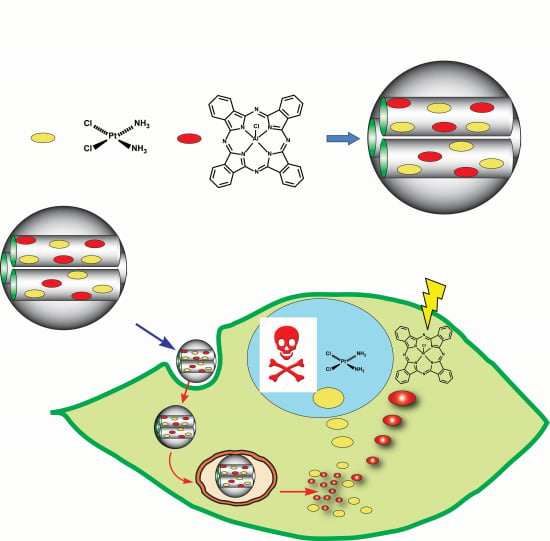
Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Cisplatin and Phthalocyanine for Combination Chemotherapy and Photodynamic Therapy in vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Structural Properties of MSNs, AlClPc–MSNs, Cisplatin-MSNs, and AlClPc/Cisplatin–MSNs


| Sample | Diameter (nm) * | PDI * | ζ-potential (mV) * | Diameter (nm) ** | PDI ** |
| MSNs | 96.5 ± 10.5 | 0.19 | −41.9 ± 2.0 | 175.5 ± 13.2 | 0.23 |
| AlClPc-MSNs | 107.8 ± 15.0 | 0.33 | −45.2 ± 3.2 | 191.3 ± 8.6 | 0.33 |
| Cisplatin-MSNs | 99.1 ± 13.9 | 0.29 | −32.1 ± 1.1 | 183.4 ± 7.1 | 0.21 |
| AlClPc/cisplatin-MSNs | 112.7 ± 19.5 | 0.39 | −23.1 ± 2.4 | 198.8 ± 12.3 | 0.32 |
| Sample | SA (m2/g) | Pore Size (nm) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | OC (%) | |
| MSNs | 819.7 | 5.3 | 1.57 | ---- | |
| AlClPc-MSNs | 712.9 | 5.0 | 1.37 | 7.4 | |
| Cisplatin-MSNs | 446.2 | 3.8 | 0.81 | 2.1 | |
| AlClPc/cisplatin-MSNs | 356.5 | 3.0 | 0.79 | 9.4 |
2.2. Photophysical Properties of AlClPc–MSNs, Cisplatin-MSNs, and AlClPc/Cisplatin–MSNs


2.3. In Vitro Internalization, Cyto- and Phototoxicity of AlClPc–MSNs, Cisplatin-MSNs, and AlClPc/Cisplatin–MSNs


3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Methods
3.2. Synthesis of MSN Materials
3.3. Characterization of the Photophysical Properties of MSN Materials
3.4. In Vitro Internalization of MSN Materials
3.5. Cyto- and Photo-Toxicity of MSN Materials
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Juarranz, A.; Jaen, P.; Sanz-Rodriguez, F.; Cuevas, J.; Gonzalez, S. Photodynamic therapy of cancer. Basic principles and applications. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2008, 10, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharman, W.M.; Allen, C.M.; van Lier, J.E. Photodynamic therapeutics: Basic principles and clinical applications. Drug Discov. Today 1999, 4, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, S.; Hirohara, S.; Obata, M.; Hagiya, Y.; Ogura, S.-I.; Ikeda, A.; Kataoka, H.; Tanaka, M.; Joh, T. Current states and future views in photodynamic therapy. J Photoch. Photobio. C 2011, 12, 46–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C.A.; Evans, D.H.; Abrahamse, H. Photodynamic therapy (PDT): A short review on cellular mechanisms and cancer research applications for PDT. J. Photoch. Photobiolo. B 2009, 96, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detty, M.R.; Gibson, S.L.; Wagner, S.J. Current clinical and preclinical photosensitizers for use in photodynamic therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 3897–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josefsen, L.B.; Boyle, R.W. Unique diagnostic and therapeutic roles of porphyrins and phthalocyanines in photodynamic therapy, imaging and theranostics. Theranostics 2012, 2, 916–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, A.E.; Gallagher, W.M.; Byrne, A.T. Porphyrin and nonporphyrin photosensitizers in oncology: Preclinical and clinical advances in photodynamic therapy. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 1053–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyokong, T. Desired properties of new phthalocyanines for photodynamic therapy. Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 1763–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, J.P.; Spring, B.Q.; Rizvi, I.; Evans, C.L.; Samkoe, K.S.; Verma, S.; Pogue, B.W.; Hasan, T. Imaging and photodynamic therapy: Mechanisms, monitoring, and optimization. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2795–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ethirajan, M.; Chen, Y.; Joshi, P.; Pandey, R.K. The role of porphyrin chemistry in tumor imaging and photodynamic therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 340–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechet, D.; Couleaud, P.; Frochot, C.; Viriot, M.-L.; Guillemin, F.; Barberi-Heyob, M. Nanoparticles as vehicles for delivery of photodynamic therapy agents. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, D.K.; Fong, L.S.; Zhang, Y. Nanoparticles in photodynamic therapy: An emerging paradigm. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2008, 60, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-Y.; Sharma, S.K.; Dai, T.; Chung, H.; Yaroslavsky, A.; Garcia-Diaz, M.; Chang, J.; Chiang, L.Y.; Hamblin, M.R. Can nanotechnology potentiate photodynamic therapy? Nanotechnol. Rev. 2012, 1, 111–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivero-Escoto, J.L. Multifunctional Nanoparticles in Photodynamic Therapy: Recent Developments. In Photodynamic Therapy: Fundamentals, Applications and Health Outcomes; Hugo, A.G., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Master, A.; Livingston, M.; Gupta, A.S. Photodynamic nanomedicine in the treatment of solid tumors: Perspectives and challenges. J. Control. Release 2013, 168, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadasivam, M.; Avci, P.; Gupta, G.K.; Lakshmanan, S.; Chandran, R.