A Versatile Nanocarrier—Cubosomes, Characterization, and Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Lipidic Systems
2.1. Self-Assembly of Lipidic Structures
2.2. Packing Parameter and Spontaneous Curvature
2.3. Cubosomes
2.3.1. Bicontinuous Cubic Phases
2.3.2. Principal Constituents
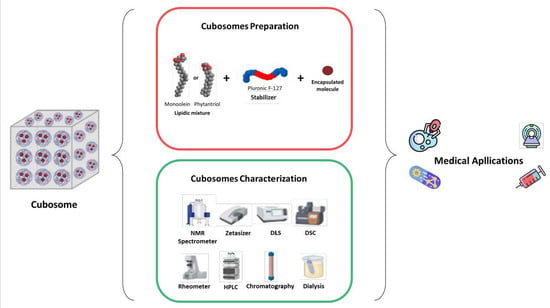
2.3.3. Cubosome Preparation
2.3.4. Cubosome Characterization
2.3.4.1. Direct Techniques
2.3.4.1.1. Electron Microscopy
2.3.4.1.2. Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)
2.3.4.2. Indirect Techniques
2.3.4.2.1. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Zeta(ζ)-Potential
2.3.4.2.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
2.3.4.2.3. Rheology
2.3.4.2.4. Polarized Light Microscopy
2.3.4.2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.3.4.2.6. Entrapment Efficiency
2.3.4.2.7. Stability Studies
3. Medical Applications of Cubosomes
3.1. Cancer Therapy
3.2. Transfection
3.3. Topical Drug Delivery and Antimicrobial Therapy
3.4. Vaccines
3.5. Imaging and Theranostic
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolfram, J.; Ferrari, M. Clinical cancer nanomedicine. Nano Today 2019, 25, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shan, X.; Gong, X.; Li, J.; Wen, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. Current approaches of nanomedicines in the market and various stage of clinical translation. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowd, V.; Ahmad, A.; Tarique, M.; Suhail, M.; Zughaibi, T.A.; Tabrez, S.; Khan, R. Advancement of cancer immunotherapy using nanoparticles-based nanomedicine. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeanbart, L.; Swartz, M.A. Engineering opportunities in cancer immunotherapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14467–14472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. Nanoparticles in the clinic: An update. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2019, 4, e10143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soares, S.; Sousa, J.; Pais, A.; Vitorino, C. Nanomedicine: Principles, Properties, and Regulatory Issues. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegra, A.; Gioacchino, M.D.; Tonacci, A.; Petrarca, C.; Gangemi, S. Nanomedicine for Immunotherapy Targeting Hematological Malignancies: Current Approaches and Perspective. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, D.J.; Dane, E.L. Enhancing cancer immunotherapy with nanomedicine. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tostanoski, L.H.; Gosselin, E.A.; Jewell, C.M. Engineering tolerance using biomaterials to target and control antigen presenting cells. Discov. Med. 2016, 21, 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y. Nanotechnology applied to overcome tumor drug resistance. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2012, 162, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steichen, S.D.; Caldorera-Moore, M.; Peppas, N.A. A review of current nanoparticle and targeting moieties for the delivery of cancer therapeutics. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, E.; Cui, Y.; Huang, Y. Nanotechnology-based combination therapy for overcoming multidrug-resistant cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 2017, 14, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y. TAT-modified nanosilver for combating multidrug-resistant cancer. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6155–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tannous, M.; Caldera, F.; Hoti, G.; Dianzani, U.; Cavalli, R.; Trotta, F. Drug-Encapsulated Cyclodextrin Nanosponges. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 2207, pp. 247–283. [Google Scholar]
- Eloy, J.O.; de Souza, M.C.; Petrilli, R.; Barcellos, J.P.A.; Lee, R.J.; Marchetti, J.M. Liposomes as carriers of hydrophilic small molecule drugs: Strategies to enhance encapsulation and delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Fan, K.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Lin, J.; et al. PEGylated lipid bilayer coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles co-delivery of paclitaxel and curcumin leads to increased tumor site drug accumulation and reduced tumor burden. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 140, 105070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, J.; Washington, M.A.; Resnick, J.L.; Nischal, K.K.; Fedorchak, M.V. A sustained release cysteamine microsphere/thermoresponsive gel eyedrop for corneal cystinosis improves drug stability. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 2224–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, J.S.; Xu, Q.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L.M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, M.; Lopes, I.; Magalhães, L.; Sárria, M.P.; Machado, R.; Sousa, J.C.; Botelho, C.; Teixeira, J.; Gomes, A.C. Novel concept of exosome-like liposomes for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Control. Release 2021, 336, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, G.