Linking Species Functional Traits to Specific Biogeochemical Processes under Trawling Pressure
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Data Collection
2.3. Physico-Chemical Analyses
2.4. Oxygen Flux Determination
- Fx
- flux of nutrient x micromol m−2 h−1)
- CI
- concentration in the reservoir tank (μM)
- Co
- concentration in the Core overlying water (μM)
- Q
- flow of water through the core (l h−1)
- A
- area of the core (m2)

2.5. Macrofaunal Community and Biological Trait Analyses
2.6. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Physico-Chemical Analyses
3.2. Link between Species Traits and Biogeochemical Processes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolam, S.G.; Garcia, C.; Eggleton, J.; Kenny, A.J.; Buhl-Mortensen, L.; Gonzalez-Mirelis, G.; van Kooten, T.; Dinesen, G.; Hansen, J.; Hiddink, J.G.; et al. Differences in Biological Traits Composition of Benthic Assemblages between Unimpacted Habitats. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 126, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J. Species’ Traits and Ecological Functioning in Marine Conservation and Management. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 366, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, R.O.; Pitcher, C.R.; Rijnsdorp, A.D.; McConnaughey, R.A.; Parma, A.M.; Suuronen, P.; Eigaard, O.R.; Bastardie, F.; Hintzen, N.T.; Althaus, F.; et al. Bottom Trawl Fishing Footprints on the World’s Continental Shelves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E10275–E10282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigaard, O.R.; Bastardie, F.; Hintzen, N.T.; Buhl-Mortensen, L.; Buhl-Mortensen, P.; Catarino, R.; Dinesen, G.E.; Egekvist, J.; Fock, H.O.; Geitner, K.; et al. The Footprint of Bottom Trawling in European Waters: Distribution, Intensity, and Seabed Integrity. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 74, 847–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigaard, O.R.; Bastardie, F.; Breen, M.; Dinesen, G.E.; Hintzen, N.T.; Laffargue, P.; Mortensen, L.O.; Nielsen, J.R.; Nilsson, H.C.; O’Neill, F.G.; et al. Estimating Seabed Pressure from Demersal Trawls, Seines, and Dredges Based on Gear Design and Dimensions. ICES J. Mar. Sci. J. Cons. 2016, 73, i27–i43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.J.; Papadopoulou, K.N.; Diliberto, S. Impact of Otter Trawling on an Eastern Mediterranean Commercial Trawl Fishing Ground. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, H.; Prieto, V.; Kaiser, M.J. Trawl Disturbance on Benthic Communities: Chronic Effects and Experimental Predications. Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillin, H.M.; Hiddink, J.G.; Jennings, S.; Kaiser, M.J. Chronic Bottom Trawling Alters the Functional Composition of Benthic Invertebrate Communities on a Sea-Basin Scale. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 318, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, S.; Kaiser, M.J. The Effects of Fishing on Marine Ecosystems. In Advances in Marine Biology; Blaxter, J.H.S., Southward, A.J., Tyler, P.A., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1998; Volume 34, pp. 1–475. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, M.J.; Clarke, K.R.; Hinz, H.; Austen, M.C.V.; Somerfield, P.J.; Karakassis, I. Global Analysis of Response and Recovery of Benthic Biota to Fishing. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 311, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, A.M.; Hiddink, J.G.; Kaiser, M.J.; Hinz, H. Effects of Chronic Bottom Trawling Disturbance on Benthic Biomass, Production and Size Spectra in Different Habitats. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 335, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Juan, S.; Thrush, S.F.; Demestre, M. Functional Changes as Indicators of Trawling Disturbance on a Benthic Community Located in a Fishing Ground (NW Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 334, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsgard, F.; Schaanning, M.T.; Widdicombe, S.; Kendall, M.A.; Austen, M.C. Effects of Bottom Trawling on Ecosystem Functioning. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 366, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Denderen, P.D.; Bolam, S.G.; Hiddink, J.G.; Jennings, S.; Kenny, A.; Rijnsdorp, A.D.; Van Kooten, T. Similar Effects of Bottom Trawling and Natural Disturbance on Composition and Function of Benthic Communities across Habitats. