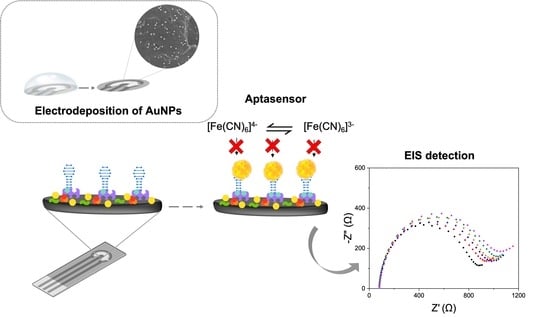
An Effective Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Gold Nanoparticles for Gluten Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) Measurements
2.4. Modification Procedure of SPCE with AuNPs
2.5. Biosensor Assembly
2.6. Gliadin Detection
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrochemical Characterization of SPCE Modified with AuNPs
3.2. SEM Characterization of Modified SPCE
3.3. Electrochemical Characterization of the Biosensor
3.4. Gliadin Quantification by Label-Free Biosensor
3.5. Real Samples Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, M.; Gu, Y.; Yun, Y.; Li, M.; Jin, X.; Wang, S. Nanomaterials for electrochemical immunosensing. Sensors 2017, 17, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bobrinetskiy, I.; Radovic, M.; Rizzotto, F.; Vizzini, P.; Jaric, S.; Pavlovic, Z.; Radonic, V.; Nikolic, M.; Vidic, J. Advances in nanomaterials-based electrochemical biosensors for foodborne pathogen detection. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, F.T.T.; de Falcão, I.R.A.; da Souza, J.E.S.; Rocha, T.G.; de Sousa, I.G.; Cavalcante, A.L.G.; de Oliveira, A.L.B.; de Sousa, M.C.M.; dos Santos, J.C.S. Designing of nanomaterials-based enzymatic biosensors: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Electrochem 2021, 2, 149–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Kang, P. Systemic review of biodegradable nanomaterials in nanomedicine. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuentes-Chust, C.; Parolo, C.; Rosati, G.; Rivas, L.; Perez-Toralla, K.; Simon, S.; Lecuona, I.; Junot, C.; Trebicka, J.; Merkoçi, A. The microbiome meets nanotechnology: Opportunities and challenges in developing new diagnostic devices. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Share, K.; Westover, A.; Li, M.; Pint, C. Surface engineering of nanomaterials for improved energy storage—A review. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 154, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, H.; Zaidi, S. Recent developments in the application of nanomaterials in agroecosystems. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Hou, B.; Wang, J.; Tian, B.; Bi, J.; Wang, N.; Li, X.; Huang, X. Nanomaterials for the removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tonelli, D.; Scavetta, E.; Gualandi, I. Electrochemical deposition of nanomaterials for electrochemical sensing. Sensors 2019, 19, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antuña-Jiménez, D.; González-García, M.B.; Hernández-Santos, D.; Fanjul-Bolado, P. Screen-printed electrodes modified with metal nanoparticles for small molecule sensing. Biosensors 2020, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alam, S.; Augustine, S.; Narayan, T.; Luong, J.H.T.; Malhotra, B.D.; Khare, S.K. A chemosensor based on gold nanoparticles and dithiothreitol (DTT) for acrylamide electroanalysis. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Li, N. Noble metal nanoparticles-based colorimetric biosensor for visual quantification: A mini review. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qing, Z.; Bai, A.; Xing, S.; Zou, Z.; He, X.; Wang, K.; Yang, R. Progress in biosensor based on DNA-templated copper nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 137, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Ma, C.; Wu, M.; Jia, C.; Feng, S.; Zhao, J.; Liang, L. Sensitivity of photoelctrocehmical aptasensor using spiral nanorods for detecting antiobiotic levels in experimental and real samples. Talanta 2022, 237, 122930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, S.; Hojjatoleslamy, M.; Kiani, H.; Molavi, H. Monitoring of aflatoxin M1 in milk using a novel electrochemical aptasensor based on reduced graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Ye, Y.; Liu, S. Gold nanoparticle-based signal amplification for biosensing. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 417, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pingarrón, J.M.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; González-Cortés, A. Gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical biosensors. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5848–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Huang, J.; Wang, D.; Meng, T.; Yang, X. Au and Au-based nanomaterials: Synthesis and recent progress in electrochemical sensor applications. Talanta 2020, 206, 120210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Bai, L.; Han, X.; Wang, J.; Shi, A.; Zhang, Y. Ultra-sensitive biosensor for K-Ras gene detection using enzyme capped gold nanoparticles conjugates for signal amplification. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 460, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Nhat Nguyen, U.T.; Hsieh, H.-Y.; Tahara, H.; Chang, Y.-S.; Wang, B.-Y.; Gu, B.-C.; Dai, Y.-H.; Wu, C.-C.; Tsai, I.-J.; et al. Peptide-based electrochemical sensor with nanogold enhancement for detecting rheumatoid arthritis. Talanta 2022, 236, 122886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neethirajan, S.; Weng, X.; Tah, A.; Cordero, J.O.; Ragavan, K.V. Nano-biosensor platforms for detecting food allergens—New trends. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2018, 18, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, A.; Conte-Junior, C.A. A systematic review of food allergy: Nanobiosensor and food allergen detection. Biosensors 2020, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.C.; Barroso, M.F.; González-García, M.B.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Delerue-Matos, C. New trends in food allergens detection: Toward biosensing strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2304–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieser, H.; Koehler, P. The biochemical basis of celiac disease. Cereal Chem. J. 2008, 85, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uche-Anya, E.; Lebwohl, B. Celiac disease: Clinical update. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2021, 37, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandi, B.; Bencivenni, M.; Faccini, A.; Tedeschi, T.; Dossena, A.; Marchelli, R.; Galaverna, G.; Sforza, S. Composition of peptide mixtures derived from simulated gastrointestinal digestion of prolamins from different wheat varieties. J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 56, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamone, G.; Ferranti, P.; Rossi, M.; Roepstorff, P.; Fierro, O.; Malorni, A.; Addeo, F. Identification of a peptide from α-Gliadin resistant to digestive enzymes: Implications for celiac disease. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 855, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Re, V.; Caggiari, L.; Tabuso, M.; Cannizzaro, R. The versatile role of gliadin peptides in celiac disease. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgrave, M.L.; Goswami, H.; Blundell, M.; Howitt, C.A.; Tanner, G.J. Using mass spectrometry to detect hydrolysed gluten in beer that is responsible for false negatives by ELISA. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1370, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morón, B.; Cebolla, A.; Manyani, H.; Alvarez-Maqueda, M.; Megías, M.; Thomas, M.D.C.; López, M.C.; Sousa, C. Sensitive detection of cereal fractions that are toxic to celiac disease patients by using monoclonal antibodies to a main immunogenic wheat peptide. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amaya-González, S.; de-los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. Aptamer binding to celiac disease-triggering hydrophobic proteins: A sensitive gluten detection approach. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2733–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaya-González, S.; López-López, L.; Miranda-Castro, R.; de-los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. Affinity of aptamers binding 33-Mer gliadin peptide and gluten proteins: Influence of immobilization and labeling tags. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 873, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svigelj, R.; Dossi, N.; Pizzolato, S.; Toniolo, R.; Miranda-Castro, R.; de-los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. Truncated aptamers as selective receptors in a gluten sensor supporting direct measurement in a deep eutectic solvent. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svigelj, R.; Dossi, N.; Grazioli, C.; Toniolo, R. Paper-based aptamer-antibody biosensor for gluten detection in a deep eutectic solvent (DES). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvano, F.; Albanese, D.; Pilloton, R.; Matteo, M.D. A New label-free impedimetric aptasensor for gluten detection. Food Control 2017, 79, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottari, F.; Moretto, L.M.; Ugo, P. Impedimetric sensing of the immuno-enzymatic reaction of gliadin with a collagen-modified electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2018, 97, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, P.; Costa-Rama, E.; Beirão, I.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Santos-Silva, A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Disposable electrochemical immunosensor for analysis of cystatin C, a CKD biomarker. Talanta 2019, 201, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.C.; Pimentel, F.B.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Correr, W.; González-García, M.B.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Delerue-Matos, C. Detection of the peanut allergen ara h 6 in foodstuffs using a voltammetric biosensing approach. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 7157–7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, Y. Preparation of aptamer-linked gold nanoparticle purple aggregates for colorimetric sensing of analytes. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitriu, C.; Constantinescu, A.; Pirvu, C. Functionalized TiO2 nanotube platform for gliadin electroanalysis. Crystals 2020, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Method | Recognition Element | LOD/mg L−1 (Gluten) | Linear Range/mg L−1 (Gluten) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label-free (impedance) | aptamer | 5 | - | [35] |
| Label-free (impedance) | antibody | 5 | 5–20 | [36] |
| Label-free (impedance) | antibody | 14 | 0–20 | [40] |
| Label-free (impedance) | aptamer | 0.1 | 0.4–2 | This work |
| Sample | Expected Gluten Concentration (mg L−1) * | Gluten Concentration (mg L−1) ** | Recovery (%) *** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beer 1 | <20 | 12.96 ± 1.68 | \ |
| Beer 1 (spiked with 5 mg L−1) | 16.66 | 16.80 ± 2.21 | 101 |
| Beer 2 | <20 | 18.38 ± 1.04 | \ |
| Beer 2 (spiked with 10 mg L−1) | 26.54 | 27.81 ± 3.49 | 105 |
| Soy sauce | <20 | 8.72 ± 0.27 | \ |
| Soy sauce (spiked with 10 mg L−1) | 17.85 | 16.59 ± 2.02 | 93 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Svigelj, R.; Zuliani, I.; Grazioli, C.; Dossi, N.; Toniolo, R. An Effective Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Gold Nanoparticles for Gluten Detection. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060987
Svigelj R, Zuliani I, Grazioli C, Dossi N, Toniolo R. An Effective Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Gold Nanoparticles for Gluten Detection. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(6):987. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060987
Chicago/Turabian StyleSvigelj, Rossella, Ivan Zuliani, Cristian Grazioli, Nicolò Dossi, and Rosanna Toniolo. 2022. "An Effective Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Gold Nanoparticles for Gluten Detection" Nanomaterials 12, no. 6: 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060987
APA StyleSvigelj, R., Zuliani, I., Grazioli, C., Dossi, N., & Toniolo, R. (2022). An Effective Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Gold Nanoparticles for Gluten Detection. Nanomaterials, 12(6), 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060987