An Origami Paper-Based Biosensor for Allergen Detection by Chemiluminescence Immunoassay on Magnetic Microbeads
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Functionalization of Magnetic Microbeads
2.3. Fabrication of the Origami µPAD Device
2.4. Assay Procedure
2.5. Data Elaboration and Statistics
2.6. Real Sample Processing
2.7. In Silico Simulations
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of OVA-MBs
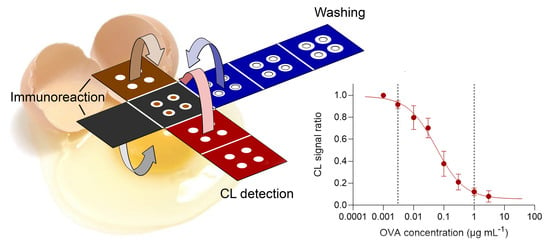
3.2. Design of the Origami µPAD
- A: base layer containing OVA-MBs (all (bio)chemical reactions took place in this layer);
- B: anti-leaching layer (a wax-coated sheet that reduced evaporation and prevented solution leaching during incubation);
- C: immunoreaction layer containing the anti-OVA-HRP immunoreagent;
- D1–D3: washing layers (collected the buffer in the washing step);
- E1–E2: CL detection layers containing the luminol/enhancer and sodium perborate CL detection reagents, respectively.
3.3. Optimization of the Origami µPAD and Assay Performance
3.4. Measurement of OVA with the Origami µPAD
3.5. Assay Specificity
3.6. Accuracy and Quantification of Ovalbumin in Real Samples
3.7. Stability of the Origami µPAD
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gargano, D.; Appanna, R.; Santonicola, A.; De Bartolomeis, F.; Stellato, C.; Cianferoni, A.; Casolaro, V.; Iovino, P. Food Allergy and Intolerance: A Narrative Review on Nutritional Concerns. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena-Torralba, A.; Pallás-Tamarit, Y.; Morais, S.; Maquieira, A. Recent advances and challenges in food-borne allergen detection. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 132, 116050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Vanga, S.K.; Wang, J.; Raghavan, V. Impact of food processing on the structural and allergenic properties of egg white. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeyrathne, E.D.N.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Ahn, D.U. Egg white proteins and their potential use in food processing or as nutraceutical and pharmaceutical agents—A review. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 3292–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.-L.; Ren, H.-L.; Li, Y.-S.; Hu, P.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.-S.; Yan, D.-M.; Hui, Q.; Liu, D.; Lin, C.; et al. A magnetic particles-based chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for rapid detection of ovalbumin. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 459, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Raghavan, V. A comprehensive overview of emerging processing techniques and detection methods for seafood allergens. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3540–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.H.; Reddy, Y.V.M.; Park, T.J.; Park, J.P. Recent advances in analytical strategies and microsystems for food allergen detection. Food Chem. 2021, 371, 131120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Ye, Y.; Ji, J.; Sun, J.; Sun, X. Advances on the rapid and multiplex detection methods of food allergens. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 6887–6907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabria, D.; Zangheri, M.; Pour, S.R.S.; Trozzi, I.; Pace, A.; Lazzarini, E.; Calabretta, M.M.; Mirasoli, M.; Guardigli, M. Luminescent Aptamer-Based Bioassays for Sensitive Detection of Food Allergens. Biosensors 2022, 12, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Hu, S.; Lai, X.; Peng, J.; Lai, W. Developmental trend of immunoassays for monitoring hazards in food samples: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 68–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabria, D.; Calabretta, M.; Zangheri, M.; Marchegiani, E.; Trozzi, I.; Guardigli, M.; Michelini, E.; Di Nardo, F.; Anfossi, L.; Baggiani, C.; et al. Recent Advancements in Enzyme-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassays. Sensors 2021, 21, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nardo, F.; Chiarello, M.; Cavalera, S.; Baggiani, C.; Anfossi, L. Ten Years of Lateral Flow Immunoassay Technique Applications: Trends, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Sensors 2021, 21, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, T.; McMahon, C.; Henry, C.S. Advances in Paper-Based Analytical Devices. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 13, 85–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calabretta, M.; Zangheri, M.; Calabria, D.; Lopreside, A.; Montali, L.; Marchegiani, E.; Trozzi, I.; Guardigli, M.; Mirasoli, M.; Michelini, E. Paper-Based Immunosensors with Bio-Chemiluminescence Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L. Microfluidic paper-based chips in rapid detection: Current status, challenges, and perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Gagandeep; Bhatia, R. Paper-based microfluidic devices: Fabrication, detection, and significant applications in various fields. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 41, 112–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.T.; Lantigua, D.; Meka, A.; Taing, S.; Pandher, M.; Camci-Unal, G. Paper-Based Sensors: Emerging Themes and Applications. Sensors 2018, 18, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roda, A.; Zangheri, M.; Calabria, D.; Mirasoli, M.; Caliceti, C.; Quintavalla, A.; Lombardo, M.; Trombini, C.; Simoni, P. A simple smartphone-based thermochemiluminescent immunosensor for valproic acid detection using 1,2-dioxetane analogue-doped nanoparticles as a label. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 279, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-A.; Yeh, W.-S.; Tsai, T.-T.; Li, Y.-D.; Chen, C.-F. Three-dimensional origami paper-based device for portable immunoassay applications. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colozza, N.; Caratelli, V.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. Origami Paper-Based Electrochemical (Bio)Sensors: State of the Art and Perspective. Biosensors 2021, 11, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noviana, E.; Ozer, T.; Carrell, C.S.; Link, J.S.; McMahon, C.; Jang, I.; Henry, C.S. Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices: From Design to Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 11835–11885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roda, A.; Arduini, F.; Mirasoli, M.; Zangheri, M.; Fabiani, L.; Colozza, N.; Marchegiani, E.; Simoni, P.; Moscone, D. A challenge in biosensors: Is it better to measure a photon or an electron for ultrasensitive detection? Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 155, 112093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.; Wang, S.; Song, X.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. 3D Origami-based multifunction-integrated immunodevice: Low-cost and multiplexed sandwich chemiluminescence immunoassay on microfluidic paper-based analytical device. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3150–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, C. A novel paper-based microfluidic enhanced chemiluminescence biosensor for facile, reliable and highly-sensitive gene detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhao, M.; Li, H. Paper-based chemiluminescence immunodevice with temporal controls of reagent transport technique. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 250, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabria, D.; Zangheri, M.; Trozzi, I.; Lazzarini, E.; Pace, A.; Mirasoli, M.; Guardigli, M. Smartphone-Based Chemiluminescent Origami µPAD for the Rapid Assessment of Glucose Blood Levels. Biosensors 2021, 11, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E.; Gabriel, E.F.M.; Benavidez, T.E.; Coltro, W.; Garcia, C.D. Modification of microfluidic paper-based devices with silica nanoparticles. Analyst 2014, 139, 5560–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunningham, J.C.; Scida, K.; Kogan, M.R.; Wang, B.; Ellington, A.D.; Crooks, R.M. Paper diagnostic device for quantitative electrochemical detection of ricin at picomolar levels. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3707–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, G.A.; Pérez-Rodríguez, S.; Reguera, E. Magnetic paper—Based ELISA for IgM-dengue detection. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 4921–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zangheri, M.; Mirasoli, M.; Guardigli, M.; Di Nardo, F.; Anfossi, L.; Baggiani, C.; Simoni, P.; Benassai, M.; Roda, A. Chemiluminescence-based biosensor for monitoring astronauts’ health status during space missions: Results from the International Space Station. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 129, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trashin, S.A.; Cucu, T.; Devreese, B.; Adriaens, A.; De Meulenaer, B. Development of a highly sensitive and robust Cor a 9 specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of hazelnut traces. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 708, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anfossi, L.; Di Nardo, F.; Russo, A.; Cavalera, S.; Giovannoli, C.; Spano, G.; Baumgartner, S.; Lauter, K.; Baggiani, C. Silver and gold nanoparticles as multi-chromatic lateral flow assay probes for the detection of food allergens. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 411, 1905–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swindells, M.B.; Porter, C.T.; Couch, M.; Hurst, J.; Abhinandan, K.; Nielsen, J.H.; Macindoe, G.; Hetherington, J.; Martin, A.C. abYsis: Integrated Antibody Sequence and Structure—Management, Analysis, and Prediction. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abysis. Available online: http://www.abysis.org (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Abymod. Available online: http://abymod.abysis.org (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, P.; Li, B.; Huang, S.-Y. HDOCK: A web server for protein–protein and protein–DNA/RNA docking based on a hybrid strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W365–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HDOCK Server. Available online: http://hdock.phys.hust.edu.cn (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Xue, L.C.; Rodrigues, J.P.; Kastritis, P.L.; Bonvin, A.M.; Vangone, A. PRODIGY: A web server for predicting the binding affinity of protein–protein complexes. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3676–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prodigy. Available online: https://wenmr.science.uu.nl/prodigy (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J.C. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RCSB Protein Data Bank. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- DeLano, W.L. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System; DeLano Scientific: San Carlos, CA, USA, 2002; Available online: http://www.pymol.org (accessed on 4 September 2022).