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 541, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimmer, M.; Petersen, J.; Sivyer, D.B.; Mills, C.; Young, E.; Parker, E.R. Impact of Long-Term Benthic Trawl Disturbance on Sediment Sorting and Biogeochemistry in the Southern North Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 298, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, L.M.; Schick, D.F.; Findlay, R.H.; Rice, D.L. Effects of Commercial Dragging on Sedimentary Organic Matter. Mar. Environ. Res. 1991, 31, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciberras, M.; Parker, R.; Powell, C.; Robertson, C.; Kröger, S.; Bolam, S.; Geert Hiddink, J. Impacts of Bottom Fishing on the Sediment Infaunal Community and Biogeochemistry of Cohesive and Non-Cohesive Sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 2076–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morys, C.; Brüchert, V.; Bradshaw, C. Impacts of Bottom Trawling on Benthic Biogeochemistry in Muddy Sediments: Removal of Surface Sediment Using an Experimental Field Study. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 169, 105384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiano, J.C.; Witbaard, R.; Bergman, M.J.N.; Van Rijswijk, P.; Tramper, A.; van Oevelen, D.; Soetaert, K. Acute Impacts of Bottom Trawl Gears on Benthic Metabolism and Nutrient Cycling. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 76, 1917–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, C.; Jakobsson, M.; Brüchert, V.; Bonaglia, S.; Mörth, C.M.; Muchowski, J.; Stranne, C.; Sköld, M. Physical Disturbance by Bottom Trawling Suspends Particulate Matter and Alters Biogeochemical Processes on and Near the Seafloor. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Borger, E.; Tiano, J.; Braeckman, U.; Rijnsdorp, A.D.; Soetaert, K. Impact of Bottom Trawling on Sediment Biogeochemistry: A Modelling Approach. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 2539–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrede, A.; Beermann, J.; Dannheim, J.; Gutow, L.; Brey, T. Organism Functional Traits and Ecosystem Supporting Services—A Novel Approach to Predict Bioirrigation. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikopoulou, I.; Lampa, M.; Tsiola, A.; Pitta, P.; Tsapakis, M.; Karakassis, I. Functional Adaptations of Benthic Communities to Organic Matter Enrichment at the Edge of an Allowable Zone of Effect (AZE). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 262, 107596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciberras, M.; Tait, K.; Brochain, G.; Hiddink, J.G.; Hale, R.; Godbold, J.A.; Solan, M. Mediation of Nitrogen by Post-Disturbance Shelf Communities Experiencing Organic Matter Enrichment. Biogeochemistry 2017, 135, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilskaln, C.H.; Churchill, J.H.; Mayer, L.M. Resuspension of Sediment by Bottom Trawling in the Gulf of Maine and Potential Geochemical Consequences. Conserv. Biol. 1998, 12, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duplisea, D.E.; Jennings, S.; Malcolm, S.J.; Parker, R.; Sivyer, D.B. Modelling Potential Impacts of Bottom Trawl Fisheries on Soft Sediment Biogeochemistry in the North Sea. Geochem. Trans. 2001, 2, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widdicombe, S.; Austen, M.C.; Kendall, M.A.; Olsgard, F.; Schaanning, M.T.; Dashfield, S.L.; Needham, H.R. Importance of Bioturbators for Biodiversity Maintenance: Indirect Effects of Fishing Disturbance. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 275, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRowe, D.E.; Arndt, S.; Bradley, J.A.; Estes, E.R.; Hoarfrost, A.; Lang, S.Q.; Lloyd, K.G.; Mahmoudi, N.; Orsi, W.D.; Shah Walter, S.R.; et al. The Fate of Organic Carbon in Marine Sediments—New Insights from Recent Data and Analysis. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 204, 103146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dounas, C.; Davies, I.; Triantafyllou, G.; Koulouri, P.; Petihakis, G.; Arvanitidis, C.; Sourlatzis, G.; Eleftheriou, A. Large-Scale Impacts of Bottom Trawling on Shelf Primary Productivity. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 2198–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petihakis, G.; Smith, C.J.; Triantafyllou, G.; Sourlantzis, G.; Papadopoulou, K.-N.; Pollani, A.; Korres, G. Scenario Testing of Fisheries Management Strategies Using a High Resolution ERSEM–POM Ecosystem Model. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2007, 64, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikopoulou, I.; Smith, C.J.; Papadopoulou, N.K.; Eleftheriadou, E.; Karakassis, I. A Fishing Ground Benthic Ecosystem Improved during the Economic Crisis. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 76, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.J.; Rumohr, H.; Karakassis, I.; Papadopoulou, K.N. Analysing the Impact of Bottom Trawls on Sedimentary Seabeds with Sediment Profile Imagery. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 285–286, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yentsch, C.S.; Menzel, D.W. A Method for the Determination of Phytoplankton Chlorophyll and Phaeophytin by Fluorescence. Deep Sea Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 1963, 10, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, T.R.; Maita, Y.; Lalli, C.M. A Manual of Chemical & Biological Methods for Seawater Analysis; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An Examination of the Degtjareff Method for Determining Soil Organic Matter, and a Proposed Modification of the Chromic Acid Titration Method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, J.D.H.; Parsons, T.R. A Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysis. In Bulletin/Fisheries Research Board of Canada, 2nd ed.; Fisheries and Marine Service: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1972; p. 167. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.; Rogers, S.; Frid, C. Assessing Functional Diversity in Marine Benthic Ecosystems: A Comparison of Approaches. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 254, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolam, S.G.; McIlwaine, P.; Garcia, C. Marine Macrofaunal Traits Responses to Dredged Material Disposal. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 168, 112412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumars, P.A.; Dorgan, K.M.; Lindsay, S.M. Diet of Worms Emended: An Update of Polychaete Feeding Guilds. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 497–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, A.M.; Birchenough, S.N.R.; Bremner, J.; Godbold, J.A.; Parker, R.E.; Romero-Ramirez, A.; Reiss, H.; Solan, M.; Somerfield, P.J.; Van Colen, C.; et al. A Bioturbation Classification of European Marine Infaunal Invertebrates. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 3958–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renz, J.R.; Powilleit, M.; Gogina, M.; Zettler, M.L.; Morys, C.; Forster, S. Community Bioirrigation Potential (BIPc), an Index to Quantify the Potential for Solute Exchange at the Sediment-Water Interface. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 141, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dray, S.; Legendre, P. Testing the Species Traits Environment Relationships: The Fourth-Corner Problem Revisited. Ecology 2008, 89, 3400–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dray, S.; Choler, P.; Dolédec, S.; Peres-Neto, P.R.; Thuiller, W.; Pavoine, S.; Ter Braak, C.J.F. Combining the Fourth-Corner and the RLQ Methods for Assessing Trait Responses to Environmental Variation. Ecology 2014, 95, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dray, S.; Dufour, A.-B.; Chessel, D. The Ade4 Package—II: Two-Table and K-Table Methods. R News 2007, 7, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- De Madron, X.D.; Ferré, B.; Le Corre, G.; Grenz, C.; Conan, P.; Pujo-Pay, M.; Buscail, R.; Bodiot, O. Trawling-Induced Resuspension and Dispersal of Muddy Sediments and Dissolved Elements in the Gulf of Lion (NW Mediterranean). Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 2387–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, S.; Pusceddu, A.; Masqué, P.; Puig, P.; Moccia, D.; Russo, T.; Lo Iacono, C. Organic Matter Contents and Degradation in a Highly Trawled Area during Fresh Particle Inputs (Gulf of Castellammare, Southwestern Mediterranean). Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 4307–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, A.; Fiordelmondo, C.; Polymenakou, P.; Polychronaki, T.; Tselepides, A.; Danovaro, R. Effects of Bottom Trawling on the Quantity and Biochemical Composition of Organic Matter in Coastal Marine Sediments (Thermaikos Gulf, Northwestern Aegean Sea). Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 2491–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solan, M.; Scott, F.; Dulvy, N.K.; Godbold, J.A.; Parker, R. Incorporating Extinction Risk and Realistic Biodiversity Futures: Implementation of Trait-Based Extinction Scenarios. In Marine Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; Volume 15, pp. 127–148. [Google Scholar]
