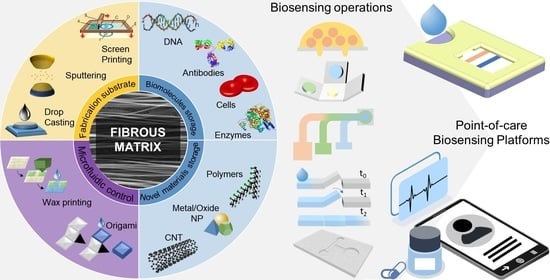
Paper and Other Fibrous Materials—A Complete Platform for Biosensing Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Paper and Fibrous Materials as a Complete Platform for Biosensors
2.1. Physical and Chemical Properties
2.2. Functions of Fibrous Materials in PADs and EFBs
2.3. Mechanisms and Modeling
3. Paper-Based Analytical Devices and Electrospun Fiber-Based Biosensors
3.1. Electrochemical Transduction
3.2. Optical Transduction
4. Biosensor Fabrication
4.1. Materials Selection
4.1.1. Filter Paper
4.1.2. Electrospun Mats
4.1.3. Novel Materials
4.2. Paper Functionalization Techniques
4.2.1. Drop Casting
4.2.2. Screen Printing
4.2.3. Dip Coating
4.2.4. Inkjet Printing
4.2.5. Wax Deposition
4.3. Bio Immobilization Approaches
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 17α-EE | 17α-ethinylestradiol | LFA | Lateral flow assay |
| 2,4-D | 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid | Lip | Lipase |
| 4-ATP | 4-aminothiophenol | LOD | Limit of detection |
| Ab | Antibody | MEF | Metal enhanced Fluorescence |
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase | MeBut | Methyl butyrate |
| AFP | Alpha-fetoprotein | MPA | Mercaptopropionic acid |
| Ag NRs | Silver nanorods | MSA | Mercaptosuccinic acid |
| Ag | Silver | Mt | Montmorillonite |
| AgNO3 | Silver nitrate | MWCT | Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes |
| Al | Aluminum | NBR | Nitrile butadiene rubber |
| AMP | Amperometry | NC | Nitrocellulose |
| Au | Gold | NHL | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| AuNPs | Gold nanoparticles | NHS | N-hydroxysuccinimide |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin | NiCoO4 | Nickel cobaltite |
| C | Carbon | NiCoS4 | Nickel cobalt sulfide |
| CA | Chronoamperometry | NPs | Nanoparticles |
| CAc | Cellulose acetate | ON | Oligonucleotides |
| CB | Carbon black | OP | Optical |
| CD | Clinical diagnostics | PA6 | Polyamide 6 |
| CEA | Carcinoembryonic antigen | PAA | Poly (acrylic acid) |
| Chi | Chitosan | PAMAM | Poly(amidoamine) |
| CHIKV | Chikungunya virus | PAN | Polyacrylonitrile |
| CL | Chemiluminescence | PANi | Polyaniline |
| COL | Colorimetry | PBNP | Prussian blue nanoparticles |
| Co-MOF | Cobalt Metal-Organic Framework | PCL | Polycaprolactone |
| CON | Conductometry | PE | Polyester |
| CoPc | Cobalt phthalocyanine | PEDOT | Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) |
| CPE | Carbon paste electrode | PEI | Poly(ethyleneimine) |
| CR | Chemoresistive | PEO | Polyethylene oxide |
| CREAT | Creatinine | PHB | Polyhydroxy butyrate |
| Cu | Copper | PHBV | Poly-hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxy valerate |
| CV | Cyclic Voltammetry | ||
| DC | Dip Coating | PMMA | Poly (methyl methacrylate) |
| DCa | Drop casting | POCT | Point of care testing |
| DDAC | Dioctadecyl dimethyl ammonium chloride | POT | Potentiometry |
| DENVCP | Dengue virus-specific consensus primer | PPO | Polypyrrole-polyethylene oxide |
| DPV | Differential pulse voltammetry | PPy | Polypyrrole |
| DW | Distilled water | PS | Polystyrene |
| E | Enzyme based | PSA | Prostate-specific antigen |
| EC | Electrochemical | PSS | Polystyrene sulfonate |
| ED | Electrodeposition | Pt | Platinum |
| EDC | 3-(Ethylimino methyleneamino)- | PV | Pulse voltammetry |
| N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine | PVA | Poly (vinyl alcohol) | |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid | PVD | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| EFB | Electrospun fiber-based biosensors | pVDB | Poly (4-vinylphenylboronic acid-co-2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate-co-n-butyl methacrylate) |
| EGF | Electrospun graphitic nanofiber | ||
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor | ||
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy | PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| EM | Environment monitoring | PyOx | Pyranose oxidase |
| ES | Electrospray | Pyr | Pyrolysis |
| EtOH | Ethanol | RGB | RED-Green-Blue |
| FLU | Fluorescence | rGO | Reduced graphene oxide |
| FQC | Food quality control | SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| FSQ | Food safety and quality | SERS | Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy |
| FTO | Fluorine doped tin oxide | Si | Silicon |
| GA | Glutaraldehyde | SM | Spectrometry |
| GC | Glassy carbon | SnO2 | Tin oxide |
| GLDH | Glycerol dehydrogenase | SP | Screen printing |
| GLU | Glucose | SPE | Spectroscopy |
| GOx | Glucose oxidase | SPM | Spectrophotometry |
| GQD | Graphene quantum dots | SPR | Surface plasmon resonance |
| GR | Graphene | SPU | Sputtering |
| HB | Human blood | SWCNTs | Single wall carbon nanotubes |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol | SWV | Square wave voltammetry |
| HPV | Human papilloma virus | Tris | Trisaminometane |
| HS | Human serum | UA | Uric acid |
| HSA | Human serum albumin | VFA | Vertical flow assay |
| I | Immuno-based | WC | Whole cell-based |
| IL | Ionic liquid | WP | Wax printing |
| IMP | Impedimetry | ZIF-8 | Zeolitic imidazolate framework 8 |
| IP | Inkjet printing | ZnO | Zinc Oxide |
| Iph | Ionophores | μPAD | Microfluidic Paper-based analytical device |
| ITO | Indium tin oxide |
References
- WHO | Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: http://origin.who.int/gho/mortality_burden_disease/causes_death/top_10/en/ (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- GHO | By Category | Health Equity Monitor. Available online: https://apps.who.int/gho/data/node.main.nHE-1540?lang=en (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- WHO | Causes of Death, by WHO Region. Available online: http://origin.who.int/gho/mortality_burden_disease/causes_death/region/en/ (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- WHO | Low-Cost Tools for Diagnosing and Monitoring HIV Infection in Low-Resource Settings. Available online: https://www.who.int/bulletin/volumes/90/12/12-102780/en/ (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Whitesides, G.M. The Origins and the Future of Microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned Paper as a Platform for Inexpensive, Low-Volume, Portable Bioassays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Hao, M.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Ramakrishna, S. A Review on Recent Advances in Application of Electrospun Nanofiber Materials as Biosensors. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 13, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Korvink, J.G.; Mager, D.; Land, K. The Potential of Paper-Based Diagnostics to Meet the ASSURED Criteria. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 34012–34034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, X.; White, I.M.; Shopova, S.I.; Zhu, H.; Suter, J.D.; Sun, Y. Sensitive Optical Biosensors for Unlabeled Targets: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 620, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.M.; Sinton, D. Turning the Page: Advancing Paper-Based Microfluidics for Broad Diagnostic Application. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8447–8480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Zapatero-Rodríguez, J.; Estrela, P.; O’Kennedy, R. Point-of-Care Diagnostics in Low Resource Settings: Present Status and Future Role of Microfluidics. Biosensors 2015, 5, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.; Yin, X.; Jin, D.; Zhang, B.; Gu, Y.; An, Y. Paper-Based Immunosensors: Current Trends in the Types and Applied Detection Techniques. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 111, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyazi, T.; Basabe-Desmonts, L.; Benito-Lopez, F. Review on Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices towards Commercialisation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1001, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, E.; Liang, T.; Spicar-Mihalic, P.; Houghtaling, J.; Ramachandran, S.; Yager, P. Two-Dimensional Paper Network Format That Enables Simple Multistep Assays for Use in Low-Resource Settings in the Context of Malaria Antigen Detection. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4574–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, X.; Tian, T.; Jia, S.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Sun, J.; Lin, Z.; Yang, C.J. Target-Responsive DNA Hydrogel Mediated Stop-Flow Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytic Device for Rapid, Portable and Visual Detection of Multiple Targets. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4275–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Li, B.; Chen, L.; Qin, W. A Three-Dimensional Origami Paper-Based Device for Potentiometric Biosensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13033–13037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, X. Fabrication of Three-Dimensional Microfluidic Channels in a Single Layer of Cellulose Paper. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 16, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuo, M.M.; Martinez, R.V.; Lan, W.J.; Liu, X.; Barber, J.; Atkinson, M.B.J.; Bandarage, D.; Bloch, J.F.; Whitesides, G.M. Fabrication of Low-Cost Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices by Embossing or Cut-and-Stack Methods. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 4230–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, H.K.; Kim, W.H.; Park, J.; Cho, J.; Jeong, T.Y.; Park, P.K. Application of Langmuir and Freundlich Isotherms to Predict Adsorbate Removal Efficiency or Required Amount of Adsorbent. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 28, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedl, R.R.; Beta, C. Hydrogel-Driven Paper-Based Microfluidics. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2452–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, K.N.; Choi, J.S.; Kwon, J. Three-Dimensional Paper-Based Slip Device for One-Step Point-of-Care Testing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hosseini, S.; Vázquez-Villegas, P.; Martínez-Chapa, S.O. Paper and Fiber-Based Bio-Diagnostic Platforms: Current Challenges and Future Needs. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desmet, C.; Marquette, C.A.; Blum, L.J.; Doumèche, B. Paper Electrodes for Bioelectrochemistry: Biosensors and Biofuel Cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahato, K.; Srivastava, A.; Chandra, P. Paper Based Diagnostics for Personalized Health Care: Emerging Technologies and Commercial Aspects. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, C.; Bo, A.; Schabel, S.; Biesalski, M. Engineering Microfluidic Papers: Effect of Fiber Source and Paper Sheet Properties on Capillary-Driven Fluid Flow. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 16, 789–799. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Bui, M.N.; Abbas, A. Biosensors and Bioelectronics Paper-Based Chemical and Biological Sensors: Engineering Aspects. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cate, D.M.; Adkins, J.A.; Mettakoonpitak, J.; Henry, C.S. Recent Developments in Paper-Based Micro Fl Uidic Devices. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reneker, D.H.; Chun, I. Nanometre Diameter Fibres of Polymer, Produced by Electrospinning. IOP Sci. 1996, 216, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; You, T. Electrospun Nanofibers: From Rational Design, Fabrication to Electrochemical Sensing Applications. Adv. Nanofibers 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radulescu, M.C.; Bucur, M.P.; Bucur, B.; Radu, G.L. Ester Flavorants Detection in Foods with a Bienzymatic Biosensor Based on a Stable Prussian Blue-Copper Electrodeposited on Carbon Paper Electrode. Talanta 2019, 199, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Chandar, Y.J.; Cao, S.; Kharasch, E.D.; Singamaneni, S.; Morrissey, J.J. Rapid, Point-of-Care, Paper-Based Plasmonic Biosensor for Zika Virus Diagnosis. Adv. Biosyst. 2017, 1, 1700096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silveira, C.M.; Monteiro, T.; Almeida, M.G. Biosensing with Paper-Based Miniaturized Printed Electrodes-A Modern Trend. Biosensors 2016, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, K.H.; Chen, P.H.; Lin, C.; Chen, C.F.; Lee, I.R.; Yeh, Y.C. Determination of Gold Ions in Human Urine Using Genetically Engineered Microorganisms on a Paper Device. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, J.; Bhardwaj, N.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Kim, K.H.; Deep, A. Recent Advances in Enzyme Immobilization Techniques: Metal-Organic Frameworks as Novel Substrates. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 322, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colozza, N.; Kehe, K.; Dionisi, G.; Popp, T.; Tsoutsoulopoulos, A.; Steinritz, D.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. A Wearable Origami-like Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for Sulfur Mustard Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 129, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Fei, A.; Huan, J.; Mao, H.; Wang, K. Effective Amperometric Biosensor for Carbaryl Detection Based on Covalent Immobilization Acetylcholinesterase on Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes/Graphene Oxide Nanoribbons Nanostructure. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 740, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbioli, G.G.; Speller, N.C.; Cato, M.E.; Cantrell, T.P.; Stockton, A.M. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical Rapid and Low-Cost Development of Micro Fl Uidic Devices Using Wax Printing and Microwave Treatment. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 284, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Asiri, A.M.; Du, D.; Wen, W.; Wang, S.; Lin, Y. Nanomaterial-Enhanced Paper-Based Biosensors. TrAC - Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 58, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chem, J.M.; Credou, J.; Berthelot, T. Cellulose: From Biocompatible to Bioactive Material. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4767–4788. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, F.; Hu, Y.F. Biomolecule Immobilization Techniques for Bioactive Paper Fabrication. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Noviana, E.; Nguyen, M.P.; Geiss, B.J.; Dandy, D.S.; Henry, C.S. Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices: Emerging Themes and Applications. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino, C.I.L.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P. Immunosensors in Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 73, ISBN 9780128046906. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Cao, R.; Wu, J.; Guan, L.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Tian, J. Directly Writing Barrier-Free Patterned Biosensors and Bioassays on Paper for Low-Cost Diagnostics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 285, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Kong, Q.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Bian, Z.; Zheng, X.; Ma, C.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. Hand-Drawn&written Pen-on-Paper Electrochemiluminescence Immunodevice Powered by Rechargeable Battery for Low-Cost Point-of-Care Testing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Ge, S.; Wang, S.; Yan, M.; Ge, L.; Yu, J. Highly Sensitive Chemiluminescence Immunoassay on Chitosan Membrane Modified Paper Platform Using TiO2nanoparticles/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes as Label. Luminescence 2013, 28, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, H.; Ding, Y.; Ge, S.; Yu, J.; Yan, M.; Song, X. Paper-Based Colorimetric Immunosensor for Visual Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigen Based on the High Peroxidase-like Catalytic Performance of ZnFe 2 O 4 -Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Analyst 2014, 139, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduini, F.; Cinti, S.; Caratelli, V.; Amendola, L.; Palleschi, G.; Moscone, D. Origami Multiple Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Pesticide Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Basso, M.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. A Paper-Based Nanomodified Electrochemical Biosensor for Ethanol Detection in Beers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 960, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthier, J.; Brakke, K.A.; Berthier, E. Paper-based Microfluidics. In Open-Microfluidics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 229–256. ISBN 9781118720806. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Jin, T.; Kou, J.; Zou, S.; Xiao, J.; Meng, Q. Lucas–Washburn Equation-Based Modeling of Capillary-Driven Flow in Porous Systems. Langmuir 2021, 37, 1623–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camplisson, C.K.; Schilling, K.M.; Pedrotti, W.L.; Stone, H.A.; Martinez, A.W. Two-Ply Channels for Faster Wicking in Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 4461–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jahanshahi-Anbuhi, S.; Chavan, P.; Sicard, C.; Leung, V.; Hossain, S.M.Z.; Pelton, R.; Brennan, J.D.; Filipe, C.D.M. Creating Fast Flow Channels in Paper Fluidic Devices to Control Timing of Sequential Reactions. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 5079–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Kim, W. Dynamics of Water Imbibition through Paper Channels with Wax Boundaries. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2015, 19, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Sun, Z.; He, M.; Liu, Q.; Qin, J.; Han, S. Capillary Filling of Confined Water in Nanopores: Coupling the Increased Viscosity and Slippage. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 186, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabovati, A.; Llewellin, E.W.; Sousa, A.C.M. A General Model for the Permeability of Fibrous Porous Media Based on Fluid Flow Simulations Using the Lattice Boltzmann Method. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaripov, S.K.; Mardanov, R.F.; Sharafutdinov, V.F. Determination of Brinkman Model Parameters Using Stokes Flow Model. Transp. Porous Media 2019, 130, 529–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Li, A.; Qu, Z.; Xu, F. Liquid Wicking Behavior in Paper-like Materials: Mathematical Models and Their Emerging Biomedical Applications. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2018, 22, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizalde, E.; Urteaga, R.; Berli, C.L.A. Rational Design of Capillary-Driven Flows for Paper-Based Microfluidics. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2173–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, I.U.; Sinha Mahapatra, P.; Sen, A.K. Self-Driven Droplet Transport: Effect of Wettability Gradient and Confinement. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 042111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzybowski, H.; Mosdorf, R. Modelling of Two-Phase Flow in a Minichannel Using Level-Set Method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Song, S.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Sherazi, T.A.; Li, S.; Zhang, S. Controllable Janus Porous Membrane with Liquids Manipulation for Diverse Intelligent Energy-Free Applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 601, 117954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, S.A. The “Barrer” Permeability Unit. J. Polym. Sci. Part A-2 Polym. Phys. 1968, 6, 1933–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsalve-Bravo, G.M.; Bhatia, S.K. Modeling Permeation through Mixed-Matrix Membranes: A Review. Processes 2018, 6, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shandilya, R.; Bhargava, A.; Bunkar, N.; Tiwari, R.