Dimethylglyoxime Clathrate as Ligand Derived Nitrogen-Doped Carbon-Supported Nano-Metal Particles as Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials Synthesis
2.2. Structure Characterization
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
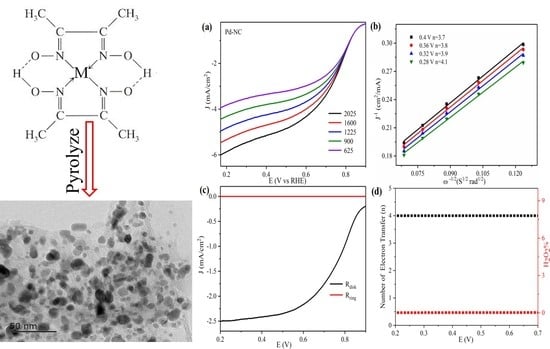
3. Result and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merle, G.; Wessling, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 377, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülzow, E. Alkaline fuel cells. Fuel Cells 2004, 4, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Huang, T.; Mao, J.; Yao, S.; Dinesh, M.M.; Sun, Y.; Liang, N.; Qi, L.; Yu, J.; Jiang, Z. Investigation on the catalytic performance of reduced-graphene-oxide-interpolated FeS2 and FeS for oxygen reduction reaction. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 10418–10427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, J.; Lu, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, A.; Zhuang, L.; Lu, J. High-Performance Alkaline Polymer Electrolyte for Fuel Cell Applications. Adv. Fun. Mater. 2010, 20, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banham, D.; Feng, F.; Pei, K.; Ye, S.; Birss, V. Effect of carbon support nanostructure on the oxygen reduction activity of Pt/C catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 2812–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Cárcamo, C.; Serp, P. Single atom catalysts on carbon-based materials. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 5058–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.R.; Jiang, J.; Yu, S.H. Solution-based synthesis and design of late transition metal chalcogenide materials for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). Small 2012, 8, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-S.; Li, S.-L.; Tang, Y.-J.; Han, M.; Dai, Z.-H.; Bao, J.-C.; Lan, Y.-Q. Nitrogen-doped Fe/Fe3C@graphitic layer/carbon nanotube hybrids derived from MOFs: Efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for ORR and OER. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2710–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Zhu, J.; Li, G.; Li, N.; Li, S.; Cano, Z.P.; Ma, L.; Cui, P.; Xu, P.; Jiang, G.; et al. A single-atom iridium heterogeneous catalyst in oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 9640–9645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Liu, P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, M.; Yang, B.; Lei, L.; et al. Efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution on atomically dispersed Ni–Nx Species anchored porous carbon with embedded Ni nanoparticles by accelerating water dissociation kinetics. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; More, K.L.; Johnston, C.M.; Zelenay, P. High-performance electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction derived from polyaniline, iron, and cobalt. Science 2011, 332, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Ko, M.; Park, M.; Kim, M.G.; Oh, P.; Chae, S.; Park, S.; Casimir, A.; Wu, G.; et al. Metal (Ni, Co)-metal oxides/graphene nanocomposites as multifunctional electrocatalysts. Adv. Fun. Mater. 2015, 25, 5799–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C. Transition metals (Fe, Co, and Ni) encapsulated in nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes as bi-functional catalysts for oxygen electrode reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.Y.; Tong, X.L.; Zhang, Y.F.; Han, X.D.; Wang, Y.Y.; Jin, G.Q.; Qin, Y.; Guo, X.Y. Cuprous oxide nanoparticles dispersed on reduced graphene oxide as an efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1892–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Z.; Liu, W.; Chang, C.; Tang, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Jia, C.; Yao, T.; Wei, S.; et al. Design of N-coordinated dual-metal sites: A stable and active Pt-free catalyst for acidic oxygen reduction reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17281–17284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, S.; Sun, S. Tuning Nanoparticle Catalysis for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8526–8544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Dou, S.; Shen, A.; Tao, L.; Dai, L.; Wang, S. Sulfur-doped graphene derived from cycled lithium-sulfur batteries as a metal-free electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 1888–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, F. Photochemical solid-phase synthesis of platinum single atoms on nitrogen-doped carbon with high loading as bifunctional catalysts for hydrogen evolution and oxygen reduction reactions. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 8450–8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shen, Z.; Xin, S.; Ma, L.; Xiao, C.; Ding, S.; Li, F.; Gao, G. Ultrafine Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide as an efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 224, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.K.; Li, X.F.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, J. Cooperative spin transition of monodispersed FeN3 sites within graphene induced by CO adsorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 15149–15152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S., Jr.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, R.; Pandey, P.; Gautam, A.; Bisen, O.Y.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Titirici, M.-M.; Nanda, K.K. Atomic Arrangement Modulation in CoFe Nanoparticles Encapsulated in N-Doped Carbon Nanostructures for Efficient Oxygen Reduction Reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 3771–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meganathan, M.D.; Mao, S.; Huang, T.; Sun, G. Reduced graphene oxide intercalated Co2C or Co4N nanoparticles as an efficient and durable fuel cell catalyst for oxygen reduction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 2972–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayati, M.; Scott, K. Synthesis and Activity of A Single Active Site N-doped Electro-catalyst for Oxygen Reduction. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 213, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; McCue, A.J.; Miao, C.; Feng, J.; Li, D.; Anderson, J.A. Palladium phosphide nanoparticles as highly selective catalysts for the selective hydrogenation of acetylene. J. Catal. 2018, 364, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hickman, A.J.; Sanford, M.S. High-valent organometallic copper and palladium in catalysis. Nature 2012, 484, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Zhang, L.; He, D.; Zhou, G.; Lin, Y.; Deng, Z.; Hong, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, Y. Amorphous nickel boride membrane on a platinum–nickel alloy surface for enhanced oxygen reduction reaction. Nat. Commun. 2015, 7, 12362–12369. [Google Scholar]
- Ci, S.; Huang, T.; Wen, Z.; Cui, S.; Mao, S.; Steeber, D.A.; Chen, J. Nickel oxide hollow microsphere for non-enzyme glucose detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhou, H.; Sun, J.; Qin, F.; Yu, F.; Bao, J.; Yu, Y.; Chen, S.; Ren, Z. Cu nanowires shelled with NiFe layered double hydroxide nanosheets as bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammon, C.; Bayer, A.; Held, G.; Richter, B.; Schmidt, T.; Steinruck, H.P. Dissociation and oxidation of methanol on Cu(110). Surf. Sci. 2002, 507, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, R.S.; Hameed, R.M.A.; El-Khatib, K.M.; El-Abd, H.; Souaya, E.R. Effect of preparation conditions on the performance of nano Pt-CuO/C electrocatalysts for methanol electro-oxidation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 18870–18881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, X.; Du, J.; Wang, H.; Huang, B.; Zhou, J.; Pan, X.; Xie, E. The carbonization temperature effect on the electrochemical performance of nitrogen-doped carbon monoliths. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 242, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.-C.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Chu, S.-Q.; Zhu, H.-W.; Liang, H.-W.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S.-H. SiO2-protected shell mediated templating synthesis of Fe–N-doped carbon nanofibers and their enhanced oxygen reduction reaction performance. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2208–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, H.S.; Krishnaraj, C.; Parwaiz, S.; Lecoeuvre, F.; Schmidt, J.; Pradhan, D.; Van Der Voort, P. Illustrating the role of quaternary-N of BINOL covalent triazine-based frameworks in oxygen reduction and hydrogen evolution reactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 44689–44699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Cheng, D.; Cao, D.; Zeng, X.C. A universal principle for a rational design of single-atom electrocatalysts. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, F.-M.; Meng, X.-Y.; Wu, X.-R.; Li, S.-N.; Chen, Y. Direct chemical synthesis of ultrathin holey iron doped cobalt oxide nanosheets on nickel foam for oxygen evolution reaction. Nano Energy 2018, 54, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Bai, J.; Han, C.; Chen, P.; Jiang, J.