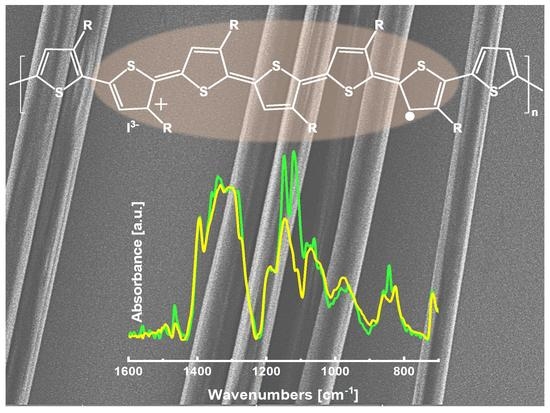
Conducting Electrospun Nanofibres: Monitoring of Iodine Doping of P3HT through Infrared (IRAV) and Raman (RaAV) Polaron Spectroscopic Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrospun Fibres
2.3. Doping
2.4. Characterisation
2.4.1. FT-IR Spectroscopy
2.4.2. FT-Raman Spectroscopy
2.4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3. Results and Discussion
- P3HT:PEO in the pristine (spun) and in the iodine-doped form;
- P3HT fibres after PEO removal, in the pristine and in the iodine-doped form;
- PEO fibres, spun.
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy: Fibre Morphology
3.2. Vibrational Spectra
3.2.1. The ECC Theory: Raman and IR Spectra of Polyconjugated Molecules
- Whether the doping is effective both in washed fibres (pure P3HT fibres) and in the presence of the PEO scaffold;
- The monitoring of the de-doping over time via IR measurements;
- The analysis of the molecular orientation in fibres and consequent polarisation properties of the IRAV bands.
3.2.2. IR Spectra of Pristine P3HT Fibres
3.2.3. IR Spectra of Iodine-Doped P3HT Nanofibres
3.2.4. Monitoring of the De-Doping Process
3.2.5. Raman Spectra of Pristine and Doped Fibres
4. Conclusions
- We show that it is possible to obtain defect-free and highly homogeneous fibres by electrospinning of a relatively high-molecular-weight P3HT in combination with PEO, which supports fibre formation. The scaffold polymer can be further removed by washing the fibres with acetonitrile without causing any remarkable change in the fibre appearance except for the expected size reduction.
- We obtained P3HT:PEO and (washed) P3HT well-aligned fibres, by collecting the fibres onto a rotating drum.
- All the fibres show marked IR dichroism, thus proving an effective molecular orientation of both PEO and P3HT, with the polymer chain axis mostly aligned parallel to the fibre axis.
- The exposure to iodine vapours allows the effective doping of both P3HT and P3HT:PEO fibres, as demonstrated by IR spectra, with very strong IRAV features, typical of doped P3HT.
- We set up a method, based on the measure of the intensity ratio between IRAVs and CH stretching absorptions, that allows the estimation of doping degree and enables the quantitative monitoring of the de-doping trends over time. These trends show that the de-doping process for both P3HT and P3HT:PEO fibres obeys an exponential decreasing law, with more rapid kinetics in the case of the P3HT:PEO. This evidence suggests that the washing procedure induces some refinement of the P3HT chain packing, which helps to stabilise the dopant–polymer complexes.
