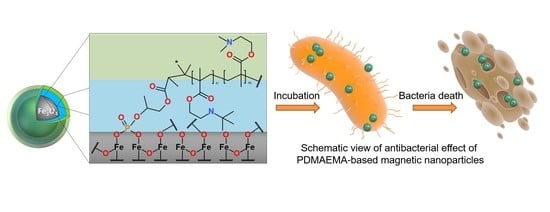
Cationic Polymer-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles with Antibacterial Properties: Synthesis and In Vitro Characterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Preparation of Sipomer PAM-200-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
2.3. Modification of MNP@S by DMAEMA-Based Polymers
2.4. Physicochemical Characterization
2.5. Antibacterial Activity of MNP@S-D and MNP@S-D-T
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of MNP and Their Physicochemical Characterization
3.2. Surface Modification of MNP with Sipomer PAM-200
3.3. Modification of MNP@S with PDMAEMA and P(DMAEMA-TBAEMA)
3.4. Antibacterial Activity of the Particles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAS | atomic absorption spectroscopy |
| Bc | coercive force |
| CFU | colony-forming units |
| Ð | dispersity |
| Dh | hydrodynamic diameter |
| DLS | dynamic light scattering |
| Dn | number-average diameter |
| Dw | weight-average diameter |
| HBSS | Hank’s balanced salt solution |
| LA | Luria agar |
| LB | Luria broth |
| MNP | magnetic nanoparticles |
| MNP@S | MNP coated by Sipomer PAM-200 |
| MNP@S-D | MNP coated by Sipomer PAM-200 and modified with poly[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate] |
| MNP@S-D-T1 | MNP coated by Sipomer PAM-200 and modified with 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate and 2-tert-butylaminoethyl methacrylate copolymer (0.75:0.25 mol/mol) |
| MNP@S-D-T2 | MNP coated by Sipomer PAM-200 and modified with 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate and 2-tert-butylaminoethyl methacrylate copolymer (0.5:0.5 mol/mol) |
| Ms | saturation magnetization |
| Mrs | remanent saturation magnetization |
| OA | oleic acid |
| OD | octadec-1-ene |
| PD | polydispersity |
| PDMAEMA | poly[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate] |
| PTBAEMA | poly(2-tert-butylaminoethyl methacrylate) |
| TEM | transmission electron microscope |
References
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Nisar, M.A.; Alvi, R.F.; Aslam, M.A.; Qamar, M.U.; et al. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Fair, R.J.; Tor, Y. Antibiotics and bacterial resistance in the 21st century, perspectives in medicinal chemistry. Perspect. Medicin. Chem. 2014, 6, 25–64. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, S.J.; Caleo, G.M.; Daulaire, N.; Elbe, S.; Matsoso, P.; Mossialos, E.; Rizvig, Z.; Røttingenh, J.A. Strategies for achieving global collective action on antimicrobial resistence. Bull. World Health Organ. 2015, 93, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, N.; Cang, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Song, X.; Farris, S.; Li, Y.; Fu, Y. Magnetism and NIR dual-response polypyrrole-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles for bacteria removal and inactivation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 126, 112143. [Google Scholar]
- Fatima, F.; Siddiqui, S.; Khan, W.A. Nanoparticles as novel emerging therapeutic antibacterial agents in the antibiotics resistant era. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 2552–2564. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, S.; Matuła, K.; Karoń, S.; Paczesny, J. Resistance and adaptation of bacteria to non-antibiotic antibacterial agents: Physical stressors, nanoparticles, and bacteriophages. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 435. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar]
- De, M.; Ghosh, P.S.; Rotello, V.M. Applications of nanoparticles in biology. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 4225–4241. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.K.; Naregalkar, R.R.; Vaidya, V.D.; Gupta, M. Recent advances on surface engineering of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Nanomedicine 2007, 2, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kostiv, U.; Farka, Z.; Mickert, M.J.; Gorris, H.H.; Velychkivska, N.; Pop-Georgievski, O.; Pastucha, M.; Odstrčilíková, E.; Skládal, P.; Horák, D. Versatile bioconjugation strategies of PEG-modified upconversion nanoparticles for bioanalytical applications. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 4502–4513. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.; Ramalho, P.; Viana, A.T.; Lopes, A.R.; Gonçalves, A.G.; Nunes, O.C.; Pereira, F.R.; Soares, S. Feasibility of using magnetic nanoparticles in water disinfection. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112410. [Google Scholar]
- Armijo, L.M.; Jain, P.; Malagodi, A.; Fornelli, Z.; Hayat, A.; Rivera, A.C.; French, M.; Smyth, H.; Osiński, M. Inhibition of bacterial growth by iron oxide nanoparticles with and without attached drug: Have we conquered the antibiotic resistance problem? Proc. SPIE 2015, 9338, 93381Q. [Google Scholar]
- De Toledo, L.A.S.; Rosseto, H.C.; Bruschi, M.L. Iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles as antimicrobials for therapeutics. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 23, 316–323. [Google Scholar]
