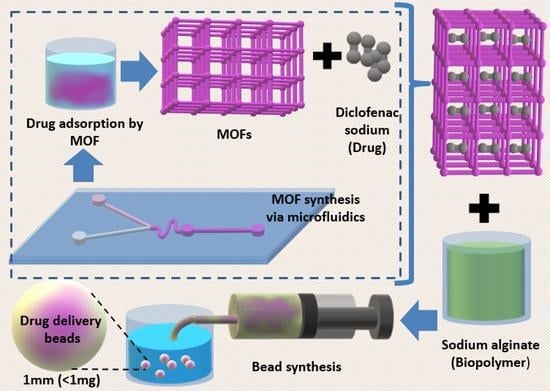
Microfluidic-Assisted Synthesis of Metal—Organic Framework —Alginate Micro-Particles for Sustained Drug Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Microfluidic Device Fabrication
2.3. Synthesis Methods
2.3.1. Synthesis of ZIF-67 and Zn-ZIF-67
2.3.2. Drug Loading
2.3.3. MOF–Alginate Bead Synthesis
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Adsorption Studies
2.6. Drug Release Studies
2.7. Cytotoxicity Studies
3. Results
3.1. Characterization
3.2. Adsorption Studies
Concentration and Time Studies
3.3. Drug Release Studies
3.4. Cytotoxicity Studies
4. Discussion
4.1. Characterization
4.2. Adsorption Studies and Drug Release Studies
4.3. Cytotoxicity Studies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uthappa, U.T.; Brahmkhatri, V.; Sriram, G.; Jung, H.-Y.; Yu, J.; Kurkuri, N.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Altalhi, T.; Neelgund, G.M.; Kurkuri, M.D. Nature engineered diatom biosilica as drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2018, 281, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Herrero, E.; Fernández-Medarde, A. Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilczewska, A.Z.; Niemirowicz, K.; Markiewicz, K.H.; Car, H. Nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Pharmacol. Rep. 2012, 64, 1020–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.; Uthappa, U.T.; Sadhasivam, T.; Altalhi, T.; Soo Han, S.; Kurkuri, M.D. Abundant cilantro derived high surface area activated carbon (AC) for superior adsorption performances of cationic/anionic dyes and supercapacitor application. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 459, 141577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruppathparambil, R.R.; Jose, T.; Babu, R.; Hwang, G.-Y.; Kathalikkattil, A.C.; Kim, D.-W.; Park, D.-W. A room temperature synthesizable and environmental friendly heterogeneous ZIF-67 catalyst for the solvent less and co-catalyst free synthesis of cyclic carbonates. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 182, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, V.; Uthappa, U.T.; Suneetha, M.; Altalhi, T.; Soo Han, S.; Kurkuri, M.D. Functional porous Ce-UiO-66 MOF@Keratin composites for the efficient adsorption of trypan blue dye from wastewater: A step towards practical implementations. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 142103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Rego, R.M.; Ajeya, K.V.; Jung, H.-Y.; Altalhi, T.; Neelgund, G.M.; Kigga, M.; Kurkuri, M.D. Underwater oleophobic-super hydrophilic strontium-MOF for efficient oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, H.D.; Walton, S.P.; Chan, C. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Drug Delivery: A Design Perspective. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 7004–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maranescu, B.; Visa, A. Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks as Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, C. Environment Responsive Metal–Organic Frameworks as Drug Delivery System for Tumor Therapy. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Ding, M.; Xie, X.; Yang, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, S.; Ouyang, R.; Miao, Y.J.R.a. Recent advances in nanosized metal organic frameworks for drug delivery and tumor therapy. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 3241–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-X.; Yang, Y.-W. Metal–Organic Framework (MOF)-Based Drug/Cargo Delivery and Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Sharabati, M.; Sabouni, R.; Husseini, G.A. Biomedical Applications of Metal & minus;Organic Frameworks for Disease Diagnosis and Drug Delivery: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bieniek, A.; Terzyk, A.P.; Wiśniewski, M.; Roszek, K.; Kowalczyk, P.; Sarkisov, L.; Keskin, S.; Kaneko, K. MOF materials as therapeutic agents, drug carriers, imaging agents and biosensors in cancer biomedicine: Recent advances and perspectives. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 117, 100743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeb, M.R.; Rabiee, N.; Mozafari, M.; Mostafavi, E. Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs)-Based Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery. Materials 2021, 14, 3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, S.; Pervaiz, E.; Ali, M. Synthesis and applications of metal oxide derivatives of ZIF-67: A mini-review. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 2253–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmykov, O.; Commenge, J.-M.; Alem, H.; Girot, E.; Mozet, K.; Medjahdi, G.; Schneider, R. Microfluidic reactors for the size-controlled synthesis of ZIF-8 crystals in aqueous phase. Mater. Des. 2017, 122, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yu, Z.; Sun, Z.; Wang, A.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y. Continuous synthesis of ZIF-67 by a microchannel mixer: A recyclable approach. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 327, 111423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazban-Shotorbani, S.; Gavins, F.; Kant, K.; Dufva, M.; Kamaly, N. A Biomicrofluidic Screening Platform for Dysfunctional Endothelium-Targeted Nanoparticles and Therapeutics. Adv. NanoBiomed Res. 2022, 2, 2270011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendre, A.; Bhat, M.P.; Lee, K.