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S. Cubosomes: An Overview. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varghese, R.; Salvi, S.; Sood, P.; Kulkarni, B.; Kumar, D. Cubosomes in cancer drug delivery: A review. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2022, 46, 100561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Wei, G.; Huang, Y.; Yu, H.; Gan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mei, L.; et al. Recent progress in drug delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 1145–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Stimuli-responsive polydopamine-based smart materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8319–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Akiva, E.; Est Witte, S.; Meyer, R.A.; Rhodes, K.R.; Green, J.J. Polymeric micro- and nanoparticles for immune modulation. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oerlemans, C.; Bult, W.; Bos, M.; Storm, G.; Nijsen, J.F.W.; Hennink, W.E. Polymeric Micelles in Anticancer Therapy: Targeting, Imaging and Triggered Release. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 2569–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bozzuto, G.; Molinari, A. Liposomes as nanomedical devices. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 975–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalepu, S.; Manthina, M.; Padavala, V. Oral lipid-based drug delivery systems—An overview. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2013, 3, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myers, D. Surfaces, Interfaces, and Colloids: Principles and Applications, 2nd ed.; WILEY-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, C.J.O. Microfluidic Methods for the Controlled Preparation of Soft Self-Assembled Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery; Universidade do Minho: Braga, Portugal, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Florenzano, F.H.; Politi, M.J. Effect of urea on biomimetic aggregates. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1997, 30, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, E.F.; Silva, B.F.B. Surfactant Self-Assembly. In Encyclopedia of Colloid and Interface Science; Tadros, T., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1290–1333. ISBN 9783642206641. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.-J.; Seo, M.-K. Interface Science and Composites, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; ISBN 9780080976051. [Google Scholar]
- Ramalheiro, A.F.M. Microneedle Arrays Loaded with Lipid Nanocarriers for the Sustained Delivery of Immunomodulatory Drugs; Universidade de Lisboa: Lisboa, Portugal, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Seddon, J.M. Structure of the inverted hexagonal (HII) phase, and non-lamellar phase transitions of lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1031, 1–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, S.B.; Boyd, B.J. Cubosomes: Structure, Preparation and Use as an Antigen Delivery System. In Subunit Vaccine Delivery; Foged, C., Rades, T., Perrie, Y., Hook, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 125–140. [Google Scholar]
- Spicer, P.T. Cubosomes: Bicontinuous Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles. In Dekker Encyclopedia of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2007; Volume 7, pp. 987–1000. ISBN 1-58883-163-9. [Google Scholar]
- Barriga, H.M.G.; Holme, M.N.; Stevens, M.M. Cubosomes: The Next Generation of Smart Lipid Nanoparticles? Angew. Chemie-Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2958–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seddon, J.M.; Templer, R.H. Polymorphism of Lipid-Water Systems. In Handbook of Biological Physics; Lipowsky, R., Sackman, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 97–160. [Google Scholar]
- Hyde, S.T. Identification of Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Mesophases. In Handbook of Biological Physics and Colloid Chemistru; Holmberg, K., Ed.; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 299–332. [Google Scholar]
- Squires, A.; Seddon, J.M.; Squires, A.M.; Conn, C.E.; Ces, O.; Andrew, J. Pressure-jump X-ray studies of liquid crystal transitions in lipids References. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2006, 364, 2635–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, K. Cubic lipid-water phases: Structures and biomembrane aspects. J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 7304–7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landh, T. Phase Behavior in the System Pine Oil Monoglycerides-Poloxamer 407-Water at 20 OC Tomas. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 8453–8467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, J.; Ljusberg-Wahren, H.; Almgren, M.; Larsson, K. Cubic Lipid−Water Phase Dispersed into Submicron Particles. Langmuir 1996, 12, 4611–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Meikle, T.G.; Drummond, C.J.; Yang, Y.; Conn, C.E. Comparison of cubosomes and liposomes for the encapsulation and delivery of curcumin. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 3306–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, E.; German, J.B. Monoglycerides in Membrane Systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1996, 36, 785–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, C.V.; Wachter, W.; Iglesias-Salto, G.; Engelskirchen, S.; Ahualli, S. Monoolein: A magic lipid? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 3004–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barauskas, J.; Landh, T. Phase Behavior of the Phytantriol/Water System. Langmuir 2003, 19, 9562–9565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-D.; Larson, I.; Hanley, T.; Boyd, B.J. Bulk and Dispersed Aqueous Phase Behavior of Phytantriol: Effect of Vitamin E Acetate and F127 Polymer on Liquid Crystal Nanostructure. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9512–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, Z.; Hamidi, M. Cubosomes: Remarkable drug delivery potential. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Anwar, A.; Ayish, A.; Elliott, J.M.; Squires, A.M. Phytantriol based smart nano-carriers for drug delivery applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 101, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hierrezuelo, J.; Sadeghpour, A.; Szilagyi, I.; Vaccaro, A.; Borkovec, M. Electrostatic stabilization of charged colloidal particles with adsorbed polyelectrolytes of opposite charge. Langmuir 2010, 26, 15109–15111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, S.; Shao, X.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Z. Increasing entropy for colloidal stabilization. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romero-Cano, M.S.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; De las Nieves, F.J. Electrosteric Stabilization of Polymer Colloids with Different Functionality. Langmuir 2001, 17, 3505–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T. Suspensions. In Encyclopedia of Colloid and Interface Science; Tadros, T., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1334–1388. ISBN 9783642206641. [Google Scholar]
- Serieye, S.; Méducin, F.; Milošević, I.; Fu, L.; Guillot, S. Interface tuning and stabilization of monoglyceride mesophase dispersions: Food emulsifiers and mixtures efficiency. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 496, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.; Hong, L.; Du, J.D.; Boyd, B.J. Self-Assembled Nanostructured Lipid Systems: Is There a Link between Structure and Cytotoxicity? Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhai, J.; Tan, F.H.; Luwor, R.B.; Srinivasa Reddy, T.; Ahmed, N.; Drummond, C.J.; Tran, N. In vitro and In vivo Toxicity and Biodistribution of Paclitaxel-Loaded Cubosomes as a Drug Delivery Nanocarrier: A Case Study Using an A431 Skin Cancer Xenograft Model. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 4198–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornasier, M.; Biffi, S.; Bortot, B.; Macor, P.; Manhart, A.; Wurm, F.R.; Murgia, S. Cubosomes stabilized by a polyphosphoester-analog of Pluronic F127 with reduced cytotoxicity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 580, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, T.M.; Grusche, F.; Acharya, D.; Shukla, R.; Bansal, V.; Waddington, L.J.; Monaghan, P.; Muir, B.W. Bicontinuous cubic phase nanoparticle lipid chemistry affects toxicity in cultured cells. Toxicol. Res. 2014, 3, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Suryadinata, R.; Luan, B.; Tran, N.; Hinton, T.M.; Ratcliffe, J.; Hao, X.; Drummond, C.J. Amphiphilic brush polymers produced using the RAFT polymerisation method stabilise and reduce the cell cytotoxicity of lipid lyotropic liquid crystalline nanoparticles. Faraday Discuss. 2016, 191, 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.; Mulet, X.; Hawley, A.M.; Hinton, T.M.; Mudie, S.T.; Muir, B.W.; Giakoumatos, E.C.; Waddington, L.J.; Kirby, N.M.; Drummond, C.J. Nanostructure and cytotoxicity of self-assembled monoolein–capric acid lyotropic liquid crystalline nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 26785–26795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abourehab, M.A.S.; Ansari, M.J.; Singh, A.; Hassan, A.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Shrivastav, P.; Abualsoud, B.M.; Amaral, L.S.; Pramanik, S. Cubosomes as an emerging platform for drug delivery: A review of the state of the art. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 2781–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakotoarisoa, M.; Angelov, B.; Drechsler, M.; Nicolas, V.; Bizien, T.; Gorshkova, Y.E.; Deng, Y.; Angelova, A. Liquid crystalline lipid nanoparticles for combined delivery of curcumin, fish oil and BDNF: In vitro neuroprotective potential in a cellular model of tunicamycin-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress. Smart Mater. Med. 2022, 3, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Gong, Y.; Fu, M.; Liu, C.; Xu, L.; Sun, C.C.; Gao, Y.; Qian, S. Cubosomes with surface cross-linked chitosan exhibit sustained release and bioavailability enhancement for vinpocetine. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 6287–6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akhlaghi, S.P.; Ribeiro, I.R.; Boyd, B.J.; Loh, W. Impact of preparation method and variables on the internal structure, morphology, and presence of liposomes in phytantriol-Pluronic® F127 cubosomes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barauskas, J.; Misiunas, A.; Gunnarsson, T.; Tiberg, F.; Johnsson, M. “Sponge” nanoparticle dispersions in aqueous mixtures of diglycerol monooleate, glycerol dioleate, and polysorbate 80. Langmuir 2006, 22, 6328–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biffi, S.; Andolfi, L.; Caltagirone, C.; Garrovo, C.; Falchi, A.M.; Lippolis, V.; Lorenzon, A.; Macor, P.; Meli, V.; Monduzzi, M.; et al. Cubosomes for in vivo fluorescence lifetime imaging. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 055102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M.; Teshigawara, T.; Sugita, A.; Leesajakul, W.; Taniguchi, A.; Kamo, T.; Matsuoka, H.; Handa, T. Dispersions of liquid crystalline phases of the monoolein/oleic acid/pluronic F127 system. Langmuir 2002, 18, 9283–9288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicer, P.T.; Hayden, K.L.; Chester, W.; Lynch, M.L.; Ofori-boateng, A.; Burns, J.L. Novel Process for Producing Cubic Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles (Cubosomes). Langmuir 2001, 17, 5748–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Lim, S.; Shim, J.; Song, J.E.; Chang, J.S.; Jin, K.S.; Cho, E.C. A Simple Evaporation Method for Large-Scale Production of Liquid Crystalline Lipid Nanoparticles with Various Internal Structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 20438–20446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Leal, C. Cuboplexes: Topologically Active siRNA Delivery. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 10214–10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar-Yuli, I.; Libster, D.; Aserin, A.; Garti, N. Solubilization of food bioactives within lyotropic liquid crystalline mesophases. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 14, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almgren, M.; Edwards, K.; Gustafsson, J. Cryotransmission electron microscopy of thin vitrified samples. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 1, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, S.B.; Boyd, B.J. Chapter 7—Cubossomes: Structure, preparation and use as an antigen delivery system. In Subunit Vaccine Delivery; Advances in Delivery Science and Technology; Foged, C., Rades, T., Perrie, Y., Hook, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-4939-1416-6. [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson, M.; Barauskas, J.; Tiberg, F. Cubic Phases and Cubic Phase Dispersions in a Phospholipid-Based System. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 1076–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cytryniak, A.; Nazaruk, E.; Bilewicz, R.; Górzyńska, E.; Żelechowska-Matysiak, K.; Walczak, R.; Mames, A.; Bilewicz, A.; Majkowska-Pilip, A. Lipidic cubic-phase nanoparticles (Cubosomes) loaded with doxorubicin and labeled with177 lu as a potential tool for combined chemo and internal radiotherapy for cancers. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelov, B.; Angelova, A.; Drechsler, M.; Garamus, V.M.; Mutafchieva, R.; Lesieur, S. Identification of large channels in cationic PEGylated cubosome nanoparticles by synchrotron radiation SAXS and Cryo-TEM imaging. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 3686–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyd, B.J.; Rizwan, S.B.; Dong, Y.-D.; Hook, S.; Rades, T. Self-assembled geometric liquid-crystalline nanoparticles imaged in three dimensions: Hexosomes are not necessarily flat hexagonal prisms. Langmuir 2007, 23, 12461–12464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, S.B.; Dong, Y.-D.; Boyd, B.J.; Rades, T.; Hook, S. Characterisation of bicontinuous cubic liquid crystalline systems of phytantriol and water using cryo field emission scanning electron microscopy (cryo FESEM). Micron 2007, 38, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demurtas, D.; Guichard, P.; Martiel, I.; Mezzenga, R.; Hébert, C.; Sagalowicz, L. Direct visualization of dispersed lipid bicontinuous cubic phases by cryo-electron tomography. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, P.; Zemb, T. Neutron, X-rays and Light. Scattering Methods Applied to Soft Condensed Matter, 1st ed.; Linder, P., Zemb, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; ISBN 9780444511225. [Google Scholar]