- We obtained good Raman spectra of the fibre samples, both in the pristine and in the doped case. The clearly recognizable shift of the ECC band of the doped samples (RaAV), which is intensified by near to resonance excitation with a laser with a wavelength of 1064 nm, suggests that the Raman spectroscopy is a very effective probe, alternative to IR, for the determination of polaron formation.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skotheim, T.A. Handbook of Conducting Polymers; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhan, X. Electron Transporting Semiconducting Polymers in Organic Electronics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3728–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ding, J.; Zou, Y.; Di, C.A.; Zhu, D. Chemical Doping of Organic Semiconductors for Thermoelectric Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7210–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüssem, B.; Keum, C.M.; Kasemann, D.; Naab, B.; Bao, Z.; Leo, K. Doped Organic Transistors. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 13714–13751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaloni, T.P.; Giesbrecht, P.K.; Schreckenbach, G.; Freund, M.S. Polythiophene: From Fundamental Perspectives to Applications. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 10248–10283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Yang, S.J.; Sung, S.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Chang, M.S.; Jung, H.; Park, C.R. Highly Reproducible Thermocontrolled Electrospun Fiber Based Organic Photovoltaic Devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4481–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiers, M.E.; Nielsen, D.J.; Pavey, K.D.; Truong, Y.B.; Rutledge, G.C.; Kingshott, P.; Eldridge, D.S. Conductive, Acid-Doped Polyaniline Electrospun Nanofiber Gas Sensing Substrates Made Using a Facile Dissolution Method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 52950–52959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Yu, G.F.; Zhang, J.; Yu, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.Z. Conductive Polymer Ultrafine Fibers via Electrospinning: Preparation, Physical Properties and Applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 115, 100704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, M.; Singh, A.; Samanta, S.; Aswal, D.K. Conductive Polymers for Thermoelectric Power Generation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 93, 270–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulam Sumdani, M.; Remanul Islam, M.; Naim Yahaya, A.A.; Izwan Safie, S.; Kuala Lumpur, U.; Seri Alam, P.; Seri Alam, B.; Gudang, P.; Bahru, J. Recent Advancements in Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Conductive Polymers for Electrochemical Energy Storage Devices: A Review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 269–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, R.; Mengistie, D.A.; Kiefer, D.; Hynynen, J.; Ryan, J.D.; Yu, L.; Müller, C. Thermoelectric Plastics: From Design to Synthesis, Processing and Structure–Property Relationships. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6147–6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Moon, G.D.; Jeong, U. Continuous Production of Uniform Poly(3-Hexylthiophene) (P3HT) Nanofibers by Electrospinning and Their Electrical Properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Kuo, C.C.; Lai, C.S.; Chen, W.C.; Chen, H.L. Manipulation on the Morphology and Electrical Properties of Aligned Electrospun Nanofibers of Poly(3-Hexylthiophene) for Field-Effect Transistor Applications. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 2883–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.J.; Liu, C.L.; Chen, W.C. Poly(3-Hexylthiophene)–Graphene Composite-Based Aligned Nanofibers for High-Performance Field Effect Transistors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 4290–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jo, S.B.; Park, J.H.; Cho, K. Flexible Lateral Organic Solar Cells with Core–Shell Structured Organic Nanofibers. Nano Energy 2015, 18, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-C.; Shih, C.-C.; Liu, C.-L.; Chen, W.-C. A 1D Electrospun Nanofiber Channel for Organic Field-Effect Transistors Using a Donor/Acceptor Planar Heterojunction Architecture. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 2, 1500054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Meguro, H.; Okamoto, S.; Kimura, M. Flexible Tactile Sensor Using the Reversible Deformation of Poly(3-Hexylthiophene) Nanofiber Assemblies. Langmuir 2012, 28, 17593–17596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Bertarelli, C.; Frisk, S.; Rabolt, J.F.; Gallazzi, M.C.; Zerbi, G. Electrospun Polyalkylthiophene/Polyethyleneoxide Fibers: Optical Characterization. Synth. Met. 2007, 157, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuangchote, S.; Fujita, M.; Sagawa, T.; Sakaguchi, H.; Yoshikawa, S. Control of Self Organization in Conjugated Polymer Fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 2995–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untilova, V.; Biskup, T.; Biniek, L.; Vijayakumar, V.; Brinkmann, M. Control of Chain Alignment and Crystallization Helps Enhance Charge Conductivities and Thermoelectric Power Factors in Sequentially Doped P3HT:F4TCNQ Films. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 2441–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.; Glaudell, A.M.; Miller, R.; Chabinyc, M.L. The Role of Ordering on the Thermoelectric Properties of Blends of Regioregular and Regiorandom Poly(3-Hexylthiophene). Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endrdi, B.; Mellár, J.; Gingl, Z.; Visy, C.; Janáky, C. Reasons behind the Improved Thermoelectric Properties of Poly(3-Hexylthiophene) Nanofiber Networks. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 55328–55333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierini, F.; Lanzi, M.; Nakielski, P.; Pawłowska, S.; Zembrzycki, K.; Kowalewski, T.A. Electrospun Poly(3-Hexylthiophene)/Poly(Ethylene Oxide)/Graphene Oxide Composite Nanofibers: Effects of Graphene Oxide Reduction. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 27, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesi, E.V.; Luzio, A.; Saglio, B.; Bianco, A.; Caironi, M.; Bertarelli, C. N-Type Semiconducting Polymer Fibers. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laforgue, A.; Robitaille, L. Fabrication of Poly-3-Hexylthiophene/Polyethylene Oxide Nanofibers Using Electrospinning. Synth. Met. 2008, 158, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanılmaz, M.; Sarac, A.S. A Review: Effect of Conductive Polymers on the Conductivities of Electrospun Mats. Text. Res. J. 2014, 84, 1325–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, D.; Pagliara, S.; Camposeo, A.; Persano, L.; Cingolani, R.; Pisignano, D. Single Light-Emitting Polymer Nanofiber Field-Effect Transistors. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 2217–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagna, R.; Momentè, R.; Pariani, G.; Zerbi, G.; Bianco, A.; Bertarelli, C. Highly Homogeneous Core-Sheath Polyaniline Nanofibers Obtained by Polymerisation on a Wire-Shaped Template. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 6779–6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, F.; Scampicchio, M.; Bianco, A.; Mannino, S.; Bertarelli, C.; Zerbi, G. Disposable Electrospun Electrodes Based on Conducting Nanofibers. Electroanalysis 2008, 20, 1374–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, F.; Bianco, A.; Bertarelli, C.; Zerbi, G. Composite Polyamide 6/Polypyrrole Conductive Nanofibers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Babel, A.; Jenekhe, S.A.; Xia, Y. Nanofibers of Conjugated Polymers Prepared by Electrospinning with a Two-Capillary Spinneret. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 2062–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Wu, H.C.; Chiu, Y.C.; Lin, C.J.; Tung, S.H.; Chen, W.C. Electrospun Poly(3-Hexylthiophene) Nanofibers with Highly Extended and Oriented Chains Through Secondary Electric Field for High-Performance Field-Effect Transistors. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1400028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Martínez, D.; Nicho, M.E.; Hu, H.; León-Silva, U.; Arenas-Arrocena, M.C.; García-Escobar, C.H. Electrospinning of P3HT-PEO-CdS Fibers by Solution Method and Their Properties. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 61, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Martínez, D.; Martínez-Alonso, C.; Castillo-Ortega, M.M.; Arenas-Arrocena, M.C.; Nicho, M.E. Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun Fibers Containing Poly(3-Hexylthiophene) and Poly(3-Hexylthiophene)/CdS. Synth. Met. 2015, 209, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Kawai, T.; Yoshino, K. Crystal Structural Change in Poly(3-Alkyl Thiophene)s Induced by Iodine Doping as Studied by an Organized Combination of X-Ray Diffraction, Infrared/Raman Spectroscopy and Computer Simulation Techniques. Polymer 1997, 38, 2867–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A Fascinating Fiber Fabrication Technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theron, S.A.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L. Experimental Investigation of the Governing Parameters in the Electrospinning of Polymer Solutions. Polymer 2004, 45, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brédas, J.L.; Silbey, R. Conjugated Polymers: The Novel Science and Technology of Highly Conducting and Nonlinear Optically Active Materials; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Heeger, A.J.; Kivelson, S.; Schrieffer, J.R.; Su, W.P. Solitons in Conducting Polymers. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1988, 60, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmany, H.; Mehring, M.; Roth, S. (Eds.) Electronic Properties of Polymers and Related Compounds; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985; Volume 63. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer, H.E.; Chance, R.R.; Silbey, R.J.; Knoll, K.; Schrock, R.R. Conjugation Length Dependence of Raman Scattering in a Series of Linear Polyenes: Implications for Polyacetylene. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 94, 4161–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gussoni, M.; Castiglioni, C.; Zerbi, G. Vibrational Spectroscopy of Polyconjugated Materials: Polyacetylene and Polyenes. In Spectroscopy of Advanced Materials; Clark, R.J.H., Hester, R.E., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 251–353. [Google Scholar]
- Castiglioni, C.; Del Zoppo, M.; Zerbi, G. Vibrational Raman Spectroscopy of Polyconjugated Organic Oligomers and Polymers. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1993, 24, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbi, G.; Gussoni, M.; Castiglioni, C. Vibrational Spectroscopy of Polyconjugated Aromatic Materials with Electrical Non-Linear Properties. In Conjugated Polymers: The Novel Science and Technology of Highly Conducting and Nonlinear Optically Active Materials; Brédas, J.L., Silbey, R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; p. 435. [Google Scholar]
- Castiglioni, C.; Tommasini, M.; Zerbi, G. Raman Spectroscopy of Polyconjugated Molecules and Materials: Confinement Effect in One and Two Dimensions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2004, 362, 2425–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, I.; Furukawa, Y.; Tasumi, M.; Shirakawa, H.; Ikeda, S. Spectroscopic Studies on Doped Polyacetylene and Β-carotene. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 73, 4746–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piaggio, P.; Dellepiane, G.; Piseri, L.; Tubino, R.; Taliani, C. Polarized Infrared Spectra of Highly Oriented Polyacetylenes. Solid State Commun. 1984, 50, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, E.J.; Rice, M.J. Vibrational Excitations of Charged Solitons in Polyacetylene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1980, 45, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemad, S.; Pron, A.; Heeger, A.J.; MacDiarmid, A.G.; Mele, E.J.; Rice, M.J. Infrared-Active Vibrational Modes of Charged Solitons in (CH)x and (CD)X. Phys. Rev. B 1981, 23, 5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Ramanan, C.; Fontanesi, C.; Frick, A.; Surana, S.; Cheyns, D.; Furno, M.; Keller, T.; Allard, S.; Scherf, U.; et al. Displacement of Polarons by Vibrational Modes in Doped Conjugated Polymers. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2017, 1, 055604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenfreund, E.; Vardeny, Z.; Brafman, O.; Horovitz, B. Amplitude and Phase Modes in Trans-Polyacetylene: Resonant Raman Scattering and Induced Infrared Activity. Phys. Rev. B. Condens. Matter 1987, 36, 1535–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painelli, A.; Girlando, A.; Del Freo, L.; Soos, Z.G. Infrared Intensity and Local Vibrations of Charged Solitons. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 56, 15100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohoo-Vallett, P.J.; Bragg, A.E. π-Delocalization and the Vibrational Spectroscopy of Conjugated Materials: Computational Insights on Raman Frequency Dispersion in Thiophene, Furan, and Pyrrole Oligomers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 3583–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, A.; Brambilla, L.; Del Zoppo, M.; Zerbi, G. Raman Dispersion and Intermolecular Interactions in Unsubstituted Thiophene Oligomers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez Navarrete, J.T.; Zerbi, G. Lattice Dynamics and Vibrational Spectra of Polythiophene. I. Oligomers and Polymer. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 94, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosti, E.; Rivola, M.; Hernandez, V.; Del Zoppo, M.; Zerbi, G. Electronic and Dynamical Effects from the Unusual Features of the Raman Spectra of Oligo and Polythiophenes. Synth. Met. 1999, 100, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louarn, G.; Mevellec, J.Y.; Buisson, J.P.; Lefrant, S. Comparison of the Vibrational Properties of Polythiophene and Polyalkylthiophenes. Synth. Met. 1993, 55, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, M.; Furukawa, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Harada, I.; Soma, Y.; Soma, M. Correlation between Vibrational Spectra and Electrical Conductivity of Polythiophene. Synth. Met. 1986, 15, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez Navarrete, J.T.; Zerbi, G. Lattice Dynamics and Vibrational Spectra of Polythiophene. II. Effective Coordinate Theory, Doping Induced, and Photoexcited Spectra. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 94, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castiglioni, C.; Lopez Navarrete, J.T.; Zerbi, G.; Gussoni, M. A Simple Interpretation of the Vibrational Spectra of Undoped, Doped and Photoexcited Polyacetylene: Amplitude Mode Theory in the GF Formalism. Solid State Commun. 1988, 65, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Navarrete, J.T.; Tian, B.; Zerbi, G. Relation between Effective Conjugation, Vibrational Force Constants and Electronic Properties in Polyconjugated Materials. Solid State Commun. 1990, 74, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.; Hollis, J.R.; Kim, J.S. Raman Spectroscopy as an Advanced Structural Nanoprobe for Conjugated Molecular Semiconductors. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 073001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, L.; Tommasini, M.; Botiz, I.; Rahimi, K.; Agumba, J.O.; Stingelin, N.; Zerbi, G. Regio-Regular Oligo and Poly(3-Hexyl Thiophene): Precise Structural Markers from the Vibrational Spectra of Oligomer Single Crystals. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 6730–6739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, L.; Capel Ferrón, C.; Tommasini, M.; Hong, K.; López Navarrete, J.T.; Hernández, V.; Zerbi, G. Infrared and Multi-Wavelength Raman Spectroscopy of Regio-Regular P3HT and Its Deutero Derivatives. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2018, 49, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, S.; Milani, A.; Castiglioni, C.; Hernández Jolín, V.; Meseguer, C.; López Navarrete, J.T.; Zhao, C.; Sugiyasu, K.; Ruiz Delgado, M.C. Raman Fingerprints of Pi-Electron Delocalization in Polythiophene-Based Insulated Molecular Wires. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 3458–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, V.; Castiglioni, C.; Del Zoppo, M.; Zerbi, G. Confinement Potential and Pi -Electron Delocalization in Polyconjugated Organic Materials. Phys. Rev. B. Condens. Matter 1994, 50, 9815–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chance, R.; Boudreaux, D.S.; Brédas, J.L.; Silbey, R. Solitons, Polarons and Bipolarons in Conjugated Polymers. In Handbook of Conducting Polymers; Chance, R., Boudreaux, D.S., Brédas, J.L., Silbey, R., Eds.; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1986; p. 825. [Google Scholar]
- Chance, R.R.; Boudreaux, D.S.; Brédas, J.L.; Silbey, R. Neutral and Charged Soliton Defects in Polyacetylene. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 27, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denti, I.; Cimò, S.; Brambilla, L.; Milani, A.; Bertarelli, C.; Tommasini, M.; Castiglioni, C. Polaron Confinement in N-Doped P(NDI2OD-T2) Unveiled by Vibrational Spectroscopy. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 6726–6739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louarn, G.; Trznadel, M.; Buisson, J.P.; Laska, J.; Pron, A.; Lapkowski, M.; Lefrant, S. Raman Spectroscopic Studies of Regioregular Poly(3-Alkylthiophenes). J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 12532–12539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Xu, J.; Fu, M. Raman Spectroscopic and Electrochemical Studies on the Doping Level Changes of Polythiophene Films during Their Electrochemical Growth Processes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokonuma, N.; Furukawa, Y.; Tasumi, M.; Kuroda, M.; Nakayama, J. Electronic Absorption and Raman Studies of BF4−-Doped Polythiophene Based on the Spectra of the Radical Cation and Dication of α-Sexithiophene. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1996, 255, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.; Renyuan, Q. IR and Raman Studies of Polythiophene Prepared by Electrochemical Polymerization. Solid State Commun. 1985, 54, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, C.; Tommasini, M. Infrared Active Vibrations in Doped π-Conjugated Materials: The Mechanism of Activation of Raman Modes. Asian J. Phys. 2022, 31, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa, Y.; Akimoto, M.; Harada, I. Vibrational Key Bands and Electrical Conductivity of Polythiophene. Synth. Met. 1987, 18, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, H.E.; Heeger, A.J. Infrared Activity of Photoexcitations in Polythiophene. Solid State Commun. 