Effect of Laser Remelting Power on Immersion Corrosion of Amorphous Al–Ti–Ni Coatings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Analysis and Discussion
3.1. Morphologies and EDS Analysis of Ti–Ni Powder
3.2. Image Mapping of Al–Ti–Ni Coating Surface
3.3. Cross-Section Analysis of Al–Ti–Ni Coating between the Coating and the Substrate
3.4. Line Scan Analysis of Al–Ti–Ni Coating Cross-Section
3.5. XRD Analysis
3.6. Scanning Analysis of Corrosion Products
3.7. Corrosion Mechanism
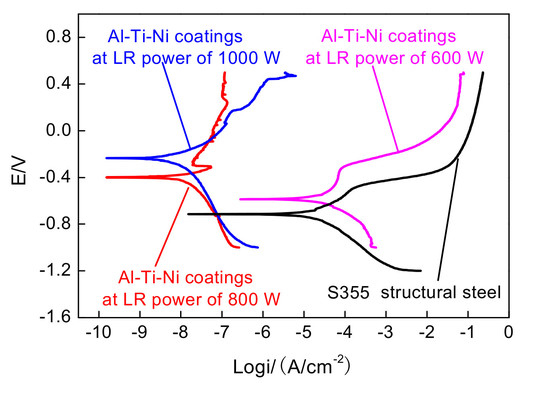
3.8. Electrochemical Corrosion
4. Conclusions
- At the LR powers of 600, 800, and 1000 W, the Al–Ti–Ni coating forms a metallurgical bonding with the substrate; the Al–Ti–Ni coating at the LR power of 1000 W shows the best surface and cross-sectional qualities and best performance. Certain amounts of AlNi, Al3Ti, Al3Ni2, Ti3O5, and Al2O3 amorphous phases are detected.
- The microstructure of Al–Ti–Ni coating at the LR power of 1000 W is uniform, and no obvious defects such as cracks and pores are observed. The corrosion mechanisms are pitting corrosion and uniform corrosion. In contrast, cracks and pores are present on the Al–Ti–Ni coating surfaces at the LR powers of 600 and 800 W, and the corrosion mechanisms are localized corrosion and pitting corrosion.
- Amorphous phases are detected in the Al–Ti–Ni coating at the LR powers of 600, 800, and 1000 W, and their corrosion potentials are higher than that of S355 steel; this indicates that the laser-remelted Al–Ti–Ni coating improves the electrochemical corrosion resistance of S355 steel. The electrochemical corrosion resistance increases with increasing LR powers.
- The corrosion potentials of Al–Ti–Ni coatings at the LR powers of 600, 800, and 1000 W are −0.586, −0.399, and −0.233 V, respectively. The corrosion potential of Al–Ti–Ni coating at the LR power of 1000 W shows a positive shift, indicating its higher electrochemical corrosion resistance.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernández, R.P.; Pardo, M.L. Offshore concrete structures. Ocean Eng. 2013, 58, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, S.B.; Lee, S.J. Effect of flow rate on electrochemical characteristics of marine material under seawater environment. Ocean Eng. 2017, 141, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.J.; Lee, H.S.; Karthick, S.; Saraswathy, V.; Yan, H.M. Long–time corrosion performance of blended cement concrete in the marine environment–A real–time study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Du, C.W.; Dai, C.D.; Li, X.G.; Zhang, B.W. Corrosion fatigue crack initiation and initial propagation mechanism of E690 steel in simulated seawater. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 708, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.B.; Wang, D.P.; Cheng, F.J.; Di, X.J.; Deng, C.Y.; Xu, W. Microstructural and mechanical performance of underwater wet welded S355 steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 238, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.J.; Zhai, Y.Z.; Leng, D.X.; Tian, X.J.; Mu, W.L. Research on structural damage detection of offshore platforms based on grouping modal strain energy. Ocean Eng. 2017, 140, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeman, P.; Zitek, M.; Zuzjakova, S.; Cerstvy, R. Amorphous Zr-Cu thin-film alloys with metallic glass behavior. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 696, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavoosi, M.; Barahimi, A. Corrosion behavior of amorphous–nanocrystalline Fe–Ni–Cr electrodeposited coatings. Surf. Interfaces 2017, 8, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.T.; Hou, J.X.; Zhang, X.R.; Guo, J.; Xu, L.F.; Fan, G.J. Influence of remelting treatment on corrosion behavior of amorphous alloys. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2017, 46, 296–300. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.B.; Wang, B.L.; Liu, Q.; Liang, X.B. In–situ synthesis of novel Al–Fe–Si metallic glass coating by arc spraying. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 716, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Xue, Y.F.; Cheng, X.W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.F.; Fu, H.M. Effect of element fitting on composition optimization of Al–Cu–Ti amorphous alloy by mechanical alloying. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 3348–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Perepezko, J.H. Al-based amorphous alloys: Glass-forming ability, crystallization behavior and effects of minor alloying additions. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 707, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhova, I.; Mironov, E.; Azarmi, F.; Safonov, A. Thermo–electrical properties of the alumina coatings deposited by different thermal spraying technologies. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 15392–15401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.X.; Yang, M.C.; Wang, R.Q.; Pang, X.M. Annealing behavior of aluminum coating prepared by arc spraying on P355NL1 steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 330, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, S.; Das, J.; Bandyopadhyay, P.P. Synthesis of mullite–based coatings from alumina and zircon powder mixtures by plasma spraying and laser remelting. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 154, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.C.; Kim, S.J. Corrosion behavior in seawater of arc thermal sprayed Inconel 625 coatings with sealing treatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 325, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.S.; Tian, Z.J.; Shen, L.D.; Liu, Z.D.; Huang, Y.H. Influences of laser remelting on microstructure of nanostructured Al2O3-13 wt.% TiO2 coatings fabricated by plasma spraying. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 4606–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Cao, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.T.; Cao, J.; Wang, L.L.; Huang, W.D. Regular eutectic and anomalous eutectic growth behavior in laser remelting of Ni-30 wt.% Sn alloys. Acta Mater. 2017, 126, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.L.; Yan, H.; Yao, C.W.; Li, Z.G.; Yu, Z.S.; Xu, P.Q. Synthesis of Fe–Ni–B–Si–Nb amorphous and crystalline composite coatings by laser cladding and remelting. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yao, J.H.; Hu, Y.; Song, S.Y. Suppression effect of a steady magnetic field on molten pool during laser remelting. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 351, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.G.; Yu, Z.S.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, P.L.; Yan, H.; Lu, Q.H.; Li, W.G.; Wang, Y. Microstructure evolution of laser remelted Al2O3 −13 wt.% TiO2 coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 576, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.B.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, F.F.; Wang, L.; Pan, Z.Y. Laser remelting of plasma–sprayed nanostructured Al2O3–20 wt.% ZrO2 coatings onto 316L stainless steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Liu, M.; Song, J.B.; Deng, C.M.; Deng, C.G. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of Fe–based amorphous coating prepared by HVOF. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 721, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, S.S.S.; Wang, X.H.; Yang, T.; Dong, C.; Hu, J.T.; Jiang, Y.Q. Mechanical and corrosion properties of Ti-Ni-Cu-Zr metallic glass matrix composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 727, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.T.; Jiang, C.H.; Xu, Z.; Cai, F.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Fu, P. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of Ti nanoparticles reinforced Ni-Ti composite coatings by electrodeposition. Mater. Des. 2015, 85, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.L.; Zhu, H.M.; Kuang, T.C.; Shi, J.; Liu, H.W.; Liu, Z.W. Laser cladding Al–based amorphous–nanocrystalline composite coatings on AZ80 magnesium alloy under water cooling condition. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 690, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Xi, Y.C.; Zhao, Y.H.; Liu, S.; Bai, S.L.; Liu, Z.D. Effects of laser re–melting and annealing on microstructure, mechanical property and corrosion resistance of Fe–based amorphous/crystalline composite coating. Mater. Charact. 2017, 127, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.F.; Jin, Y.J.; Li, Z.G.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Wu, M.F. Effect of the remelting scanning speed on the amorphous forming ability of Ni–based alloy using laser cladding plus a laser remelting process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 259, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Gong, Y.B.; Nie, G.M. Microstructures and corrosion resistance of Fe–based amorphous/nanocrystalline coating fabricated by laser cladding. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 728, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 6458-86 Metallic Coatings—Neutral Salt Spray Test (Nss Test); Standards Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1986.