-H.; Altalhi, T.; Alruqi, M.A.; Kurkuri, M. Recent developments in microfluidic technology for synthesis and toxicity-efficiency studies of biomedical nanomaterials. Mater. Today Adv. 2022, 13, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Hui, Y.; Ranaweera, S.; Zhao, C.-X. Microfluidic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Small 2022, 18, 2106580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, B.; Peng, J.; Gao, D. Recent Development of Drug Delivery Systems through Microfluidics: From Synthesis to Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahme, K.; Dagher, N. Chemistry Routes for Copolymer Synthesis Containing PEG for Targeting, Imaging, and Drug Delivery Purposes. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Hu, D.; Yang, L.Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.-G.; Ouyang, X.k. Efficient adsorption of Levofloxacin from aqueous solution using calcium alginate/metal organic frameworks composite beads. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Gao, J.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Q. Recent progress in metal-organic frameworks-based hydrogels and aerogels and their applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 398, 213016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zou, L.; Zhou, X.; Hong, S.; Yao, L.; Li, C. Highly effective antibacterial zeolitic imidazolate framework-67/alginate fibers. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 375707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, S. Alginate Hydrogel: A Shapeable and Versatile Platform for In Situ Preparation of Metal–Organic Framework–Polymer Composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17395–17401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, M.P.; Kurkuri, M.; Losic, D.; Kigga, M.; Altalhi, T. New optofluidic based lab-on-a-chip device for the real-time fluoride analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1159, 338439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Ren, Q.; Wu, X.; Sun, J.; Wu, H.; Lei, J. Enhanced Water Stability in Zn-Doped Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-67 (ZIF-67) for CO2 Capture Applications. Chemistryselect 2018, 3, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, K.; Hussain, I.; Yao, F.; Fu, G. Sodium Alginate/Carboxyl-Functionalized Graphene Composite Hydrogel Via Neodymium Ions Coordination. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Feng, X.; Yu, J.-G.; Jiang, X. High performance of 3D porous graphene/lignin/sodium alginate composite for adsorption of Cd(II) and Pb(II). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 15651–15661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew Lin, K.-Y.; Yang, H.; Lee, W.-D. Enhanced removal of diclofenac from water using a zeolitic imidazole framework functionalized with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB). RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 81330–81340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Keywanlu, M.; Tayebee, R. Experimental and molecular dynamics simulation study on the delivery of some common drugs by ZIF-67, ZIF-90, and ZIF-8 zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 35, e6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jejurikar, A.; Seow, X.T.; Lawrie, G.; Martin, D.; Jayakrishnan, A.; Grøndahl, L.J.J.o.M.C. Degradable alginate hydrogels crosslinked by the macromolecular crosslinker alginate dialdehyde. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 9751–9758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molavi, H.; Moghimi, H.; Taheri, R.A. Zr-Based MOFs with High Drug Loading for Adsorption Removal of Anti-Cancer Drugs: A Potential Drug Storage. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bendre, A.; Hegde, V.; Ajeya, K.V.; Thagare Manjunatha, S.; Somasekhara, D.; Nadumane, V.K.; Kant, K.; Jung, H.-Y.; Hung, W.-S.; Kurkuri, M.D. Microfluidic-Assisted Synthesis of Metal—Organic Framework —Alginate Micro-Particles for Sustained Drug Delivery. Biosensors 2023, 13, 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070737
Bendre A, Hegde V, Ajeya KV, Thagare Manjunatha S, Somasekhara D, Nadumane VK, Kant K, Jung H-Y, Hung W-S, Kurkuri MD. Microfluidic-Assisted Synthesis of Metal—Organic Framework —Alginate Micro-Particles for Sustained Drug Delivery. Biosensors. 2023; 13(7):737. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070737
Chicago/Turabian StyleBendre, Akhilesh, Vinayak Hegde, Kanalli V. Ajeya, Subrahmanya Thagare Manjunatha, Derangula Somasekhara, Varalakshmi K. Nadumane, Krishna Kant, Ho-Young Jung, Wei-Song Hung, and Mahaveer D. Kurkuri. 2023. "Microfluidic-Assisted Synthesis of Metal—Organic Framework —Alginate Micro-Particles for Sustained Drug Delivery" Biosensors 13, no. 7: 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070737
APA StyleBendre, A., Hegde, V., Ajeya, K. V., Thagare Manjunatha, S., Somasekhara, D., Nadumane, V. K., Kant, K., Jung, H. -Y., Hung, W. -S., & Kurkuri, M. D. (2023). Microfluidic-Assisted Synthesis of Metal—Organic Framework —Alginate Micro-Particles for Sustained Drug Delivery. Biosensors, 13(7), 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070737