Influence of Dispersion and Orientation on Polyamide-6 Cellulose Nanocomposites Manufactured through Liquid-Assisted Extrusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of NC Suspensions
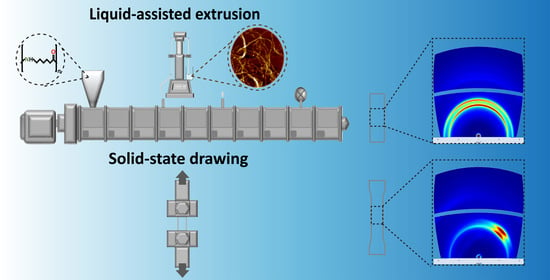
2.2.2. Liquid-Assisted Extrusion and Film Preparation
2.2.3. SSD
2.3. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Effect of the Addition of NC and NC/PEG to PA6
3.2. Effect of Orientation on PA6 and PA6-Nanocomposites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gilbert, M. Aliphatic polyamides. In Brydson’s Plastics Materials, 8th ed.; Gilbert, M., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017; Chapter 18; pp. 487–511. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, Y.; Spencer, M.W.; Paul, D.R. Morphology and Mechanical Properties of Glass Fiber Reinforced Nylon 6 Nanocomposites. Polymer 2011, 52, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, M.V.; Steinert, B.W.; Thomas, V.; Dean, D.R.; Abdalla, M.A.; Price, G.; Janowski, G.M. Morphology and Mechanical Properties of Nylon 6/MWNT Nanofibers. Polymer 2007, 48, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Usuki, A.; Kawasumi, M.; Okada, A.; Kurauchi, T.; Kamigaito, O. Synthesis of Nylon 6–Clay Hybrid by Montmorillonite Intercalated with ε-Caprolactam. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1993, 31, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Usuki, A.; Kawasumi, M.; Okada, A.; Fukushima, Y.; Kurauchi, T.; Kamigaito, O. Mechanical Properties of Nylon 6-Clay Hybrid. J. Mater. Res. 1993, 8, 1185–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, K.D.; Jacobson, R.E.; Caulfield, D.F.; Underwood, J. Composites Containing Cellulosic Pulp Fibers and Methods of Making and Using the Same. US Patent 6270883B1, 7 August 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, R.; Caulfield, D.; Sears, K.; Underwood, J. Low temperature processing of ultra-pure cellulose fibers into nylon 6 and other thermoplastics. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Woodfiber-Plastic Composites, Madison, WI, USA, 15–16 May 2001; Forest Products Society: LaGrange, GA, USA, 2002; pp. 127–133, ISBN 0892529181. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Gardner, D.J.; Han, Y. Characterization of Mechanical and Morphological Properties of Cellulose Reinforced Polyamide 6 Composites. Cellulose 2015, 22, 3199–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Walsh, P.J.; Sabo, R.C.; Turng, L.-S.; Clemons, C.M. Water-Assisted Compounding of Cellulose Nanocrystals into Polyamide 6 for Use as a Nucleating Agent for Microcellular Foaming. Polymer 2016, 84, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yousefian, H.; Rodrigue, D. Morphological, Physical and Mechanical Properties of Nanocrystalline Cellulose Filled Nylon 6 Foams. J. Cell. Plast. 2017, 53, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, P.; Trotto, E.; Burgoyne, I.; Foster, E.J. Premixed Cellulose Nanocrystal Reinforcement of Polyamide 6 for Melt Processing. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 4353–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, D.A.; Niinivaara, E.; Jankovic, N.C.; Demir, E.C.; Benkaddour, A.; Jarvis, V.; Ayranci, C.; McDermott, M.T.; de Lannoy, C.-F.; Cranston, E.D. Cellulose Nanocrystals Influence Polyamide 6 Crystal Structure, Spherulite Uniformity, and Mechanical Performance of Nanocomposite Films. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 4673–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhara, P.K.; Vilaseca, F. High Performance PA 6/Cellulose Nanocomposites in the Interest of Industrial Scale Melt Processing. Polymers 2021, 13, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-A.; Yoon, M.-J.; Lee, E.-S.; Lim, D.-Y.; Kim, K.-Y. Preparation and Characterization of Cellulose Nanofibers (CNFs) from Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) and CNF/Polyamide 6 Composites. Macromol. Res. 2014, 22, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semba, T.; Ito, A.; Kitagawa, K.; Kataoka, H.; Nakatsubo, F.; Kuboki, T.; Yano, H. Polyamide 6 Composites Reinforced with Nanofibrillated Cellulose Formed during Compounding: Effect of Acetyl Group Degree of Substitution. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 145, 106385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qua, E.H.; Hornsby, P.R. Preparation and Characterisation of Nanocellulose Reinforced Polyamide-6. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2011, 40, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, A.C.; de Morais Teixeira, E.; Carmona, V.B.; Teodoro, K.B.R.; Ribeiro, C.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Marconcini, J.M. Obtaining Nanocomposites of Polyamide 6 and Cellulose Whiskers via Extrusion and Injection Molding. Cellulose 2014, 21, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, N.; Singh, A.A.; Salaberria, A.M.; Labidi, J.; Mathew, A.P.; Oksman, K. Triethyl Citrate (TEC) as a Dispersing Aid in Polylactic Acid/Chitin Nanocomposites Prepared via Liquid-Assisted Extrusion. Polymers 2017, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera, N.; Mathew, A.P.; Oksman, K. Plasticized Polylactic Acid/Cellulose Nanocomposites Prepared Using Melt-Extrusion and Liquid Feeding: Mechanical, Thermal and Optical Properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 106, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksman, K.; Mathew, A.P.; Bondeson, D.; Kvien, I. Manufacturing Process of Cellulose Whiskers/Polylactic Acid Nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 2776–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, F.; Tu, W.; Bilotti, E.; Peijs, T. The Influence of Solid-State Drawing on Mechanical Properties and Hydrolytic Degradation of Melt-Spun Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA) Tapes. Fibers 2015, 3, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bugatti, V.; Viscusi, G.; Naddeo, C.; Gorrasi, G. Nanocomposites Based on PCL and Halloysite Nanotubes Filled with Lysozyme: Effect of Draw Ratio on the Physical Properties and Release Analysis. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.A.; Geng, S.; Herrera, N.; Oksman, K. Aligned Plasticized Polylactic Acid Cellulose Nanocomposite Tapes: Effect of Drawing Conditions. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 104, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penel-Pierron, L.; Depecker, C.; Séguéla, R.; Lefebvre, J.-M. Structural and Mechanical Behavior of Nylon 6 Films Part I: Identification and Stability of the Crystalline Phases. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2001, 39, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bradford, P.D.; Liu, W.; Zhao, H.; Inoue, Y.; Maria, J.-P.; Li, Q.; Yuan, F.-G.; Zhu, Y. Mechanical and Electrical Property Improvement in CNT/Nylon Composites through Drawing and Stretching. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1677–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Ye, L.; Li, G. Structure and Hydrothermal Stability of Highly Oriented Polyamide 6 Produced by Solid Hot Stretching. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30160–30169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, Y.P. Overview of Transition Phenomenon in Nylon 6. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 3298–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltahir, Y.A.; Saeed, H.A.M.; Yuejun, C.; Xia, Y.; Yimin, W. Effect of Hot Drawing on the Structure and Properties of Novel Polyamide 5,6 Fibers. Text. Res. J. 2014, 84, 1700–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, K.S.; Patel, A. Influence of Moisture/Water Absorption on Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Polyamide6/Boric Oxide Composites. Pigment Resin Technol. 2021, 12, 743–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, R.P.; da Rosa, M.P.; Beck, P.H.; Tienne, L.G.; de Marques, M.F.V. Thermal, Morphological and Mechanical Properties of Composites Based on Polyamide 6 with Cellulose, Silica and Their Hybrids from Rice Husk. J. Compos. Mater. 2020, 55, 1811–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramoda, K.P.; Liu, T. Effect of Moisture on the Dynamic Mechanical Relaxation of Polyamide-6/Clay Nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-R.; Ren, X.-K.; Yang, T.; Jiang, X.-Q.; Chang, W.-Y.; Yang, S.; Stroeks, A.; Chen, E.-Q. Revisiting the Thermal Transition of β-Form Polyamide-6: Evolution of Structure and Morphology in Uniaxially Stretched Films. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, C.; Gowd, E.B. High-Temperature X-ray Diffraction Studies on the Crystalline Transitions in the R- and γ-Forms of Nylon-6. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkoula, N.-M.; Peijs, T.; Schimanski, T.; Loos, J. Processing of Single Polymer Composites Using the Concept of Constrained Fibers. Polym. Compos. 2005, 26, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, W.G.; Porter, R.S. Solid-State Deformation of Polyethylene and Nylon and Its Effects on Their Structure and Morphology. J. Mater. Sci. 1977, 12, 2355–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, N.S. Hydrogen Bonding, Mobility, and Structural Transitions in Aliphatic Polyamides. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 1763–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotter, G.; Ishida, H. FTIR Separation of Nylon-6 Chain Conformations: Clarification of the Mesomorphous and γ-Crystalline Phases. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1992, 30, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, X.; Berglund, L.A. FT-IR Spectroscopic Study of Hydrogen Bonding in PA6/Clay Nanocomposites. Polymer 2002, 43, 2445–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Sample Code | NC (wt.%) | PEG (wt.%) | Pumping Rate (mL/min) | Evaporation (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA6 | 0 | 0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| PA6/0.5NC | 0.5 | 0 | 5.0 | 4.9 |
| PA6/5PEG/0.5NC | 0.5 | 5 | 5.3 | 4.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Völtz, L.R.; Geng, S.; Teleman, A.; Oksman, K. Influence of Dispersion and Orientation on Polyamide-6 Cellulose Nanocomposites Manufactured through Liquid-Assisted Extrusion. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12050818
Völtz LR, Geng S, Teleman A, Oksman K. Influence of Dispersion and Orientation on Polyamide-6 Cellulose Nanocomposites Manufactured through Liquid-Assisted Extrusion. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(5):818. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12050818
Chicago/Turabian StyleVöltz, Luísa Rosenstock, Shiyu Geng, Anita Teleman, and Kristiina Oksman. 2022. "Influence of Dispersion and Orientation on Polyamide-6 Cellulose Nanocomposites Manufactured through Liquid-Assisted Extrusion" Nanomaterials 12, no. 5: 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12050818
APA StyleVöltz, L. R., Geng, S., Teleman, A., & Oksman, K. (2022). Influence of Dispersion and Orientation on Polyamide-6 Cellulose Nanocomposites Manufactured through Liquid-Assisted Extrusion. Nanomaterials, 12(5), 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12050818