- Montiel, V.R.-V.; Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Campuzano, S.; Pellicanò, A.; Reviejo, J.; Cosio, M.S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Simultaneous Determination of the Main Peanut Allergens in Foods Using Disposable Amperometric Magnetic Beads-Based Immunosensing Platforms. Chemosensors 2016, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Q.; Zheng, H.-N.; Jiang, C.; Li, K.; Xiao, S.-J. EDC/NHS activation mechanism of polymethacrylic acid: Anhydride versus NHS-ester. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 69939–69947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, A.; Montero-Calle, A.; Barderas, R.; Calero, M.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J. Electrochemical immunoplatform to unravel neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s disease through the determination of neurofilament light protein. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 371, 137815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidal, J.M.G.; Valverde, A.; Benedé, S.; Molina, E.; Moreno-Guzmán, M.; López, M.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Escarpa, A.; Campuzano, S. Rapid diagnosis of egg allergy by targeting ovalbumin specific IgE and IgG4 in serum on a disposable electrochemical immunoplatform. Sens. Diagn. 2021, 1, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, S.; Fenton, E.M.; Gallegos, G.R.; Petsev, D.N.; Sibbett, S.S.; Stone, H.A.; Zhang, Y.; López, G.P. Imbibition in Porous Membranes of Complex Shape: Quasi-stationary Flow in Thin Rectangular Segments. Langmuir 2009, 26, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deegan, R.D.; Bakajin, O.; Dupont, T.F.; Huber, G.; Nagel, S.R.; Witten, T.A. Capillary flow as the cause of ring stains from dried liquid drops. Nature 1997, 389, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.K.; Joung, H.-A.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.-G. Vertical flow immunoassay (VFA) biosensor for a rapid one-step immunoassay. Lab Chip 2012, 13, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wu, J.; Gan, Y.; Hanaor, D.A.H.; Chen, C. Evaporation Limited Radial Capillary Penetration in Porous Media. Langmuir 2016, 32, 9899–9904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modha, S.; Castro, C.; Tsutsui, H. Recent developments in flow modeling and fluid control for paper-based microfluidic biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178, 113026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, E.W. The Dynamics of Capillary Flow. Phys. Rev. (Ser. I) 1921, 17, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darcy, H. Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon: Exposition et Application, 1st ed.; Victor Dalmont Libraire des Corps imperiaux des ponts et chaussées et des mines: Paris, France, 1856. [Google Scholar]
- Gasperino, D.; Baughman, T.; Hsieh, H.V.; Bell, D.; Weigl, B.H. Improving Lateral Flow Assay Performance Using Computational Modeling. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2018, 11, 219–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Bhushan, P.; Bhattacharya, S. Fluid transport mechanisms in paper-based microfluidic devices. In Paper Microfluidics. Advanced Functional Materials and Sensors, 1st ed.; Bhattacharya, S., Kumar, S., Agarwal, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 7–28. [Google Scholar]
- Das, D.; Singh, T.; Ahmed, I.; Masetty, M.; Priye, A. Effects of Relative Humidity and Paper Geometry on the Imbibition Dynamics and Reactions in Lateral Flow Assays. Langmuir 2022, 38, 9863–9873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordorwu, V.; Tegladza, I.; Okoampah, E. A simple two-dimensional convective-diffusive based modelling study of a biosensor for glucose detection. J. Chem. Stud. 2022, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, C.Y. An Introduction to Computational Fluid Mechanics, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Oneill, M.E.; Chorlton, F. Ideal and Incompressible Fluid Dynamics, 1st ed.; Halsted Press: Chichester, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Khetan, R.; Curtis, R.; Deane, C.M.; Hadsund, J.T.; Kar, U.; Krawczyk, K.; Kuroda, D.; Robinson, S.A.; Sormanni, P.; Tsumoto, K.; et al. Current advances in biopharmaceutical informatics: Guidelines, impact and challenges in the computational developability assessment of antibody therapeutics. mAbs 2022, 14, 2020082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummer, A.M.; Abanades, B.; Deane, C.M. Advances in computational structure-based antibody design. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2022, 74, 102379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.H.B. Immunochemical techniques. In Clinical Chemistry: Principles, Techniques, and Correlations, 7th ed.; Bishop, M.L., Fody, E.P., Schoeff, L.E., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 160–178. [Google Scholar]
