Applications of Nanocellulose/Nanocarbon Composites: Focus on Biotechnology and Medicine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Nanocellulose/Fullerene Composites
2.1. Characterization of Fullerenes
2.2. Preparation and (Bio)Application of Nanocellulose/Fullerene Composites
3. Nanocellulose/Graphene Composites
3.1. Characterization of Graphene
3.2. Preparation and Industrial Application of Nanocellulose/Graphene Composites
3.3. Biomedical Application of Nanocellulose/Graphene Composites
4. Nanocellulose/Carbon Nanotube Composites
4.1. Characterization of Carbon Nanotubes
4.2. Preparation and Industrial Application of Nanocellulose/CNT Composites
4.3. Biomedical Application of Nanocellulose/CNT Composites
5. Nanocellulose/Nanodiamond Composites
5.1. Characterization of Nanodiamond
5.2. Preparation and (Bio)Application of Nanocellulose/Nanodiamond Composites
6. Composites of Nanocellulose with Other Carbon Nanoparticles
6.1. Composites of Nanocellulose and Carbon Nanofibers
6.2. Composites of Nanocellulose and Carbon Quantum Dots
6.3. Composites of Nanocellulose and Activated Carbon
6.4. Composites of Nanocellulose and Carbon Black
7. Potential Cytotoxicity and Immunogenicity of Nanocellulose/Nanocarbon Composites
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



References
- Zhang, H.; Dou, C.; Pal, L.; Hubbe, M.A. Review of Electrically Conductive Composites and Films Containing Cellulosic Fibers or Nanocellulose. Bioresources 2019, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Bacakova, L.; Pajorova, J.; Bacakova, M.; Skogberg, A.; Kallio, P.; Kolarova, K.; Svorcik, V. Versatile Application of Nanocellulose: From Industry to Skin Tissue Engineering and Wound Healing. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2019, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Nypelo, T.; Salas, C.; Arboleda, J.; Hoeger, I.C.; Rojas, O.J. Cellulose Nanofibrils: From Strong Materials to Bioactive Surfaces. J Renew Mater 2013, 1, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, N.; Dufresne, A. Nanocellulose in biomedicine: Current status and future prospect. Eur Polym J 2014, 59, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Malinen, M.M.; Lauren, P.; Lou, Y.R.; Kuisma, S.W.; Kanninen, L.; Lille, M.; Corlu, A.; GuGuen-Guillouzo, C.; Ikkala, O.; et al. Nanofibrillar cellulose hydrogel promotes three-dimensional liver cell culture. J Control Release 2012, 164, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.R.; Kanninen, L.; Kuisma, T.; Niklander, J.; Noon, L.A.; Burks, D.; Urtti, A.; Yliperttula, M. The Use of Nanofibrillar Cellulose Hydrogel As a Flexible Three-Dimensional Model to Culture Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cells Dev 2014, 23, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Julkapli, N.M.; Bagheri, S. Nanocellulose as a green and sustainable emerging material in energy applications: a review. Polym Advan Technol 2017, 28, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanotechnologies — Standard terms and their definition for cellulose nanomaterial. ISO/TS 20477:2017(E), 1st ed.; ISO/TS 20477:2017; ISO: Vernier, Switzerland; Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Habibi, Y.; Lucia, L.A.; Rojas, O.J. Cellulose Nanocrystals: Chemistry, Self-Assembly, and Applications. Chem Rev 2010, 110, 3479–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacakova, L.; Grausova, L.; Vandrovcova, M.; Vacik, J.; Frazcek, A.; Blazewicz, S.; Kromka, A.; Vanecek, M.; Nesladek, M.; Svorcik, V.; et al. Carbon nanoparticles as substrates for cell adhesion and growth. In Nanoparticles: New Research; Lombardi, S.L., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 39–107. ISBN 978-1-60456-704-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bacakova, L.; Grausova, L.; Vacik, J.; Kromka, A.; Biederman, H.; Choukourov, A.; Stary, V. Nanocomposite and nanostructured carbon-based films as growth substrates for bone cells. In Advances in Diverse Industrial Applications of Nanocomposites; Reddy, B., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; pp. 399–435. ISBN 978-953-307-202-9. [Google Scholar]
- Bacakova, L.; Kopova, I.; Vacik, J.; Lavrentiev, V. Interaction of fullerenes and metal-fullerene composites with cells. In Fullerenes: Chemistry, Natural Sources and Technological Applications; Ellis, S.B., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Bacakova, L.; Kopova, I.; Stankova, L.; Liskova, J.; Vacik, J.; Lavrentiev, V.; Kromka, A.; Potocky, S.; Stranska, D. Bone cells in cultures on nanocarbon-based materials for potential bone tissue engineering: A review. Phys Status Solidi A 2014, 211, 2688–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacakova, L.; Filova, E.; Liskova, J.; Kopova, I.; Vandrovcova, M.; Havlikova, J. Nanostructured materials as substrates for the adhesion, growth, and osteogenic differentiation of bone cells. Appl Nanobiomater 2016, 4, 103–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacakova, L.; Broz, A.; Liskova, J.; Stankova, L.; Potocky, S.; Kromka, A. Application of nanodiamond in biotechnology and tissue engineering. In Diamond and Carbon Composites and Nanocomposites; Aliofkhazraei, M., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; pp. 59–88. ISBN 978-953-51-2453-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, B.S.; Yoong, S.L.; Jagusiak, A.; Panczyk, T.; Ho, H.K.; Ang, W.H.; Pastorin, G. Carbon nanotubes for delivery of small molecule drugs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2013, 65, 1964–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Anoshkin, I.V.; Nasibulin, A.G.; Korhonen, J.T.; Seitsonen, J.; Pere, J.; Kauppinen, E.I.; Ras, R.H.; Ikkala, O. Modifying native nanocellulose aerogels with carbon nanotubes for mechanoresponsive conductivity and pressure sensing. Adv Mater 2013, 25, 2428–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Agrawal, T.; Khan, U.; Gupta, G.K.; Rai, V.; Huang, Y.Y.; Hamblin, M.R. Antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation in nanomedicine: small light strides against bad bugs. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2015, 10, 2379–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, C.; Li, Y.; Tjong, S.C. Graphene Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Biocompatibility, and Cytotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Placha, D.; Jampilek, J. Graphenic Materials for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2019, 9, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Liu, R.; Niu, H.; Xing, L.