Gas Crosstalk between PFPE–PEG–PFPE Triblock Copolymer Surfactant-Based Microdroplets and Monitoring Bacterial Gas Metabolism with Droplet-Based Microfluidics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Process of Synthesis of PFPE–PEG–PFPE Surfactant
2.3. Fabrication of Microfluidic Chip
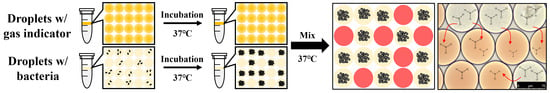
2.4. Cell Culture and Droplet Generation
2.5. Detection of E. coli K-12 with Phenol Red, pH Indicator
2.6. Identification of Crosstalk between Droplets
2.7. Identification of Ammonia Gas Production in Bacterial Cells
2.8. Validation of Ammonia Gas Crosstalk between Droplets
2.9. Effect of Ammonia Gas Concentration on Gas Permeability
2.10. Effect of Surfactant Concentration on Gas Permeability
2.11. Time-Course Measurement of Ammonia Gas Crosstalk through Droplet Barrier
3. Results
3.1. Leaking of the Droplets during Determination of Bacteria with pH Indicator
3.2. Identification of Crosstalk between Droplets
3.3. Validation of Ammonia Gas Crosstalk between Droplets
3.4. Effects of Ammonia Gas Concentration and Surfactant Concentration on Crosstalk between Droplets
3.5. Time-Course Measurement of Ammonia Gas Crosstalk through Droplet Barrier
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mashaghi, S.; Abbaspourrad, A.; Weitz, D.A.; van Oijen, A.M. Droplet microfluidics: A tool for biology, chemistry and nanotechnology. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seemann, R.; Brinkmann, M.; Pfohl, T.; Herminghaus, S. Droplet based microfluidics. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2011, 75, 016601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teh, S.-Y.; Lin, R.; Hung, L.-H.; Lee, A.P. Droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 198–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joensson, H.N.; Andersson Svahn, H. Droplet microfluidics—A tool for single-cell analysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12176–12192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, T.S.; Scheler, O.; Garstecki, P. Droplet microfluidics for microbiology: Techniques, applications and challenges. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 2168–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solvas, X.C.; DeMello, A. Droplet microfluidics: Recent developments and future applications. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1936–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakszewska, A.; Tel, J.; Chokkalingam, V.; Huck, W.T. One drop at a time: Toward droplet microfluidics as a versatile tool for single-cell analysis. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, M.T.; Rotem, A.; Heyman, J.A.; Weitz, D.A. Droplet microfluidics for high-throughput biological assays. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2146–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekin, D.; Skhiri, Y.; Baret, J.-C.; Le Corre, D.; Mazutis, L.; Salem, C.B.; Millot, F.; El Harrak, A.; Hutchison, J.B.; Larson, J.W. Quantitative and sensitive detection of rare mutations using droplet-based microfluidics. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2156–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fang, Q. Analytical detection techniques for droplet microfluidics—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 787, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouzes, E.; Medkova, M.; Savenelli, N.; Marran, D.; Twardowski, M.; Hutchison, J.B.; Rothberg, J.M.; Link, D.R.; Perrimon, N.; Samuels, M.L. Droplet microfluidic technology for single-cell high-throughput screening. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14195–14200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shembekar, N.; Chaipan, C.; Utharala, R.; Merten, C.A. Droplet-based microfluidics in drug discovery, transcriptomics and high-throughput molecular genetics. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1314–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terekhov, S.S.; Smirnov, I.V.; Stepanova, A.V.; Bobik, T.V.; Mokrushina, Y.A.; Ponomarenko, N.A.; Belogurov, A.A.; Rubtsova, M.P.; Kartseva, O.V.; Gomzikova, M.O. Microfluidic droplet platform for ultrahigh-throughput single-cell screening of biodiversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2550–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sabhachandani, P.; Sarkar, S.; Zucchi, P.C.; Whitfield, B.A.; Kirby, J.E.; Hirsch, E.B.; Konry, T. Integrated microfluidic platform for rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing and bacterial growth analysis using bead-based biosensor via fluorescence imaging. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 4619–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.-K.; Ali, M.M.; Zhang, K.; Huang, S.S.; Peterson, E.; Digman, M.A.; Gratton, E.; Zhao, W. Rapid detection of single bacteria in unprocessed blood using Integrated Comprehensive Droplet Digital Detection. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baret, J.-C. Surfactants in droplet-based microfluidics. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.-K.; Ali, M.M.; Zhang, K.; Pone, E.J.; Zhao, W. Droplet microfluidics for single-molecule and single-cell analysis in cancer research, diagnosis and therapy. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 58, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtze, C.; Rowat, A.; Agresti, J.; Hutchison, J.; Angile, F.; Schmitz, C.; Köster, S.; Duan, H.; Humphry, K.; Scanga, R. Biocompatible surfactants for water-in-fluorocarbon emulsions. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-L.; Chan, H.F.; Phua, K.K.; Zhang, Y.; Juul, S.; Knudsen, B.R.; Ho, Y.-P.; Leong, K.W. Synthesis of fluorosurfactants for emulsion-based biological applications. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3913–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, D.J.; Payne, R.J.; Abell, C. Synthesis of novel fluorous surfactants for microdroplet stabilisation in fluorous oil streams. J. Fluor. Chem. 2010, 131, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzman, I.; Janiesch, J.-W.; Spatz, J.P. Synthesis of nanostructured and biofunctionalized water-in-oil droplets as tools for homing T cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 3339–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruner, P.; Riechers, B.; Orellana, L.A.C.; Brosseau, Q.; Maes, F.; Beneyton, T.; Pekin, D.; Baret, J.-C. Stabilisers for water-in-fluorinated-oil dispersions: Key properties for microfluidic applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 20, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, O.; Thiele, J.; Weinhart, M.; Mazutis, L.; Weitz, D.A.; Huck, W.T.; Haag, R. Biocompatible fluorinated polyglycerols for droplet microfluidics as an alternative to PEG-based copolymer surfactants. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vince, A.J.; Burridge, S.M. Ammonia production by intestinal bacteria: The effects of lactose, lactulose and glucose. J. Med. Microbiol. 1980, 13, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hills, G.M. Ammonia production by pathogenic bacteria. Biochem. J. 1940, 34, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cummings, J.H.; Macfarlane, G.T. Role of intestinal bacteria in nutrient metabolism. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 16, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezonov, G.; Joseleau-Petit, D.; d’Ari, R. Escherichia coli physiology in Luria-Bertani broth. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 8746–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.; Collins, J.W.; Aubrecht, D.M.; Sperling, R.A.; Solomon, L.; Ha, J.-W.; Yi, G.-R.; Weitz, D.A.; Manoharan, V.N. Synchronized reinjection and coalescence of droplets in microfluidics. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scanga, R.; Chrastecka, L.; Mohammad, R.; Meadows, A.; Quan, P.-L.; Brouzes, E. Click chemistry approaches to expand the repertoire of PEG-based fluorinated surfactants for droplet microfluidics. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 12960–12974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khademhosseini, A.; Suh, K.Y.; Jon, S.; Eng, G.; Yeh, J.; Chen, G.-J.; Langer, R. A soft lithographic approach to fabricate patterned microfluidic channels. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 3675–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Kwon, K.W.; Park, M.C.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.M.; Suh, K.Y. Soft lithography for microfluidics: A review. Biochip J. 2008, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, J.C.; Duffy, D.C.; Anderson, J.R.; Chiu, D.T.; Wu, H.; Schueller, O.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Fabrication of microfluidic systems in poly (dimethylsiloxane). Electrophor. Int. J. 2000, 21, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Zhou, J.; Wu, H. Materials for microfluidic chip fabrication. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2396–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, K.; Fujii, T.; Endo, I. Handling of picoliter liquid samples in a poly (dimethylsiloxane)-based microfluidic device. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 4781–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.-C.; Cristini, V.; Lee, A.P. Monodispersed microfluidic droplet generation by shear focusing microfluidic device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 114, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfbeis, O.S.; Posch, H.E. Fibre-optic fluorescing sensor for ammonia. Anal. Chim. Acta 1986, 185, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ki, S.; Kang, D.-K. Gas Crosstalk between PFPE–PEG–PFPE Triblock Copolymer Surfactant-Based Microdroplets and Monitoring Bacterial Gas Metabolism with Droplet-Based Microfluidics. Biosensors 2020, 10, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10110172
Ki S, Kang D-K. Gas Crosstalk between PFPE–PEG–PFPE Triblock Copolymer Surfactant-Based Microdroplets and Monitoring Bacterial Gas Metabolism with Droplet-Based Microfluidics. Biosensors. 2020; 10(11):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10110172
Chicago/Turabian StyleKi, Sunghyun, and Dong-Ku Kang. 2020. "Gas Crosstalk between PFPE–PEG–PFPE Triblock Copolymer Surfactant-Based Microdroplets and Monitoring Bacterial Gas Metabolism with Droplet-Based Microfluidics" Biosensors 10, no. 11: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10110172
APA StyleKi, S., & Kang, D. -K. (2020). Gas Crosstalk between PFPE–PEG–PFPE Triblock Copolymer Surfactant-Based Microdroplets and Monitoring Bacterial Gas Metabolism with Droplet-Based Microfluidics. Biosensors, 10(11), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10110172