- Safinya, C.R.; Sirota, E.B.; Bruinsma, R.F.; Jeppesen, C.; Plano, R.J.; Wenzel, L.J. Structure of membrane surfactant and liquid crystalline smectic lamellar phases under flow. Science 1993, 261, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.F.B. SAXS on a chip: From dynamics of phase transitions to alignment phenomena at interfaces studied with microfluidic devices. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 23690–23703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, T.; Konovalov, O. Synchrotron Scattering Methods for Nanomaterials and Soft Matter Research. Materials 2020, 13, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathews, P.D.; Mertins, O.; Angelov, B.; Angelova, A. Cubosomal lipid nanoassemblies with pH-sensitive shells created by biopolymer complexes: A synchrotron SAXS study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; La, Y.; Kim, K.T. Polymer Cubosomes: Infinite Cubic Mazes and Possibilities. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Cortesi, R.; Drechsler, M.; Paccamiccio, L.; Mariani, P.; Contado, C.; Stellin, E.; Menegatti, E.; Bonina, F.; Puglia, C. Cubosome dispersions as delivery systems for percutaneous administration of indomethacin. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 2163–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Han, K.; Qin, L.; Dian, L.; Li, G.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Characterization of cubosomes as a targeted and sustained transdermal delivery system for capsaicin. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 4209–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramalheiro, A.; Paris, J.L.; Silva, B.F.B.; Pires, L.R. Rapidly dissolving microneedles for the delivery of cubosome-like liquid crystalline nanoparticles with sustained release of rapamycin. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 591, 119942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montis, C.; Castroflorio, B.; Mendozza, M.; Salvatore, A.; Berti, D.; Baglioni, P. Magnetocubosomes for the delivery and controlled release of therapeutics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 449, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Tian, D.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Tian, M. Theranostic combinatorial drug-loaded coated cubosomes for enhanced targeting and efficacy against cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Peng, X.; Tan, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhu, X.; Feng, M.; Xu, Y.; Wu, C. Optimization of the Preparation Process for an Oral Phytantriol-Based Amphotericin B Cubosomes. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 308016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisken, B.J. Revisiting the method of cumulants for the analysis of dynamic light-scattering data. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 4087–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hassan, P.A.; Rana, S.; Verma, G. Making Sense of Brownian Motion: Colloid Characterization by Dynamic Light Scattering. Langmuir 2015, 31, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malheiros, B.; de Castro, R.D.; Lotierzo, M.C.; Casadei, B.R.; Mariani, P.; Barbosa, L.R.S. Influence of hexadecylphosphocholine (Miltefosine) in phytantriol-based cubosomes: A structural investigation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 632, 127720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victorelli, F.D.; Salvati Manni, L.; Biffi, S.; Bortot, B.; Buzzá, H.H.; Lutz-Bueno, V.; Handschin, S.; Calixto, G.; Murgia, S.; Chorilli, M.; et al. Potential of curcumin-loaded cubosomes for topical treatment of cervical cancer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 620, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.M.; Sawant, S.S.; Kunda, N.K. Inhalable bedaquiline-loaded cubosomes for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 121046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.W.; Cullis, P.R.; Madden, T.D. Poly(ethylene glycol)-lipid conjugates promote bilayer formation in mixtures of non-bilayer-forming lipids. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 2610–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.K.K.; Hafez, I.M.; Baoukina, S.; Belliveau, N.M.; Zhigaltsev, I.V.; Afshinmanesh, E.; Tieleman, D.P.; Hansen, C.L.; Hope, M.J.; Cullis, P.R. Lipid Nanoparticles Containing siRNA Synthesized by Microfluidic Mixing Exhibit an Electron-Dense Nanostructured Core. J. Phys. Chem. C. Nanomater. Interfaces 2012, 116, 18440–18450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullis, P.R.; De Kruijff, B. Lipid polymorphism and the functional roles of lipids in biological membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Biomembr. 