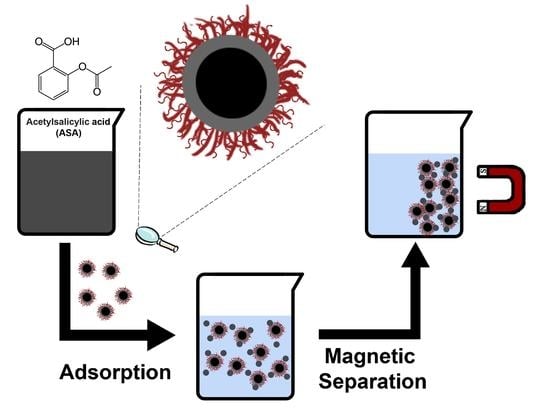
L-Lysine-Coated Magnetic Core–Shell Nanoparticles for the Removal of Acetylsalicylic Acid from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Reagents and Equipment
2.2. Synthesis of the Magnetic Nanoadsorbents
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization
2.4. Batch Adsorption and Desorption Experiments
2.5. Equilibrium and Kinetic Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Nanoadsorbents
3.2. Influence of pH: Mechanism of Adsorption
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics Studies
3.4. Adsorption Equilibrium Studies
3.5. Recovery and Reuse Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- aus der Beek, T.; Weber, F.-A.; Bergmann, A.; Carius, A.; Grüttner, G. Pharmaceuticals in the Environment: Global Occurrence and Potential Cooperative Action under the Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM); Umweltbundesamt: Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, G.; Ng, W.J.; Tan, S.K. A Review on Removing Pharmaceutical Contaminants from Wastewater by Constructed Wetlands: Design, Performance and Mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 908–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fent, K.; Weston, A.A.; Caminada, D. Ecotoxicology of Human Pharmaceuticals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 76, 122–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadegh, H.; Ali, G.A.M.; Gupta, V.K.; Makhlouf, A.S.H.; Shahryari-ghoshekandi, R.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Sillanpää, M.; Megiel, E. The Role of Nanomaterials as Effective Adsorbents and Their Applications in Wastewater Treatment. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, I. New Generation Adsorbents for Water Treatment. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5073–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ul-Islam, M.; Ullah, M.W.; Khan, S.; Manan, S.; Khattak, W.A.; Ahmad, W.; Shah, N.; Park, J.K. Current Advancements of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Adsorption and Degradation of Organic Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 12713–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Magnetic Magnetite (Fe3O4) Nanoparticle Synthesis and Applications for Lead (Pb2+) and Chromium (Cr6+) Removal from Water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 468, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.B.; Vakili, M.; Horri, B.A.; Poh, P.E.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Salamatinia, B. Adsorption of Dyes by Nanomaterials: Recent Developments and Adsorption Mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 150, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebodos, R.L.; Vikesland, P.J. Effects of Oxidation on the Magnetization of Nanoparticulate Magnetite. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16745–16753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.F.C.; Michels-Brito, P.H.; Da Silva, F.G.; Gomes, R.C.; Gomide, G.; Depeyrot, J. Removal of Direct Yellow 12 from Water Using CTAB-Coated Core-Shell Bimagnetic Nanoadsorbents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, M.H.; Tourinho, F.A.; Depeyrot, J.; da Silva, G.J.; Lara, M.C.F.L. New Electric Double-Layered Magnetic Fluids Based on Copper, Nickel, and Zinc Ferrite Nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourinho, F.A.; Franck, R.; Massart, R. Aqueous Ferrofluids Based on Manganese and Cobalt Ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 3249–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.R.; Zheng, J.; Fang, W.J.; Chen, C.; Cheng, C.; Yan, R.W.; Huang, S.G.; Wang, C.C. Synthesis of Porous Magnetic Fe3O4/Fe@ZnO Core-Shell Heterostructure with Superior Capability for Water Treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 650, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.F.C.; de Oliveira, H.A.L.; da Silva, F.N.; da Silva, F.G.; Coppola, P.; Aquino, R.; Mezzi, A.; Depeyrot, J. Core-Shell Bimagnetic Nanoadsorbents for Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Aqueous Solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, J.A.; Sousa, M.H.; Tourinho, F.A.; Aquino, R.; Depeyrot, J.; Dubois, E.; Perzynski, R. Synthesis of Core-Shell Ferrite Nanoparticles for Ferrofluids: Chemical and Magnetic Analysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 6220–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A. Chemistry: An Introduction for Medical and Health Sciences; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2005; ISBN 0470092882. [Google Scholar]