1986, 59, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Spiegel, D.; Hotta, S.; Heeger, A.J. Photoexcitation and Doping Studies of Poly(3-Hexylthienylene). Phys. Rev. B 1988, 38, 5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Hotta, S.; Heeger, A.J. Infrared Photoexcitation and Doping Studies of Poly(3-Methylthienylene). Phys. Rev. B 1987, 36, 7486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Wang, Z.; Fazzi, D.; Shen, Z.; Soci, C. First-Principles Study of the Nuclear Dynamics of Doped Conjugated Polymers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 1994–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyazawa, T.; Fukushima, K.; Ideguchi, Y. Molecular Vibrations and Structure of High Polymers. III. Polarized Infrared Spectra, Normal Vibrations, and Helical Conformation of Polyethylene Glycol. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 37, 2764–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedde, U.W. Polymer Physics; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Brambilla, L.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, B.J.; Hernandez, V.; Lopez Navarrete, J.T.; Zerbi, G. Poly(3-hexylthiophene-2.5-diyl): Evidence of different polymer chain conformations in the solid state from a combined study of regioregularity control and Raman spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1221, 128882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, W.; Yu, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.J.; Song, I.; Shin, M.; Oh, J.H.; Jeong, U.; et al. Tuning mechanical and optoelectrical properties of poly(3-hexylthiophene) through systematic regioregularity control. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 4339–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremel, K.; Ludwigs, S. Morphology of P3HT in thin films in relation to optical and electrical properties. In P3HT Revisited—From Molecular Scale to Solar Cell Devices; Advances in Polymer Science; Ludwigs, S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 265, pp. 39–82. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Im, J.H.; Choi, H.S.; Yang, S.J.; Kim, S.W.; Park, C.R. Preparation and photoluminescence (PL) performance of a nanoweb of P3HT nanofibers with diameters below 100 nm. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 14231–14239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trznadel, M.; Zagórska, M.; Lapkowski, M.; Louarn, G.; Lefrant, S.; Pron, A. UV–VIS–NIR and Raman Spectroelectrochemistry of Regioregular Poly(3-Octylthiophene): Comparison with Its Non-Regioregular Analogue. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1996, 92, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| ν (cm−1) | Vibrational Assignment | |
|---|---|---|
| A | 1510 | Antisymmetric C=C str of thiophene ring C–C str (alkyl chain); CH wagging |
| B | 1455–1465 | ECC mode–CH2 bending |
| C | 1377 | CH3 umbrella motion |
| D | 823 | Thiophene ring CH out-of-plane bending; CH2 rocking |
| R = A///A⊥ | f | Φ (deg) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| P3HT | 5.93 | 0.62 | 30.14 |
| PEO:P3HT | 5.80 | 0.61 | 30.43 |
| P3HT | P3HT:PEO | |
|---|---|---|
| R = A1430−1220/A3000−2800 | R = A1430−1220/A3000−2800 | |
| Pristine | 0.169 | 0.227 |
| Highly doped | 4.715 | 2.899 |
| [Rdoped/Rpristine] | 28 | 13 |
| P3HT | P3HT:PEO | P3HT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| powder | fibres | washed fibres | |
| Hairy A | 54% | 44% | 53% |
| Hairy B | 45% | 53% | 46% |
| Fully amorphous | 1% | 3% | 1% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arrigoni, A.; Brambilla, L.; Castiglioni, C.; Bertarelli, C. Conducting Electrospun Nanofibres: Monitoring of Iodine Doping of P3HT through Infrared (IRAV) and Raman (RaAV) Polaron Spectroscopic Features. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4308. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12234308
Arrigoni A, Brambilla L, Castiglioni C, Bertarelli C. Conducting Electrospun Nanofibres: Monitoring of Iodine Doping of P3HT through Infrared (IRAV) and Raman (RaAV) Polaron Spectroscopic Features. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(23):4308. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12234308
Chicago/Turabian StyleArrigoni, Alessia, Luigi Brambilla, Chiara Castiglioni, and Chiara Bertarelli. 2022. "Conducting Electrospun Nanofibres: Monitoring of Iodine Doping of P3HT through Infrared (IRAV) and Raman (RaAV) Polaron Spectroscopic Features" Nanomaterials 12, no. 23: 4308. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12234308
APA StyleArrigoni, A., Brambilla, L., Castiglioni, C., & Bertarelli, C. (2022). Conducting Electrospun Nanofibres: Monitoring of Iodine Doping of P3HT through Infrared (IRAV) and Raman (RaAV) Polaron Spectroscopic Features. Nanomaterials, 12(23), 4308. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12234308