroscopy. J. Control. Release 1991, 16, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A. Role of Surfactants as Penetration Enhancer in Transdermal Drug Delivery System. J. Mol. Pharm Org. Process. Res. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Sundaram, C.; Malani, N.; Ichikawa, H. Curcumin: The Indian solid gold. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 595, 1–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluhr, J.W.; Darlenski, R.; Surber, C. Glycerol and the skin: Holistic approach to its origin and functions. Br. J. Derm. 2008, 159, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodén, M.; Wessman, W. The influence of a cream containing 20% glycerin and its vehicle on skin barrier properties. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2001, 23, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluhr, J.W.; Gloor, M.; Lehmann, L.; Lazzerini, S.; Distante, F.; Berardesca, E. Glycerol accelerates recovery of barrier function in vivo. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1999, 79, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paepe, K.; Wibaux, A.; Ward, C.; Rogiers, V. Skin efficacy and biophysical assessment of glycerol-containing hydrocolloid patches. Ski. Pharm. Physiol. 2009, 22, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.; Oliveira, J.S.L.; Barker, R.; Trapp, M.; Schroeter, A.; Brezesinski, G.; Neubert, R.H.H. The effect of urea and taurine as hydrophilic penetration enhancers on stratum corneum lipid models. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 2006–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.; Trapp, M.; Neubert, R.H.H. The effect of hydrophilic penetration/diffusion enhancer on stratum corneum lipid models: Part II*: DMSO. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2019, 225, 104816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J. Einfluss Hydrophiler Penetrationsenhancer auf die Nanostruktur von Stratum Corneum Lipidmodellen. Ph.D. Thesis, Martin Luther Universität Halle-Wittenberg, Halle, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Grether-Beck, S.; Felsner, I.; Brenden, H.; Kohne, Z.; Majora, M.; Marini, A.; Jaenicke, T.; Rodriguez-Martin, M.; Trullas, C.; Hupe, M.; et al. Urea uptake enhances barrier function and antimicrobial defense in humans by regulating epidermal gene expression. J. Invest. Derm. 2012, 132, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, R.H.; Sinambela, P.; Keck, C.M. NLC—The invisible dermal patch for moisturizing & skin protection. Euro Cosmet. 2013, 6, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lautenschläger, H. Glykole in Hautpflegemitteln und Dermatika. Med. Beauty Forum 2017, 5, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum, J.; Bennett, B.T. Russell and Burch’s 3Rs then and now: The need for clarity in definition and purpose. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2015, 54, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009; European Parliament: Brussels, Belgium, 2009.
- Pillemer, D.B. One- Versus Two-Tailed Hypothesis Tests in Contemporary Educational Research. Educ. Res. 1991, 20, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lademann, J.; Patzelt, A.; Richter, H.; Antoniou, C.; Sterry, W.; Knorr, F. Determination of the cuticula thickness of human and porcine hairs and their potential influence on the penetration of nanoparticles into the hair follicles. J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 21014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patzelt, A.; Knorr, F.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Hair follicles, their disorders and their opportunities. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2008, 5, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illel, B. Formulation for transfollicular drug administration: Some recent advances. Crit. Rev. Drug Carr. Syst. 1997, 14, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauer, A.C.; Lieb, L.M.; Ramachandran, C.; Flynn, G.L.; Weiner, N.D. Transfollicular drug delivery. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lademann, J.; Weigmann, H.; Rickmeyer, C.; Barthelmes, H.; Schaefer, H.; Mueller, G.; Sterry, W. Penetration of titanium dioxide microparticles in a sunscreen formulation into the horny layer and the follicular orifice. Ski. Pharm. Physiol. 