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y. Flexible and Freestanding Supercapacitor Electrodes Based on Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Networks/Graphene/Bacterial Cellulose with Ultrahigh Areal Capacitance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2016, 8, 33608–33618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Tan, S.; Jiang, X.; Wu, W.; Shi, J.; Chen, P. Ultralight super-hydrophobic carbon aerogels based on cellulose nanofibers/poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide (CNFs/PVA/GO) for highly effective oil-water separation. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 2018, 9, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Islam, N.; Ren, G.; Li, S.; Fan, Z. AC-Filtering Supercapacitors Based on Edge Oriented Vertical Graphene and Cross-Linked Carbon Nanofiber. Materials (Basel) 2019, 12, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Q.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Huang, J. High-Performance Sodium-Ion Battery Anode via Rapid Microwave Carbonization of Natural Cellulose Nanofibers with Graphene Initiator. Small 2019, 15, e1901724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, R.L.; Ellison, K.; Haberstroh, K.M.; Webster, T.J. Nanometer surface roughness increases select osteoblast adhesion on carbon nanofiber compacts. J Biomed Mater Res A 2004, 70, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi-Moayed, S.; Golmohammadi, H.; Bigdeli, A.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. A rainbow ratiometric fluorescent sensor array on bacterial nanocellulose for visual discrimination of biothiols. Analyst 2018, 143, 3415–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, F.; Lv, Y.; Liu, J.; Bian, H.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Shao, Z. CQDs-Doped Magnetic Electrospun Nanofibers: Fluorescence Self-Display and Adsorption Removal of Mercury(II). ACS Omega 2018, 3, 4220–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shamsipour, M.; Mansouri, A.M.; Moradipour, P. Temozolomide Conjugated Carbon Quantum Dots Embedded in Core/Shell Nanofibers Prepared by Coaxial Electrospinning as an Implantable Delivery System for Cell Imaging and Sustained Drug Release. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Abou-Zeid, R.; Hassan, E.; Berglund, L.; Aitomaki, Y.; Oksman, K. Membranes Based on Cellulose Nanofibers and Activated Carbon for Removal of Escherichia coli Bacteria from Water. Polymers (Basel) 2017, 9, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashfaq, M.; Verma, N.; Khan, S. Highly effective Cu/Zn-carbon micro/nanofiber-polymer nanocomposite-based wound dressing biomaterial against the P. aeruginosa multi- and extensively drug-resistant strains. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 2017, 77, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhiago, M.; Correa, C.C.; Bernardes, J.S.; Pereira, M.P.; Oliveira, L.J.M.; Strauss, M.; Bufon, C.C.B. Flexible and Foldable Fully-Printed Carbon Black Conductive Nanostructures on Paper for High-Performance Electronic, Electrochemical, and Wearable Devices. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2017, 9, 24365–24372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, S.; Shahrokhian, S. Design and fabrication of an electrochemical aptasensor using Au nanoparticles/carbon nanoparticles/cellulose nanofibers nanocomposite for rapid and sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 123, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.D.; Zhang, D.B.; Liu, X.H.; He, Y.X.; Mi, L.W.; Zhang, J.X.; Liu, C.T.; Shen, C.Y.; et al. Superhydrophobic Electrically Conductive Paper for Ultrasensitive Strain Sensor with Excellent Anticorrosion and Self-Cleaning Property. Acs Appl Mater Inter 2019, 11, 21904–21914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhong, Z.; Li, Q.; Tan, Z.; Lin, T.; Quan, Y.; Zhang, D. Facile Low-Temperature Synthesis of Cellulose Nanocrystals Carrying Buckminsterfullerene and Its Radical Scavenging Property in Vitro. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 4034–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herreros-Lopez, A.; Carini, M.; Da Ros, T.; Carofiglio, T.; Marega, C.; La Parola, V.; Rapozzi, V.; Xodo, L.E.; Alshatwi, A.A.; Hadad, C.; et al. Nanocrystalline cellulose-fullerene: Novel conjugates. Carbohydr Polym 2017, 164, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, H.S.; Yun, Y.S.; Bak, H.; Jin, H.J. Ag-doped multiwalled carbon nanotube/polymer composite electrodes. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 2010, 10, 3571–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Zeng, Z.; Kuddannaya, S.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Biocompatible, Free-Standing Film Composed of Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers-Graphene Composite. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2016, 8, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Xiong, R.; Tsukruk, V.V. Probing Flexural Properties of Cellulose Nanocrystal-Graphene Nanomembranes with Force Spectroscopy and Bulging Test. Langmuir 2016, 32, 5383–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siljander, S.; Keinanen, P.; Raty, A.; Ramakrishnan, K.R.; Tuukkanen, S.; Kunnari, V.; Harlin, A.; Vuorinen, J.; Kanerva, M. Effect of Surfactant Type and Sonication Energy on the Electrical Conductivity Properties of Nanocellulose-CNT Nanocomposite Films. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Wang, S.; Zhu, S.; Huang, C.; Yue, Y.; Mei, C.; Xu, X.; Xia, C. Electrospun Core-Shell Nanofibrous Membranes with Nanocellulose-Stabilized Carbon Nanotubes for Use as High-Performance Flexible Supercapacitor Electrodes with Enhanced Water Resistance, Thermal Stability, and Mechanical Toughness. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019, 11, 44624–44635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.K.; Bae, J.; Hur, J.; Park, S.J.; Park, M.S.; Kim, I.T. Tailoring of Aqueous-Based Carbon Nanotube(-)Nanocellulose Films as Self-Standing Flexible Anodes for Lithium-Ion Storage. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2019, 9, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, M.; Seney, R.; Bayliss, P.C.; Kitchens, C.L. Carbon Nanotube and Cellulose Nanocrystal Hybrid Films. Molecules 2019, 24, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Zhu, C.; Mathew, A.P. Mechanically robust high flux graphene oxide - nanocellulose membranes for dye removal from water. J Hazard Mater 2019, 371, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.Q.; Yuen, J.; Slaughter, G. Carbon Nanotube-Cellulose Pellicle for Glucose Biofuel Cell. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2018, 2018, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, M.M.; Hajian, A.; Fall, A.B.; Hakansson, K.; Salajkova, M.; Lundell, F.; Wagberg, L.; Berglund, L.A. Highly conducting, strong nanocomposites based on nanocellulose-assisted aqueous dispersions of single-wall carbon nanotubes. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2467–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajian, A.; Lindstrom, S.B.; Pettersson, T.; Hamedi, M.M.; Wagberg, L. Understanding the Dispersive Action of Nanocellulose for Carbon Nanomaterials. Nano Lett 2017, 17, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamedi, M.; Karabulut, E.; Marais, A.; Herland, A.; Nystrom, G.; Wagberg, L. Nanocellulose aerogels functionalized by rapid layer-by-layer assembly for high charge storage and beyond. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2013, 52, 12038–12042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicklein, B.; Kocjan, A.; Salazar-Alvarez, G.; Carosio, F.; Camino, G.; Antonietti, M.; Bergstrom, L. Thermally insulating and fire-retardant lightweight anisotropic foams based on nanocellulose and graphene oxide. Nat Nanotechnol 2015, 10, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, N.; Wong, K.K.W.; Hosseinidoust, Z.; Sorensen, H.O.; Bruns, S.; Zheng, Y.; Tufenkji, N. Hierarchically porous, ultra-strong reduced graphene oxide-cellulose nanocrystal sponges for exceptional adsorption of water contaminants. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 7171–7184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siljander, S.; Keinanen, P.; Ivanova, A.; Lehmonen, J.; Tuukkanen, S.; Kanerva, M.; Bjorkqvist, T. Conductive Cellulose based Foam Formed 3D Shapes-From Innovation to Designed Prototype. Materials (Basel) 2019, 12, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuzmenko, V.; Karabulut, E.; Pernevik, E.; Enoksson, P.; Gatenholm, P. Tailor-made conductive inks from cellulose nanofibrils for 3D printing of neural guidelines. Carbohydr Polym 2018, 189, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrotty, D.M.; Kuzmenko, V.; Karabulut, E.; Sugrue, A.M.; Livia, C.; Vaidya, V.R.; McLeod, C.J.; Asirvatham, S.J.; Gatenholm, P.; Kapa, S. Three-Dimensional Printed Biopatches With Conductive Ink Facilitate Cardiac Conduction When Applied to Disrupted Myocardium. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2019, 12, e006920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Ul-Islam, M.; Khattak, W.A.; Park, J.K. Overview of bacterial cellulose composites: a multipurpose advanced material. Carbohydr Polym 2013, 98, 1585–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Jiang, Q.; Ghim, D.; Liu, K.K.; Sun, H.; Derami, H.G.; Wang, Z.; Tadepalli, S.; Jun, Y.S.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Catalytically Active Bacterial Nanocellulose-Based Ultrafiltration Membrane. Small 2018, 14, e1704006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Y.S.; Wu, X.; Ghim, D.; Jiang, Q.; Cao, S.; Singamaneni, S. Photothermal Membrane Water Treatment for Two Worlds. Acc Chem Res 2019, 52, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Ghim, D.; Cao, S.; Tadepalli, S.; Liu, K.K.; Kwon, H.; Luan, J.; Min, Y.; Jun, Y.S.; Singamaneni, S. Photothermally Active Reduced Graphene Oxide/Bacterial Nanocellulose Composites as Biofouling-Resistant Ultrafiltration Membranes. Environ Sci Technol 2019, 53, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abol-Fotouh, D.; Dorling, B.; Zapata-Arteaga, O.; Rodriguez-Martinez, X.; Gomez, A.; Reparaz, J.S.; Laromaine, A.; Roig, A.; Campoy-Quiles, M. Farming thermoelectric paper. Energy Environ Sci 2019, 12, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahdavi, M.; Mahmoudi, N.; Rezaie Anaran, F.; Simchi, A. Electrospinning of Nanodiamond-Modified Polysaccharide Nanofibers with Physico-Mechanical Properties Close to Natural Skins. Mar Drugs 2016, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Shen, H.; Song, S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Z. Accelerated biomineralization of graphene oxide - incorporated cellulose acetate nanofibrous scaffolds for mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.Y.; Yu, H.; Choi, J.; Kang, H.; Park, S.; Jang, J.S.; Hong, H.J.; Kim, I.D.; Lee, S.K.; Jeong, H.S.; et al. Continuous Meter-Scale Synthesis of Weavable Tunicate Cellulose/Carbon Nanotube Fibers for High-Performance Wearable Sensors. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 9332–9341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, P.; Mathew, A.P. Self-Assembled TEMPO Cellulose Nanofibers: Graphene Oxide-Based Biohybrids for Water Purification. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2017, 9, 21048–21058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ostadhossein, F.; Mahmoudi, N.; Morales-Cid, G.; Tamjid, E.; Navas-Martos, F.J.; Soriano-Cuadrado, B.; Paniza, J.M.L.; Simchi, A. Development of Chitosan/Bacterial Cellulose Composite Films Containing Nanodiamonds as a Potential Flexible Platform for Wound Dressing. Materials (Basel) 2015, 8, 6401–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Yue, Y.; Gan, L.; Xu, X.; Mei, C.; Han, J. Highly Stretchable and Self-Healing Strain Sensors Based on Nanocellulose-Supported Graphene Dispersed in Electro-Conductive Hydrogels. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2019, 9, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, J.; Tao, P.; Wu, Z.; Xing, C.; Liao, X.; Nie, S. Nanocellulose-graphene composites: A promising nanomaterial for flexible supercapacitors. Carbohydr Polym 2019, 207, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Phillips, G.O.; Yang, G. Nanocellulose electroconductive composites. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3194–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzid, A.; Hayes, P.E.; Glennon, J.D.; Luong, J.H.T. Captavidin as a regenerable biorecognition element on boron-doped diamond for biotin sensing. Anal Chim Acta 2019, 1059, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Yu, H.