1979, 559, 399–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, I.M.; Ansell, S.; Cullis, P.R. Tunable pH-Sensitive Liposomes Composed of Mixtures of Cationic and Anionic Lipids. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 1438–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fenske, D.B.; Cullis, P.R. Chemical exchange between lamellar and non-lamellar lipid phases. A one- and two-dimensional 31P-NMR study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 1992, 1108, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilcock, C.P.S.; Cullis, P.R.; Gruner, S.M. On the validity of 31P-NMR determinations of phospholipid polymorphic phase behaviour. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1986, 40, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, K.W.; Cullis, P.R. Structural and fusogenic properties of cationic liposomes in the presence of plasmid DNA. Biophys. J. 1997, 73, 2534–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hope, M.J.; Cullis, P.R. Effects of divalent cations and pH on phosphatidylserine model membranes: A 31P NMR study. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1980, 92, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullis, P.R.; De Kruijff, B. The polymorphic phase behaviour of phosphatidylethanolamines of natural and synthetic origin. A 31P NMR study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 1978, 513, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullis, P.R.; Hope, M.J. The bilayer stabilizing role of sphingomyelin in the presence of cholesterol. A 31P NMR study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 1980, 597, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kruijff, B.; Cullis, P.R.; Verkleij, A.J. Non-bilayer lipid structures in model and biological membranes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1980, 5, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, S.; Leiske, M.N.; Leitch, V.; Zhai, J.; Drummond, C.J.; Kempe, K.; Tran, N. Lipidic Poly (2-oxazoline)s as PEG Replacement Steric Stabilisers for Cubosomes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 623, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.F.; Wennerström, H. The Colloidal Domian-Where Physics, Chemistry, and Biology Meet; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; ISBN 0471242470. [Google Scholar]
- Evenbratt, H.; Ström, A. Phase behavior, rheology, and release from liquid crystalline phases containing combinations of glycerol monooleate, glyceryl monooleyl ether, propylene glycol, and water. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 32966–32973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sagalowicz, L.; Mezzenga, R.; Leser, M.E. Investigating reversed liquid crystalline mesophases. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 11, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitzalis, P.; Monduzzi, M.; Krog, N.; Larsson, H.; Ljusberg-Wahren, H.; Nylander, T. Characterization of the Liquid−Crystalline Phases in the Glycerol Monooleate/Diglycerol Monooleate/Water System. Langmuir 2000, 16, 6358–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzenga, R.; Meyer, C.; Servais, C.; Romoscanu, A.I.; Sagalowicz, L.; Hayward, R.C. Shear rheology of lyotropic liquid crystals: A case study. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3322–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.L.; McLeish, T.C.B. Concentration Fluctuations in Surfactant Cubic Phases: Theory, Rheology, and Light Scattering. Langmuir 1999, 15, 7495–7503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacucina, G.; Palmieri, G.F.; Craig, D.Q.M. Rheological and dielectric characterization of monoolein/water mesophases in the presence of a peptide drug. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 2452–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalvo, G.; Valiente, M.; Rodenas, E. Rheological Properties of the L Phase and the Hexagonal, Lamellar, and Cubic Liquid Crystals of the CTAB/Benzyl Alcohol/Water System. Langmuir 1996, 12, 5202–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalva, D.G.; França, C.G.; Loh, W. Characterization of cubosomes immobilized in hydrogels of hyaluronic acid and their use for diclofenac controlled delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 212, 112352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moud, A.A. Fluorescence Recovery after Photobleaching in Colloidal Science: Introduction and Application. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 1028–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorén, N.; Hagman, J.; Jonasson, J.K.; Deschout, H.; Bernin, D.; Cella-Zanacchi, F.; Diaspro, A.; McNally, J.G.; Ameloot, M.; Smisdom, N.; et al. Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching in material and life sciences: Putting theory into practice. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2015, 48, 323–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cribier, S.; Gulik, A.; Fellmann, P.; Vargas, R.; Devaux, P.F.; Luzzati, V. Cubic Phase of Lipid-containing Systems: A Translational Diffusion Study by Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 229, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Han, K.; Peng, X.; Yang, Z.; Qin, L.; Zhu, C.; Huang, X.; Shi, X.; Dian, L.; Lu, M.; et al. Nanostructured cubosomes as advanced drug delivery system. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 6290–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, R.R.; Osmani, R.A.M.; Harkare, B.R.; Ghodake, P.P. Cubosomes: The Inimitable Nanoparticulate Drug Carriers. Sch. Acad. J. Pharm. 2013, 2, 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, R.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Tan, Y.; Niu, M.; Guan, P.; Hu, F.; Wu, W. Silymarin glyceryl monooleate/poloxamer 407 liquid crystalline matrices: Physical characterization and enhanced oral bioavailability. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angelova, A.; Drechsler, M.; Garamus, V.M.; Angelov, B. Liquid Crystalline Nanostructures as PEGylated Reservoirs of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Structural Insights toward Delivery Formulations against Neurodegenerative Disorders. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 3235–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.; Li, J.-C.; Zhu, J.-X.; Zhu, N.; Zhang, H.-M.; Liang, L.; Sun, L. Folic Acid-Targeted Etoposide Cubosomes for Theranostic Application of Cancer Cell Imaging and Therapy. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2017, 23, 2426–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wan, F.; Peng, T.; Pan, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, C. Taste-masking and colloidal-stable cubosomes loaded with Cefpodoxime proxetil for pediatric oral delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 575, 118875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, M.; Abo El Ezz, T.A.; Fattoh, F.N.; AbouelFadl, D.M.; Gad, H.A. Delineating the usage of dexamethasone-loaded cubosomes as a therapeutic armamentarium for hearing loss versus its protective effect: In-vitro and in-vivo animal study. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, W.S.; Hosny, K.M. Development and optimization of ocular in situ gels loaded with ciprofloxacin cubic liquid crystalline nanoparticles. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elakkad, Y.E.; Younis, M.K.; Allam, R.M.; Mohsen, A.F.; Khalil, I.A. Tenoxicam loaded hyalcubosomes for osteoarthritis. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessone, C.D.V.; Akhlaghi, S.P.; Tártara, L.I.; Quinteros, D.A.; Loh, W.; Allemandi, D.A. Latanoprost-loaded phytantriol cubosomes for the treatment of glaucoma. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 160, 105748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnelli, C.; Moretti, P.; Laudadio, E.; Gerelli, Y.; Pigozzo, A.; Armeni, T.; Galeazzi, R.; Mariani, P.; Mobbili, G. Tuning curvature and phase behavior of monoolein bilayers by epigallocatechin-3-gallate: Structural insight and cytotoxicity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 209, 112171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sombié, B.C.; Yameogo, J.G.; Semdé, R.; Henschel, V.; Amighi, K.; Goole, J. Ciprofloxacin monoolein water gels as implants for the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis: In vitro characterization. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2014, 5, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Luwor, R.B.; Ahmed, N.; Escalona, R.; Tan, F.H.; Fong, C.; Ratcliffe, J.; Scoble, J.A.; Drummond, C.J.; Tran, N. Paclitaxel-Loaded Self-Assembled Lipid Nanoparticles as Targeted Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Aggressive Ovarian Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 25174–25185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgia, S.; Bonacchi, S.; Falchi, A.M.; Lampis, S.; Lippolis, V.; Meli, V.; Monduzzi, M.; Prodi, L.; Schmidt, J.; Talmon, Y.; et al. Drug-loaded fluorescent cubosomes: Versatile nanoparticles for potential theranostic applications. Langmuir 2013, 29, 6673–6679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazylińska, U.; Kulbacka, J.; Schmidt, J.; Talmon, Y.; Murgia, S. Polymer-free cubosomes for simultaneous bioimaging and photodynamic action of photosensitizers in melanoma skin cancer cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 522, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanikolaou, E.; Bosio, A. The Promise and the Hope of Gene Therapy. Front. Genome Ed. 2021, 3, 618346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, N.; Allawadhi, P.; Khurana, A.; Singh, V.; Navik, U.; Pasumarthi, S.K.; Khurana, I.; Banothu, A.K.; Weiskirchen, R.; Bharani, K.K. Gene therapy: Comprehensive overview and therapeutic applications. Life Sci. 2022, 294, 120375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Tran, N.; Soni, S.K.; Nasa, Z.; Drummond, C.J.; Conn, C.E. Cuboplex-mediated