- McLaverty, C.; Dinesen, G.; Gislason, H.; Brooks, M.; Eigaard, O. Biological Traits of Benthic Macrofauna Show Size-Based Differences in Response to Bottom Trawling Intensity. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 671, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.U.; Chapin, F.S.; Ewel, J.J.; Hector, A.; Inchausti, P.; Lavorel, S.; Lawton, J.H.; Lodge, D.M.; Loreau, M.; Naeem, S.; et al. Effects of Biodiversity on Ecosystem Functioning: A Consensus of Current Knowledge. Ecol. Monogr. 2005, 75, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, R.; Godbold, J.A.; Sciberras, M.; Dwight, J.; Wood, C.; Hiddink, J.G.; Solan, M. Mediation of Macronutrients and Carbon by Post-Disturbance Shelf Sea Sediment Communities. Biogeochemistry 2017, 135, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braeckman, U.; Provoost, P.; Gribsholt, B.; Van Gansbeke, D.; Middelburg, J.J.; Soetaert, K.; Vincx, M.; Vanaverbeke, J. Role of Macrofauna Functional Traits and Density in Biogeochemical Fluxes and Bioturbation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 399, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, E.; De Borger, E.; Braeckman, U.; De Backer, A.; Soetaert, K.; Vanaverbeke, J. Faunal and Environmental Drivers of Carbon and Nitrogen Cycling along a Permeability Gradient in Shallow North Sea Sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchenough, S.N.R.; Parker, R.E.; McManus, E.; Barry, J. Combining Bioturbation and Redox Metrics: Potential Tools for Assessing Seabed Function. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 12, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogina, M.; Morys, C.; Forster, S.; Gräwe, U.; Friedland, R.; Zettler, M.L. Towards Benthic Ecosystem Functioning Maps: Quantifying Bioturbation Potential in the German Part of the Baltic Sea. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 73, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogina, M.; Zettler, M.L.; Vanaverbeke, J.; Dannheim, J.; Van Hoey, G.; Desroy, N.; Wrede, A.; Reiss, H.; Degraer, S.; Van Lancker, V.; et al. Interregional Comparison of Benthic Ecosystem Functioning: Community Bioturbation Potential in Four Regions along the NE Atlantic Shelf. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braeckman, U.; Foshtomi, M.Y.; Van Gansbeke, D.; Meysman, F.; Soetaert, K.; Vincx, M.; Vanaverbeke, J. Variable Importance of Macrofaunal Functional Biodiversity for Biogeochemical Cycling in Temperate Coastal Sediments. Ecosystems 2014, 17, 720–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josefson, A.B.; Norkko, J.; Norkko, A. Burial and Decomposition of Plant Pigments in Surface Sediments of the Baltic Sea: Role of Oxygen and Benthic Fauna. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 455, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelburg, J.J. Reviews and Syntheses: To the Bottom of Carbon Processing at the Seafloor. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, G.; Middelburg, J.J.; Hawkins, J.P.; Norris, C.R.; Roberts, C.M. The Impact of Mobile Demersal Fishing on Carbon Storage in Seabed Sediments. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 2875–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijnsdorp, A.D.; Bolam, S.G.; Garcia, C.; Hiddink, J.G.; Hintzen, N.T.; van Denderen, P.D.; van Kooten, T. Estimating Sensitivity of Seabed Habitats to Disturbance by Bottom Trawling Based on the Longevity of Benthic Fauna. Ecol. Appl. 2018, 28, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnaughey, R.A.; Hiddink, J.G.; Jennings, S.; Pitcher, C.R.; Kaiser, M.J.; Suuronen, P.; Sciberras, M.; Rijnsdorp, A.D.; Collie, J.S.; Mazor, T.; et al. Choosing Best Practices for Managing Impacts of Trawl Fishing on Seabed Habitats and Biota. Fish Fish. 2020, 21, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Trait | Modalities | Code | Trait Definition | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect traits | Maximum body size (length) | <10 | S.10 | <10 mm |
| 11–20 | S.20 | 11–20 mm | ||
| 21–100 | S.100 | 21–100 mm | ||
| Longevity (max) | <1 | L.1 | <1 year | |
| 1–3 | L.3 | 1–3 years | ||
| 3–10 | L.10 | 3–10 years | ||
| Feeding mode | Suspension & filter | FM.suspension | obtains food from water | |
| Surface deposit | FM.sdeposit | including grazers | ||
| Sub-surface deposit | FM.subsdeposit | sub-surface deposit | ||
