Radiative and Non-Radiative Decay Pathways in Carbon Nanodots toward Bioimaging and Photodynamic Therapy
Abstract
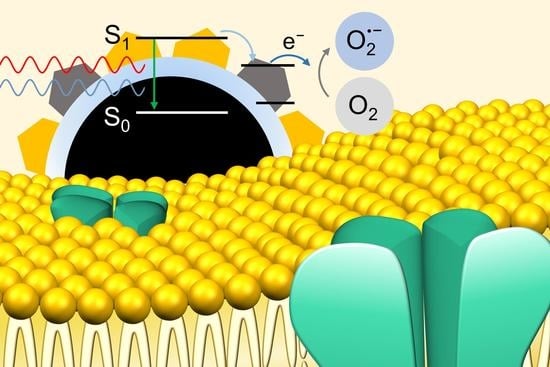
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of CNDs
2.3. Material Analysis
2.4. Chemical Analysis
2.5. Optical Analysis
2.6. ROS Measurement
2.7. Cell Viability Test
2.8. In Vitro Confocal Microscopy Imaging
2.9. In Vitro PDT Test
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, L.; Choi, K.Y.; Guo, N.; Guo, J.; Tackett, K.; Anilkumar, P.; Liu, G.; Quan, Q.; et al. Effect of Injection Routes on the Biodistribution, Clearance, and Tumor Uptake of Carbon Dots. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5684–5693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Tang, S.; Qiao, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.; et al. Surface Chemistry Routes to Modulate the Photoluminescence of Graphene Quantum Dots: From Fluorescence Mechanism to Up-Conversion Bioimaging Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4732–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, S.K.; Saha, A.; Maity, A.R.; Ray, S.C.; Jana, N.R. Carbon Nanoparticle-based Fluorescent Bioimaging Probes. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tong, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Guo, X.; He, L.; Qiu, F.; Wang, G.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, X.; Liu, T. Amorphous carbon dots with high two-photon fluorescence for cellular imaging passivated by hyperbranched poly(amino amine). J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasouni, A.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Stalikas, C. Bioimaging Applications of Carbon Nanodots: A Review. C—J. Carbon Res. 2019, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, H.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Hu, J.; Ni, P.; Li, Z. A carbon dot based biosensor for melamine detection by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Zhou, J.; Feng, H.; Tang, C.; Huang, Y.; Qian, Z. Functionalized Carbon Quantum Dots with Dopamine for Tyrosinase Activity Monitoring and Inhibitor Screening: In Vitro and Intracellular Investigation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 23564–23574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.-J.; Park, S.-Y. Carbon-dot-based ratiometric fluorescence glucose biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Bose, M.; Das, A.K.; Banerjee, S.; Das, N.C. One-Step Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Bio-Labeling Assay. Macromol. Symp. 2018, 382, 1800077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrat, P.; Wang, R.; Kereselidze, D.; Lux, M.; Didier, P.; Kichler, A.; Pons, F.; Lebeau, L. Efficient in vitro and in vivo pulmonary delivery of nucleic acid by carbon dot-based nanocarriers. Biomaterials 2015, 51, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, X.; Long, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, R.; Liang, L.; Teng, P.; Zheng, H. Hollow luminescent carbon dots for drug delivery. Carbon N. Y. 2013, 59, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Ai, X.; An, G.; Yang, P.; Zhao, Y. Charge-Convertible Carbon Dots for Imaging-Guided Drug Delivery with Enhanced in Vivo Cancer Therapeutic Efficiency. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4410–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Kong, B.; Wu, H.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, G. Carbon Nanodots Featuring Efficient FRET for Real-Time Monitoring of Drug Delivery and Two-Photon Imaging. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6569–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, S.; Choi, M.-H.; Ryoo, S.-R.; Park, J.; Min, D.-H.; Kim, B.-S. Highly Biocompatible Carbon Nanodots for Simultaneous Bioimaging and Targeted Photodynamic Therapy In Vitro and In Vivo. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5781–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Bhattacharyya, S.K.; Banerji, P.; Das, N.C. Acoustic cavitation assisted synthesis and characterization of photoluminescent carbon quantum dots for biological applications and their future prospective. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2021, 25, 100641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Banerjee, D.; Ghorai, U.K.; Das, N.S.; Chattopadhyay, K.K. Size dependent photoluminescence property of hydrothermally synthesized crystalline carbon quantum dots. J. Lumin. 2016, 178, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhenadhayalan, N.; Lin, K.-C.; Suresh, R.; Ramamurthy, P. Unravelling the Multiple Emissive States in Citric-Acid-Derived Carbon Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, X.; Kang, Z.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Lian, S.; Tsang, C.H.A.; Yang, X.; Lee, S.-T. Water-Soluble Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots and Photocatalyst Design. Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 4532–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Yu, S.-B.; Wei, J.-S.; Xiong, H.-M. Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots with a Surface-State-Controlled Luminescence Mechanism. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, S.X.-A. Reply to Comment on “Carbon Dots with Continuously Tunable Full-Color Emission and Their Application in Ratiometric pH Sensing”. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.H.; Liu, Z.X.; Li, R.S.; Zou, H.Y.; Lin, M.; Liu, H.; Huang, C.Z. Synthesis of nitrogen-doping carbon dots with different photoluminescence properties by controlling the surface states. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 6770–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Pan, W.; Yu, G.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, J. Carbon dots originated from methyl red with molecular state and surface state controlled emissions for sensing and imaging. J. Lumin. 2018, 204, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galande, C.; Mohite, A.D.; Naumov, A.V.; Gao, W.; Ci, L.; Ajayan, A.; Gao, H.; Srivastava, A.; Weisman, R.B.; Ajayan, P.M. Quasi-Molecular Fluorescence from Graphene Oxide. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krysmann, M.J.; Kelarakis, A.; Dallas, P.; Giannelis, E.P. Formation Mechanism of Carbogenic Nanoparticles with Dual Photoluminescence Emission. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Gao, H.; Chen, X.; Fang, G.; Yuan, S.; Yuan, Y. Excitation-Independent Dual-Color Carbon Dots: Surface-State Controlling and Solid-State Lighting. ACS Photon. 2017, 4, 2352–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Wen, Z.; Wang, C.; Thomas, T.; Wang, C.; Song, Q.; Yang, M. Temperature-controlled spectral tuning of full-color carbon dots and their strongly fluorescent solid-state polymer composites for light-emitting diodes. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fathi, P.; Khamo, J.S.; Huang, X.; Srivastava, I.; Esch, M.B.; Zhang, K.; Pan, D. Bulk-state and single-particle imaging are central to understanding carbon dot photo-physics and elucidating the effects of precursor composition and reaction temperature. Carbon N. Y. 2019, 145, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X.; Haddad, R.E.; Fan, H.; Sun, Z. Formation mechanism and optimization of highly luminescent N-doped graphene quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, W.; Do, S.; Lee, J.; Hwang, S.; Kim, J.K.; Rhee, S.-W. Freestanding Luminescent Films of Nitrogen-Rich Carbon Nanodots toward Large-Scale Phosphor-Based White-Light-Emitting Devices. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 1893–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Pang, H.; Bin Yang, H.; Guo, C.; Shao, J.; Chi, Y.; Li, C.M.; Yu, T. Carbon-Based Dots Co-doped with Nitrogen and Sulfur for High Quantum Yield and Excitation-Independent Emission. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7800–7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.-H.; Tang, W.-Q.; Deng, Z.-Y.; Liu, S.-S.; Wang, C.-F.; Chen, S. Facile Access to White Fluorescent Carbon Dots toward Light-Emitting Devices. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 6417–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Kreiter, M.; He, B.; Pang, S.; Liu, C.-Y. Synthesis of direct white-light emitting carbogenic quantum dots. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3309–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Cheng, L.; Wang, N.; Sun, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, W. Surface passivated carbon nanodots prepared by microwave assisted pyrolysis: Effect of carboxyl group in precursors on fluorescence properties. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 18818–18826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Yang, B. Investigation from chemical structure to photoluminescent mechanism: A type of carbon dots from the pyrolysis of citric acid and an amine. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 5976–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Schneider, J.; Ushakova, E.V.; Rogach, A.L. Influence of molecular fluorophores on the research field of chemically synthesized carbon dots. Nano Today 2018, 23, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Reckmeier, C.J.; Xiong, Y.; Von Seckendorff, M.; Susha, A.S.; Kasák, P.; Rogach, A.L. Molecular Fluorescence in Citric Acid-Based Carbon Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Hsieh, C.-T.; Yuan, C.-Y.; Gandomi, Y.A.; Chang, J.-K.; Fu, C.-C.; Yang, J.-W.; Juang, R.-S. Fluorescence of functionalized graphene quantum dots prepared from infrared-assisted pyrolysis of citric acid and urea. J. Lumin. 2020, 217, 116774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, S. Creating high yield water soluble luminescent graphene quantum dots via exfoliating and disintegrating carbon nanotubes and graphite flakes. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10177–10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, A.-M.B.; Malachias, A.; Mazzoni, M.S.; Lacerda, R.G.; Magalhães-Paniago, R. Metastable phase formation and structural evolution of epitaxial graphene grown on SiC(100) under a temperature gradient. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 175603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vevelstad, S.J.; Grimstvedt, A.; Elnan, J.; da Silva, E.F.; Svendsen, H.F. Oxidative degradation of 2-ethanolamine: The effect of oxygen concentration and temperature on product formation. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2013, 18, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Liu, L.; Shen, Z.; Xu, G.Q.; Hor, T.S.A. Formation of hydrogenated amorphous carbon films from polymer pyrolysis. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2002, 74, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, W.; Patel, M.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xie, Q.; Lockard, J.V.; Gao, Y.; He, H. π-Plasmon absorption of carbon nanotubes for the selective and sensitive detection of Fe3+ ions. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 5192–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.-P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Pathak, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Harruff, B.A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Quantum-Sized Carbon Dots for Bright and Colorful Photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kalytchuk, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Kershaw, S.V.; Rogach, A.L. Thickness-Dependent Full-Color Emission Tunability in a Flexible Carbon Dot Ionogel. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 1412–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Park, Y.; Beack, S.; Han, S.; Jung, D.; Cha, H.J.; Kwon, W.; Hahn, S.K. Dual-Color-Emitting Carbon Nanodots for Multicolor Bioimaging and Optogenetic Control of Ion Channels. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1700325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, H.; Zhou, X.-X.; Wei, J.-S.; Li, X.-B.; Qin, B.-T.; Chen, X.-B.; Xiong, H.-M. Carbon dots with red/near-infrared emissions and their intrinsic merits for biomedical applications. Carbon N. Y. 2020, 167, 322–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Tran, M.D.; Kim, Y.; Won, S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, T.-W.; Gregorkiewicz, T.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kwon, W. Unraveling the origin of near-infrared emission in carbon dots by ultrafast spectroscopy. Carbon 2022, 188, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, L.; Brown, J.; Salim, M.G.; May, D.; Guilvaiee, B.; Hawkins, A.; Cathles, L. Optimization of fluorescence and surface adsorption of citric acid/ethanolamine carbon nanoparticles for subsurface tracers. Carbon 2020, 169, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-B.; Jin, J.-C.; Xu, Z.-Q.; Jiang, Z.-W.; Li, X.; Jiang, F.-L.; Liu, Y. Single-step synthesis of highly photoluminescent carbon dots for rapid detection of Hg2+ with excellent sensitivity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 551, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | τ1 (ns) | A1 | τ2 (ns) | A2 | τ3 (ns) | A3 | τavg (ns) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CND1 | 4.05 | 58.96 | 10.45 | 29.12 | 1.18 | 11.92 | 3.65 |
| CND2 | 5.03 | 30.50 | 12.66 | 63.44 | 1.39 | 6.07 | 6.47 |
| CND3 | 4.19 | 24.54 | 12.49 | 69.27 | 0.84 | 6.18 | 5.32 |
| CND4 | 3.91 | 24.96 | 11.71 | 60.67 | 0.88 | 14.37 | 3.58 |
| Precursors | Reaction Condition | Size (nm) | PL Ex/Em Wavelength | QY | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citric acid Ethanolamine | 190 °C, 2 h | 12.4 ± 5.6 | 376 nm/ 466 nm | 11% | Subsurface tracer | [48] |
| Citric acid Ethanolamine | 230 °C, 30 m | 19 | 375 nm/ 455 nm | 50% | − | [24] |
| Citric acid Ethylenediamine | 140 °C, 5 h | 2~6 (carbon core) | 361 nm/ 442 nm | 70% (relative) | − | [34] |
| Citric acid Ethylenediamine | 120 °C, 15 h | 3.5 ± 0.3 | 340 nm/ 440 nm | 21.8% (relative) | − | [17] |
| Citric acid Triethylamine | 160 °C, 4 h | 1.7 ± 0.21 | 350 nm/ 437 nm | 18.8% | Hg2+ detection | [49] |
| Citric acid Ethanolamine | 90 °C, 24 h | 10.25±1.84 | 360 nm/ 450 nm | 15.24% | Bioimaging and PDT | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.; Park, Y.; Han, S.; Park, W.; Kim, M.; Kim, K.; Joo, J.; Hahn, S.K.; Kwon, W. Radiative and Non-Radiative Decay Pathways in Carbon Nanodots toward Bioimaging and Photodynamic Therapy. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010070
Kim Y, Park Y, Han S, Park W, Kim M, Kim K, Joo J, Hahn SK, Kwon W. Radiative and Non-Radiative Decay Pathways in Carbon Nanodots toward Bioimaging and Photodynamic Therapy. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(1):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010070
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yujin, Yoonsang Park, Seulgi Han, Wonchan Park, Mungu Kim, Kyunghwan Kim, Jinmyoung Joo, Sei Kwang Hahn, and Woosung Kwon. 2022. "Radiative and Non-Radiative Decay Pathways in Carbon Nanodots toward Bioimaging and Photodynamic Therapy" Nanomaterials 12, no. 1: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010070
APA StyleKim, Y., Park, Y., Han, S., Park, W., Kim, M., Kim, K., Joo, J., Hahn, S. K., & Kwon, W. (2022). Radiative and Non-Radiative Decay Pathways in Carbon Nanodots toward Bioimaging and Photodynamic Therapy. Nanomaterials, 12(1), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010070