nonviral delivery of functional siRNA to Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 2336–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zeng, X.; Liu, M.; Deng, Y.; He, N. Current progress in gene delivery technology based on chemical methods and nano-carriers. Theranostics 2014, 4, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Sung, J.; Chang, Y.; Alfeche, A.; Leal, C. Microfluidics Synthesis of Gene Silencing Cubosomes. ACS Nano 2019, 12, 9196–9205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajda, E.; Godlewska, M.; Mariak, Z.; Nazaruk, E.; Gawel, D. Combinatory Treatment with miR-7-5p and Drug-Loaded Cubosomes Effectively Impairs Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boge, L.; Hallstensson, K.; Ringstad, L.; Johansson, J.; Andersson, T.; Davoudi, M.; Tomas, P.; Mahlapuu, M.; Håkansson, J.; Andersson, M. Cubosomes for topical delivery of the antimicrobial peptide LL-37. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 134, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-mahallawi, A.M.; Abdelbary, A.A.; El-Zahaby, S.A. Norfloxacin loaded nano-cubosomes for enhanced management of otitis externa: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 600, 120490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teba, H.E.; Khalil, I.A.; El Sorogy, H.M. Novel cubosome based system for ocular delivery of acetazolamide. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjana, A.; Ahmed, M.G.; Gowda, B.H.J. Development and evaluation of dexamethasone loaded cubosomes for the treatment of vitiligo. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 50, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapalli, V.K.; Banerjee, S.; Khan, S.; Jha, P.N.; Gupta, G.; Dua, K.; Hasnain, M.S.; Nayak, A.K.; Dubey, S.K.; Singhvi, G. QbD-driven formulation development and evaluation of topical hydrogel containing ketoconazole loaded cubosomes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 119, 111548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, X.; Han, M.-L.; Ding, Y.; Chow, S.H.; Le Brun, A.P.; Wu, C.-M.; Bergen, P.J.; Jiang, J.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Muir, B.W.; et al. A polytherapy based approach to combat antimicrobial resistance using cubosomes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, T.; Gu, P.; Wusiman, A.; Ni, H.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, T.; He, J.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; et al. Immunoenhancement effects of chitosan-modified ginseng stem-leaf saponins-encapsulated cubosomes as an ajuvant. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 204, 111799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, D.P.; Moffat, B.A.; Polyzos, A.; Waddington, L.; Coia, G.; Wright, D.K.; Wang, H.X.; Egan, G.F.; Muir, B.W.; Hartley, P.G. Cubic mesophase nanoparticles doped with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: A new class of MRI contrast agent. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 6655–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caltagirone, C.; Falchi, A.M.; Lampis, S.; Lippolis, V.; Meli, V.; Monduzzi, M.; Prodi, L.; Schmidt, J.; Sgarzi, M.; Talmon, Y.; et al. Cancer-cell-targeted theranostic cubosomes. Langmuir 2014, 30, 6228–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazylińska, U.; Wawrzyńczyk, D.; Kulbacka, J.; Picci, G.; Manni, L.S.; Handschin, S.; Fornasier, M.; Caltagirone, C.; Mezzenga, R.; Murgia, S. Hybrid Theranostic Cubosomes for Efficient NIR-Induced Photodynamic Therapy. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 5427–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, C.; Ferreira, C.J.O.; Sousa, M.; Paris, J.L.; Gaspar, R.; Silva, B.F.B.; Teixeira, J.A.; Ferreira-Santos, P.; Botelho, C.M. A Versatile Nanocarrier—Cubosomes, Characterization, and Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12132224
Oliveira C, Ferreira CJO, Sousa M, Paris JL, Gaspar R, Silva BFB, Teixeira JA, Ferreira-Santos P, Botelho CM. A Versatile Nanocarrier—Cubosomes, Characterization, and Applications. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(13):2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12132224
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Cristiana, Celso J. O. Ferreira, Miguel Sousa, Juan L. Paris, Ricardo Gaspar, Bruno F. B. Silva, José A. Teixeira, Pedro Ferreira-Santos, and Claudia M. Botelho. 2022. "A Versatile Nanocarrier—Cubosomes, Characterization, and Applications" Nanomaterials 12, no. 13: 2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12132224
APA StyleOliveira, C., Ferreira, C. J. O., Sousa, M., Paris, J. L., Gaspar, R., Silva, B. F. B., Teixeira, J. A., Ferreira-Santos, P., & Botelho, C. M. (2022). A Versatile Nanocarrier—Cubosomes, Characterization, and Applications. Nanomaterials, 12(13), 2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12132224