- Portet, D.; Denizot, B.; Rump, E.; Lejeune, J.-J.; Jallet, P. Nonpolymeric coatings of iron oxide colloids for biological use as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 238, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konefał, M.; Cérnoch, P.; Patsula, V.; Pavlova, E.; Dybal, J.; Załęski, K.; Zhigunov, A. Enhanced ordering of block copolymer thin films upon addition of magnetic nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 9195–9205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tocchio, A.; Horák, D.; Babič, M.; Trchová, M.; Veverka, M.; Beneš, M.J.; Šlouf, M.; Fojtík, A. Magnetic poly(glycidyl metha-crylate) particles prepared in the presence of surface-modified γ-Fe2O3. J. Polym. Sci. A 2009, 47, 4982–4994. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.; Duvvuri, L.S.; Farah, S.; Beyth, N.; Domb, A.J.; Khan, W. Antimicrobial polymers. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 1969–1985. [Google Scholar]
- Milovic, N.M.; Wang, J.; Lewis, K.; Klibanov, A.M. Immobilized N-alkylated polyethylenimine avidly kills bacteria by rupturing cell membranes with no resistance developed. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 90, 715–722. [Google Scholar]
- Timofeeva, L.; Kleshcheva, N. Antimicrobial polymers: Mechanism of action, factors of activity, and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 475–492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cerichelli, G.; La Mesa, C.; Luchetti, L.; Mancini, G. Role of counterions in the catalytic activity and phase equilibria of phosphonium salts in water. Langmuir 2000, 16, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Hugues, C.; Bessy, C.; Bartolomeo, P.; Margaillan, A. Complexation of an acrylic resin by tertiary amines: Synthesis and chara-cterisation of new binders for antifouling paints. Eur. Polym. J. 2003, 39, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, A.; Ikeda, T. Multifunctional tetracoordinate phosphorus species with high self-organizing ability. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2000, 198, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Shen, J.; Zhu, Y. A study of pyridinium-type functional polymers. III. Preparation and characterization of insoluble pyridinium-type polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 78, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurdin, N.; Helary, G.; Sauvet, G. Biocidal polymers active by contact. III. Ageing of biocidal polyurethane coatings in water. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1993, 50, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlinson, L.B.; Ryan, S.M.; Mantovani, G.; Syrett, J.A.; Haddleton, D.M.; Brayden, D.J. Antibacterial effects of poly(2-(dimethylamino ethyl)methacrylate) against selected Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.; Sanchez, M.; Elasri, M.O.; Lowe, A.B. Antimicrobial activity of statistical polymethacrylic sulfopropylbetaines against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancheva, E.; Paneva, D.; Maximova, V.; Mespouille, L.; Dubois, P.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Polyelectrolyte complexes between (cross-linked) N-carboxyethylchitosan and (quaternized) poly[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate]: Preparation, cha-racterization, and antibacterial properties. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Yuan, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, M.; Ni, P. Facile approach for DNA encapsulation in functional polyion complex for triggered intracellular gene delivery: Design, synthesis, and mechanism. Langmuir 2009, 25, 5199–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keely, S.; Ryan, S.M.; Haddleton, D.M.; Limer, A.; Mantovani, G.; Murphy, E.P.; Colgan, S.P.; Brayden, D.J. Dexamethasone–pDMAEMA polymeric conjugates reduce inflammatory biomarkers in human intestinal epithelial monolayers. J. Control. Release 2009, 135, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Yang, N.; Zhang, D. Poly(N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) modification of activated carbon for copper ions removal. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumo, A.; Bombalski, L.; Lin, Q.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Schneider, J.W.; Tilton, R.D. High capacity, charge-selective protein uptake by polyelectrolyte brushes. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4448–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.R.; Xiao, J.G.; Yang, B.; Wang, T.; Du, J.Z. Rationally engineering dual missions in one statistical copolymer nanocapsule: Bacterial inhibition and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon capturing. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, S.; Pagnoulle, C.; Galleni, M.; Compere, P.; Jerome, R.; Detrembleur, C. Polyolefin matrixes with permanent antibacterial activity: Preparation, antibacterial activity, and action mode of the active species. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2291–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, H.; Wu, D.; Fu, R. Preparation of antibacterial poly(methyl methacrylate) by solution blending with water-insoluble antibacterial agent poly[(tert-buty1amino) ethyl methacrylate]. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 3537–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-L.; Lee, K.-M.; Liu, Z.-X.; Lai, R.-Y.; Chen, C.-K.; Chen, W.-C.; Hsu, J.-F. Antimicrobial activity of electrospun polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers filled with poly[2-(tert-butylaminoethyl) methacrylate]-grafted graphene oxide nanosheets. Polymers 2020, 12, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsula, V.; Petrovský, E.; Kovářová, J.; Konefal, R.; Horák, D. Monodisperse superparamagnetic nanoparticles by thermolysis of Fe(III) oleate and mandelate complexes. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 2097–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsula, V.; Horák, D.; Kučka, J.; Macková, H.; Lobaz, V.; Francová, P.; Herynek, V.; Heizer, T.; Páral, P.; Šefc, L. Synthesis and modification of uniform PEG-neridronate-modified magnetic nanoparticles determines prolonged blood circulation and biodistribution in a mouse preclinical model. Sci Rep. 2019, 9, 10765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatan, A.B.; Venclíková, K.; Zasońska, B.A.; Patsula, V.; Pop-Georgievski, O.; Petrovský, E.; Horák, D. Antibacterial silver-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles: Design, synthesis and bactericidal effect. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsula, V.; Moskvin, M.; Dutz, S.; Horák, D. Size-dependent magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 2016, 88, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsula, V.; Kosinová, L.; Lovrić, M.; Ferhatovic Hamzić, L.; Rabyk, M.; Konefal, R.; Paruzel, A.; Šlouf, M.; Herynek, V.; Gajović, S.; et al. Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Synthesis by thermal decomposition of iron(III) glucuronate and application in magnetic resonance imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7238–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomassin, J.-M.; Lenoir, S.; Riga, J.; Jérôme, J.; Detrembleur, C. Grafting of poly[2-(tert-butylamino)ethyl methacrylate] onto polypropylene by reactive blending and antibacterial activity of the copolymer. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horák, D. Magnetic nano and microparticles in life sciences and medical imaging. In Magnetic Nanoheterostructures: Diagnostic, Imaging and Treatment; Sharma, S.K., Javed, Y., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 161–221. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Cha, J.M.; Yoon, J.Y.; Lee, J.-K.; Kim, Y.K. Magnetic multi-granule nanoclusters: A model system that exhibits universal size effect of magnetic coercivity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12135. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Kartikowati, C.W.; Horie, S.; Ogi, T.; Iwaki, T.; Okuyama, K. Correlation between particle size/domain structure and magnetic properties of highly crystalline Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-K.; Lee, M.-C.; Lin, Z.-I.; Lee, C.-A.; Tung, Y.-C.; Lou, C.-W.; Law, W.-C.; Chen, N.-T.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Lin, J.H. Intensifying the antimicrobial activity of poly[2-(tert-butylamino)ethyl methacrylate]/polylactide composites by tailoring their chemical and physical structures. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Xiao, S.; Chen, F.; Fan, P.; Yang, J. Salt-responsive “killing and release” antibacterial surfaces of mixed polymer brushes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 8938–8945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Particles | Dn (nm) | Ð | Dh (nm) | PD | ζ-Potential (mV) | Bc (mT) | Mrs (10−3 A∙m2/kg) | Ms (A∙m2/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNP | 16 | 1.02 | 36 a | 0.13 | - | - | - | - |
| MNP@-S | 16 | 1.03 | 28 a | 0.16 | - | - | - | - |
| MNP@S-D | 16 | 1.03 | 140 b | 0.19 | 48 | 0.0292 | 6.584 | 7.190 |
| MNP@S-D-T1 | 16 | 1.02 | 110 b | 0.18 | 51 | 0.0371 | 8.851 | 11.228 |
| MNP@S-D-T2 | 16 | 1.03 | 98 b | 0.17 | 46 | 0.0469 | 10.395 | 7.163 |
| Particles | Content (wt.%) | Coating c (wt.%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P a | Fe b | UV-Vis | Magnetometry | TGA | |
| MNP@S-D | 0.88 | 14.4 | 80 | 87 | 79 |
| MNP@S-D-T1 | 0.69 | 25.0 | 65 | 80 | 66 |
| MNP@S-D-T2 | 0.42 | 13.2 | 82 | 87 | 78 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shatan, A.B.; Patsula, V.; Dydowiczová, A.; Gunár, K.; Velychkivska, N.; Hromádková, J.; Petrovský, E.; Horák, D. Cationic Polymer-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles with Antibacterial Properties: Synthesis and In Vitro Characterization. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10091077
Shatan AB, Patsula V, Dydowiczová A, Gunár K, Velychkivska N, Hromádková J, Petrovský E, Horák D. Cationic Polymer-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles with Antibacterial Properties: Synthesis and In Vitro Characterization. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(9):1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10091077
Chicago/Turabian StyleShatan, Anastasiia B., Vitalii Patsula, Aneta Dydowiczová, Kristýna Gunár, Nadiia Velychkivska, Jiřina Hromádková, Eduard Petrovský, and Daniel Horák. 2021. "Cationic Polymer-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles with Antibacterial Properties: Synthesis and In Vitro Characterization" Antibiotics 10, no. 9: 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10091077
APA StyleShatan, A. B., Patsula, V., Dydowiczová, A., Gunár, K., Velychkivska, N., Hromádková, J., Petrovský, E., & Horák, D. (2021). Cationic Polymer-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles with Antibacterial Properties: Synthesis and In Vitro Characterization. Antibiotics, 10(9), 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10091077