| Scavenger/opportunist | FM.scavenger | feeds upon dead animals | ||
| Surface predator | FM.predator | actively predates upon animals | ||
| Bioturbation mode | Diffusive mixers | BM.diffusive | vertical and/or horizontal movement of sediment or particles, organisms with activities that result in a constant and random local sediment biomixing over short distances | |
| Surface depositors | BM.deposition | deposition of particles at the sediment surface, species whose activities are restricted to <1–2 cm of the sediment | ||
| Upward conveyors | BM.upConveyors | upwards movement of particles resulting from biological activity, head down feeders that actively transport sediment to the sediment surface | ||
| Downward conveyors | BM.downConveyors | downwards movement of particles resulting from biological activity, head up feeders that actively transport sediment from the sediment surface | ||
| Response traits | Living habit | Tube-dwelling | LH.tube | builds a tube |
| Burrow-dwelling | LH.burrow | builds a burrow, includes mucus-lined burrows | ||
| Free-living | LH.free | freely moves around sediment/water | ||
| Inhabits crevices | LH.crevices | Inhabits crevices/holes/under stones | ||
| Sediment position | Surface | Pos.S | surface dwellers | |
| Infauna: 0–5 cm | Pos.5 | shallow-dwellers | ||
| Infauna: 6–10 cm | Pos.10 | buried deeper | ||
| Infauna: >10 cm | Pos.deep | deep-dwelling | ||
| Mobility | Sessile | M.sessile | immobile, fixed in a place, stalked or not | |
| Swim | M.swim | includes those which may stop swimming temporarily | ||
| Crawl/creep/climb | M.crawl | those which move above bed slowly | ||
| Burrower | M.burrower | Infers relatively low mobility |
| Bottom Water | Sediment | Flux | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyll a | Phaeopigments | Organic Carbon | Chlorophyll a | Phaeopigments | Organic Carbon | Oxygen | |||||||||
| Source of Variation | DF | F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p |
| trawling | 1 | 22.55 | ** | 1.40 | ns | 0.75 | ns | 0.02 | ns | 0.31 | ns | 116.96 | ** | 0.03 | ns |
| season | 1 | 17.93 | ** | 1.38 | ns | 16.51 | ** | 1.30 | ns | 0.23 | ns | 16.30 | ** | 33.84 | ** |
| site | 1 | - | - | - | - | 2.71 | ns | 2.04 | ns | 9.55 | * | 16.53 | ** | ||
| season × trawling | 1 | 19.80 | ** | 0.49 | ns | 0.92 | ns | 0.02 | ns | 0.47 | ns | 0.51 | ns | 3.55 | ns |
| trawling × site | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.29 | ns | 1.68 | ns | 8.46 | * | 2.23 | ns |
| season × site | 1 | . | - | - | - | - | - | 3.62 | ns | 1.57 | ns | 8.85 | * | 2.23 | ns |
| trawling × season × site | 1 | . | - | - | - | - | - | 0.33 | ns | 0.46 | ns | 0.18 | ns | 0.53 | ns |
| Season | Trawling | Description | Sediment Chl a | OC | Silt and Clay | Oxygen | Water Chl a | POC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
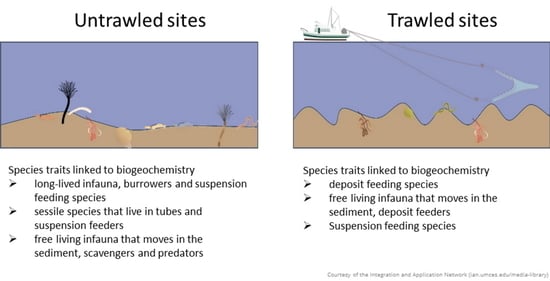
| summer | untrawled | Group 1 | long-lived infauna, burrowers and suspension feeding species | − | − | − | |||
| winter | Group 2 | sessile species that live in tubes and suspension feeders | − | − | − | ||||
| Group 3 | free living infauna that moves in the sediment, scavengers and predators | + | + | + | + | ||||
| summer | trawled | Group 4 | deposit feeding species | − | |||||
| winter | Group 5 | free living infauna that moves in the sediment, deposit feeders | − | − | + | + | |||
| Group 6 | Suspension feeding species | − |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsikopoulou, I.; Smith, C.J.; Papadopoulou, K.N.; Austen, M.C. Linking Species Functional Traits to Specific Biogeochemical Processes under Trawling Pressure. Biology 2022, 11, 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101378
Tsikopoulou I, Smith CJ, Papadopoulou KN, Austen MC. Linking Species Functional Traits to Specific Biogeochemical Processes under Trawling Pressure. Biology. 2022; 11(10):1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101378
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsikopoulou, Irini, Christopher J. Smith, Konstantia Nadia Papadopoulou, and Melanie C. Austen. 2022. "Linking Species Functional Traits to Specific Biogeochemical Processes under Trawling Pressure" Biology 11, no. 10: 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101378
APA StyleTsikopoulou, I., Smith, C. J., Papadopoulou, K. N., & Austen, M. C. (2022). Linking Species Functional Traits to Specific Biogeochemical Processes under Trawling Pressure. Biology, 11(10), 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101378