Functional Nanoparticles with Magnetic 3D Covalent Organic Framework for the Specific Recognition and Separation of Bovine Serum Albumin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Preparation of COOH-Tp
2.4. Preparation of Fe3O4@cTp-TAM (Magnetic 3D COFs)
2.5. Preparation of Magnetic-3D COF–GSH
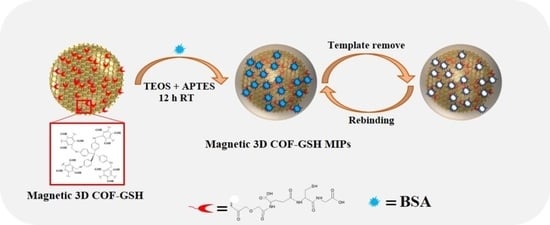
2.6. Preparation of Magnetic 3D COF–GSH MIPs/Nonimprinted Polymers (NIPs)
3. Binding Experiments
Preliminary Application
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Preparation and Characterization of the Magnetic 3D COF–GSH MIPs
4.2. Optimization of the Adsorption Conditions
4.2.1. Optimization of Monomer and Crosslinker on Adsorption
4.2.2. Optimization of pH on Adsorption
4.2.3. Optimization of GSH on Adsorption
4.2.4. Optimization of BSA on Adsorption
4.3. Adsorption Kinetics
4.4. Isothermal Adsorption Properties
4.5. Rebinding Selectivity
4.6. Preliminary and Practical Application
4.7. Regeneration Ability
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Côté, A.P.; Benin, A.; Ockwig, N.; Okeeffe, M.; Matzger, A.; Yaghi, O. Covalent Organic Frameworks. Science 2005, 310, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.H.; Yang, C.X.; Yan, X.P. Methacrylate-bonded covalent-organic framework monolithic columns for high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1479, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.Y.; Wang, W. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs): From design to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 548–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Riduan, S.N. Functional porous organic polymers for heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2083–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Li, X.; Ning, G.; Leng, K.; Tian, B.; Liu, C.; Tang, W.; Xu, H.; Loh, K. Highly photoluminescent two-dimensional imine-based covalent organic frameworks for chemical sensing. Chem Commun 2018, 54, 2349–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynek, J.; Zelenka, J.; Ruthousky, J.; Kubat, P.; Ruml, T.; Demel, J.; Lang, K. Designing Porphyrinic Covalent Organic Frameworks for the Photodynamic Inactivation of Bacteria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 8527–8535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, M.S.; Bein, T. Covalent organic frameworks: Structures, synthesis, and applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; Song, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, C.; He, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z. Two-dimensional porphyrin-based covalent organic framework: A novel platform for sensitive epidermal growth factor receptor and living cancer cell detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kaderi, H.M.; Hunt, J.R.; Mendoza-Cortes, J.; Corte, A.; Taylor, R.; Okeeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. Designed Synthesis of 3D Covalent Organic Frameworks. Science 2007, 316, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz, U.; Corma, A. Ordered covalent organic frameworks, COFs and PAFs. From preparation to application. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 311, 85–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Dai, Q.; Chen, J.; Dai, L. Edge functionalization of graphene and two-dimensional covalent organic polymers for energy conversion and storage. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6253–6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, G.; Puyvelde, P.; Bruggen, B. Covalent organic frameworks for membrane separation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2665–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wu, D.; Hu, N.; Fang, G.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Chen, X.; Suo, Y.; Li, G.; Wu, Y. Effective Enrichment and Detection of Trace Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Food Samples based on Magnetic Covalent Organic Framework Hybrid Microspheres. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3572–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, B.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liang, H.; Wu, D. Self-assembling hydrophilic magnetic covalent organic framework nanospheres as a novel matrix for phthalate ester recognition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 26539–26545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, H.; Lv, F.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gan, N. A headspace sorptive extraction method with magnetic mesoporous titanium dioxide@covalent organic frameworks composite coating for selective determination of trace polychlorinated biphenyls in soils. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1572, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Yan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lan, F.; Wu, Y. Bifunctional magnetic covalent organic framework for simultaneous enrichment of phosphopeptides and glycopeptides. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1177, 338761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Chen, F.; Fang, Q.; Qiu, S. Design and applications of three dimensional covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1357–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, B.; Liao, X. Strategy of Fusion Covalent Organic Frameworks and Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: A Surprising Effect in Recognition and Loading of Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 8751–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanban-Esfahlan, A.; Roufegarinejad, L.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R.; Tabibiazar, M.; Amarowicz, R. Latest developments in the detection and separation of bovine serum albumin using molecularly imprinted polymers. Talanta 2020, 207, 120317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.Y.; Zhao, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Dong, A.; Wang, J.; Li, B. Selective recognition and fast enrichment of anthocyanins by dummy molecularly imprinted magnetic nanoparticles. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1572, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, C.