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yao, J.M.; Abdalkarim, S.Y.H.; Tam, K.C. Natural Biodegradable Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Nanocomposites with Multifunctional Cellulose Nanocrystals/Graphene Oxide Hybrids for High-Performance Food Packaging. J Agric Food Chem 2019, 67, 10954–10967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, N.; Banerjee, S.; Roy, P.; Pal, K. Melt-blending of unmodified and modified cellulose nanocrystals with reduced graphene oxide into PLA matrix for biomedical application. Polym Advan Technol 2019, 30, 3049–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Banerjee, S.; Roy, P.; Pal, K. Reduced graphene oxide and PEG-grafted TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanocrystal reinforced poly-lactic acid nanocomposite film for biomedical application. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 2019, 104, 109956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.; Cui, S.; Hou, X.; Ding, P.; Shi, L. Significant Enhancement of Thermal Conductivity in Nanofibrillated Cellulose Films with Low Mass Fraction of Nanodiamond. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2017, 9, 40766–40773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Palomero, C.; Benitez-Martinez, S.; Soriano, M.L.; Valcarcel, M. Fluorescent nanocellulosic hydrogels based on graphene quantum dots for sensing laccase. Anal Chim Acta 2017, 974, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javanbakht, S.; Namazi, H. Doxorubicin loaded carboxymethyl cellulose/graphene quantum dot nanocomposite hydrogel films as a potential anticancer drug delivery system. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 2018, 87, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Deepa, J.R. Nano-zinc oxide incorporated graphene oxide/nanocellulose composite for the adsorption and photo catalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride from aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 2017, 490, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, X.; Li, J.; Huang, F. Facile synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/trimethyl chlorosilane-coated cellulose nanofibres aerogel for oil absorption. IET Nanobiotechnol 2017, 11, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Fan, B.; Xiong, Y.; Jin, C.; Sun, Q.; Sheng, C. 3D assembly based on 2D structure of Cellulose Nanofibril/Graphene Oxide Hybrid Aerogel for Adsorptive Removal of Antibiotics in Water. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 45914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alizadehgiashi, M.; Khuu, N.; Khabibullin, A.; Henry, A.; Tebbe, M.; Suzuki, T.; Kumacheva, E. Nanocolloidal Hydrogel for Heavy Metal Scavenging. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 8160–8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Wan, Y.; Shen, J.; Bai, Q. Metal affinity-carboxymethyl cellulose functionalized magnetic graphene composite for highly selective isolation of histidine-rich proteins. Talanta 2019, 195, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.X.; Ma, C.; Wang, T.; Xu, Y.Y.; Yuan, B.B.; Li, P.; Kong, Y. Preparation and Characterization of C60-Filled Ethyl Cellulose Mixed-Matrix Membranes for Gas Separation of Propylene/Propane. Chem Eng Technol 2014, 37, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrivel, S.; Saraswathi, M.S.A.; Rana, D.; Nagendran, A. Fabrication of cellulose acetate nanocomposite membranes using 2D layered nanomaterials for macromolecular separation. Int J Biol Macromol 2018, 107, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomquist, N.; Wells, T.; Andres, B.; Backstrom, J.; Forsberg, S.; Olin, H. Metal-free supercapacitor with aqueous electrolyte and low-cost carbon materials. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 39836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Hsieh, Y.L. Aqueous exfoliated graphene by amphiphilic nanocellulose and its application in moisture-responsive foldable actuators. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 11719–11729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Tian, L.; Liu, K.K.; Tadepalli, S.; Raliya, R.; Biswas, P.; Naik, R.R.; Singamaneni, S. Bilayered Biofoam for Highly Efficient Solar Steam Generation. Adv Mater 2016, 28, 9400–9407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shao, C.; Zhuo, B.; Yang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Su, C.; Yuan, Q. The use of nanofibrillated cellulose to fabricate a homogeneous and flexible graphene-based electric heating membrane. Int J Biol Macromol 2019, 139, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizling, M.; Draminska, S.; Stolarczyk, K.; Tammela, P.; Wang, Z.; Nyholm, L.; Bilewicz, R. Biosupercapacitors for powering oxygen sensing devices. Bioelectrochemistry 2015, 106, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generalov, A.A.; Anoshkin, I.V.; Erdmanis, M.; Lioubtchenko, D.V.; Ovchinnikov, V.; Nasibulin, A.G.; Raisanen, A.V. Carbon nanotube network varactor. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 045201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmat, S.; Husain, Q. Exquisite stability and catalytic performance of immobilized lipase on novel fabricated nanocellulose fused polypyrrole/graphene oxide nanocomposite: Characterization and application. Int J Biol Macromol 2018, 117, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, N.; Dubey, P.; Gopinath, P.; Pal, K. Combined effect of cellulose nanocrystal and reduced graphene oxide into poly-lactic acid matrix nanocomposite as a scaffold and its anti-bacterial activity. Int J Biol Macromol 2017, 95, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini, L.; Cardinali, M.; Fortunati, E.; Kenny, J.M. Nonvolatile memory behavior of nanocrystalline cellulose/graphene oxide composite films. Appl Phys Lett 2014, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, L.; Li, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Pan, L.; Luo, Q.; Xu, X.; Lu, S. Water-Induced shape memory effect of nanocellulose papers from sisal cellulose nanofibers with graphene oxide. Carbohydr Polym 2018, 179, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Gu, Y.; Hou, X.; Li, R.; Ke, H.; Xiao, X. Hybrid Nanocomposites of Cellulose/Carbon-Nanotubes/Polyurethane with Rapidly Water Sensitive Shape Memory Effect and Strain Sensing Performance. Polymers (Basel) 2019, 11, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Q. Highly Sensitive, Ultrastretchable Strain Sensors Prepared by Pumping Hybrid Fillers of Carbon Nanotubes/Cellulose Nanocrystal into Electrospun Polyurethane Membranes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019, 11, 12968–12977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, F.; Bulger, E.; Berry, R.M.; Tam, K.C. Enhanced radical scavenging activity of polyhydroxylated C-60 functionalized cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 2016, 23, 3589–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Deng, W.; Yang, F.; Wu, Z.; Huang, M.; Gu, M. Gold nanoparticles decorated graphene oxide/nanocellulose paper for NIR laser-induced photothermal ablation of pathogenic bacteria. Carbohydr Polym 2018, 198, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Sekhar, V.C.; Shainy, F.; Thomas, J.P. Effect of dual stimuli responsive dextran/nanocellulose polyelectrolyte complexes for chemophotothermal synergistic cancer therapy. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2019, 135, 776–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoulzadeh, M.; Namazi, H. Carboxymethyl cellulose/graphene oxide bio-nanocomposite hydrogel beads as anticancer drug carrier agent. Carbohydr Polym 2017, 168, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Yu, K.X.; An, R.; Han, L.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Shi, L.Y.; Ran, R. Self-assembling GO/modified HEC hybrid stabilized pickering emulsions and template polymerization for biomedical hydrogels. Carbohyd Polym 2019, 207, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Z.; Cai, N.; Xue, Y.; Yu, F. A simple route to develop transparent doxorubicin-loaded nanodiamonds/cellulose nanocomposite membranes as potential wound dressings. Carbohydr Polym 2016, 143, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Deepa, J.R.; Binussreejayan. Electrochemical sensing of cholesterol by molecularly imprinted polymer of silylated graphene oxide and chemically modified nanocellulose polymer. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 2018, 92, 942–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Dai, Y.; Meng, X.; Xu, W.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Z.; Lu, W.; Wang, S.; Huang, C.; Sun, Y. Electronic textiles based on aligned electrospun belt-like cellulose acetate nanofibers and graphene sheets: portable, scalable and eco-friendly strain sensor. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 045602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; Lyu, Y.; Duan, H.; Chen, Z.; Tan, W. Portable and Label-Free Detection of Blood Bilirubin with Graphene-Isolated-Au-Nanocrystals Paper Strip. Anal Chem 2018, 90, 13687–13694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, F.; Li, Z. Cellulose acetate nanofibers coated layer-by-layer with polyethylenimine and graphene oxide on a quartz crystal microbalance for use as a highly sensitive ammonia sensor. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2016, 148, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, T.; Sheng, Y.Y.; Xu, J.K.; Li, Y.Y.; Lu, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.F.; Duan, X.M.; Wen, Y.P. In-situ reduction of Ag+ on black phosphorene and its NH2-MWCNT nanohybrid with high stability and dispersibility as nanozyme sensor for three ATP metabolites. Biosens Bioelectron 2019, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Kim, K.; Kim, B.; Lee, K.J.; Kang, J.W.; Jeon, S. Vertically stacked nanocellulose tactile sensor. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 17212–17219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, C.; Chen, G. Flexible and Highly Sensitive Humidity Sensor Based on Cellulose Nanofibers and Carbon Nanotube Composite Film. Langmuir 2019, 35, 4834–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhu, C.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, D. Biointerface by Cell Growth on Graphene Oxide Doped Bacterial Cellulose/Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) Nanofibers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2016, 8, 10183–10192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Quan, Q.; Meng, H.; Zheng, Y.; Peng, J.; Hu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Sang, X.; Qiao, K.; He, W.; et al. Enhanced Neurite Outgrowth on a Multiblock Conductive Nerve Scaffold with Self-Powered Electrical Stimulation. Adv Healthc Mater 2019, 8, e1900127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Ponrasu, T.; Chandel, S.; Dixit, M.; Muthuvijayan, V. Reduced graphene oxide-loaded nanocomposite scaffolds for enhancing angiogenesis in tissue engineering applications. R Soc Open Sci 2018, 5, 172017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.Y.; Low, H.R.; Loi, X.Y.; Merel, L.; Mohd Cairul Iqbal, M.A. Fabrication and evaluation of bacterial nanocellulose/poly(acrylic acid)/graphene oxide composite hydrogel: Characterizations and biocompatibility studies for wound dressing. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 2019, 107, 2140–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, L.; Wu, H.; Li, Q.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, D.; Deng, S.; et al. Graphene Oxide-IPDI-Ag/ZnO@Hydroxypropyl Cellulose Nanocomposite Films for Biological Wound-Dressing Applications. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15373–15381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burrs, S.L.; Bhargava, M.; Sidhu, R.; Kiernan-Lewis, J.; Gomes, C.; Claussen, J.C.; McLamore, E.S. A paper based graphene-nanocauliflower hybrid composite for point of care biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron 2016, 85, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Dong, J.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Ai, S.Y. Electrochemical immunosensor with nanocellulose-Au composite assisted multiple signal amplification for detection of avian leukosis virus subgroup J. Biosens Bioelectron 2018, 101, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, X.X.; Wu, X.D.; Wang, S.M.; Lu, C.H. Cellulose nanocrystals mediated assembly of graphene in rubber composites for chemical sensing applications. Carbohyd Polym 2016, 140, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, C.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Kang, W.B.; Cui, M.Q.; Wang, X.; Foo, C.Y.; Chee, K.J.; Lee, P.S. Highly Stretchable Piezoresistive Graphene-Nanocellulose Nanopaper for Strain Sensors. Advanced Materials 2014, 26, 2022–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Lu, C. Tailoring percolating conductive networks of natural rubber composites for flexible strain sensors via a cellulose nanocrystal templated assembly. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baleizao, C.; Nagl, S.; Schaferling, M.; Berberan-Santos, M.N.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Dual fluorescence sensor for trace oxygen and temperature with unmatched range and sensitivity. Anal Chem 2008, 80, 6449–6457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochmann, S.; Baleizao, C.; Berberan-Santos, M.N.