- Stumpf, M.; Ternes, T.A.; Willken, R.-D.; Rodrigues, S.V.; Baumann, W. Polar Drug Residues in Sewage and Natural Waters in the State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 225, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannou, C.I.; Kosma, C.I.; Albanis, T.A.; Nannou, C.I.; Kosma, C.I.; Albanis, T.A.; Kosma, C.I.; Albanis, T.A. Occurrence of Pharmaceuticals in Surface Waters: Analytical Method Development and Environmental Risk Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2015, 95, 1242–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shan, C.; Jin, Y.; Tong, M. Enhanced Removal of Trace Arsenate by Magnetic Nanoparticles Modified with Arginine and Lysine. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, R.; Tourinho, F.A.; Itri, R.; Lara, M.C.F.L.E.; Depeyrot, J. Size Control of MnFe2O4 Nanoparticles in Electric Double Layered Magnetic Fluid Synthesis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 252, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilati, V.; Cabreira Gomes, R.; Gomide, G.; Coppola, P.; Silva, F.G.; Paula, F.L.O.; Perzynski, R.; Goya, G.F.; Aquino, R.; Depeyrot, J. Core/Shell Nanoparticles of Non-Stoichiometric Zn-Mn and Zn-Co Ferrites as Thermosensitive Heat Sources for Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 3028–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreira, A.F.L.; Paula, F.L.O.; Campos, A.F.C.; Depeyrot, J. Local Structure Investigation of Cobalt Ferrite-Based Nanoparticles by Synchrotron X-Ray Diffraction and Absorption Spectroscopy. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 286, 121269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, R.; Titus, E.; Krishna, R.; Bardhan, N.; Bahadur, D.; Gracio, J. Wet-Chemical Green Synthesis of L-Lysine Amino Acid Stabilized Biocompatible Iron-Oxide Magnetic Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 6645–6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and Zeta Potential—What They Are and What They Are Not? J. Control Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Din, M.I.; Naseem, K.; Mirza, M.L.; Batool, M. Evaluation of Saccharum Bengalense as a Non-Conventional Biomaterial for Biosorption of Mn (II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2018, 37, 179–189. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-G.; Kim, S.-B. Removal of Arsenic and Selenium from Aqueous Solutions Using Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle/multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Adsorbents. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 28323–28339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.P. Mistakes and Inconsistencies Regarding Adsorption of Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions: A Critical Review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William Kajjumba, G.; Emik, S.; Öngen, A.; Kurtulus Özcan, H.; Aydın, S. Modelling of Adsorption Kinetic Processes—Errors, Theory and Application. In Advanced Sorption Process Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Debrassi, A.; Baccarin, T.; Demarchi, C.A.; Nedelko, N.; Ślawska-Waniewska, A.; Dluzewski, P.; Bilska, M.; Rodrigues, C.A. Adsorption of Remazol Red 198 onto Magnetic N-Lauryl Chitosan Particles: Equilibrium, Kinetics, Reuse and Factorial Design. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1594–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolli, E.; Kaciulis, S.; Mezzi, A. ESCA as a Tool for Exploration of Metals’ Surface. Coatings 2020, 10, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomide, G.; Cabreira Gomes, R.; Gomes Viana, M.; Cortez Campos, A.F.; Aquino, R.; López-Ortega, A.; Perzynski, R.; Depeyrot, J. Nanoparticle Size Distribution and Surface Effects on the Thermal Dependence of Magnetic Anisotropy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Olmos, A.R.; Abatal, M.; Sato-Berru, R.Y.; Pedraza-Basulto, G.K.; Garcia-Vazquez, V.; Sainz-Vidal, A.; Perez-Bañuelos, R.; Quiroz, A. Mechanosynthesis of MFe2O4 (M = Co, Ni, and Zn) Magnetic Nanoparticles for Pb Removal from Aqueous Solution. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 9182024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durmus, Z.; Kavas, H.; Toprak, M.S.; Baykal, A.; Altinçekiç, T.G.; Aslan, A.; Bozkurt, A.; Coşgun, S. L-Lysine Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Structural and Conductivity Characterization. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 484, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.F.C.; de Medeiros, W.C.; Aquino, R.; Depeyrot, J. Surface Charge Density Determination in Water Based Magnetic Colloids. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campos, A.F.C.; Aquino, R.; Tourinho, F.A.; Paula, F.L.O.; Depeyrot, J. Influence of the Spatial Confinement at Nanoscale on the Structural Surface Charging in Magnetic Nanocolloids. Eur. Phys. J. E 2013, 36, e13042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, Y.S. Review of Second-Order Models for Adsorption Systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohan, D.; Rajput, S.; Singh, V.K.; Steele, P.H.; Pittman, C.U. Modeling and Evaluation of Chromium Remediation from Water Using Low Cost Bio-Char, a Green Adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, A.K.; Mandal, S.N.; Das, S.K. Adsorption of Zn(II) from Aqueous Solution by Using Different Adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 123, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestre, A.S.; Pires, R.A.; Aroso, I.; Fernandes, E.M.; Pinto, M.L.; Reis, R.L.; Andrade, M.A.; Pires, J.; Silva, S.P.; Carvalho, A.P. Activated Carbons Prepared from Industrial Pre-Treated Cork: Sustainable Adsorbents for Pharmaceutical Compounds Removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 253, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.W.; Choi, B.H.; Song, K.G.; Choi, J.W. Statistical Optimization of Preparing Marine Macroalgae Derived Activated Carbon/iron Oxide Magnetic Composites for Sequestering Acetylsalicylic Acid from Aqueous Media Using Response Surface Methodologys. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakić, V.; Rac, V.; Krmar, M.; Otman, O.; Auroux, A. The Adsorption of Pharmaceutically Active Compounds from Aqueous Solutions onto Activated Carbons. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 282, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessa, E.F.; Nunes, M.L.; Fajardo, A.R. Chitosan/waste Coffee-Grounds Composite: An Efficient and Eco-Friendly Adsorbent for Removal of Pharmaceutical Contaminants from Water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Sample | dXR (nm) | <a> (nm) | d0 (nm) | s | SBET (m2/g) | MS (emu/g) | HC (Oe) | χ0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PACo | 13.9 ± 1.4 | 0.836 | 11.1 | 0.18 | 88 | 63.4 | 150 ± 10 | 2.0 |
| PACoM | 7.9 ± 0.8 | 0.834 | 5.1 | 0.25 | 130 | 54.8 | 25 ± 10 | 2.3 |
| PACo–Lys | 13.5 ± 1.4 | 0.832 | 10.4 | 0.43 | 103 | 60.5 | 155 ± 10 | 1.6 |
| PACoM–Lys | 8.5 ± 0.9 | 0.833 | 6.1 | 0.28 | 154 | 31.7 | 10 ± 10 | 1.8 |
| Sample | Co2p3/2 | Fe2p3/2 | O1s | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxides | Water | ||||
| PACo | BE (eV) | 781.2 | 711.5 | 530.8 | 533.2 |
| at.% | 1.2 | 34.9 | 53.3 | 10.5 | |
| PACoM | BE | 781.2 | 711.5 | 530.8 | 533.1 |
| at.% | 2.1 | 30.6 | 52.2 | 15.1 | |
| Sample | teq (min) | k2 (g mg−1 min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | h (min mg g−1) | t1/2 (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PACo–Lys | 150 | 8.6 × 10−3 | 5.4 | 0.981 | 0.25 | 21.8 |
| PACoM–Lys | 300 | 1.1 × 10−2 | 1.8 | 0.997 | 0.05 | 48.1 |
| Model | PACo–Lys | PACoM–Lys | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qmax (mg/g) | 16.4 | 8.5 |
| KL (L/mg) | 0.05 | 0.03 | |
| R2 | 0.984 | 0.992 | |
| MAPE (%) | 3.52 | 1.18 | |
| Freundlich | KF (mg1−1/n g/L1/n) | 1.6 | 0.5 |
| 1/n | 1.9 | 1.7 | |
| R2 | 0.997 | 0.999 | |
| MAPE (%) | 1.24 | 0.37 |
| Adsorbent | qmax (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial pretreated cork | 174.4 | [40] |
| Macroalgae-derived activated carbon/iron oxide magnetic composites | 140.3 | [41] |
| Activated carbon | 45.0 | [42] |
| PACo–Lys | 16.4 | This study |
| Chitosan/waste coffee-grounds composite | 10.4 | [43] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maciel, A.P.; Gomide, G.; da Silva, F.G.; Guerra, A.A.A.M.; Depeyrot, J.; Mezzi, A.; Campos, A.F.C. L-Lysine-Coated Magnetic Core–Shell Nanoparticles for the Removal of Acetylsalicylic Acid from Aqueous Solutions. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030514
Maciel AP, Gomide G, da Silva FG, Guerra AAAM, Depeyrot J, Mezzi A, Campos AFC. L-Lysine-Coated Magnetic Core–Shell Nanoparticles for the Removal of Acetylsalicylic Acid from Aqueous Solutions. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(3):514. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030514
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaciel, Ayessa P., Guilherme Gomide, Franciscarlos G. da Silva, Ana Alice A. M. Guerra, Jerome Depeyrot, Alessio Mezzi, and Alex F. C. Campos. 2023. "L-Lysine-Coated Magnetic Core–Shell Nanoparticles for the Removal of Acetylsalicylic Acid from Aqueous Solutions" Nanomaterials 13, no. 3: 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030514
APA StyleMaciel, A. P., Gomide, G., da Silva, F. G., Guerra, A. A. A. M., Depeyrot, J., Mezzi, A., & Campos, A. F. C. (2023). L-Lysine-Coated Magnetic Core–Shell Nanoparticles for the Removal of Acetylsalicylic Acid from Aqueous Solutions. Nanomaterials, 13(3), 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030514