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, B.; Yang, X. Synthesis of magnetic covalent organic framework molecularly imprinted polymers at room temperature: A novel imprinted strategy for thermo-sensitive substance. Talanta 2021, 225, 121958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Shen, N.; Zhao, J.; Su, Y.; Ren, H. Glutathione-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles with enhanced Fenton-like activity at neutral pH for degrading 2,4-dichlorophenol. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinluan, R.D.; Liu, J.; Zhou, C.; Yu, M.; Yang, S.; Kumar, A.; Sun, S.; Dean, A.; Sun, X.; Zheng, J. Glutathione-coated luminescent gold nanoparticles: A surface ligand for minimizing serum protein adsorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 11829–11833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, B.; He, J.; Li, Z.; Lan, F.; Wu, Y. Glutathione-Functionalized Magnetic Covalent Organic Framework Microspheres with Size Exclusion for Endogenous Glycopeptide Recognition in Human Saliva. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 47218–47226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Chiba, J. Rheological and small-angle X-ray scattering investigations on the shape and ordered arrangement of native ovalbumin molecules in aqueous colloids. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1990, 86, 2877–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Deng, Q.; Fang, G.; Wu, J.; Li, W.; Wang, S. Protein imprinted ionic liquid polymer on the surface of multiwall carbon nanotubes with high binding capacity for lysozyme. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 960, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.Y.; Wu, H.H.; Chou, B.C.; Li, C.S.; Gau, B.Z.; Lin, Z.Y.; Fuh, C.B. A magneto-microfluidic platform for fluorescence immunosensing using quantum dot nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 505101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Lin, J.; Lin, C.; Qi, G.; Lin, X.; Xie, Z. Heteroporous 3D covalent organic framework-based magnetic nanospheres for sensitive detection of bisphenol A. Talanta 2021, 231, 122343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, B.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; He, J.; Zhou, J.; Wu, L.; Lan, F.; Wu, Y. Construction of a magnetic covalent organic framework with synergistic affinity strategy for enhanced glycopeptide enrichment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6377–6386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, F.; Wei, X.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; He, X.; Zhou, Y. A new magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer based on deep eutectic solvents as functional monomer and cross-linker for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1129, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Q. Surface molecularly imprinted thermo-sensitive polymers based on light-weight hollow magnetic microspheres for specific recognition of BSA. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 486, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boitard, C.; Rollet, A.; Menager, C.; Griffete, N. Surface-initiated synthesis of bulk-imprinted magnetic polymers for protein recognition. Chem Commun 2017, 53, 8846–8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Q.-Q.; Qu, F.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y. The preparation of bovine serum albumin surface-imprinted superparamagnetic polymer with the assistance of basic functional monomer and its application for protein separation. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 3489–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, H.; Deng, Z.; Chen, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, Y.; Tan, Z.; Zhong, S. Pegylated thermo-sensitive bionic magnetic core-shell structure molecularly imprinted polymers based on halloysite nanotubes for specific adsorption and separation of bovine serum albumin. Polymers 2020, 12, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, J.P.; Yu, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, T.; Peng, H. Preparation, characterization, and application of multiple stimuli-responsive rattle-type magnetic hollow molecular imprinted poly (ionic liquids) nanospheres (Fe3O4@void@PILMIP) for specific recognition of protein. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Sun, J.; Hou, C.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Lei, D.; Yang, M.; Zhang, S. Immobilization of BSA on ionic liquid functionalized magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for use in surface imprinting strategy. Talanta 2017, 168, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | Qmax_ mg g−1 | Linear Range_ mg mL−1 | IF | Equilibrium Absorption Time in Hour | Year and Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MHNTs@PEG@4-VP MMIP | 258 | 0.2–1.4 | 2.44 | 1.3 | 2020, [34] |
| HMS@MIPs. | 431 | 0.0–0.8 | 2.01 | 2 | 2019, [30] |
| Fe3O4@void@BSA-pIL | 130 | 0.1–0.5 | 2.79 | 1 | 2018, [35] |
| γ-Fe2O3@PIP | 300 | 0.0–2.4 | 4 | 24 | 2017, [32] |
| Fe3O4@IL@MIP | 51 | 0.1–0.9 | 3.33 | 1 | 2017, [36] |
| magnetic 3D COF–GSH MIPs | 429 | 0.1–1.0 | 4.79 | 1.5 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bettada, L.; Tsai, H.; Fuh, C.B. Functional Nanoparticles with Magnetic 3D Covalent Organic Framework for the Specific Recognition and Separation of Bovine Serum Albumin. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030411
Bettada L, Tsai H, Fuh CB. Functional Nanoparticles with Magnetic 3D Covalent Organic Framework for the Specific Recognition and Separation of Bovine Serum Albumin. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(3):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030411
Chicago/Turabian StyleBettada, Lokesh, Hweiyan Tsai, and C. Bor Fuh. 2022. "Functional Nanoparticles with Magnetic 3D Covalent Organic Framework for the Specific Recognition and Separation of Bovine Serum Albumin" Nanomaterials 12, no. 3: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030411
APA StyleBettada, L., Tsai, H., & Fuh, C. B. (2022). Functional Nanoparticles with Magnetic 3D Covalent Organic Framework for the Specific Recognition and Separation of Bovine Serum Albumin. Nanomaterials, 12(3), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030411