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Sensing and imaging of oxygen with parts per billion limits of detection and based on the quenching of the delayed fluorescence of (13)C70 fullerene in polymer hosts. Anal Chem 2013, 85, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, S.; Shen, M.; Qi, R.; Fang, Y.; Guo, R.; Cai, H.; Cao, X.; Tomas, H.; Zhu, M.; et al. Carbon nanotube-incorporated multilayered cellulose acetate nanofibers for tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr Polym 2013, 91, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duri, S.; Harkins, A.L.; Frazier, A.J.; Tran, C.D. Composites Containing Fullerenes and Polysaccharides: Green and Facile Synthesis, Biocompatibility, and Antimicrobial Activity. Acs Sustain Chem Eng 2017, 5, 5408–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopova, I.; Bacakova, L.; Lavrentiev, V.; Vacik, J. Growth and potential damage of human bone-derived cells on fresh and aged fullerene c60 films. Int J Mol Sci 2013, 14, 9182–9204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopova, I.; Lavrentiev, V.; Vacik, J.; Bacakova, L. Growth and potential damage of human bone-derived cells cultured on fresh and aged C60/Ti films. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0123680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheka, E.F. Chapter 1: Concepts and grounds. In Fullerenes: Nanochemistry, Nanomagnetism, Nanomedicine, Nanophotonics; Sheka, E.F., Ed.; CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 1–14. ISBN 9781439806425. [Google Scholar]
- Sheka, E.F. Chapter 9: Nanomedicine of fullerene C60. In Fullerenes: Nanochemistry, Nanomagnetism, Nanomedicine, Nanophotonics, 1st ed.; Sheka, E.F., Ed.; CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 175–191. ISBN 9781439806425. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Kee, C.D.; Vadahanambi, S.; Oh, I.K. A Novel Biocompatible Actuator based on Electrospun Cellulose Acetate. Adv Mater Res-Switz 2011, 214, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseeva, O.V.; Bagrovskaya, N.A.; Noskov, A.V. The Sorption Activity of a Cellulose-Fullerene Composite Relative to Heavy Metal Ions. Prot Met Phys Chem+ 2019, 55, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, S.S.; Zhang, R.Y.; Zhu, J. Graphene synthesis: a Review. Mater Sci-Poland 2015, 33, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coros, M.; Pogacean, F.; Magerusan, L.; Socaci, C.; Pruneanu, S. A brief overview on synthesis and applications of graphene and graphene-based nanomaterials. Front Mater Sci 2019, 13, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malho, J.M.; Laaksonen, P.; Walther, A.; Ikkala, O.; Linder, M.B. Facile Method for Stiff, Tough, and Strong Nanocomposites by Direct Exfoliation of Multilayered Graphene into Native Nanocellulose Matrix. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Lu, Z.X.; Zhao, J.Q.; Li, Q.Y.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C.H. Exfoliation/dispersion of low-temperature expandable graphite in nanocellulose matrix by wet co-milling. Carbohyd Polym 2017, 157, 1434–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Lv, J.L.; Yang, F.L. Optimized anti-biofouling performance of bactericides/cellulose nanocrystals composites modified PVDF ultrafiltration membrane for micro-polluted source water purification. Water Sci Technol 2019, 79, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Pan, H.; Meng, X.; Zhu, C.L.; Liu, S.Y.; Chen, Z.X.; Ma, J.; Zhu, S.M. Assembly of MnO/CNC/rGO fibers from colloidal liquid crystal for flexible supercapacitors via a continuous one-process method. Nanotechnology 2019, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, P.; Gaur, S.S.; Kumar, A.; Katiyar, V. Cellulose Nanocrystal Templated Graphene Nanoscrolls for High Performance Supercapacitors and Hydrogen Storage: An Experimental and Molecular Simulation Study. Sci Rep-Uk 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.X.; Yu, J.Y.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Li, R.K.; Xiang, Z.H.; Cao, Q.; Zhao, L.L.; Peng, X.W.; Liu, H.; Zhou, W.J. N-Doped Mo2C Nanobelts/Graphene Nanosheets Bonded with Hydroxy Nanocellulose as Flexible and Editable Electrode for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Iscience 2019, 19, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.M.; Liu, Y.; Du, C.Y.; Ren, Y.; Li, X.L.; Zuo, P.J.; Yin, G.P.; Ma, Y.L.; Cheng, X.Q.; Gao, Y.Z. Free-Standing Sandwich-Type Graphene/Nanocellulose/Silicon Laminar Anode for Flexible Rechargeable Lithium Ion Batteries. Acs Appl Mater Inter 2018, 10, 29638–29646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Tammela, P.; Stromme, M.; Nyholm, L. Nanocellulose coupled flexible polypyrrole@graphene oxide composite paper electrodes with high volumetric capacitance. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 3418–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Rao, K.M.; Han, S.S. Mechanically viscoelastic nanoreinforced hybrid hydrogels composed of polyacrylamide, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, graphene oxide, and cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohyd Polym 2018, 193, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laaksonen, P.; Walther, A.; Malho, J.M.; Kainlauri, M.; Ikkala, O.; Linder, M.B. Genetic Engineering of Biomimetic Nanocomposites: Diblock Proteins, Graphene, and Nanofibrillated Cellulose. Angew Chem Int Edit 2011, 50, 8688–8691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.L.; Huang, X.Y.; Liang, H.E.; Tao, Q. Enhanced hydrophilic and antibacterial efficiencies by the synergetic effect TiO2 nanofiber and graphene oxide in cellulose acetate nanofibers. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2019, 132, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Helical Microtubules of Graphitic Carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankova, L.; Fraczek-Szczypta, A.; Blazewicz, M.; Filova, E.; Blazewicz, S.; Lisa, V.; Bacakova, L. Human osteoblast-like MG 63 cells on polysulfone modified with carbon nanotubes or carbon nanohorns. Carbon 2014, 67, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Kuramae, R.; Wohlert, J.; Berglund, L.A.; Isogai, A. An Ultrastrong Nanofibrillar Biomaterial: The Strength of Single Cellulose Nanofibrils Revealed via Sonication-Induced Fragmentation. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, H.; Saito, T.; Kitaoka, T.; Nogi, M.; Suganuma, K.; Isogai, A. Transparent, Conductive, and Printable Composites Consisting of TEMPO-Oxidized Nanocellulose and Carbon Nanotube. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Linder, M.B.; Laaksonen, P. Modification of carbon nanotubes by amphiphilic glycosylated proteins. J Colloid Interf Sci 2018, 512, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougel, J.B.; Bertoncini, P.; Cathala, B.; Chauvet, O.; Capron, I. Macroporous hybrid Pickering foams based on carbon nanotubes and cellulose nanocrystals. J Colloid Interf Sci 2019, 544, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigueiro, J.P.C.; Silva, G.G.; Pereira, F.V.; Lavall, R.L. Layer-by-layer assembled films of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with chitosan and cellulose nanocrystals. J Colloid Interf Sci 2014, 432, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Shi, K.Y.; Zhitomirsky, I.; Cranston, E.D. Cellulose Nanocrystal Aerogels as Universal 3D Lightweight Substrates for Supercapacitor Materials. Advanced Materials 2015, 27, 6104–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZabihiSahebi, A.; Koushkbaghi, S.; Pishnamazi, M.; Askari, A.; Khosravi, R.; Irani, M. Synthesis of cellulose acetate/chitosan/SWCNT/Fe3O4/TiO2 composite nanofibers for the removal of Cr(VI), As(V), Methylene blue and Congo red from aqueous solutions. Int J Biol Macromol 2019, 140, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Chun, S.J.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, B.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, W. All-solid-state flexible supercapacitors fabricated with bacterial nanocellulose papers, carbon nanotubes, and triblock-copolymer ion gels. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6400–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lee, Y.; Sun, H.; Wallas, J.M.; George, S.M.; Xie, M. Coating Solution for High-Voltage Cathode: AlF3 Atomic Layer Deposition for Freestanding LiCoO2 Electrodes with High Energy Density and Excellent Flexibility. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2017, 9, 9614–9619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Dominguez, J.M.; Anson-Casaos, A.; Grasa, L.; Abenia, L.; Salvador, A.; Colom, E.; Mesonero, J.E.; Garcia-Bordeje, J.E.; Benito, A.M.; Maser, W.K. Unique Properties and Behavior of Nonmercerized Type-II Cellulose Nanocrystals as Carbon Nanotube Biocompatible Dispersants. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 3147–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Hubbe, M.A.; Pal, L. Highly conductive carbon nanotubes and flexible cellulose nanofibers composite membranes with semi-interpenetrating networks structure. Carbohydr Polym 2019, 222, 115013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, H.; Zeng, Y.; Yin, Z.; Li, L. Electrochemical Molecular Imprinted Sensors Based on Electrospun Nanofiber and Determination of Ascorbic Acid. Anal Sci 2015, 31, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broz, A.; Bacakova, L.; Stenclova, P.; Kromka, A.; Potocky, S. Uptake and intracellular accumulation of diamond nanoparticles - a metabolic and cytotoxic study. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 2017, 8, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, O.A. Ultrananocrystalline diamond for electronic applications. Semicond Sci Tech 2006, 21, R49–R56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenderova, O.A.; Gruen, D.M. Ultrananocrystalline Diamond: Synthesis, Properties and Applications of UNCD, 2nd ed.; Shenderova, O.A., Gruen, D.M., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2012; p. 584. ISBN 9781437734652. [Google Scholar]
- Mochalin, V.N.; Shenderova, O.; Ho, D.; Gogotsi, Y. The properties and applications of nanodiamonds. Nat Nanotechnol 2011, 7, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankova, L.; Musilkova, J.; Broz, A.; Potocky, S.; Kromka, A.; Kozak, H.; Izak, T.; Artemenko, A.; Stranska, D.; Bacakova, L. Alterations to the adhesion, growth and osteogenic differentiation of human osteoblast-like cells on nanofibrous polylactide scaffolds with diamond nanoparticles. Diam Relat Mater 2019, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grausova, L.; Kromka, A.; Burdikova, Z.; Eckhardt, A.; Rezek, B.; Vacik, J.; Haenen, K.; Lisa, V.; Bacakova, L. Enhanced Growth and Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Osteoblast-Like Cells on Boron-Doped Nanocrystalline Diamond Thin Films. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liskova, J.; Babchenko, O.; Varga, M.; Kromka, A.; Hadraba, D.; Svindrych, Z.; Burdikova, Z.; Bacakova, L. Osteogenic cell differentiation on H-terminated and O-terminated nanocrystalline diamond films. Int J Nanomed 2015, 10, 869–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morimune-Moriya, S.; Salajkova, M.; Zhou, Q.; Nishino, T.; Berglund, L.A. Reinforcement Effects from Nanodiamond in Cellulose Nanofibril Films. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 2423–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juknius, T.; Ruzauskas, M.; Tamulevicius, T.; Siugzdiniene, R.; Jukniene, I.; Vasiliauskas, A.; Jurkeviciute, A.; Tamulevicius, S. Antimicrobial Properties of Diamond-Like Carbon/Silver Nanocomposite Thin Films Deposited on Textiles: Towards Smart Bandages. Materials 2016, 9, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, F.S.; Huang, Y.; Fan, M.M.; Chen, C.T.; Qian, J.S.; Hao, Q.L.; Yang, J.Z.; Sun, D.P. N-Doped Carbon Nanofibrous Network Derived from Bacterial Cellulose for the Loading of Pt Nanoparticles for Methanol Oxidation Reaction. Chem-Eur J 2018, 24, 1844–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, M.Y.; Luo, Y.; Huang, J.G. Bio-Inspired Hierarchical Nanofibrous Fe3O4-TiO2-Carbon Composite as a High-Performance Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Acs Appl Mater Inter 2016, 8, 17343–17351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, K.B.; Cengiz, E.C.; Sar, T.; Dursun, B.; Ozturk, O.; Akbas, M.Y.; Demir-Cakan, R. In-situ wrapping of tin oxide nanoparticles by bacterial cellulose derived carbon nanofibers and its application as freestanding interlayer in lithium sulfide based lithium-sulfur batteries. J Colloid Interf Sci 2018, 530, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.C.; Rong, J.; Qiu, F.X.; Zhu, Y.; Mao, K.L.; Fang, Y.Y.; Yang, D.Y.; Zhang, T. Highly dispersive NiCo2S4 nanoparticles anchored on nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. J Colloid Interf Sci 2019, 555, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Amora, M.; Giordani, S. Carbon Nanomaterials for