- He, J. Practical guide to ELISA development. In The Immunoassay Handbook: Theory and Applications of Ligand Binding, ELISA and Related Techniques, 4th ed.; Wild, D., Ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 381–393. [Google Scholar]
- Leelananda, S.P.; Lindert, S. Computational methods in drug discovery. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 2694–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, F.; Lai, L.; Pei, J. Computational Chemical Synthesis Analysis and Pathway Design. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakliang, P.; Yoon, S.; Choi, S. Emerging computational approaches for the study of regio- and stereoselectivity in organic synthesis. Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 5165–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, V.; Alessandrini, S.; Biczysko, M.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Clary, D.C.; McCoy, A.B.; DiRisio, R.J.; Neese, F.; Melosso, M.; Puzzarini, C. Computational molecular spectroscopy. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2021, 1, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dattamajumdar, A.; Jacobson, D.; Hood, L.; Osman, G. Rapid cloning of any rearranged mouse immunoglobulin variable genes. Immunogenetics 1996, 43, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Tao, H.; He, J.; Huang, S.-Y. The HDOCK server for integrated protein–protein docking. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 1829–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasson, U.; Perret-Liaudet, A.; van Waalwijk van Doorn, L.J.C.; Blennow, K.; Chiasserini, D.; Engelborghs, S.; Fladby, T.; Genc, S.; Kruse, N.; Kuiperij, H.B.; et al. A Practical Guide to Immunoassay Method Validation. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoud, L.; Cohrs, N.; Arosio, P.; Norrant, E.; Morbidelli, M. Effect of polyol sugars on the stabilization of monoclonal antibodies. Biophys. Chem. 2015, 197, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahanshahi-Anbuhi, S.; Kannan, B.; Leung, V.; Pennings, K.; Liu, M.; Carrasquilla, C.; White, D.; Li, Y.; Pelton, R.H.; Brennan, J.D.; et al. Simple and ultrastable all-inclusive pullulan tablets for challenging bioassays. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 2342–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangheri, M.; Di Nardo, F.; Calabria, D.; Marchegiani, E.; Anfossi, L.; Guardigli, M.; Mirasoli, M.; Baggiani, C.; Roda, A. Smartphone biosensor for point-of-need chemiluminescence detection of ochratoxin A in wine and coffee. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1163, 338515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Target Protein | Binding Affinity (ΔGbind) (kcal mol−1) | Dissociation Constant (Kd) (mol L−1) |
|---|---|---|
| OVA | −12.3 | 8.9 × 10−10 |
| Lys | −10.9 | 1.1 × 10−8 |
| BSA | −9.1 | 2.1 × 10−7 |
| Concentration of OVA Spiked (µg mL−1) | Concentration of OVA Measured (µg mL−1) | Recovery (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 133 |
| Sample 2 | 0.010 | 0.009 | 89.2 |
| Sample 3 | 0.020 | 0.025 | 124 |
| Sample 4 | 0.100 | 0.083 | 82.6 |
| Sample 5 | 0.400 | 0.383 | 95.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lazzarini, E.; Pace, A.; Trozzi, I.; Zangheri, M.; Guardigli, M.; Calabria, D.; Mirasoli, M. An Origami Paper-Based Biosensor for Allergen Detection by Chemiluminescence Immunoassay on Magnetic Microbeads. Biosensors 2022, 12, 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100825
Lazzarini E, Pace A, Trozzi I, Zangheri M, Guardigli M, Calabria D, Mirasoli M. An Origami Paper-Based Biosensor for Allergen Detection by Chemiluminescence Immunoassay on Magnetic Microbeads. Biosensors. 2022; 12(10):825. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100825
Chicago/Turabian StyleLazzarini, Elisa, Andrea Pace, Ilaria Trozzi, Martina Zangheri, Massimo Guardigli, Donato Calabria, and Mara Mirasoli. 2022. "An Origami Paper-Based Biosensor for Allergen Detection by Chemiluminescence Immunoassay on Magnetic Microbeads" Biosensors 12, no. 10: 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100825
APA StyleLazzarini, E., Pace, A., Trozzi, I., Zangheri, M., Guardigli, M., Calabria, D., & Mirasoli, M. (2022). An Origami Paper-Based Biosensor for Allergen Detection by Chemiluminescence Immunoassay on Magnetic Microbeads. Biosensors, 12(10), 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100825