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; Mishra, P.K. Nanobiosensors: Point-of-Care Approaches for Cancer Diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirzada, M.; Altintas, Z. Recent Progress in Optical Sensors for Biomedical Diagnostics. Micromachines 2020, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, P.; Zhu, X.; Li, C.Z. Development of Paper-Based Analytical Kit for Point-of-Care Testing. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2013, 13, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Whitesides, G.M.; Carrilho, E.; Chem, A. Diagnostics for the Developing World: Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Du, D.; Hua, X.; Yu, X.Y.; Lin, Y. Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensors: From Test Strips to Paper-Based Microfluidics. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Dong, Y. State of the Art: Lateral Fl Ow Assay ( LFA ) Biosensor for on-Site Rapid Detection. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 1567–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolo, C.; Sena-Torralba, A.; Bergua, J.F.; Calucho, E.; Fuentes-Chust, C.; Hu, L.; Rivas, L.; Álvarez-Diduk, R.; Nguyen, E.P.; Cinti, S.; et al. Tutorial: Design and Fabrication of Nanoparticle-Based Lateral-Flow Immunoassays. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 3788–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadır, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Lateral Flow Assays: Principles, Designs and Labels. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral Flow Assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Song, S.; Park, S.; Joo, C. Recent Advances in High-Sensitivity Detection Methods for Paper-Based Lateral-Flow Assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 152, 112015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, C.; Hou, C.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices for Environmental Analysis of Soil, Air, Ecology and River Water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 301, 126855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuswandi, B.; Ensafi, A.A.; Soc, J.E.; Ensafi, A.A. Paper-Based Biosensors: Trending Topic in Clinical Diagnostics Developments and Commercialization. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-marzo, A.M.; Merkoçi, A. Paper-Based Sensors and Assays: A Success of the Engineering Design and the Convergence of Knowledge Areas. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3150–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, D.L.; Lipson, R.H.; Nann, T. Comprehensive Nanoscience and Nanotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 1–5, ISBN 9780128122952. [Google Scholar]
- Lawal, A.T. Progress in Utilisation of Graphene for Electrochemical Biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 106, 149–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanam, A.; Mohammadi, H.; Amine, A.; Haddour, N.; Buret, F. Chemical Sensors: Electrochemical Sensors; Voltammetry/Amperometry. In Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Thévenot, D.R.; Toth, K.; Durst, R.A.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical Biosensors: Recommended Definitions and Classification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronkainen, N.J.; Brian, H.; Heineman, W.R. Electrochemical Biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 1747–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Umar, M.; Saifi, A.; Kumar, S.; Augustine, S.; Srivastava, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Electrochemical Paper Based Cancer Biosensor Using Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Decorated PEDOT:PSS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1056, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teengam, P.; Siangproh, W.; Tuantranont, A.; Henry, C.S.; Vilaivan, T.; Chailapakul, O. Electrochemical Paper-Based Peptide Nucleic Acid Biosensor for Detecting Human Papillomavirus. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 952, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Ge, P.; Wang, L.; Jiang, H.; Yang, M.; Yuan, L.; Ge, Q.; Fang, W.; Ju, X. A Novel Electrochemical Mast Cell-Based Paper Biosensor for the Rapid Detection of Milk Allergen Casein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, C.; Dubey, A.; Mathur, A.; Pundir, C.S.; Narang, J. Paper Based DNA Biosensor for Detection of Chikungunya Virus Using Gold Shells Coated Magnetic Nanocubes. Process Biochem. 2018, 74, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruecha, N.; Rangkupan, R.; Rodthongkum, N.; Chailapakul, O. Novel Paper-Based Cholesterol Biosensor Using Graphene/Polyvinylpyrrolidone/Polyaniline Nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Liu, H.; Li, L.; Yu, J.; Ge, S.; Song, X.; Yan, M. Paper-Based Biosensor for Noninvasive Detection of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 251, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuek Lawrence, C.S.; Tan, S.N.; Floresca, C.Z. A “Green” Cellulose Paper Based Glucose Amperometric Biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Cusenza, R.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. Paper-Based Synthesis of Prussian Blue Nanoparticles for the Development of Whole Blood Glucose Electrochemical Biosensor. Talanta 2018, 187, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadarrama-Fernández, L.; Novell, M.; Blondeau, P.; Andrade, F.J. A Disposable, Simple, Fast and Low-Cost Paper-Based Biosensor and Its Application to the Determination of Glucose in Commercial Orange Juices. Food Chem. 2018, 265, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Zhu, Q.; Fang, L.; Cao, Q.; Liang, X.; Ye, X. An Origami Paper Device for Complete Elimination of Interferents in Enzymatic Electrochemical Biosensors. Electrochem. Commun. 2017, 82, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas-Ardisana, P.J.; Martínez-Paredes, G.; Añorga, L.; Grande, H.J. Glucose Biosensor Based on Disposable Electrochemical Paper-Based Transducers Fully Fabricated by Screen-Printing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 109, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Ma, P.; Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Chen, F.; Li, M. 3D Coral-like Gold/Carbon Paper Electrode Modified with Covalent and Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates for Electrochemical Sensing of Glucose. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Weng, B.; Li, C. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical Flexible Paper Sensor Fabricated via in Situ Growth of Cu Nanoflower on RGO Sheets towards Amperometrically Non-Enzymatic Detection of Glucose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Jen, S.; Settu, K.; Chen, C.; Liu, J. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical An Anti-HCT-Interference Glucose Sensor Based on a Fi Ber Paper-Based Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 297, 126763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatmah, E.; Hemmateenejad, B. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical Dendrite Gold Nanostructures Electrodeposited on Paper Fi Bers: Application to Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Determination of Glucose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Guo, J.; Lian, H.; Sun, X.; Liu, B. Sensors and Actuators: B. Chemical Cobalt Metal-Organic Framework Modified Carbon Cloth/Paper Hybrid Electrochemical Button-Sensor for Nonenzymatic Glucose Diagnostics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyo, S.; Mehmeti, E.; Siangproh, W.; Long, T.; Phong, H. Biosensors and Bioelectronics Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Detection of Glucose with a Disposable Paper-Based Sensor Using a Cobalt Phthalocyanine – Ionic Liquid – Graphene Composite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.; Ko, E.; Geng, Y.; Kim, M.K.; Jin, G.H.; Son, S.E.; Hur, W. Micro-Patterning of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Its Surface Modi Fi Cation with Gold Nanoparticles for Electrochemical Paper-Based Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 826, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, N.C.; Ge, L.; Mousavi Shaegh, S.A.; Ng, S.H.; Tan, S.N. A Mediated Turnip Tissue Paper-Based Amperometric Hydrogen Peroxide Biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 210, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Tran, T.T.; Modha, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Mulchandani, A. A Paper-Based Chemiresistive Biosensor Employing Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Low-Cost, Point-of-Care Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi-Mohseni, M.; Raoof, J.B.; Ojani, R.; Aghajanzadeh, T.A.; Bagheri Hashkavayi, A. Development of a New Paper Based Nano-Biosensor Using the Co-Catalytic Effect of Tyrosinase from Banana Peel Tissue (Musa Cavendish) and Functionalized Silica Nanoparticles for Voltammetric Determination of L-Tyrosine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Minotti, C.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G.; Arduini, F. Fully Integrated Ready-to-Use Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensor to Detect Nerve Agents. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Jian, Y.; Wang, H.; Ge, S.; Yan, M.; Yu, J. Ultrasensitive Microfluidic Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Film and Boronate Affinity Sandwich Assay for Glycoprotein Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Lee, M.; Kim, D. Detection of Early Stage Prostate Cancer by Using a Simple Carbon Nanotube@paper Biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cincotto, F.H.; Fava, E.L.; Moraes, F.C.; Fatibello-Filho, O.; Faria, R.C. A New Disposable Microfluidic Electrochemical Paper-Based Device for the Simultaneous Determination of Clinical Biomarkers. Talanta 2019, 195, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cánovas, R.; Parrilla, M.; Blondeau, P.; Andrade, F.J. A Novel Wireless Paper-Based Potentiometric Platform for Monitoring Glucose in Blood. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 2500–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cánovas, R.; Blondeau, P.; Andrade, F.J. Modulating the Mixed Potential for Developing Biosensors: Direct Potentiometric Determination of Glucose in Whole, Undiluted Blood. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 163, 112302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, B.; Evrim, E.; Odaci, D.; Timur, S. Applied Surface Science An Electrospun Nanofiber Matrix Based on Organo-Clay for Biosensors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 444, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavinatto, A.; Mercante, L.A.; Facure, M.H.M.; Pena, R.B. Applied Surface Science Ultrasensitive Biosensor Based on Polyvinylpyrrolidone/Chitosan/Reduced Graphene Oxide Electrospun Nano Fi Bers for 17 α – Ethinylestradiol Electrochemical Detection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 458, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apetrei, R.; Camurlu, P. Electrochimica Acta The Effect of Montmorillonite Functionalization on the Performance of Glucose Biosensors Based on Composite Montmorillonite/PAN Nano Fi Bers. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 353, 136484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, K.; Ali, A.; Singh, C.; Sumana, G.; Malhotra, B.D.; Sharma, A. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical Highly Sensitive Porous Carbon and Metal/Carbon Conducting Nanofiber Based Enzymatic Biosensors for Triglyceride Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wu, T.; Liu, L.; He, Y.; Liu, D.; You, T. Hierarchically Porous NiCo2S4 Nanowires Anchored on Fl Exible Electrospun Graphitic Nano Fi Ber for High-Performance Glucose Biosensing. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 819, 153376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, G.; Li, J.; Guo, L.; Chen, S. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical NiCo2O4 Nanoneedle-Decorated Electrospun Carbon Nanofiber Nanohybrids for Sensitive Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supraja, P.; Tripathy, S.; Rama, S.; Vanjari, K.; Singh, V.; Govind, S. Biosensors and Bioelectronics Electrospun Tin ( IV ) Oxide Nano Fi Ber Based Electrochemical Sensor for Ultra- Sensitive and Selective Detection of Atrazine in Water at Trace Levels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr-Phillips, T.E.; Aydemir, N.; Wai, E.; Chan, C.; Barker, D. Biosensors and Bioelectronics Conducting Electrospun Fi Bres with Polyanionic Grafts as Highly Selective, Label-Free, Electrochemical Biosensor with a Low Detection Limit for Non- Hodgkin Lymphoma Gene. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Azizi-lalabadi, M.; Bagheri, V.; Sadeghi, E. Sensing and Bio-Sensing Research Fabrication of Electrospun Sensor Based on a Synthesized Component Doped into PAN ( Polyacrylonitrile ) Nanofibers for Electrochemical Detection of Zearalenone Mycotoxin in Foods Simulant. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2020, 28, 100321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, Q.; Lu, K.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Qiao, H.; Li, D.; Wei, Q. Biosensors and Bioelectronics Encapsulating Enzyme into Metal-Organic Framework during in-Situ Growth on Cellulose Acetate Nanofibers as Self-Powered Glucose Biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, F.L.; Sanfelice, R.C.; Mercante, L.A.; Andre, R.S.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Correa, D.S. Applied Surface Science Urea Impedimetric Biosensing Using Electrospun Nanofibers Modified with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 443, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapountzi, E.; Braiek, M.; Vocanson, F.; Jaffrezic-renault, N.; Lagarde, F. Chemical Gold Nanoparticles Assembly on Electrospun Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Poly (Ethyleneimine)/Glucose Oxidase Nanofibers for Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Glucose Biosensing. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 238, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paimard, G.; Shahlaei, M.; Moradipour, P.; Akbari, H.; Jafari, M. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical An Impedimetric Immunosensor Modi Fi Ed with Electrospun Core-Shell Nano Fi Bers for Determination of the Carcinoma Embryonic Antigen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 311, 127928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; Bhandari, V.; Sharma, P.; Rama, S.; Vanjari, K. Biosensors and Bioelectronics Chemiresistive DNA Hybridization Sensor with Electrospun Nano Fi Bers: A Method to Minimize Inter-Device Variability. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 133, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldea, A.; Matei, E.; Leote, R.J.B.; Rau, I.; Enculescu, I.; Diculescu, V.C. Electrochimica Acta Ionophore- Nafion TM Modified Gold-Coated Electrospun Polymeric Fibers Electrodes for Determination of Electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 363, 137239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, T.; Jackson, D.; Baldwin, R.; Keynton, R. Amperometric techniques. In Encyclopedia of Microfluidics and Nanofluidics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Akanda, M.R.; Joung, H.A.; Tamilavan, V.; Park, S.; Kim, S.; Hyun, M.H.; Kim, M.G.; Yang, H. An Interference-Free and Rapid Electrochemical Lateral-Flow Immunoassay for One-Step Ultrasensitive Detection with Serum. Analyst 2014, 139, 1420–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Ying, Y. New Trends in Impedimetric Biosensors for the Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria. Sensors 2012, 12, 3449–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, S.; Tang, Y.; Tang, D.; Cai, Y. Analytica Chimica Acta Highly Sensitive Impedimetric Biosensor for Hg 2 þ Detection Based on Manganese Porphyrin-Decorated DNA Network for Precipitation Polymerization. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1023, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prodromidis, M.I. Electrochimica Acta Impedimetric Immunosensors: A Review. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 4227–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Deiss, F.; Liu, X.; Akbulut, O.; Whitesides, G.M. Integration of Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices with Commercial Electrochemical Readers. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 3163–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shirshahi, V.; Liu, G. Enhancing the Analytical Performance of Paper Lateral Flow Assays: From Chemistry to Engineering. TrAC - Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 136, 116200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damborsky, P.; Svitel, J.; Katrlík, J. Optical Biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Shadjou, N.; Soleymani, J.; Omidinia, E.; De, M. Optical Immunosensing of Effective Cardiac Biomarkers on Acute Myocardial Infarction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 51, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, H.; Liao, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhou, X.; Xing, D. Multiplex Detection and Genotyping of Pathogenic Bacteria on Paper-Based Biosensor with a Novel Universal Primer Mediated Asymmetric PCR. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba-Patiño, A.; Russell, S.M.; de la Rica, R. Origami-Enabled Signal Amplification for Paper-Based Colorimetric Biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, K.; Chandra, P. Paper-Based Miniaturized Immunosensor for Naked Eye ALP Detection Based on Digital Image Colorimetry Integrated with Smartphone. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 128, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, S.; Azari, P.; Farahmand, E.; Gan, S.N.; Rothan, H.A.; Yusof, R.; Koole, L.H.; Djordjevic, I.; Ibrahim, F. Polymethacrylate Coated Electrospun PHB Fibers: An Exquisite Outlook for Fabrication of Paper-Based Biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 69, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duyen, T.T.M.; Matsuura, H.; Ujiie, K.; Muraoka, M.; Harada, K.; Hirata, K. Paper-Based Colorimetric Biosensor for Antibiotics Inhibiting Bacterial Protein Synthesis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 123, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, A.; Jha, S.K. A Paper Strip Based Non-Invasive Glucose Biosensor for Salivary Analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, B.S.; Linares, E.M.; Thalhammer, S.; Kubota, L.T. Development of a Disposable and Highly Sensitive Paper-Based Immunosensor for Early Diagnosis of Asian Soybean Rust. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, H.; Liu, W.; Chu, W.; Chen, Y. Paper-Based Laser Induced Fluorescence Immunodevice Combining with CdTe Embedded Silica Nanoparticles Signal Enhancement Strategy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 242, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Ahmed, S.R.; Neethirajan, S. A Nanocomposite-Based Biosensor for Bovine Haptoglobin on a 3D Paper-Based Analytical Device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 265, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, B.J.; Kwon, J.E.; Lee, K.; Koh, W.G. Highly Sensitive Metal-Enhanced Fluorescence Biosensor Prepared on Electrospun Fibers Decorated with Silica-Coated Silver Nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 284, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirós, J.; Amaral, A.J.R.; Pasparakis, G.; Williams, G.R.; Rosal, R. Electrospun Boronic Acid-Containing Polymer Membranes as Fl Uorescent Sensors for Bacteria Detection. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 121, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhao, X.; Ji, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Wen, X.; Li, J. Electrospinning Graphene Quantum Dots into a Nano Fi Brous Membrane for Dual-Purpose Fl Uorescent and Electrochemical Biosensors. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2487–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhuang, J.; Lou, S.; Lin, S.; Hsin, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, H. Immobilizing Laccase on Electrospun Chitosan Fiber to Prepare Time- Temperature Indicator for Food Quality Monitoring. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 63, 102370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, B.; Koh, W. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Highly-Sensitive SERS-Based Immunoassay Platform Prepared on Silver Nanoparticle-Decorated Electrospun Polymeric Fi Bers. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 82, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Maftoonazad, N.; Ramaswamy, H. Design and Testing of an Electrospun Nanofiber Mat as a PH Biosensor and Monitor the PH Associated Quality in Fresh Date Fruit (Rutab). Polym. Test. 2019, 75, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciotti, I.; Pallotto, F.; Scognamiglio, V.; Moscone, D.; Niccolò, R.; Don, V.; Gnocchi, C. Materials Science & Engineering C Reusable Optical Multi-Plate Sensing System for Pesticide Detection by Using Electrospun Membranes as Smart Support for Acetylcholinesterase Immobilisation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110744. [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi, S.; Achla, R.; Mondal, S.K. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical Electrospun Polypyrrole-Polyethylene Oxide Coated Optical Fiber Sensor Probe for Detection of Volatile Compounds. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 250, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, T.S.; Sgobbi, L.F.; Delezuk, J.; Pessoa, R.S.; Lobo, A.O.; Rodrigues, B.V.M. ScienceDirect Glucose Sensing via a Green and Low-Cost Platform from Electrospun Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Graphene Quantum Dots Fibers. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 14, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-naggar, M.E.; El-newehy, M.H.; Aldalbahi, A.; Salem, W.M.; Khattab, T.A. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering Immobilization of Anthocyanin Extract from Red-Cabbage into Electrospun Polyvinyl Alcohol Nanofibers for Colorimetric Selective Detection of Ferric Ions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Su, R.; Song, Y.; Zhu, D. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical Functionalized Paper Microzone Plate for Colorimetry and up-Conversion Fluorescence Dual-Mode Detection of Telomerase Based on Elongation and Capturing Amplification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 259, 642–649. [Google Scholar]
- Dodeigne, C.; Thunus, L.; Lejeune, R. Chemiluminescence as a Diagnostic Tool. A Review. Talanta 2000, 51, 415–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggeling, C.; Kask, P.; Winkler, D.; Ja, S. Rapid Analysis of Förster Resonance Energy Transfer by Two-Color Global Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy: Trypsin Proteinase Reaction. Biophys. J. 2005, 89, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lansdown, A.B.G. GOLD: Human Exposure and Update on Toxic Risks. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2018, 48, 596–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T. Recent Developments in Chemiluminescence Sensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 1999, 18, 384–391. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, M.M. Electrochemiluminescence ( ECL ). Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 3003–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.-I.; Desmulliez, M.P.Y. Lab-on-a-Chip Based Immunosensor Principles and Technologies for the Detection of Cardiac Biomarkers: A Review. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 569–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojic, B. Introduction and Overview of Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2020; ISBN 9781788015776. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.K.; Chen, A.Y.; Chai, Y.Q.; Yuan, R.; Zhuo, Y. Electrochemiluminescence Aptasensor Based on Cascading Amplification of Nicking Endonuclease-Assisted Target Recycling and Rolling Circle Amplifications for Mucin 1 Detection. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 212, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, F.; Deng, P.; Wang, Y.; Cai, K.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z. Biosensors and Bioelectronics Sensitive Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence Biosensors for Protein Kinase Activity Analysis Based on Bimetallic Catalysis Signal Ampli Fi Cation and Recognition of Au and Pt Loaded Metal-Organic Frameworks Nanocomposites. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 109, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Kiani, M. Optimal Resonance Configuration for Ultrasonic Wireless Power Transmission to Millimeter-Sized Biomedical Implants. 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 1934–1937. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. Auto-Cleaning Paper-Based Electrochemiluminescence Biosensor Coupled with Binary Catalysis of Cubic Cu 2 O-Au and Polyethyleneimine for Quantification of Ni 2+ and Hg 2+. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, H.; Ma, C.; Li, L.; Ge, S.; Song, X.; Yu, J.; Yan, M. Electrochemiluminescence of Peroxydisulfate Using Flower-like Ag@Au-Paper Electrode and Pd@Au-Assisted Multiple Enzymatic Labels. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 141, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnadayyala, S.R.; Park, J.; Le, H.T.N.; Santhosh, M.; Kadam, A.N.; Cho, S. Recent Advances in Microfluidic Paper-Based Electrochemiluminescence Analytical Devices for Point-of-Care Testing Applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Dosso, F.; Decrop, D.; Pérez-Ruiz, E.; Daems, D.; Agten, H.; Al-Ghezi, O.; Bollen, O.; Breukers, J.; De Rop, F.; Katsafadou, M.; et al. Creasensor: SIMPLE Technology for Creatinine Detection in Plasma. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1000, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ruiz, N.; Curto, V.F.; Erenas, M.M.; Benito-Lopez, F.; Diamond, D.; Palma, A.J.; Capitan-Vallvey, L.F. Smartphone-Based Simultaneous PH and Nitrite Colorimetric Determination for Paper Microfluidic Devices. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9554–9562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Gómez, I.; Toral-López, V.; Romero, F.J.; de Orbe-Payá, I.; García, A.; Rodríguez, N.; Capitán-Vallvey, L.F.; Morales, D.P.; Salinas-Castillo, A. In Situ Synthesis of Fluorescent Silicon Nanodots for Determination of Total Carbohydrates in a Paper Microfluidic Device Combined with Laser Prepared Graphene Heater. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 332, 129506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapountzi, E.; Braiek, M.; Chateaux, J.F.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Lagarde, F. Recent Advances in Electrospun Nanofiber Interfaces for Biosensing Devices. Sensors 2017, 17, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mi, S.; Kong, B.; Wu, Z.; Sun, W.; Xu, Y.; Su, X. A Novel Electrospinning Setup for the Fabrication of Thickness-Controllable 3D Scaffolds with an Ordered Nano Fi Brous Structure. Mater. Lett. 2015, 160, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduraiveeran, G.; Sasidharan, M.; Ganesan, V. Electrochemical Sensor and Biosensor Platforms Based on Advanced Nanomaterials for Biological and Biomedical Applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 103, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struss, A.; Pasini, P.; Ensor, C.M.; Raut, N.; Daunert, S. Paper Strip Whole Cell Biosensors: A Portable Test for the Semiquantitative Detection of Bacterial Quorum Signaling Molecules. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4457–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Halluin, M.; Rull-Barrull, J.; Bretel, G.; Labrugère, C.; Le Grognec, E.; Felpin, F.X. Chemically Modified Cellulose Filter Paper for Heavy Metal Remediation in Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1965–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Proietti, E.; Casotto, F.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. Paper-Based Strips for the Electrochemical Detection of Single and Double Stranded DNA. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13680–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xue, P.; Kang, Y.; Hui, K.M. Paper-Based Microfluidic Electrochemical Immunodevice Integrated with Nanobioprobes onto Graphene Film for Ultrasensitive Multiplexed Detection of Cancer Biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 8661–8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of Nanofibers: Reinventing the Wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A Review on Polymer Nanofibers by Electrospinning and Their Applications in Nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, L.M.; Gonzalez, E.; Chen, E.X.; Frey, M.W. Increasing Stability of Biotin Functionalized Electrospun Fibers for Biosensor Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 1968–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabu, C.; Henna, T.K.; Raphey, V.R.; Nivitha, K.P.; Pramod, K. Biosensors and Bioelectronics Advanced Biosensors for Glucose and Insulin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yao, S.; Liu, Y.; Wei, S.; Su, J.; Hu, G. Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on Au Nanoparticles in Carboxylated Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Sensitive Determination of Olaquindox in Food and Feedstuffs. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, F.; Liao, X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, W. A Subfemtomolar Electrochemical DNA Biosensor Realized by In-Situ Grafting of Gold Nanoparticle/Neutral Red on the Terminal of Hairpin Probe as the Signal Tag. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, 106079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z. Target Binding and DNA Hybridization-Induced Gold Nanoparticle Aggregation for Colorimetric Detection of Thrombin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 262, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirasirichote, A.; Punrat, E.; Suea-Ngam, A.; Chailapakul, O.; Chuanuwatanakul, S. Voltammetric Detection of Carbofuran Determination Using Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes Modified with Gold Nanoparticles and Graphene Oxide. Talanta 2017, 175, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G. Early Detection of Cancer: Focus on Antibody Coated Metal and Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based Biosensors. Sens. Int. 2020, 1, 100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuchamy, N.; Atchudan, R.; Nesakumar, T.; Immanuel, J. High-Performance Glucose Biosensor Based on Green Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Embedded Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Sheet. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 816, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, M.; Wuzella, G.; Lammer, H.; Mahendran, A.R. Smart Paper from Graphene Coated Cellulose for High-Performance Humidity and Piezoresistive Force Sensor. Synth. Met. 2020, 266, 116420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Zeng, X. ScienceDirect Electrochemistry Interfacial Composition, Structure, and Properties of Ionic Liquids and Conductive Polymers for the Construction of Chemical Sensors and Biosensors: A Perspective. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2020, 23, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Kaiser, A. Electrospinning of Metal–Organic Frameworks for Energy and Environmental Applications. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K.E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. The Chemistry and Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Kaskel, S. Porphyrin-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for Biomedical Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 2–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrasco, S. Metal-Organic Frameworks for the Development of Biosensors: A Current Overview. Biosensors 2018, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chunsheng, W.; Liping, D.; Wei, C.; Ping, Z.; Yulan, T.; Yating, C. Applications of Functional Metal-Organic Frameworks in Biosensors. Proteomics 2013, 16, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L.; Qi, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Yao, C.; Song, W.; Wang, Y. Biosensors and Bioelectronics A Facile DNA Strand Displacement Reaction Sensing Strategy of Electrochemical Biosensor Based on N-Carboxymethyl Chitosan/Molybdenum Carbide Nanocomposite for MicroRNA-21 Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 122, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Wolfbeis, O.S.; Hahn, Y.B.; Alshareef, H.N.; Torsi, L.; Salama, K.N. Deposition of Nanomaterials: A Crucial Step in Biosensor Fabrication. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 17, 289–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farag, A.A.M.; Yahia, I.S. Structural, Absorption and Optical Dispersion Characteristics of Rhodamine B Thin Fi Lms Prepared by Drop Casting Technique. OPTICS 2010, 283, 4310–4317. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, A.; Eng, S.; Chua, C.K.; Pumera, M. Intrinsic Electrochemical Performance and Precise Control of Surface Porosity of Graphene-Modi Fi Ed Electrodes Using the Drop-Casting Technique. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 59, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Eslamian, M.; Soltani-Kordshuli, F. Development of Multiple-Droplet Drop-Casting Method for the Fabrication of Coatings and Thin Solid Films. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2018, 15, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussetti, G.; Trabattoni, S.; Uttiya, S.; Sassella, A.; Riva, M.; Picone, A.; Brambilla, A.; Duò, L.; Ciccacci, F.; Finazzi, M. Controlling Drop-Casting Deposition of 2D Pt-Octaethyl Porphyrin Layers on Graphite. Synth. Met. 2014, 195, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xing, L.; Xiang, J.; Cui, L.; Jiao, J.; Sai, H. Formation of Uniform Reduced Graphene Oxide Films on Modified PET Substrates Using Drop-Casting Method. Particuology 2014, 17, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrijo, M.M.M.; Lorenz, H.; Rambo, C.R.; Greil, P.; Travitzky, N. Fabrication of Ti3SiC2-Based Pastes for Screen Printing on Paper-Derived Al2O3 Substrates. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 8116–8124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faddoul, R.; Reverdy-bruas, N.; Blayo, A. Formulation and Screen Printing of Water Based Conductive Flake Silver Pastes.Pdf. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2012, 177, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebler, A.; Hahn, U.; Beier, W.; Lasch, N.; Fischer, T. High Volume Printing Technologies for the Production of Polymer Electronic Structures. In Proceedings of the 2nd International IEEE Conference on Polymers and Adhesives in Microelectronics and Photonics, POLYTRONIC 2002, Conference Proceedings (Cat. No.02EX599), Zalaegerszeg, Hungary, 26–26 June 2002; pp. 172–176. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, H.D.; Brown, R.B.; Liu, D.P.; Meyerhoff, M.E. Screen Printing: A Technology for the Batch Fabrication of Integrated Chemical-Sensor Arrays. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1994, 21, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, R.; Li, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Briand, D.; Camara, M.; Zhou, G.; de Rooij, N.F. Highly Transparent Humidity Sensor with Thin Cellulose Acetate Butyrate and Hydrophobic AF1600X Vapor Permeating Layers Fabricated by Screen Printing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrilho, E.; Martinez, A.W.; Whitesides, G.M. Understanding Wax Printing: A Simple Micropatterning Process for Paper-Based Microfluidics. Adv. Chem. 2009, 81, 7091–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juang, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, P. Fabrication of Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices by Filtration-Assisted Screen Printing. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 80, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, C. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical A Novel Paper-Based Microfluidic Enhanced Chemiluminescence Biosensor for Facile, Reliable and Highly-Sensitive Gene Detection of Listeria Monocytogenes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yan, X. Dip-Coating for Fibrous Materials: Mechanism, Methods and Applications. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 378–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, M. Numerical Simulation of Dip-Coating in the Evaporative Regime. Eur. Phys. J. E 2016, 39, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Srivastava, S.; Yadav, B.K.; Lee, S.H.; Sharma, J.G.; Doval, D.C.; Malhotra, B.D. Biosensors and Bioelectronics Reduced Graphene Oxide Modified Smart Conducting Paper for Cancer Biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 73, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Smeets, N.M.B.; Wang, J.; Brennan, J.D.; Filipe, C.D.M.; Hoare, T. Poly(Oligoethylene Glycol Methacrylate) Dip-Coating: Turning Cellulose Paper into a Protein-Repellent Platform for Biosensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12852–15855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, A.; Gabriel, G.; Villa, R.; Javier, F. Inkjet-Printed Electrochemical Sensors. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2017, 3, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Suzuki, K.; Citterio, D. Inkjet-Printed Microfluidic Multianalyte Chemical Sensing Paper. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6928–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Henares, T.G.; Suzuki, K.; Citterio, D. Paper-Based Inkjet-Printed Microfluidic Analytical Devices. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5294–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, G.; Ravarotto, M.; Scaramuzza, M.; De Toni, A.; Paccagnella, A. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical Silver Nanoparticles Inkjet-Printed Flexible Biosensor for Rapid Label-Free Antibiotic Detection in Milk. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 280, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, F.; Wu, Z.; Yu, R. Sensitive Inkjet Printing Paper-Based Colormetric Strips for Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors with Indoxyl Acetate Substrate. Talanta 2017, 162, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihalainen, P.; Pesonen, M.; Sund, P.; Viitala, T.; Määttänen, A.; Sarfraz, J.; Wilén, C.; Österbacka, R.; Peltonen, J. Applied Surface Science Printed Biotin-Functionalised Polythiophene Films as Biorecognition Layers in the Development of Paper-Based Biosensors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 364, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ge, L.; Song, X.; Yu, J.; Ge, S. Biosensors and Bioelectronics Paper-Based Chemiluminescence ELISA: Lab-on-Paper Based on Chitosan Modified Paper Device and Wax-Screen-Printing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Songjaroen, T.; Dungchai, W.; Chailapakul, O.; Laiwattanapaisal, W. Talanta Novel, Simple and Low-Cost Alternative Method for Fabrication of Paper-Based Microfluidics by Wax Dipping. Talanta 2011, 85, 2587–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tarso Garcia, P.; Garcia Cardoso, T.M.; Garcia, C.D.; Carrilho, E.; Tomazelli Coltro, W.K. A Handheld Stamping Process to Fabricate Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices with Chemically Modified Surface for Clinical Assays. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 37637–37644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Shi, W.; Jiang, L.; Qin, J.B.L. Rapid Prototyping of Paper-Based Microfluidics with Wax for Low-Cost, Portable Bioassay. Electrophoresis 2009, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungchai, W.; Chailapakul, O.; Henry, C.S. A Low-Cost, Simple, and Rapid Fabrication Method for Paper-Based Microfluidics Using Wax Screen-Printing. Analyst 2011, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.; Kurniawan, A.; Kao, C.; Wang, M. Talanta Single Step and Mask-Free 3D Wax Printing of Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices for Glucose and Nitrite Assays. Talanta 2019, 194, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, M.D.; Nimse, S.B. Surface Modification Chemistries of Materials Used in Diagnostic Platforms with Biomolecules. J. Chem. 2016, 2016, 9241378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Güemes, M.; Rahman, A.; Hussain, K. What Is a Normal Blood Glucose? Arch. Dis. Child. 2016, 101, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, K.H.; Jensen, G.C.; Balijepalli, A.S.; Cohan, B.E. Measurement of Glucose in Tears. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1902–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Li, H.; Hou, T.; Duan, W.; Li, F. Biosensors and Bioelectronics Paper-Based Fluorescent Sensor via Aggregation Induced Emission Fluorogen for Facile and Sensitive Visual Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide and Glucose. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 104, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, N.; Ali, S.; Shaegh, M.; Huan, S.; Ge, L.; Ngin, S. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical A Paper-Based Amperometric Glucose Biosensor Developed with Prussian Blue-Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, M.; Cánovas, R.; Andrade, F.J. Paper-Based Enzymatic Electrode with Enhanced Potentiometric Response for Monitoring Glucose in Biological Fl Uids. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, C. A Novel Screen-Printed Microfluidic Paper-Based Electrochemical Device for Detection of Glucose and Uric Acid in Urine. Biomed. Microdevices 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flávia, E.; Gabriel, M.; Garcia, P.T.; Lopes, F.M.; Karlos, W.; Coltro, T. Paper-Based Colorimetric Biosensor for Tear Glucose Measurements. Micromachines 2017, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X. An Electrochemical Microfluidic Paper-Based Glucose Sensor Integrating Zinc Oxide Nanowires. IEEE Xplore 2015, 447–450. [Google Scholar]
- Núnez-Bajo, E.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Costa-García, A.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T. Biosensors and Bioelectronics Integration of Gold-Sputtered Electro Fl Uidic Paper on Wire-Included Analytical Platforms for Glucose Biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rungsawang, T.; Punrat, E.; Adkins, J.; Henry, C. Development of Electrochemical Paper-Based Glucose Sensor Using Cellulose-4-Aminophenylboronic Acid-Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama, E.C. Biosensors and Bioelectronics Paper-Based Maskless Enzymatic Sensor for Glucose Determination Combining Ink and Wire Electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Yin, F. Sensitive Enzymatic Glucose Biosensor Fabricated by Electrospinning Composite Nanofibers and Electrodepositing Prussian Blue Film. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 694, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, X.; Ju, H. Amperometric Glucose Sensor Based on Catalytic Reduction of Dissolved Oxygen at Soluble Carbon Nanofiber. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Teng, H.; Hou, H.; You, T. Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensor Based on Renewable Electrospun Ni Nanoparticle-Loaded Carbon Nanofiber Paste Electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3329–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaofang, S.; Jun, R.; Xianwei, M.; Xiangling, R.; Fangqiong, T. A Novel Platform for Enhanced Biosensing Based on the Synergy Effects of Electrospun Polymer Nanof Bers And. Analyst 2013, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Su, L.; Filosa, R., Jr.; Lei, Y. Glucose Biosensor Using Glucose Oxidase and Electrospun Mn2O3-Ag Nanofibers. Electroanalysis 2011, 1912–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapountzi, E.; Soc, J.E.; Sapountzi, E.; Braiek, M.; Farre, C.; Arab, M. One-Step Fabrication of Electrospun Photo-Cross-Linkable Polymer Nanofibers Incorporating Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes and Enzyme for Biosensing One-Step Fabrication of Electrospun Photo-Cross-Linkable Polymer Nanofibers Incorporating Multiwall Carbon Nanot. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhen-Gang, W.; You, W.; Hui, X.; Guang, L.; Zhi-Kang, X. Carbon Nanotube-Filled Nanofibrous Membranes Electrospun from Poly(Acrylonitrile-Co-Acrylic Acid) for Glucose Biosensor. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 2955–2960. [Google Scholar]
- Demirci Uzun, S.; Kayaci, F.; Uyar, T.; Timur, S.; Toppare, L. Bioactive Surface Design Based on Functional Composite Electrospun Nanofibers for Biomolecule Immobilization and Biosensor Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5235–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



















| Model | Equation | Purpose | Assumptions | Definitions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classical model | Lucas-Washburn (L-W) | (1) | To describe capillary flow in parallel cylindrical tubes | 1. Constant cross-sectional area; 2. Inertial and gravitational forces are ignored; 3. Uniform pores and pore distribution; 4. Unlimited fluid reservoir volume; 5. No wicking effect due to channel boundaries; 6. Laminar flow; 7. Low-viscosity incompressible fluid; 8. No evaporation; 9. Single-phase fluid | l(t), distance traveled by the fluid σ, surface tension r, effective pore radius θ, liquid–fiber contact angle μ, fluid viscosity t, time ϕ, paper porosity h, paper thickness qo, evaporation rate δ, the gap between materials enclosing paper ρ, fluid density g, gravity k, experimental constant β, experimental constant θb, contact angle at boundary μe, effective viscosity c, constant for water | |
| Alternative models | L-W modified eq. by Camplisson et al. | (2) | To describe capillary flow in parallel cylindrical tubes, including fluid evaporation effects | 1. Same as those mentioned in the L-W model with the exemption of evaporation effects. | ||
| L-W modified eq. by Jahanshahi et al. | (3) | To describe the flow rate of fluids within paper-based microfluidic analytical devices evaluating the gravitational effects, inclination angles, and covering films. | 1. Same as those mentioned in the L-W model with the exemption that the time scale associated with full penetration of the fluid into the paper is much smaller than the time scale associated with liquid rise. | |||
| L-W modified eq. by Hong and Kim | (4) | To describe capillary flow in parallel cylindrical tubes considering the effect due to hydrophobic barriers | 1. Same as those mentioned in the L-W model: 2. Capillaries next to a hydrophobic barrier have a contact angle (θb) different from those in bulk; θb > 90° to prevent imbibition through the boundary | |||
| L-W modified eq. by Feng et al. | (5) | To describe capillary flow in parallel cylindrical tubes considering viscosity and slippage | 1. Same as those mentioned in the L-W model with the exemption of no-slip fluid-solid boundary condition and effective viscosity. | |||
| Classical model | Darcy’s Law | (6) | To describe flow through porous media. It can be used to characterize the flow rate in fibrous mats. | 1. Incompressible fluid; 2. Viscous effects neglected; 3. Single-phase fluid; 4. Laminar flow; 5. Uniform pores and pore distribution | Q, volumetric flow rate κ, paper permeability W, channel width H, channel height L, paper length ΔP, Pressure difference V, voltage Ri, ith electric resistance μb, effective flow viscosity u = (ux,uy), average flow velocity in the porous medium S, saturation θi, inclination angles of paper strip with respect to horizontal direction R0, initial load D, diffusive coefficient k, experimental constant β, experimental constant θb, contact angle at boundary | |
| Alternative models | Darcy’s Law electrical circuit analogy | (7) | To describe a system with n-connected sections of varying geometry. The flow rate through the fluidic circuit can be modeled using an electrical circuit analogy. | 1. Incompressible fluid; 2. Viscous effects neglected; 3. Single-phase fluid; 4. Laminar flow; 5. Uniform pores and pore distribution | ||
| Brinkman | (8) | To describe fluid flow in a porous medium with high porosity. | 1.Effective viscosity is assumed to be equal to the fluid viscosity; Laminar flow; 3. Incompressible fluid; 4. Single-phase fluid; 5. Uniform pores and pore distribution | |||
| Richards | (9) | To describe liquid wicking behavior in thin saturated or unsaturated fibrous materials. | 1. Capillary pressure and relative permeability depend on local saturation and volume of porous material. 2. Viscous effects neglected; 3. Single-phase fluid; 4. effects of inertial force and hydrostatic pressure are ignored; 5. Laminar flow | |||
| Elizalde et al. | (10) | To address fluid transport in paper with non-uniform cross-sections. | 1.Inertial and gravitational forces are ignored; 2. Viscous effects neglected; 3. Single-phase fluid; 4. Laminar flow; 5. Uniform pores and pore distribution 6. Environmental effects ignored |
| Transduction | Working Electrode | Analyte | Sample | Analytical Performance | App | Ref. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Technique | Material | Fabrication | Functionalization | Source | Vol [L] | LOD [M] | Linear Range [M] | |||
| AMP/Con | CA/EIS | PEDOT:PSS | DC | Iron Oxide NPs | CEA | Artificial serum | Not reported | Not reported | 4–25 ng/mL * | CD | [82] |