- Cong, D.L.; Li, Z.S.; He, Q.B.; Chen, D.J.; Chen, H.B.; Yang, J.Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, H. Effects of unit size on thermal fatigue behavior of hot work steel repaired by a biomimetic laser remelting process. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 98, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, M.R.; Gargarella, P.; Gustmann, T.; Botta Filho, W.J.; Kiminami, C.S.; Eckert, J.; Pauly, S.; Bolfarini, C. Laser surface remelting of a Cu-Al-Ni-Mn shape memory alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 661, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sichani, H.R.; Salehi, M.; Edris, H.; Farani, M.T. The effect of APS parameter on the microstructural, mechanical and corrosion properties of plasma sprayed Ni–Ti–Al intermetallic coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 309, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Gibson, D.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, L.; Fu, Y.Q. Surface microstructures and corrosion resistance of Ni–Ti–Nb shape memory thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 414, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.J.; Wang, K.D.; Dong, X.; Duan, W.Q.; Wang, R.J.; Mei, X.S.; Wang, W.J.; Cui, J.L.; Zhang, S.; Xu, C.H. Evaluation of microstructural evolution and corrosion types in ultrasonic assisted laser re-melted thermal barrier coatings under exposure to molten salts. Mater. Lett. 2017, 188, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Annergren, I.; Pan, D.; Mai, T.A. Effect of laser surface remelting on the corrosion behavior of commercially pure titanium sheet. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 345, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mi, G.Y.; Xiong, L.D.; Wang, C.M. Effects of interlaminar microstructural inhomogeneity on mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of multi-layer fiber laser welded high strength low alloy steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 252, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.C.; Mao, Y.Q.; Lin, X.; Zhou, B.S.; Qian, T. Microstructure and high temperature oxidation resistance of Ti-Ni gradient coating on TA2 titanium alloy fabricated by laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 83, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



















| C | Si | Mn | P | Cr | S | Ni | Mo | Zr | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.17 | 0.55 | 0.94 | 0.035 | 0.065 | 0.035 | 0.065 | 0.30 | 0.15 | Bal. |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Diameter of Al wire/mm | 2 |
| Spraying voltage/V | 30–32 |
| Spraying current/A | 160 |
| Spraying distance/mm | 150 |
| Spraying angle/° | 80 |
| Spraying pressure/MPa | 0.6 |
| Overlap ratio | 35% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Kong, D. Effect of Laser Remelting Power on Immersion Corrosion of Amorphous Al–Ti–Ni Coatings. Coatings 2018, 8, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8020046
Chen H, Kong D. Effect of Laser Remelting Power on Immersion Corrosion of Amorphous Al–Ti–Ni Coatings. Coatings. 2018; 8(2):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8020046
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Haixiang, and Dejun Kong. 2018. "Effect of Laser Remelting Power on Immersion Corrosion of Amorphous Al–Ti–Ni Coatings" Coatings 8, no. 2: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8020046
APA StyleChen, H., & Kong, D. (2018). Effect of Laser Remelting Power on Immersion Corrosion of Amorphous Al–Ti–Ni Coatings. Coatings, 8(2), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8020046