1999, 12, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, A.; Mayer, A.; Augustin, M. Keratolytics and Emollients and Their Role in the Therapy of Psoriasis: A Systematic Review. Derm. Ther. 2015, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celleno, L. Topical urea in skincare: A review. Dermatol. Ther. 2018, 31, e12690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, K.H.; Pflugshaupt, C. Harnstoff in der Dermatologie I. Hautarzt 1989, 40 (Suppl. 9), 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Fluhr, J.W.; Cavallotti, C.; Berardesca, E. Emollients, moisturizers, and keratolytic agents in psoriasis. Clin. Dermatol. 2008, 26, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 1030, Propylene glycol. 2020. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Propylene-glycol (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 24753271, Fatty acids, olive-oil, Et esters. 2020. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Fatty-acids_-olive-oil_-Et-esters (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 702, Ethanol. 2020. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Ethanol (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Gupta, R.; Badhe, Y.; Rai, B.; Mitragotri, S. Molecular mechanism of the skin permeation enhancing effect of ethanol: A molecular dynamics study. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 12234–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; de Vries, M.A.; Gooris, G.S.; Bras, W.; Brussee, J.; Ponec, M. Thermodynamic and structural aspects of the skin barrier. J. Control. Release 1991, 15, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Formulation Code | Type of Excipient | Concentration of Excipient (w/w) |
|---|---|---|
| NS | - | - |
| Gly 2% | glycerol | 2% |
| Gly 5% | glycerol | 5% |
| Urea 5% | urea | 5% |
| Urea 10% | urea | 10% |
| PG 5% | propylene glycol | 5% |
| EtOH 2% | ethanol | 2% |
| oil 2% | olive oil | 2% |
| Formulation | DLS Data | LD Data | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z-average [nm] | PDI | d(v) 0.5 [µm] | d(v) 0.9 [µm] | d(v) 0.95 [µm] | d(v) 0.99 [µm] | |||||||||||||
| bulk material | n.a. | 22.6 | ± | 0.2 | 50.3 | ± | 0.5 | 60.1 | ± | 0.9 | 77.3 | ± | 1.7 | |||||
| NS d1 | 253 | ± | 6 | 0.25 | ± | 0.05 | 0.7 | ± | 0.0 | 4.2 | ± | 0.1 | 5.5 | ± | 0.1 | 8.2 | ± | 0.2 |
| NS d14 | 483 | ± | 75 | 0.48 | ± | 0.05 | 1.1 | ± | 0.0 | 4.8 | ± | 0.1 | 6.5 | ± | 0.1 | 10.6 | ± | 0.2 |
| Gly 2% | 325 | ± | 10 | 0.25 | ± | 0.03 | 0.7 | ± | 0.0 | 4.3 | ± | 0.1 | 5.6 | ± | 0.1 | 8.4 | ± | 0.1 |
| Gly 5% | 278 | ± | 7 | 0.30 | ± | 0.03 | 0.8 | ± | 0.0 | 4.4 | ± | 0.1 | 5.7 | ± | 0.1 | 8.5 | ± | 0.1 |
| Urea 5% | 270 | ± | 7 | 0.24 | ± | 0.05 | 0.5 | ± | 0.0 | 4.0 | ± | 0.0 | 5.2 | ± | 0.0 | 7.7 | ± | 0.1 |
| Urea 10% | 277 | ± | 7 | 0.29 | ± | 0.02 | 0.4 | ± | 0.0 | 3.8 | ± | 0.0 | 5.0 | ± | 0.0 | 7.5 | ± | 0.1 |
| PG 5% | 389 | ± | 47 | 0.39 | ± | 0.07 | 1.1 | ± | 0.0 | 4.6 | ± | 0.1 | 6.0 | ± | 0.2 | 8.9 | ± | 0.3 |
| EtOH 2% | 389 | ± | 37 | 0.45 | ± | 0.09 | 1.1 | ± | 0.0 | 4.7 | ± | 0.1 | 6.1 | ± | 0.1 | 9.4 | ± | 0.2 |
| oil 2% | 459 | ± | 169 | 0.54 | ± | 0.25 | 1.4 | ± | 0.1 | 8.5 | ± | 0.9 | 13.0 | ± | 1.6 | 27.0 | ± | 3.6 |
| Type and Concentration of Excipient | Effect on Passive Dermal Diffusion | Effect on Hair Follicle Targeting |
|---|---|---|
| Glycerol 2% | ↑ | ↔ |
| Glycerol 5% * | ↑↑↑↑ | ↓ |
| Urea 5% | ↑↑ | ↔ |
| Urea 10% | ↑ | ↓ |
| Propylene glycol 5% ** | ↑↑↑↑ | ↑↑↑ |
| EtOH 2% *** | ↓ | ↑↑↑ |
| Olive oil 2% | ↔ | ↑ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pelikh, O.; Keck, C.M. Hair Follicle Targeting and Dermal Drug Delivery with Curcumin Drug Nanocrystals—Essential Influence of Excipients. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112323
Pelikh O, Keck CM. Hair Follicle Targeting and Dermal Drug Delivery with Curcumin Drug Nanocrystals—Essential Influence of Excipients. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(11):2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112323
Chicago/Turabian StylePelikh, Olga, and Cornelia M. Keck. 2020. "Hair Follicle Targeting and Dermal Drug Delivery with Curcumin Drug Nanocrystals—Essential Influence of Excipients" Nanomaterials 10, no. 11: 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112323
APA StylePelikh, O., & Keck, C. M. (2020). Hair Follicle Targeting and Dermal Drug Delivery with Curcumin Drug Nanocrystals—Essential Influence of Excipients. Nanomaterials, 10(11), 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112323