| AMP | SWV | Cellulose | IP | GR-PANI | HPV | Synthetic HPV solution | Not reported | 2.3 | 10–200 | CD | [83] |
| AMP | CV/PV | Cellulose | SP | GR | Casein | Bovine milk | Not reported | 15.5 | 48.5–485 | FQC | [84] |
| AMP | CV/DPV | Cellulose | SP/WP/DCa | AuNPs/Iron Oxide | CHIKV | Tris-EDTA buffer | 3 | 0.1 | 0.001–100 | CD | [85] |
| AMP | CV | Cellulose | SP/ES/DC | GR/PVD/PANI + SDS | Cholesterol | Human serum | Not reported | 1 | 50–10 | CD | [86] |
| AMP | DPV | Cellulose | SP | AuNPs | EGFR | Saliva | 10 | 0.167 | 0.5–500 | CD | [87] |
| AMP | CV | GR | SP | CB-PBNPs | EtOH | Beer | 100 | 0.52 | up to 10 | FQC | [48] |
| AMP | CV | Cellulose | SP | - | Glucose | Sodas | 5 | 0.18 | 0.5–5 | FQC | [88] |
| AMP | CV/CA | Cellulose | SP | Glucose | Human blood | 10 | Not reported | up to 25 | CD | [89] | |
| POT | - | Pt | SPU | Nafion | Glucose | Orange Juice | Not reported | 0.5 | 0.03–1.0 | FQC | [90] |
| AMP | - | - | SP | - | Glucose | Human serum | 0.5 | Not reported | 0–24 | POCT | [91] |
| AMP | CA | Graphite | SP | - | Glucose | Soft drinks | 10 | 0.33 | 0.5–50 | FQC | [92] |
| AMP | CA | Au/Carbon | ED | MSA/EDC/NHS | Glucose | Artificial serum | Not reported | 0.6 | 2–21.97 | CD | [93] |
| AMP | - | Cu/RGO | PD | - | Glucose | Artificial serum | 0.1 | 0.5 | 2 –2 2–13 | CD | [94] |
| AMP | CA | C/PE | SP | Glucose | Glucose solution | 16 | 470 | 0–16 | CD | [95] | |
| AMP | CA | Au/Cellulose | ED | Nano-Dendritic Au | Glucose | Glucose solution | Not reported | 0.6 | 10–15 | CD | [96] |
| AMP | - | Co-MOF/C cloth/filter paper | - | Glucose | Glucose solution | Not reported | 0.15 | 0.8–16 | CD | [97] | |
| AMP | CA | CoPc/GR/IL/C/filter paper | SP | Glucose | Human serum/Honey | 50 | 0.67 | 0.01–1.3/1.3 | CD | [98] | |
| AMP | CV | Au NPs/SWCNTs/NC | ED/WP | - | Glucose | Glucose solution | Not reported | 148 | 0.5–10 | POCT | [99] |
| AMP | CV | Cellulose | SP | - | H2O2 | Lens cleaning sol. | 5 | 4.1 | 0.02–0.5 | CD/Env. | [100] |
| Con | LSV | Ag | Brush painting | - | HSA | HSA-PB/BSA-PB sol. | 20 | 1 | 0.015–9.43 | CD | [101] |
| AMP/IMP | CV/EIS | Graphite | SP | - | L-Tyrosine | HB plasma | 3 | 0.02 | 50–600 | CD | [102] |
| AMP | CV | Cellulose | - | PBNPs + Cu | MeBut | Candies/Essences | Not reported | 0.8 | 0.25–30 | FQC | [30] |
| AMP | CV/CA | Cellulose | SP | CB-PBNPs | Nerve agents | Paraoxon | 5 | 3 μg/L * | 0–25 μg/L * | EM | [103] |
| AMP | CV/DPV | Cellulose | SP | Au NRs | Ovalbumin | - | 5 | 19 | 22–22 | CD | [104] |
| AMP | CA | Graphite | SP | CB + PBNPs | Atrazine | River water | 5 | 9.3 | 93–464 | EM. | [47] |
| IMP | - | Ag | DC | - | PSA | PSA + PB solutions | Not reported | 39 | 0–17 | CD | [105] |
| AMP | - | GR | SP | CB-PBNPs | Sulfur mustard | Mustard agent solutions | 1.5 | 1 | 0–6 | POCT | [35] |
| AMP | SWV | Cellulose | SP | GR quantum dots | UA/CREAT | Human urine | Not reported | 3.7 1 | 10–3 | CD | [106] |
| POT | - | Pt/filter paper | SPU | Nafion | Glucose | Artificial serum | 25 | 0.1 | 0.3–3 | POCT | [107] |
| POT | - | Pt/filter paper | SPU | Aquivion | Glucose | Artificial serum | 25 | 0.16 | 0.5–10 | POCT | [108] |
| Transduction | Electrospun Mats | Analyte | Recognition | Sample | Analytical Performance | App. | Ref. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Technique | Collector | ES Solution | Function | Functionalization Post-ES | LOD [M] | Linear Range [M] | |||||
| AMP | CV | - | PVA/PAMAM-Mt/GC | Substrate | GA | Glucose | E: PyOx | Soft drink cola | 0.7 | 5–0.25 | FQC | [109] |
| AMP | CA | FTO | PVP/Chi/rGO | Substrate | GA | 17α-EE | E: Laccase | Human urine | 0.15 | Not reported | CD | [110] |
| AMP | - | Pt | PAN/Mt | Substrate | DDAC | Glucose | E: GOx | Fruit juices | 2.4 | 1–2.452.45–15 | FCQ | [111] |
| AMP | CV | ITO | PAN/AgNO3 | Coating | EDC/NHS | Triglyceride | E: Lip-GLDH | Artificial sample | 0.6 | 2.3– | CD | [112] |
| AMP | CV | GC | PAN | Precursor | Pyrolysis: NiCo2S4/EGF | Glucose | - | Glucose solution | 0.167 | 0.5–3.571 | POCT | [113] |
| AMP | CV | GC | PAN | Precursor | Carbonization: NiCo2O4/ECF | Glucose | - | Glucose solution | 1.5 | –19.175 | POCT | [114] |
| AMP/IMP | CV/EIS | GC | PAN/SnO2 | Coating | MPA/EDC-NHS | Atrazine | I: anti-atrazine Ab | Spiked water | 0.9 | 1–1 | EM | [115] |
| IMP | ElS | - | PEDOT/NBR | Substrate | ON probes/PAA brushes | NHL gene | DNA | Artificial solution | 1 | 1 to 100 | CD | [116] |
| IMP | EIS | - | PAN | Coating | - | Zearalenone | - | Artificial food | 1.66 | 5–30 60 to 100 | - | [117] |
| IMP | EIS | - | CAc | Substrate | ZIF-8/MWCNTs/Au | Glucose | E: GOx | Synthetic sample | 5.347 | 1–10 | CD | [118] |
| IMP | EIS | FTO | PA6/PPy | Coating | ZnO NPs | Urea | E: Urease | Milk | 1.8 | 17–42 | FQC | [119] |
| IMP | EIS | Au | PVA/PEI | Coating | Au NPs | Glucose | E: GOx | Synthetic sample | 0.9 | 10–200 | CD | [120] |
| IMP | EIS | CPE | PVA/Honey | Coating | Au NPs/MWCNTs | CEA | I: Anti-CEA | Clinical serum | 0.5 | 2.2 –694 | CD | [121] |
| IMP | CR | Si glass | PANi/PEO | Coating | - | DENVCP | DNA probe | Blood serum | 1.9 | 10 –1 | CD | [122] |
| POT | - | - | PMMA | Substrate | Ca2+ Ionophores/Nafion/Au | Calcium ions | Ionophores | Artificial sweat | 14 | 1 | CD | [123] |
| Transduction | Analyte | Sample | Recognition Element | Analytical Performance | Response Time [min] | App. | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Principle | Source | Volume [μL] | Type | LOD [M] | Linear Range [M] | ||||
| Spectroscopy | CL | PSA | HS | 5 | I: Anti-PSA Ab | 26 | 33–0.67 | 10 | CD | [45] |
| Colorimetry | - | CEA | HS | 5 | I: Anti-CEA Ab | 14 | 28–167 | 120 | CD | [46] |
| Colorimetry | - | E. coli/L. monocytogenes/S. aureus | Synthetic sample | 40 | DNA: Biotinylate capture probes | 1 pg/μL * | 1 ng/μL–1 pg/μL * | 40–50 | FQC/CD | [133] |
| Colorimetry | - | Immunoglobulins | Bovine serum albumin | 5 | I: Biotinylated antimouse IgG Ab | 2 | Not reported | 24 | CD | [134] |
| Colorimetry | - | Alkaline phosphatase | Milk | - | I: Anti-ALP Ab | 0.87 U/mL * | 10–1000 U/mL * | 13 | FQC | [135] |
| Colorimetry | - | Glucose | Artificial Urine | 5 | E: GOx+HRP | Not reported | 0–2 | 30 | CD | [43] |
| Colorimetry | - | Dengue | Synthetic sample | 100 | I: Anti-Dengue Ab | 8 p.f.u/mL * | Not reported | - | CD | [136] |
| Colorimetry | - | Paromomycin sulfate/Tetracycline/Hydrochloride/chloramphenicol/erythromycin | Water | 2 | E: b-galactosidase | 0.5, 2.1, 0.8 6.1 μg/mL * | Not reported | 120–1440 | Env. | [137] |
| Colorimetry | - | Glucose | Human Saliva | 50 | E: GOx | 1.2 | 0.5–75 | 0.75 | CD | [138] |
| Spectroscopy | Fluorescence | Phakopsora Pachyrhizi | Soybean | 2 | I: Anti-Phakopsora Pachyrhizi Ab | 2.2 ng/mL | 0.0032–3.2 μg/mL * | 60 | FQC | [139] |
| Spectroscopy | Fluorescence | Gold ions | Human Urine | 1 | WC: Cupriavidus metallidurans | 110 | Not reported | - | CD | [140] |
| - | Fluorescence | AFP | HS | 2.5 | I: Anti-AFP Ab | 6 | 14.3–12.9 | 60 | CD | [141] |
| Spectroscopy | SPR | Bovine haptoglobin | Bovine serum | 10 | I: Anti-haptoglobin Ab | 28 μg/mL * | 0.01–0.9 mg/mL * | 5 | CD | [142] |
| Transduction | Electrospun Mats | Analytical Performance | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Technique | Collector | ES Solution | Function | Functionalization Post-ES | Analyte | Recognition | Sample | LOD [M] | Linear Range [M] | App. | Ref. |
| FLU | MEF | - | PCL | Substrate | Ag@SiO2/PCL | IgG | Immuno-based | Artificial solution | Not reported | CD | [143] | |
| FLU | SM | Al foil | PAN/pVDB | Substrate | Boronic acid | S. aureus/E. coli | - | Beef-based nutrient broth | Not reported | Not reported | CD | [144] |
| FLU | SM | ITO | PVA/GQD | Coating | - | Glucose | GOx | Glucose solution | 10 | 0.25–24 | CD | [145] |
| SPE | SPM | - | Chi/PVA | Substrate | Guaiacol | Time/Temperature | Laccase | 4 °C Environment | Not reported | 1–38 days * | FCQ | [146] |
| SPE | SERS | - | PCL | Substrate | 4-MB/Au NPs/Ag NPs | PSA | Anti-PSA | Artificial solution | 0.03 | Not reported | CD | [147] |
| SPE | COL | - | PVA | Precursor | Red Cabbage Pigment | pH | Pigment | Fruit surfaces | Not reported | 2–12 pH * | FQC | [148] |
| SPE | COL | - | PHBV | Substrate | Nafion/BSA/GA | Paraoxon | AChE | Artificial solution | 36.3 | 36.3–0.2 | EM | [149] |
| SPE | UV-vis | Optical fiber | PPO | Coating | - | Ammonia | - | Volatile Vapor | 5.87 | Not reported | CD | [150] |
| - | SPM | ITO | PVA/GQD | Coating/Substrate | graphene QD | Glucose | GOx | Artificial solution | 12 | 1–10 | CD | [151] |
| SPE | COL/SPM | Al foil | PVA/anthocyanin | Substrate | Glutaraldehyde | Ferric ions | Anthocyanin | Water | 17.9 | 17.9–6.3 | POCT | [152] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores-Hernandez, D.R.; Santamaria-Garcia, V.J.; Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Bonilla-Rios, J. Paper and Other Fibrous Materials—A Complete Platform for Biosensing Applications. Biosensors 2021, 11, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050128
Flores-Hernandez DR, Santamaria-Garcia VJ, Melchor-Martínez EM, Sosa-Hernández JE, Parra-Saldívar R, Bonilla-Rios J. Paper and Other Fibrous Materials—A Complete Platform for Biosensing Applications. Biosensors. 2021; 11(5):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050128
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores-Hernandez, Domingo R., Vivian J. Santamaria-Garcia, Elda M. Melchor-Martínez, Juan Eduardo Sosa-Hernández, Roberto Parra-Saldívar, and Jaime Bonilla-Rios. 2021. "Paper and Other Fibrous Materials—A Complete Platform for Biosensing Applications" Biosensors 11, no. 5: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050128
APA StyleFlores-Hernandez, D. R., Santamaria-Garcia, V. J., Melchor-Martínez, E. M., Sosa-Hernández, J. E., Parra-Saldívar, R., & Bonilla-Rios, J. (2021). Paper and Other Fibrous Materials—A Complete Platform for Biosensing Applications. Biosensors, 11(5), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050128