Nanomedicine. In Micro and Nano Technologies; Ciofani, G., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 103–113. ISBN 978-0-12-814156-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, I.; Fruijtier-Polloth, C.; Ngiewih, Y.; Levy, L. Evaluating the evidence on genotoxicity and reproductive toxicity of carbon black: a critical review. Crit Rev Toxicol 2018, 48, 143–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niranjan, R.; Thakur, A.K. The Toxicological Mechanisms of Environmental Soot (Black Carbon) and Carbon Black: Focus on Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Pathways. Front Immunol 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, W.X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, L.; Zhang, X.Z.; Chen, N.; Sun, Y.H.; Chen, W.; Tai, R.Z.; et al. Excessive Sodium Ions Delivered into Cells by Nanodiamonds: Implications for Tumor Therapy. Small 2012, 8, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, T.; Naish, V.; O’Connor, B.; Blaise, C.; Gagne, F.; Hall, L.; Trudeau, V.; Martel, P. An ecotoxicological characterization of nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC). Nanotoxicology 2010, 4, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvedova, A.A.; Kisin, E.R.; Yanamala, N.; Farcas, M.T.; Menas, A.L.; Williams, A.; Fournier, P.M.; Reynolds, J.S.; Gutkin, D.W.; Star, A.; et al. Gender differences in murine pulmonary responses elicited by cellulose nanocrystals. Part Fibre Toxicol 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sunasee, R.; Araoye, E.; Pyram, D.; Hemraz, U.D.; Boluk, Y.; Ckless, K. Cellulose nanocrystal cationic derivative induces NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent IL-1beta secretion associated with mitochondrial ROS production. Biochem Biophys Rep 2015, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ede, J.D.; Ong, K.J.; Goergen, M.; Rudie, A.; Pomeroy-Carter, C.A.; Shatkin, J.A. Risk Analysis of Cellulose Nanomaterials by Inhalation: Current State of Science. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2019, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Przekora, A.; Vandrovcova, M.; Travnickova, M.; Pajorova, J.; Molitor, M.; Ginalska, G.; Bacakova, L. Evaluation of the potential of chitosan/beta-1,3-glucan/hydroxyapatite material as a scaffold for living bone graft production in vitro by comparison of ADSC and BMDSC behaviour on its surface. Biomed Mater 2017, 12, 015030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacakova, L.; Zarubova, J.; Travnickova, M.; Musilkova, J.; Pajorova, J.; Slepicka, P.; Kasalkova, N.S.; Svorcik, V.; Kolska, Z.; Motarjemi, H.; et al. Stem cells: their source, potency and use in regenerative therapies with focus on adipose-derived stem cells - a review. Biotechnol Adv 2018, 36, 1111–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filova, E.; Bullett, N.A.; Bacakova, L.; Grausova, L.; Haycock, J.W.; Hlucilova, J.; Klima, J.; Shard, A. Regionally-selective cell colonization of micropatterned surfaces prepared by plasma polymerization of acrylic acid and 1,7-octadiene. Physiol Res 2009, 58, 669–684. [Google Scholar]




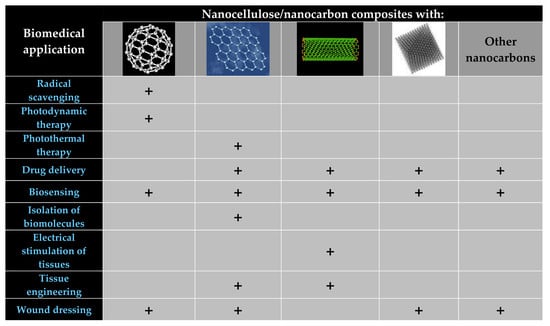
| Application | Nanocellulose/Nanocarbon Composites Containing: | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fullerenes | Graphene | CNTs | Nanodiamonds | Others | |
| Radical scavenging | NH2-CNC/C60 [34]; CNC/C60(OH)30 [92] | ||||
| Photodynamic cancer therapy | TEMPO-oxidized CNC/C60-NH2 [35] | ||||
| Photothermal, chemo-photothermal therapy | Bacteria: [93] | ||||
| Cancer: [94] | |||||
| Drug delivery | Anticancer drugs (doxorubicin) [72,95,96] | Anticancer and other drugs [16] | Anticancer drugs (doxorubicin) [97] | Carbon quantum dots: Anticancer drugs (temozolomide) [28] | |
| (Bio)sensors | Electrochemical: cholesterol [98]; glucose and bacteria [110]; avian leucosis virus [111]; organic liquids [112] | Electrochemical: ATP metabolites [102]; oxygen [84] | Electrochemical: Biotin [66] | Carbon black: Electrochemical aptasensor for S. aureus [32]; electrochemical sensor for H2O2 [33] | |
| Piezoelectric: strain, human motion [63,99,113] | Piezoresistance and thermoelectric-based: pressure and temperature [103]; pressure [17]; strain, human motion [90,91,114]; humidity, human breath [104] | Carbon black: Strain, human motion [31,33] | |||
| Optical: oxygen and temperature [115]; oxygen [116] | Optical: SERS: bilirubin [100]; Fluorescence: laccase [71] | Carbon quantum dots: optical sensor for biothiols [26] | |||
| Acoustic: ammonia [101] | |||||
| Isolation of biomolecules | Histidine-rich proteins, hemoglobin [77]; bovine serum albumin [79] | ||||
| Electrical stimulation of tissues | Cardiac tissue [52]; neural tissue [106] | ||||
| Tissue engineering (TE) | General cell biocompatibility [68,69,87]; bone TE [37,59]; neural TE [105]; vascular TE [107] | Neural tissue engineering [51]; TE in general [117] | |||
| Wound dressing/healing | Polysaccharides/fullerene C60 derivatives [118] | Human dermal fibroblasts in vitro [108]; mouse model in vivo [109] | L929 fibroblasts in vitro [58,62]; HeLa cells in vitro, wound dressings delivering doxorubicin [97] | Activated carbon: antibacterial wound dressing [30] | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bacakova, L.; Pajorova, J.; Tomkova, M.; Matejka, R.; Broz, A.; Stepanovska, J.; Prazak, S.; Skogberg, A.; Siljander, S.; Kallio, P. Applications of Nanocellulose/Nanocarbon Composites: Focus on Biotechnology and Medicine. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020196
Bacakova L, Pajorova J, Tomkova M, Matejka R, Broz A, Stepanovska J, Prazak S, Skogberg A, Siljander S, Kallio P. Applications of Nanocellulose/Nanocarbon Composites: Focus on Biotechnology and Medicine. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(2):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020196
Chicago/Turabian StyleBacakova, Lucie, Julia Pajorova, Maria Tomkova, Roman Matejka, Antonin Broz, Jana Stepanovska, Simon Prazak, Anne Skogberg, Sanna Siljander, and Pasi Kallio. 2020. "Applications of Nanocellulose/Nanocarbon Composites: Focus on Biotechnology and Medicine" Nanomaterials 10, no. 2: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020196
APA StyleBacakova, L., Pajorova, J., Tomkova, M., Matejka, R., Broz, A., Stepanovska, J., Prazak, S., Skogberg, A., Siljander, S., & Kallio, P. (2020). Applications of Nanocellulose/Nanocarbon Composites: Focus on Biotechnology and Medicine. Nanomaterials, 10(2), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020196