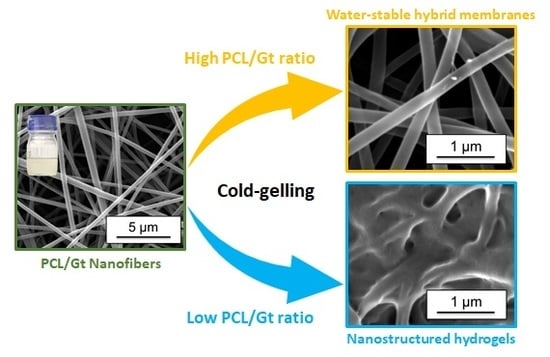
Nanostructured Hydrogels by Blend Electrospinning of Polycaprolactone/Gelatin Nanofibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrospinning
2.3. Water Treatment of PCL/Gt Blends
2.4. Materials Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrospinning of PCL/Gt Blend Nnanofibers Using AA/FA
3.2. Stabilizing the Electrospinning Emulsions by Tuning the Solvent System
3.3. Interactions between the PCL and Gt Components by Thermal Analysis
3.4. Cold-Water Solubility of the Gelatin Component
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, E.-H.; Sardinha, J.P.; Myers, S. Nanotechnology Biomimetic Cartilage Regenerative Scaffolds. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2014, 41, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, D.; Jin, G.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun synthetic and natural nanofibers for regenerative medicine and stem cells. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 8, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.W.; Achuth, H.N.; Moochhala, S.; Lim, T.C.; Hutmacher, D.W. In vivo evaluation of an ultra-thin polycaprolactone film as a wound dressing. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2007, 18, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bölgen, N.; Menceloğlu, Y.Z.; Acatay, K.; Vargel, I.; Pişkin, E. In vitro and in vivo degradation of non-woven materials made of poly(epsilon-caprolactone) nanofibers prepared by electrospinning under different conditions. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2005, 16, 1537–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van der Schueren, L.; De Schoenmaker, B.; Kalaoglu, Ö.I.; De Clerck, K. An alternative solvent system for the steady state electrospinning of polycaprolactone. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrero-Herrero, M.; Gómez-Tejedor, J.A.; Vallés-Lluch, A. PLA/PCL electrospun membranes of tailored fibres diameter as drug delivery systems. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 99, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves da Silva, M.L.; Martins, A.; Costa-Pinto, A.R.; Costa, P.; Faria, S.; Gomes, M.; Reis, R.L.; Neves, N.M. Cartilage tissue engineering using electrospun PCL Nanofiber Meshes and MSCs. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 3228–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, K.; Wang, Y.; Sun, T.; Yue, W.; Zhang, H. Electrospun PCL/gelatin composite nanofiber structures for effective guided bone regeneration membranes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopal, J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Ramakrishna, S. Fabrication of modified and functionalized polycaprolactone nanofibre scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2138–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafiej, P.; Küng, F.; Thieme, D.; Czugala, M.; Kruse, F.E.; Schubert, D.W.; Fuchsluger, T.A. Adhesion and metabolic activity of human corneal cells on PCL based nanofiber matrices. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, N.; Li, Z.; Gunn, J.; Leung, M.; Cooper, A.; Edmondson, D.; Veiseh, O.; Chen, M.H.; Zhang, Y.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; et al. Natural-synthetic polyblend nanofibers for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2792–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beachley, V.; Wen, X. Polymer nanofibrous structures: Fabrication, biofunctionalization, and cell interactions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 868–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cipitria, A.; Skelton, A.; Dargaville, T.R.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Design, fabrication and characterization of PCL electrospun scaffolds—A review. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 9419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunn, J.; Zhang, M. Polyblend nanofibers for biomedical applications: Perspectives and challenges. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffman, J.D.; Schauer, C.L. A review: Electrospinning of biopolymer nanofibers and their applications. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 317–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, A.D.; Ferguson, M.W.J. Tissue engineering of replacement skin: The crossroads of biomaterials, wound healing, embryonic development, stem cells and regeneration. J. R. Soc. Interface 2007, 4, 413–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Venugopal, J.; Huang, Z.M.; Lim, C.T.; Ramakrishna, S. Crosslinking of the electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Polymer 2006, 47, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-C.; Chang, W.-H.; Dong, G.-C.; Chen, K.-Y.; Chen, Y.-S.; Yao, C.-H. Cell adhesion and proliferation enhancement by gelatin nanofiber scaffolds. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2011, 26, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzavolta, S.; Gioffrè, M.; Focarete, M.L.; Gualandi, C.; Foroni, L.; Bigi, A. Electrospun gelatin nanofibers: Optimization of genipin cross-linking to preserve fiber morphology after exposure to water. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyaert, I.; Rahier, H.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Olijve, J.; De Clerck, K. Gelatin nanofibers: Analysis of triple helix dissociation temperature and cold-water-solubility. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 57, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Chwee, T.L.; Ramakrishna, S.; Huang, Z.M. Electrospinning of gelatin fibers and gelatin/PCL composite fibrous scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2005, 72, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, B.; Tu, H.; Yuan, H.; Peng, H.; Zhang, Y. Acetic-acid-mediated miscibility toward electrospinning homogeneous composite nanofibers of GT/PCL. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 3917–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakaran, M.P.; Venugopal, J.R.; Chyan, T.T.; Hai, L.B.; Chan, C.K.; Lim, A.Y.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun biocomposite nanofibrous scaffolds for neural tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. A 2008, 14, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daelemans, L.; van der Heijden, S.; De Baere, I.; Rahier, H.; Van Paepegem, W.; De Clerck, K. Nanofibre bridging as a toughening mechanism in carbon/epoxy composite laminates interleaved with electrospun polyamide nanofibrous veils. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daelemans, L.; van der Heijden, S.; De Baere, I.; Rahier, H.; Van Paepegem, W.; De Clerck, K. Using aligned nanofibres for identifying the toughening micromechanisms in nanofibre interleaved laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 124, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Z.; Teng, W.; Markle, V.; Dai, Z.; Wu, X. Fabrication of gelatin nanofibrous scaffolds using ethanol/phosphate buffer saline as a benign solvent. Biopolymers 2012, 97, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, L.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Morshed, M.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone)/gelatin nanofibrous scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4532–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathot, V.B.F. Calorimetry and Thermal Analysis of Polymers; Carl Hanser Verlag: München, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Senda, T.; He, Y.; Inoue, Y. Biodegradable blends of poly(epsilon-caprolactone) with alpha-chitin and chitosan: Specific interactions, thermal properties and crystallization behavior. Polym. Int. 2002, 51, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, F.; Alves, M.; Azevedo, J.V. Development of new poly(ε-caprolactone )/chitosan films. Polym. Int. 2013, 62, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasam, A.; Madihally, S.V. Characterization of chitosan-polycaprolactone blends for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5500–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.J.; Lovell, P.A. Introduction to Polymers, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, I.H.L.; Ayres, E.; Averous, L.; Schlatter, G.; Hebraud, A.; De Paula, A.C.C.; Viana, P.H.L.; Goes, A.M.; Oréfice, R.L. Differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells seeded on mineralized electrospun co-axial poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL)/gelatin nanofibers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonsomboon, K.; Oyen, M.L. Composite electrospun gelatin fiber-alginate gel scaffolds for mechanically robust tissue engineered cornea. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 21, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, M.; Gupta, A.; Dinda, A.K.; Koul, V. An investigation study of gelatin release from semi-interpenetrating polymeric network hydrogel patch for excision wound healing on Wistar rat model. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, H.; Lei, L.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y. Incorporating protein gradient into electrospun nanofibers as scaffolds for tissue engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Nanofibrous Membranes | ∆Hm (Joules per Gram Fiber) | ∆Hm (Joules per Gram PCL) |
|---|---|---|
| PCL | 71 | 71 |
| 85/15 PCL/Gt | 61 | 72 |
| 50/50 PCL/Gt | 29 | 68 |
| 15/85 PCL/Gt | 12 | 80 |
| Nanofibrous Membranes | APCL/AGt before Water Treatment | APCL/AGt after Water Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| 85/15 PCL/Gt | 4.9 | 5 |
| 70/30 PCL/Gt | 2.3 | 4.7 |
| 50/50 PCL/Gt | 0.9 | 3.1 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daelemans, L.; Steyaert, I.; Schoolaert, E.; Goudenhooft, C.; Rahier, H.; De Clerck, K. Nanostructured Hydrogels by Blend Electrospinning of Polycaprolactone/Gelatin Nanofibers. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8070551
Daelemans L, Steyaert I, Schoolaert E, Goudenhooft C, Rahier H, De Clerck K. Nanostructured Hydrogels by Blend Electrospinning of Polycaprolactone/Gelatin Nanofibers. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(7):551. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8070551
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaelemans, Lode, Iline Steyaert, Ella Schoolaert, Camille Goudenhooft, Hubert Rahier, and Karen De Clerck. 2018. "Nanostructured Hydrogels by Blend Electrospinning of Polycaprolactone/Gelatin Nanofibers" Nanomaterials 8, no. 7: 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8070551
APA StyleDaelemans, L., Steyaert, I., Schoolaert, E., Goudenhooft, C., Rahier, H., & De Clerck, K. (2018). Nanostructured Hydrogels by Blend Electrospinning of Polycaprolactone/Gelatin Nanofibers. Nanomaterials, 8(7), 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8070551