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Kumar, R.; Hamblin, M.R. Self-assembled liposomal nanoparticles in photodynamic therapy. Eur. J. Nanomed. 2013, 5, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuruppuarachchi, M.; Savoie, H.; Lowry, A.; Alonso, C.; Boyle, R.W. Polyacrylamide nanoparticles as a delivery system in photodynamic therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouikrat, R.; Seve, A.; Vanderesse, R.; Benachour, H.; Barberi-Heyob, M.; Richeter, S.; Raehm, L.; Durand, J.O.; Verelst, M.; Frochot, C. Non polymeric nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy applications: Recent developments. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couleaud, P.; Morosini, V.; Frochot, C.; Richeter, S.; Raehm, L.; Durand, J.-O. Silica-based nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy applications. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Vega, D.L. Stimuli-responsive protoporphyrin IX silica-based nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy in vitro. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 14400–14407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; DeCillis, D.; Fritts, L.; Vega, D.L. Porphyrin-based polysilsesquioxane nanoparticles to improve photodynamic therapy for cancer treatment. Proc. SPIE 2014, 8931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagnin, C.; Bau, L.; Mognato, M.; Celotti, L.; Miotto, G.; Arduini, M.; Moret, F.; Fede, C.; Selvestrel, F.; Echevarria, I.M.R.; et al. The cellular uptake of meta-tetra (hydroxyphenyl)chlorin entrapped in organically modified silica nanoparticles is mediated by serum proteins. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 345101–345112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohulchanskyy, T.Y.; Roy, I.; Goswami, L.N.; Chen, Y.; Bergey, E.J.; Pandey, R.K.; Oseroff, A.R.; Prasad, P.N. Organically modified silica nanoparticles with covalently incorporated photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy of cancer. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2835–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Slowing, I.I.; Trewyn, B.G.; Lin, V.S.Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular controlled drug delivery. Small 2010, 6, 1952–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Yang, C.-S.; Tseng, F.-G.; Mou, C.-Y.; Lo, L.-W. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with an oxygen-sensing probe for cell photodynamic therapy: Potential cancer theranostics. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 1252–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackowiak, S.A.; Schmidt, A.; Weiss, V.; Argyo, C.; von Schirnding, C.; Bein, T.; Braeuchle, C. Targeted drug delivery in cancer cells with red-light photoactivated mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2576–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, X.; Sun, Y.; Feng, W.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, F. Hollow silica nanoparticles loaded with hydrophobic phthalocyanine for near-infrared photodynamic and photothermal combination therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7905–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Gharibi, A.; He, S. Colloidal mesoporous silica nanoparticles with protoporphyrin IX encapsulated for photodynamic therapy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 014012–014016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, I.T.; Chang, Y.-J.; Wang, L.-S.; Lu, H.-Y.; Wu, L.-C.; Yang, C.-M.; Chiu, C.-C.; Yang, C.-H.; Hsu, S.-L.; Ho, J.-A.A. Phospholipid-functionalized mesoporous silica nanocarriers for selective photodynamic therapy of cancer. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7462–7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, H.-L.; Lin, Y.-S.; Lin, H.-Y.; Hung, Y.; Lo, L.-W.; Chen, Y.-F.; Mou, C.-Y. In vitro studies of functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Wang, T.; Shi, W.; Wu, G.; Tian, X.; Wang, Y.; Ge, D.; Ren, L. Multifunctional ZnPc-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles for enhancement of photodynamic therapy efficacy by endolysosomal escape. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7903–7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Chen, L.; Chen, X. Dual pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient combination of chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 4707–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, M.; Song, H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C. Preparation of fluorescent mesoporous hollow silica-fullerene nanoparticles via selective etching for combined chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11894–11898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gary-Bobo, M.; Hocine, O.; Brevet, D.; Maynadier, M.; Raehm, L.; Richeter, S.; Charasson, V.; Loock, B.; Morere, A.; Maillard, P.; et al. Cancer therapy improvement with mesoporous silica nanoparticles combining targeting, drug delivery and PDT. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 423, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postiglione, I.; Chiaviello, A.; Palumbo, G. Enhancing photodynamyc therapy efficacy by combination therapy: Dated, current and oncoming strategies. Cancers 2011, 3, 2597–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khdair, A.; Di, C.; Patil, Y.; Ma, L.; Dou, Q.P.; Shekhar, M.P.V.; Panyam, J. Nanoparticle-mediated combination chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy overcomes tumor drug resistance. J. Control. Release 2010, 141, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Gong, H.; Qian, X.; Tan, P.; Li, Z.; Liu, T.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. Mesoporous silica nanorods intrinsically doped with photosensitizers as a multifunctional drug carrier for combination therapy of cancer. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Shen, B.; Bu, W.; Chen, F.; He, Q.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, L.; Peng, W.; Xiao, Q.; et al. A smart upconversion-based mesoporous silica nanotheranostic system for synergetic chemo-/radio-/photodynamic therapy and simultaneous MR/UCL imaging. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8992–9002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Su, Z.; Wang, C.; Liao, Y.; Fu, Q. Multifunctional hollow mesoporous silica nanocages for cancer cell detection and the combined chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2479–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Hall, M.D.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, P.C.; Gottesman, M.M.; Liang, X.-J. Nanoscale drug delivery platforms overcome platinum-based resistance in cancer cells due to abnormal membrane protein trafficking. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 10452–10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartalou, M.; Essigmann, J.M. Mechanisms of resistance to cisplatin. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2001, 478, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Taylor-Pashow, K.M.; Huxford, R.C.; Della Rocca, J.; Okoruwa, C.; An, H.; Lin, W.; Lin, W. Multifunctional Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres with Cleavable Gd(III) Chelates as MRI Contrast Agents: Synthesis, Characterization, Target-Specificity, and Renal Clearance. Small 2011, 7, 3519–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Yang, S.; Li, Z.; Xia, T.; Chen, J.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, S.; Huang, C.; et al. Aspect ratio determines the quantity of mesoporous silica nanoparticle uptake by a small gtpase-dependent macropinocytosis mechanism. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4434–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.; Fernandes, E.; Lima, J.L.F.C. Fluorescence probes used for detection of reactive oxygen species. J. Biochem. Bioph. Meth. 2005, 65, 45–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratton, S.E.A.; Ropp, P.A.; Pohlhaus, P.D.; Luft, J.C.; Madden, V.J.; Napier, M.E.; De Simone, J.M. The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11613–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.-C.; Biswas, R.; Mondal, A.; Lee, Y.-K.; Chung, P.-S. Cisplatin enhances the efficacy of 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated photodynamic therapy in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2014, 33, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Elnagheeb, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Cisplatin and Phthalocyanine for Combination Chemotherapy and Photodynamic Therapy in vitro. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 2302-2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5042302
Vivero-Escoto JL, Elnagheeb M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Cisplatin and Phthalocyanine for Combination Chemotherapy and Photodynamic Therapy in vitro. Nanomaterials. 2015; 5(4):2302-2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5042302
Chicago/Turabian StyleVivero-Escoto, Juan L., and Maram Elnagheeb. 2015. "Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Cisplatin and Phthalocyanine for Combination Chemotherapy and Photodynamic Therapy in vitro" Nanomaterials 5, no. 4: 2302-2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5042302
APA StyleVivero-Escoto, J. L., & Elnagheeb, M. (2015). Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Cisplatin and Phthalocyanine for Combination Chemotherapy and Photodynamic Therapy in vitro. Nanomaterials, 5(4), 2302-2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5042302