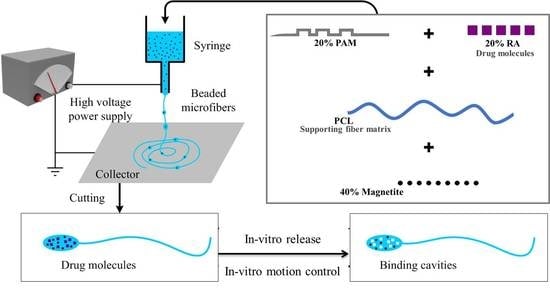
Fabrication of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Beaded Fibers for Rosmarinic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication and Characterization of Magnetic MI Fibers
2.2. Design of Experiment Methodology
2.3. Optimization of Fiber Fabrication
2.4. Characterization of Optimized MI Fibers
2.5. Drug Encapsulation and In Vitro Release Studies
2.6. Magnetic Actuation System
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. MI Fiber Preparation
3.2. Design of Experiments Methodology
3.2.1. Regression Analysis
CD2 − 0.01528 FR2 − 0.01090 V2 + 0.01077 PC × FR
3.2.2. Graphic Modeling
3.2.3. Test of the Model Predictions
3.3. Optimization of the Fiber Fabrication
3.4. Characterization of Optimized MI Fibers
3.5. In Vitro Release Studies
3.6. Magnetic Control of MI Sperm-Shaped Magnetic Beaded Fibers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wulff, G.; Sarhan, A.; Zabrocki, K. Enzyme-analogue built polymers and their use for the resolution of racemates. Tetrahedron Lett. 1973, 14, 4329–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E. Einfluss der Configuration auf die Wirkung der Enzyme. Berichte der Dtsch. Chem. Gesellschaft 1894, 27, 2985–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, J.; Chen, W.; Ma, Y.; Pan, G. Molecularly imprinted polymers as receptor mimics for selective cell recognition. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5574–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lei, J. Synthesis and evaluation of molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres for chloramphenicol by aqueous suspension polymerization as a high performance liquid chromatography stationary phase. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, 34, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cela-Perez, M.C.; Lasagabaster-Latorre, A.; Abad-Lopez, M.J.; Lopez-Vilarino, J.M.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, M.V. A study of competitive molecular interaction effects on imprinting of molecularly imprinted polymers. Vib. Spectrosc. 2013, 65, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Row, K.H. Characteristic and synthetic approach of molecularly imprinted polymer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2006, 7, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooley, J.F. Apparatus for Electrically Dispersing Fluids. U.S. Patent 692631, 4 February 1902. [Google Scholar]
- Boys, C.V. On the production, properties, and some suggested uses of the finest threads. Proc. Phys. Soc. Lond. 1887, 9, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Weng, J. Investigation on process parameters of electrospinning system through orthogonal experimental design. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 3105–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, G.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for drug delivery applications. J. Control. Release 2014, 185, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorani, B.; Tucker, N.; Yoshikawa, M. Approaches for the assembly of molecularly imprinted electrospun nanofibre membranes and consequent use in selected target recognition. Food Res. Int. 2015, 78, 448–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Wu, D. Effect of different solvents on poly (caprolactone)(PCL) electrospun nonwoven membranes. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 107, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, H.; Chun, I.; Reneker, D.H. Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymer (Guildf) 1999, 40, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döpke, C.; Grothe, T.; Steblinski, P.; Klöcker, M.; Sabantina, L.; Kosmalska, D.; Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Magnetic nanofiber mats for data storage and transfer. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brito-Pereira, R.; Correia, D.M.; Ribeiro, C.; Francesko, A.; Etxebarria, I.; Pérez-Álvarez, L.; Vilas, J.L.; Martins, P.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Silk fibroin-magnetic hybrid composite electrospun fibers for tissue engineering applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 141, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, I.S.M.; Tabak, A.F.; Hamed, Y.; Mitwally, M.E.; Tawakol, M.; Klingner, A.; Sitti, M. Swimming back and forth using planar flagellar propulsion at low Reynolds numbers. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, I.S.M.; Fatih Tabak, A.; Klingner, A.; Sitti, M. Magnetic propulsion of robotic sperms at low-Reynolds number. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 033701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiter, F.A.A.; Alexander, C.; Rose, F.R.A.J.; Segal, J.I. A design of experiments approach to identify the influencing parameters that determine poly-D, L-lactic acid (PDLLA) electrospun scaffold morphologies. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 12, 055009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, L.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, L.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospraying and Electrospinning for Nanobiomaterial Fabrication. In Nanobiomaterials: Classification, Fabrication and Biomedical Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2017; pp. 143–163. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Xiao, J.; Xi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, Q.; Zheng, H.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y. Rosmarinic acid improved antioxidant properties and healthspan via the IIS and MAPK pathways in Caenorhabditis elegans. BioFactors 2019, 45, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-H.; Kee, J.-Y.; Hong, S.-H. Rosmarinic acid activates AMPK to inhibit metastasis of colorectal cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Feng, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, B.; Tian, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, M.; Liu, G. Rosmarinic acid protects mice from lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting MAPKs/NF-κB and activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 67, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, S. Molecular pharmacology of rosmarinic and salvianolic acids: Potential seeds for Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lasprilla-Botero, J.; Alvarez-Lainez, M.; Lagaron, J.M. The influence of electrospinning parameters and solvent selection on the morphology and diameter of polyimide nanofibers. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Khanlou, H.; Chin Ang, B.; Talebian, S.; Muhammad Afifi, A.; Andriyana, A. Electrospinning of polymethyl methacrylate nanofibers: Optimization of processing parameters using the Taguchi design of experiments. Text. Res. J. 2015, 85, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, C. Effects of working parameters on electrospinning. In One-Dimensional Nanostructures; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Provan, G.J.; Helliwell, K. Determination of rosmarinic acid and caffeic acid in aromatic herbs by HPLC. Food Chem. 2004, 87, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultanova, Z.; Kaleli, G.; Kabay, G.; Mutlu, M. Controlled release of a hydrophilic drug from coaxially electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 505, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Gong, S.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Shen, C.; Turng, L.-S. Fabrication of polycaprolactone electrospun fibers with different hierarchical structures mimicking collagen fibrils for tissue engineering scaffolds. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofidfar, M.; Prausnitz, M.R. Electrospun Transdermal Patch for Contraceptive Hormone Delivery. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronakis, I.S.; Milosevic, B.; Frenot, A.; Ye, L. Generation of molecular recognition sites in electrospun polymer nanofibers via molecular imprinting. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.J.; Stride, E.; Edirisinghe, M. Mapping the influence of solubility and dielectric constant on electrospinning polycaprolactone solutions. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 4669–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Bickford, T.; Haroosh, H.J.; Lau, K.-T.; Takagi, H. Multi-response analysis in the material characterisation of electrospun poly (lactic acid)/halloysite nanotube composite fibres based on Taguchi design of experiments: Fibre diameter, non-intercalation and nucleation effects. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 112, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, X.; Lu, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Molecularly imprinted electrospun nanofibers for adsorption of 2, 4-dinitrotoluene in water. Analyst 2018, 143, 3465–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matabola, K.P.; Moutloali, R.M. The influence of electrospinning parameters on the morphology and diameter of poly (vinyledene fluoride) nanofibers-effect of sodium chloride. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 5475–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: Methods, materials, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokalp, N.; Ulker, C.; Guvenilir, Y.A. Enzymatic ring opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone by using a novel immobilized biocatalyst. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2016, 7, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N. Preparation of biocompatible magnetite-carboxymethyl cellulose nanocomposite: Characterization of nanocomposite by FTIR, XRD, FESEM and TEM. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 131, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carolan, D.; Doyle, H. Size and emission color tuning in the solution phase synthesis of highly luminescent germanium nanocrystals. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 3562–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Celik, S.E.; Ozyurek, M.; Tufan, A.N.; Guclu, K.; Apak, R. Spectroscopic study and antioxidant properties of the inclusion complexes of rosmarinic acid with natural and derivative cyclodextrins. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 78, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, M. The evidence from infrared spectroscopy for hydrogen bonding: A case history of the correlation and interpretation of data. J. Chem. Educ. 1957, 34, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, I.S.M.; Tabak, A.F.; Hamed, Y.; Tawakol, M.; Klingner, A.; El Gohary, N.; Mizaikoff, B.; Sitti, M. Independent actuation of two-tailed microrobots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Run | ln FD | ln NB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | Predicted | Prediction Range | Experimental | Predicted | Prediction Range | |
| A | 4.64 | 4.42 | 4.05–4.79 | −2.98 | −2.22 | (−3.16)–(−1.28) |
| B | 6.33 | 6.12 | 5.81–6.44 | −5.01 | −4.58 | (−5.48)–(−3.69) |
| C | 6.88 | 6.70 | 6.37–7.03 | −9.00 | −9.31 | (−10.23)–(−8.39) |
| Sample | C % | N % | O % | Fe % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head | 70.21 | 4.47 | 23.65 | 1.67 |
| Tail | 74.51 | 3.95 | 21.53 | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saad, E.M.; El Gohary, N.A.; El-Shenawy, B.M.; Handoussa, H.; Klingner, A.; Elwi, M.; Hamed, Y.; Khalil, I.S.M.; El Nashar, R.M.; Mizaikoff, B. Fabrication of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Beaded Fibers for Rosmarinic Acid. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081478
Saad EM, El Gohary NA, El-Shenawy BM, Handoussa H, Klingner A, Elwi M, Hamed Y, Khalil ISM, El Nashar RM, Mizaikoff B. Fabrication of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Beaded Fibers for Rosmarinic Acid. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(8):1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081478
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaad, Engy M., Nesrine Abdelrehim El Gohary, Basma M. El-Shenawy, Heba Handoussa, Anke Klingner, Mohamed Elwi, Youssef Hamed, Islam S. M. Khalil, Rasha Mohamed El Nashar, and Boris Mizaikoff. 2020. "Fabrication of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Beaded Fibers for Rosmarinic Acid" Nanomaterials 10, no. 8: 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081478
APA StyleSaad, E. M., El Gohary, N. A., El-Shenawy, B. M., Handoussa, H., Klingner, A., Elwi, M., Hamed, Y., Khalil, I. S. M., El Nashar, R. M., & Mizaikoff, B. (2020). Fabrication of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Beaded Fibers for Rosmarinic Acid. Nanomaterials, 10(8), 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081478