-X.; Chen, Y. Au nanowires@Pd-polyethylenimine nanohybrids as highly active and methanol-tolerant electrocatalysts toward oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline media. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 11287–11295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyeva, E.; Fako, E.; Chen, Z.; Collins, S.M.; Johnstone, D.; Midgley, P.A.; Hauert, R.; Safonova, O.V.; Vilé, G.; López, N.; et al. Atom-by-atom resolution of structure-function relations over low-nuclearity metal catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 8724–8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gokhale, R.; Serov, A.; Artyushkova, K.; Atanassov, P. Novel highly active and selective Fe-N-C oxygen reduction electrocatalysts derived from in-situ polymerization pyrolysis. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.-L.; Su, P.; Kang, X.; Ning, S.-K. Synthesis and characterization of nitrogen-doped graphene hydrogels by hydrothermal route with urea as reducing-doping agents. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 2248–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Regier, T.; Dai, H. Co3O4 nanocrystals on graphene as a synergistic catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, Y.; Ma, D.; Foucher, A.C.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, J.; Stach, E.A.; Yue, Q.; Kang, Y. Atomic Fe Dispersed Hierarchical Mesoporous Fe–N–C Nanostructures for an Efficient Oxygen Reduction Reaction. ACS Catal. 2020, 11, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, H.; Diao, P.; Chang, W.; Hong, G.; Li, Y.; Gong, M.; Xie, L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Oxygen reduction electrocatalyst based on strongly coupled cobalt oxide nanocrystals and carbon nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15849–15857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, C.W.B.; Zhang, L.; Lee, K.; Liu, H.; Marques, A.L.B.; Marques, E.P.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J. A review of Fe–N/C and Co–N/C catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 4937–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Dai, H. Strongly coupled inorganic/nanocarbon hybrid materials for advanced electrocatalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2013–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Qi, D.; Zhi, Q.; Liu, W.; Li, W.; Wang, K.; Jiang, J. Atomic Zn Sites on N and S Codoped Biomass-Derived Graphene for a High-Efficiency Oxygen Reduction Reaction in both Acidic and Alkaline Electrolytes. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 2481–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yu, Y.; Dou, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, F. Edge-functionalized polyphthalocyanine networks with high oxygen reduction reaction activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 17524–17530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisaka, M.; Xiang, R.; Maruyama, S.; Daiguji, H. Efficient phosphorus doping into the surface oxide layers on TiN to enhance oxygen reduction reaction activity in acidic media. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 9866–9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Material | R0 (Ω) | R1 (Ω) | R2 (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-NC | 10 | 75 | 1620 |
| Ni-NC | 8 | 72 | 1580 |
| Pd-NC | 7 | 68 | 1380 |
| Fe-NC | 11 | 82 | 1468 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, H.; Xu, S.; Ma, J.; Hu, M.; Yu, J.; Zhao, F.; Huang, T. Dimethylglyoxime Clathrate as Ligand Derived Nitrogen-Doped Carbon-Supported Nano-Metal Particles as Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051329
Xu L, Guo Z, Jiang H, Xu S, Ma J, Hu M, Yu J, Zhao F, Huang T. Dimethylglyoxime Clathrate as Ligand Derived Nitrogen-Doped Carbon-Supported Nano-Metal Particles as Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(5):1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051329
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Luping, Zhongqin Guo, Hanyu Jiang, Siyu Xu, Juanli Ma, Mi Hu, Jiemei Yu, Fengqi Zhao, and Taizhong Huang. 2021. "Dimethylglyoxime Clathrate as Ligand Derived Nitrogen-Doped Carbon-Supported Nano-Metal Particles as Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction" Nanomaterials 11, no. 5: 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051329
APA StyleXu, L., Guo, Z., Jiang, H., Xu, S., Ma, J., Hu, M., Yu, J., Zhao, F., & Huang, T. (2021). Dimethylglyoxime Clathrate as Ligand Derived Nitrogen-Doped Carbon-Supported Nano-Metal Particles as Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Nanomaterials, 11(5), 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051329